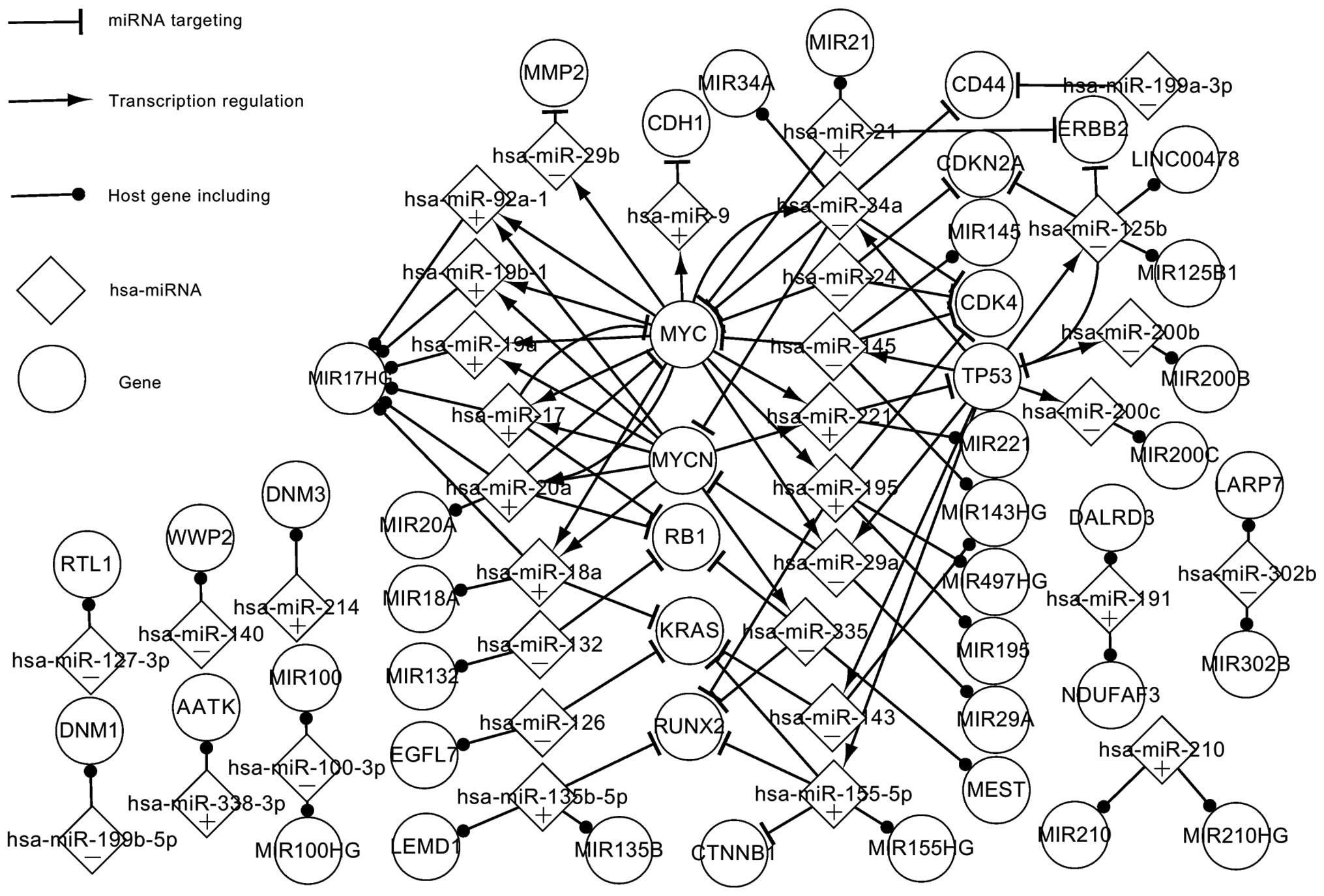
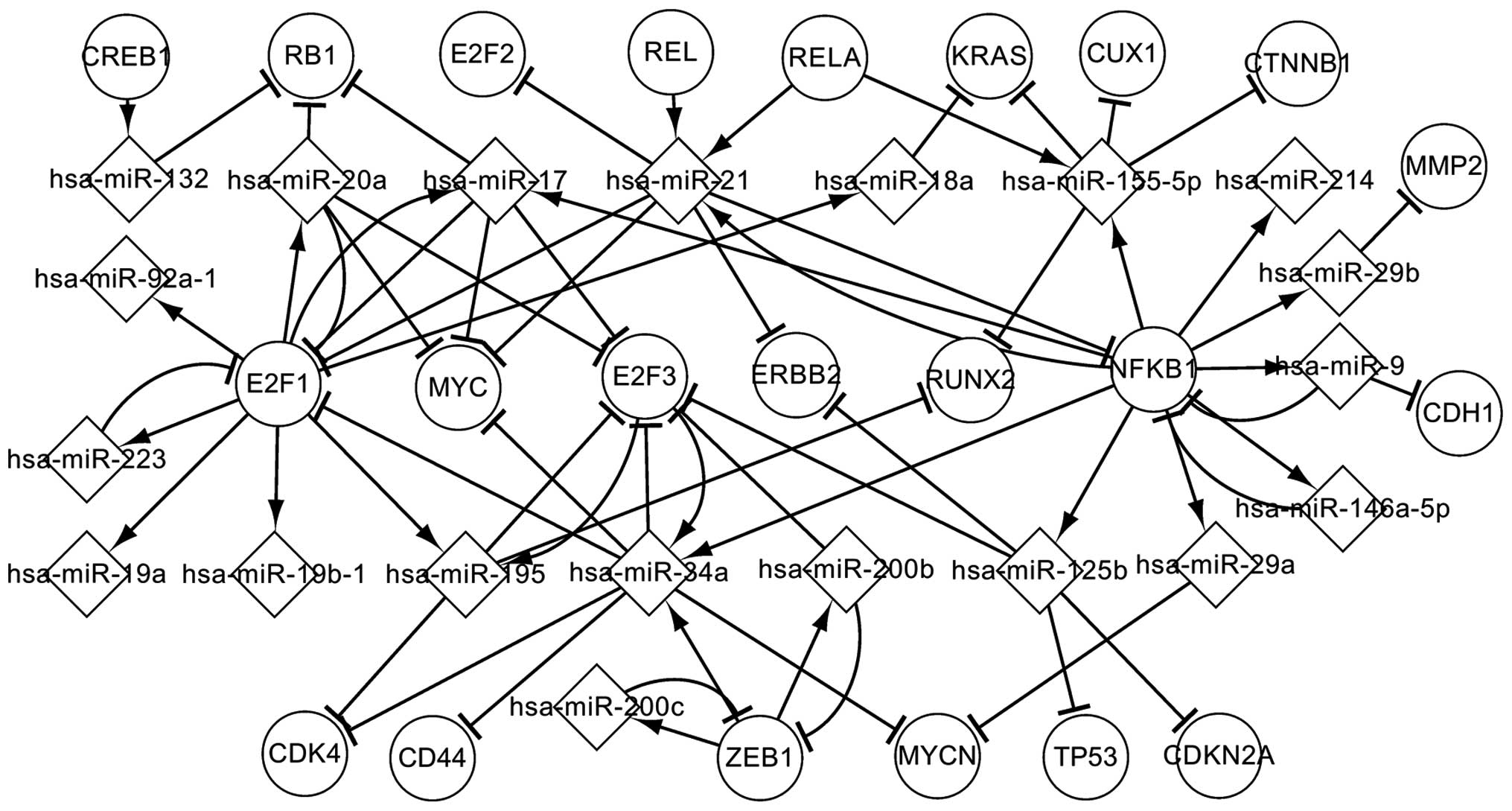
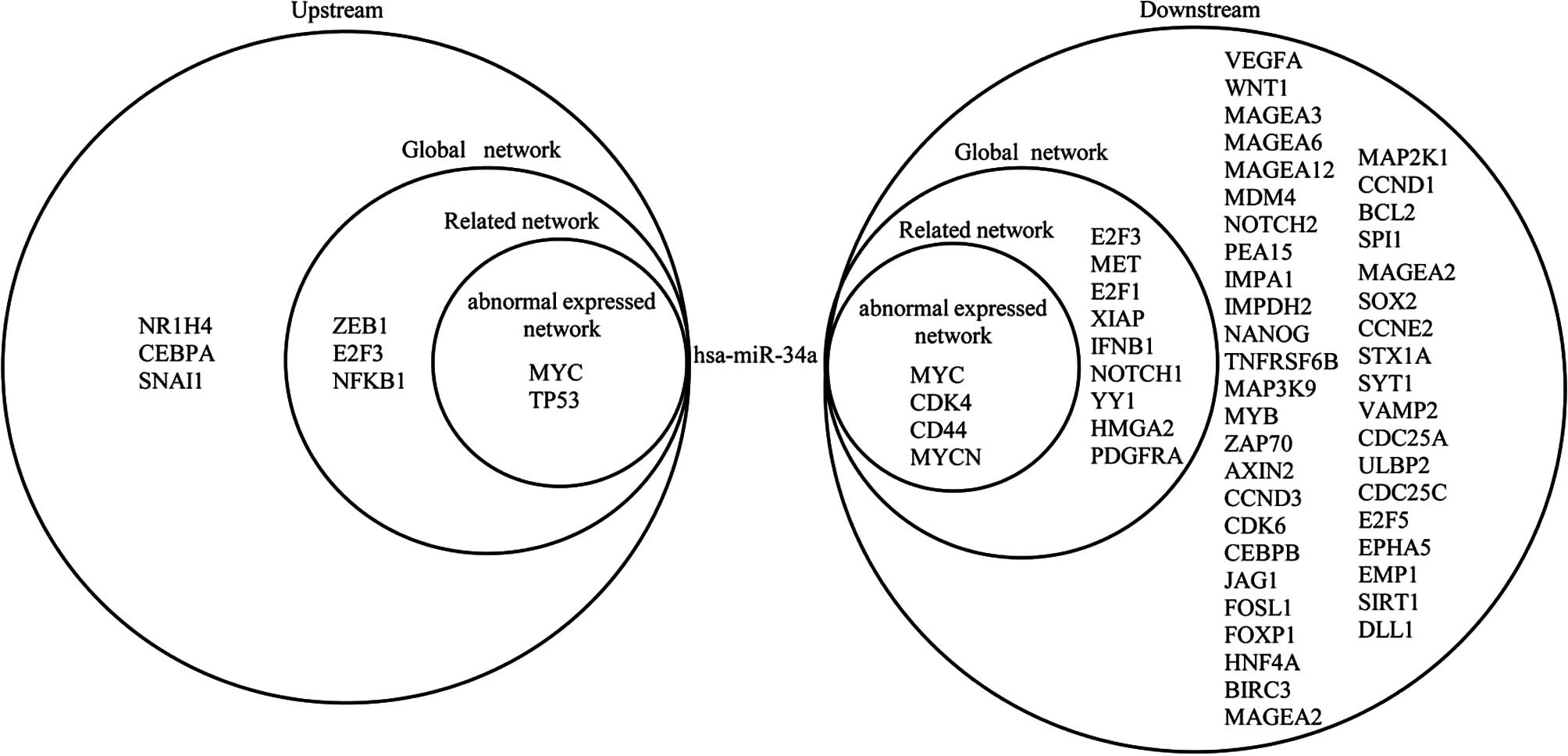
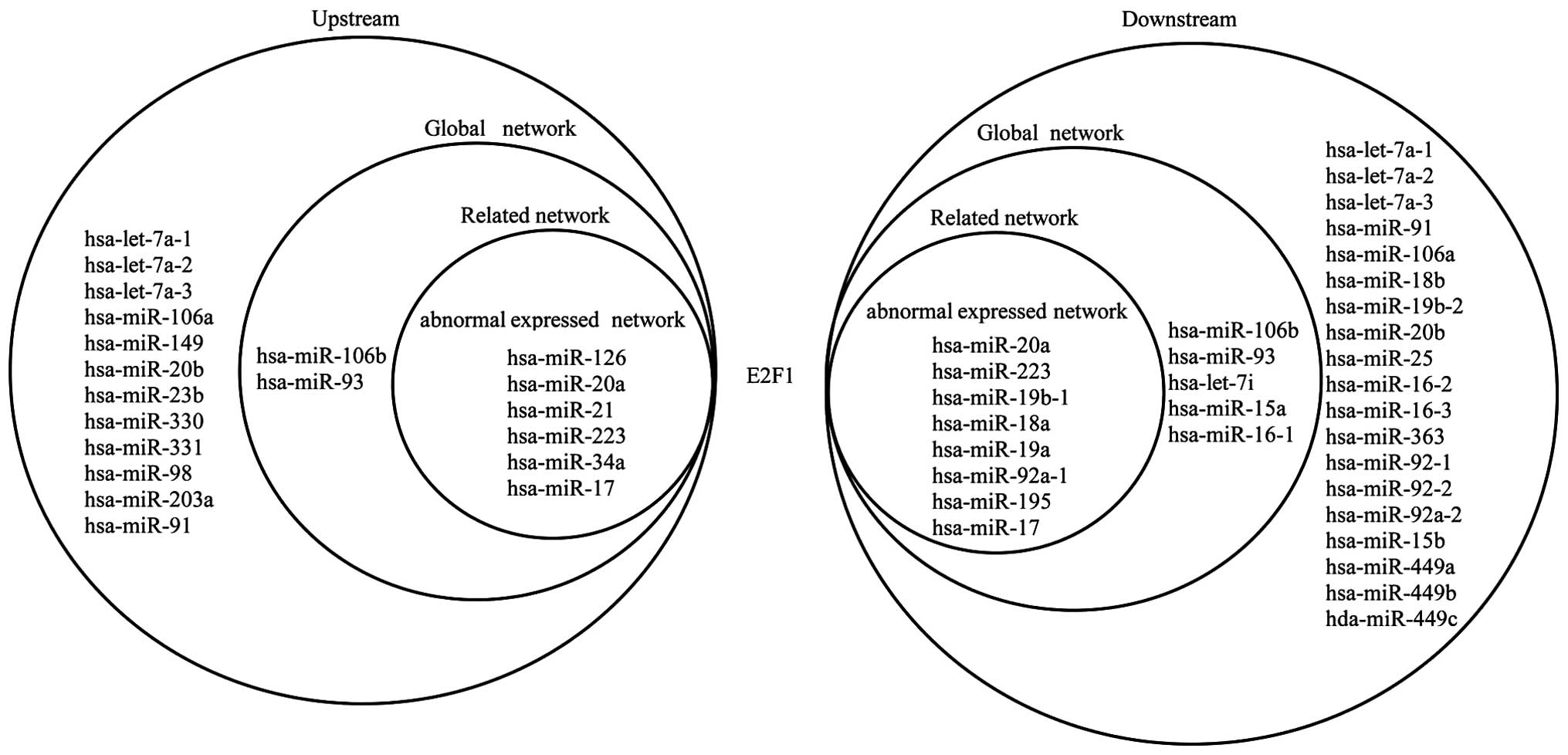
|
1
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hobert O: Gene regulation by transcription
factors and microRNAs. Science. 319:1785–1786. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tran DH, Satou K, Ho TB and Pham TH:
Computational discovery of miR-TF regulatory modules in human
genome. Bioinformation. 4:371–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yue J and Tigyi G: MicroRNA trafficking
and human cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:573–578. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McManus MT: MicroRNAs and cancer. Semin
Cancer Biol. 13:253–258. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baskerville S and Bartel DP: Microarray
profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with
neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA. 11:241–247. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rodriguez A, GriffithsJones S, Ashurst JL
and Bradley A: Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and
transcription units. Genome Res. 14:1902–1910. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Naeem H, Küffner R and Zimmer R: MIRTFnet:
Analysis of miRNA regulated transcription factors. PLoS One.
6:e225192011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N,
Fang Z, Khanin R and Rajewsky N: Widespread changes in protein
synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. 455:58–63. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lim LP, Lau NC, GarrettEngele P, Grimson
A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS and Johnson JM:
Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large
numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 433:769–773. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang JC, Babak T, Corson TW, Chua G, Khan
S, Gallie BL, Hughes TR, Blencowe BJ, Frey BJ and Morris QD: Using
expression profiling data to identify human microRNA targets. Nat
Methods. 4:1045–1049. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sztán M, Pápai Z, Szendrôi M, Looij M and
Oláh E: Allelic losses from chromosome 17 in human osteosarcomas.
Pathol Oncol Res. 3:115–120. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choy E, Hornicek F, MacConaill L, Harmon
D, Tariq Z, Garraway L and Duan Z: High-throughput genotyping in
osteosarcoma identifies multiple mutations in
phosphoinositide-3-kinase and other oncogenes. Cancer.
118:2905–2914. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kansara M and Thomas DM: Molecular
pathogenesis of osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 26:1–18. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hong Q, Fang J, Pang Y and Zheng J:
Prognostic value of the microRNA-29 family in patients with primary
osteosarcomas. Med Oncol. 31:372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Z and Cai H, Lin L, Tang M and Cai H:
Upregulated expression of microRNA-214 is linked to tumor
progression and adverse prognosis in pediatric osteosarcoma.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 61:206–210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lulla RR, Costa FF, Bischof JM, Chou PM,
de F Bonaldo M, Vanin EF and Soares MB: Identification of
differentially expressed microRNAs in osteosarcoma. Sarcoma.
2011:7326902011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39:D152–D157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang J, Lu M, Qiu C and Cui Q: TransmiR: A
transcription factor-microRNA regulation database. Nucleic Acids
Res. 38:D119–D122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hsu SD, Lin FM, Wu WY, Liang C, Huang WC,
Chan WL, Tsai WT, Chen GZ, Lee CJ, Chiu CM, et al: miRTarBase: A
database curates experimentally validated microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:D163–D169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Papadopoulos GL, Reczko M, Simossis VA,
Sethupathy P and Hatzigeorgiou AG: The database of experimentally
supported targets: A functional update of TarBase. Nucleic Acids
Res. 37:D155–D158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Safran M, Dalah I, Alexander J, Rosen N,
Iny Stein T, Shmoish M, Nativ N, Bahir I, Doniger T, Krug H, et al:
GeneCards Version 3: The human gene integrator. Database (Oxford).
2010:baq0202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chekmenev DS, Haid C and Kel AE: P-Match:
Transcription factor binding site search by combining patterns and
weight matrices. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:W432–W437. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fujita PA, Rhead B, Zweig AS, Hinrichs AS,
Karolchik D, Cline MS, Goldman M, Barber GP, Clawson H, Coelho A,
et al: The UCSC genome browser database: Update 2011. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:D876–D882. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang Q, Wang Y, Hao Y, Juan L, Teng M,
Zhang X, Li M, Wang G and Liu Y: miR2Disease: A manually curated
database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids
Res. 37:D98–D104. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kranenburg O: The KRAS oncogene: Past,
present, and future. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1756:81–82.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Marks JL, Broderick S, Zhou Q, Chitale D,
Li AR, Zakowski MF, Kris MG, Rusch VW, Azzoli CG, Seshan VE, et al:
Prognostic and therapeutic implications of EGFR and KRAS mutations
in resected lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 3:111–116. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Suda K, Tomizawa K and Mitsudomi T:
Biological and clinical significance of KRAS mutations in lung
cancer: an oncogenic driver that contrasts with EGFR mutation.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29:49–60. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hershkovitz D, Vlodavsky E, Simon E and
Ben-Izhak O: KRAS mutation positive mucinous adenocarcinoma
originating in mature ovarian teratoma: Case report and review of
literature. Pathol Int. 63:611–614. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yatsuoka T, Sunamura M, Furukawa T,
Fukushige S, Yokoyama T, Inoue H, Shibuya K, Takeda K, Matsuno S
and Horii A: Association of poor prognosis with loss of 12q, 17p,
and 18q, and concordant loss of 6q/17p and 12q/18q in human
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 95:2080–2085.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Abubaker J, Bavi P, Al Haqawi W, Sultana
M, Al Harbi S, Al Sanea N, Abduljabbar A, Ashari LH, Alhomoud S, Al
Dayel F, et al: Prognostic significance of alterations in KRAS
isoforms KRAS-4A/4B and KRAS mutations in colorectal carcinoma. J
Pathol. 219:435–445. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Smakman N, Borel Rinkes IH, Voest EE and
Kranenburg O: Control of colorectal metastasis formation by K-Ras.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1756:103–114. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Neilsen PM, Noll JE, Mattiske S, Bracken
CP, Gregory PA, Schulz RB, Lim SP, Kumar R, Suetani RJ, Goodall GJ
and Callen DF: Mutant p53 drives invasion in breast tumors through
up-regulation of miR-155. Oncogene. 32:2992–3000. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|