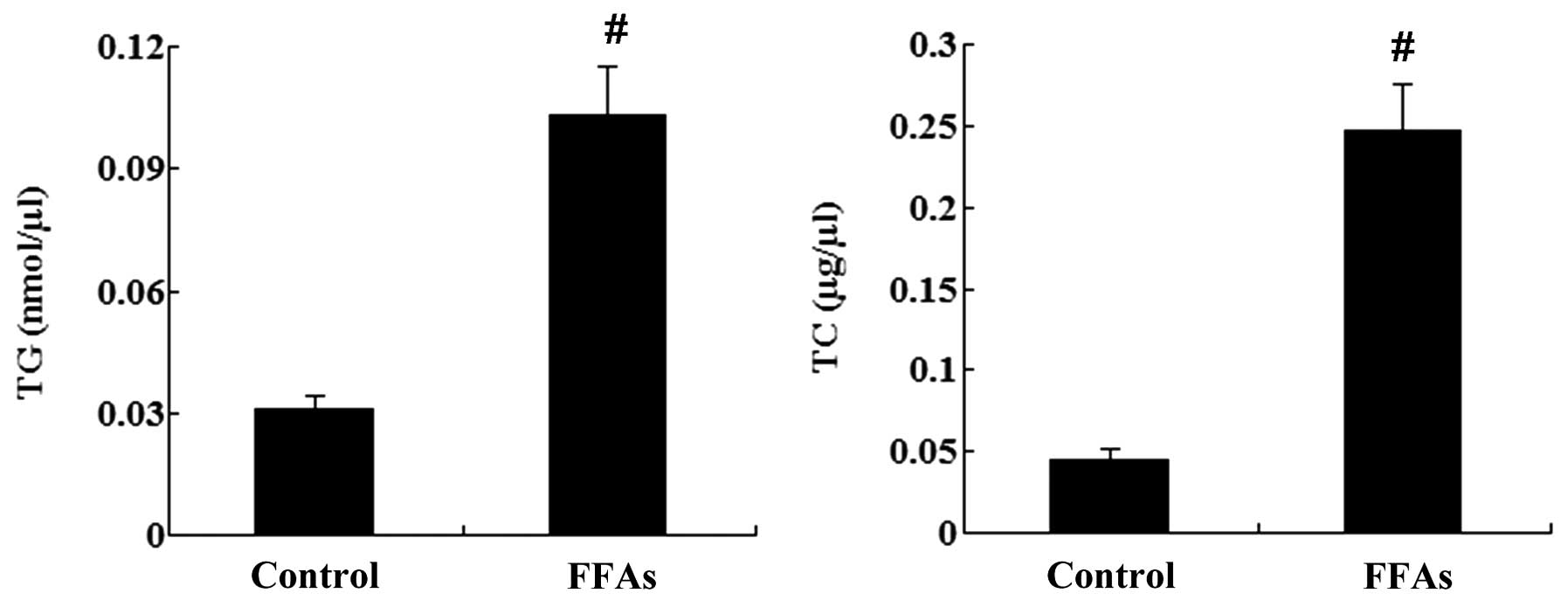
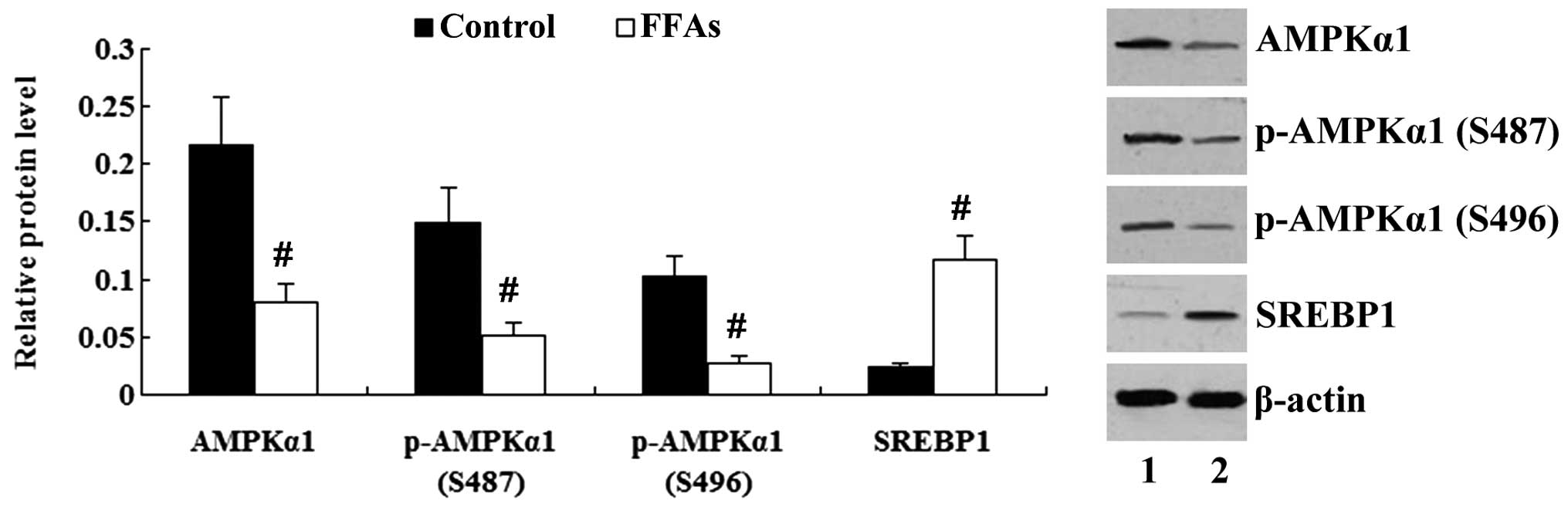
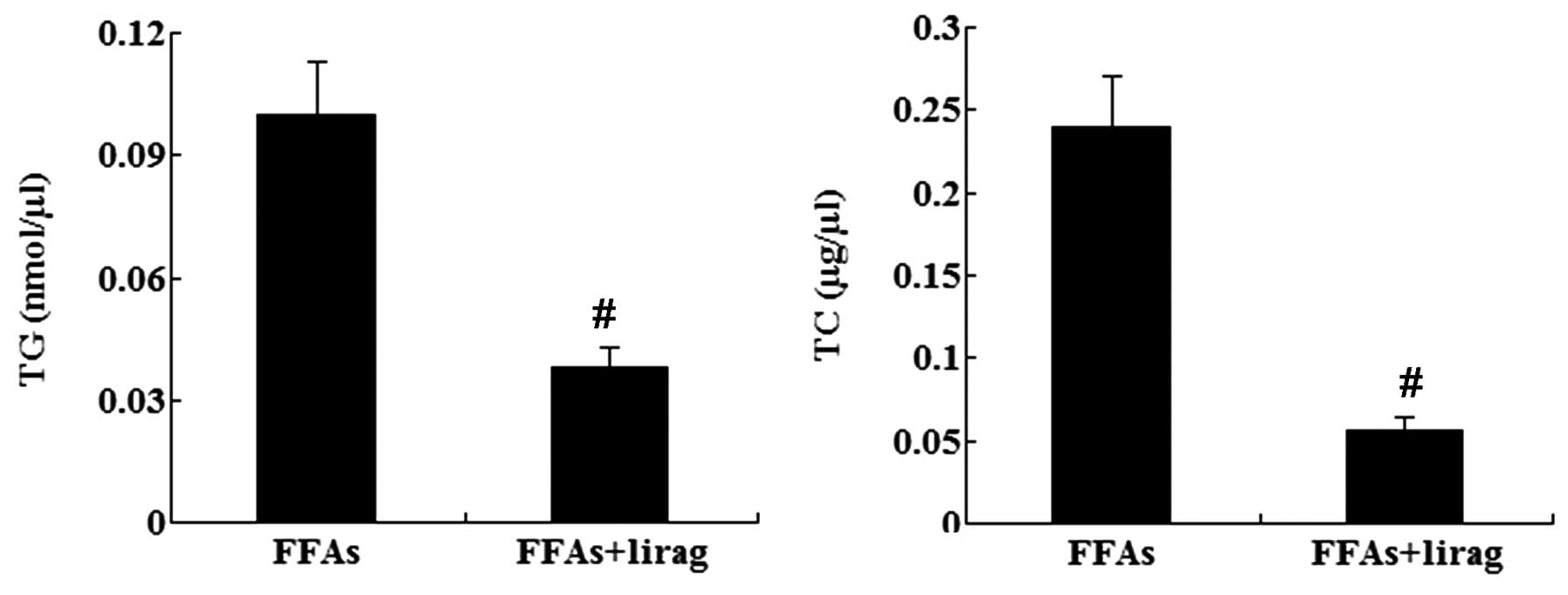
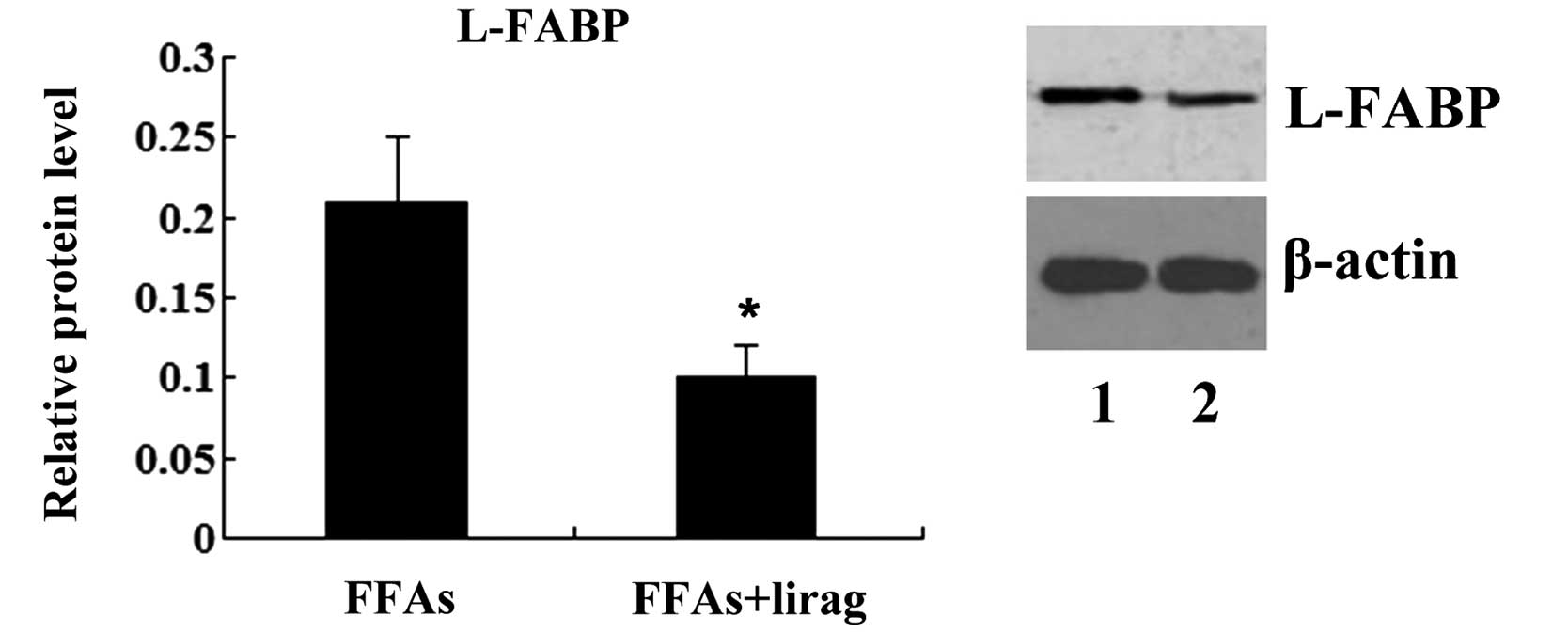
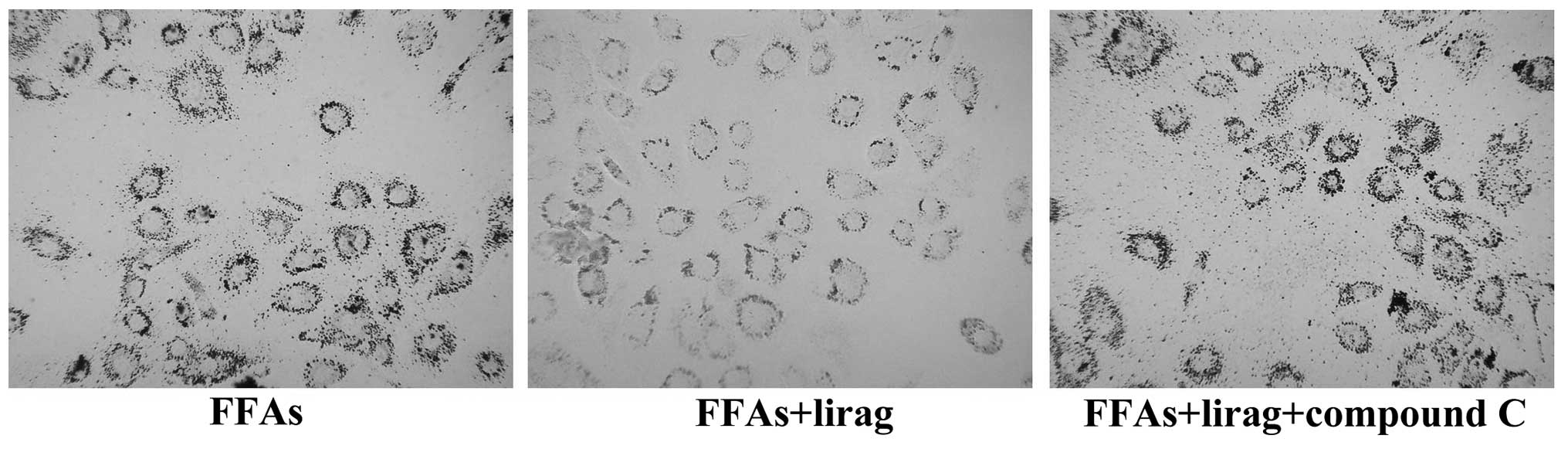
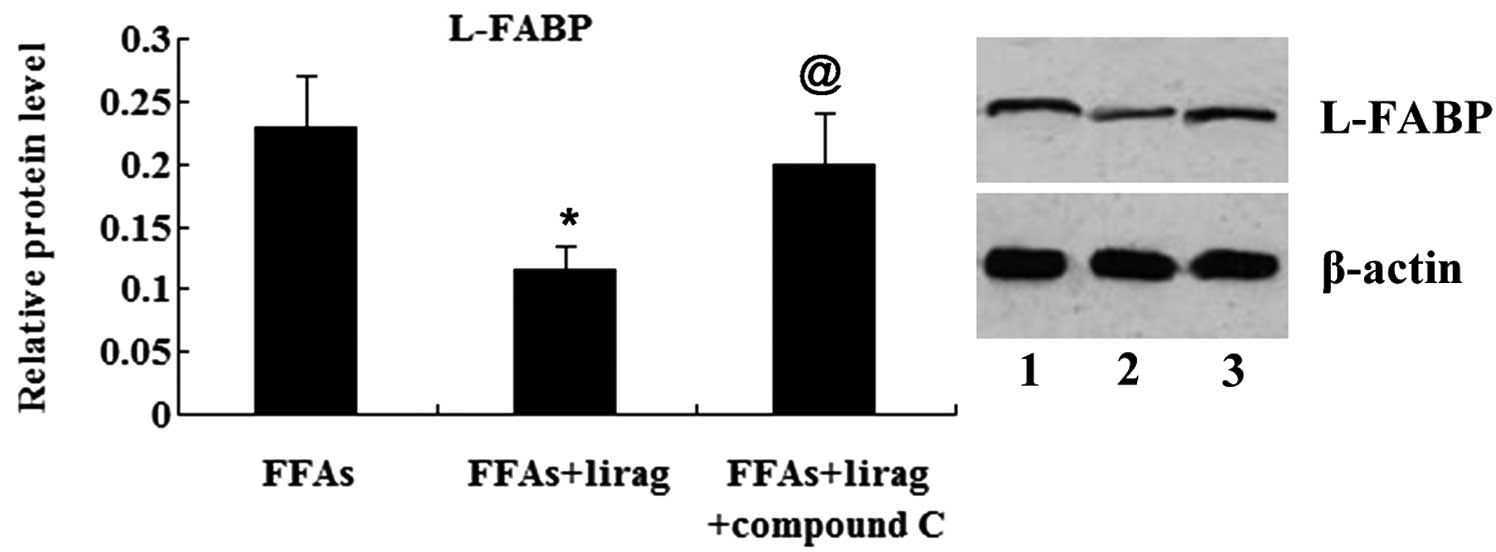
|
1
|
Clark JM and Diehl AM: Hepatic steatosis
and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diab Rep. 2:210–215. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bedogni G, Miglioli L, Masutti F,
Tiribelli C, Marchesini G and Bellentani S: Prevalence of and risk
factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The Dionysos
nutrition and liver study. Hepatology. 42:44–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R,
Nuremberg P, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Grundy SM and Hobbs HH:
Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the
United States: Impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 40:1387–1395. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vernon G, Baranova A and Younossi ZM:
Systematic review: The epidemiology and natural history of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 34:274–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fan JG: An introduction of strategies for
the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
recommended by Asia Pacific Working Party on NAFLD. Zhonghua Gan
Zang Bing Za Zhi. 15:552–553. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Petta S, Muratore C and Craxì A:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis: The present and the
future. Dig Liver Dis. 41:615–625. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schwenger KJ and Allard JP: Clinical
approaches to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:1712–1723. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Knudsen LB, Nielsen PF, Huusfeldt PO,
Johansen NL, Madsen K, Pedersen FZ, Thøgersen H, Wilken M and
Agersø H: Potent derivatives of glucagon-like peptide-1 with
pharmacokinetic properties suitable for once daily administration.
J Med Chem. 43:1664–1669. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gao H, Xu L, Li D, Guang L and Deng W:
Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 on liver oxidative stress, TNF-α
and TGF-β1 in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nan Fang
Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 33:1661–1664. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Olaywi M, Bhatia T, Anand S and Singhal S:
Novel anti-diabetic agents in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A
mini-review. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 12:584–588. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morrison A, Yan X, Tong C and Li J: Acute
rosiglitazone treatment is cardioprotective against
ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating AMPK, Akt, and JNK
signaling in nondiabetic mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
301:H895–H902. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X,
Fenyk-Melody J, Wu M, Ventre J, Doebber T, Fujii N, et al: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J
Clin Invest. 108:1167–1174. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang L, Yang M, Ren H, Hu H, Boden G, Li
L and Yang G: GLP-1 analogue prevents NAFLD in ApoE KO mice with
diet and Acrp30 knockdown by inhibiting c-JNK. Liver Int.
33:794–804. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Buse JB, Rosenstock J, Sesti G, Schmidt
WE, Montanya E, Brett JH, Zychma M and Blonde L: LEAD-6 Study
Group: Liraglutide once a day versus exenatide twice a day for type
2 diabetes: A 26-week randomised, parallel-group, multinational,
open-label trial (LEAD-6). Lancet. 374:39–47. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marre M, Shaw J, Brändle M, Bebakar WM,
Kamaruddin NA, Strand J, Zdravkovic M, Le Thi TD and Colagiuri S:
LEAD-1 SU Study Group: Liraglutide, a once-daily human GLP-1
analogue, added to a sulphonylurea over 26 weeks produces greater
improvements in glycaemic and weight control compared with adding
rosiglitazone or placebo in subjects with Type 2 diabetes (LEAD-1
SU). Diabet Med. 26:268–278. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nauck M, Frid A, Hermansen K, Shah NS,
Tankova T, Mitha IH, Zdravkovic M, Düring M and Matthews DR: LEAD-2
Study Group: Efficacy and safety comparison of liraglutide,
glimepiride, and placebo, all in combination with metformin, in
type 2 diabetes: The LEAD (liraglutide effect and action in
diabetes)-2 study. Diabetes Care. 32:84–90. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Garber A, Henry R, Ratner R,
Garcia-Hernandez PA, Rodriguez-Pattzi H, Olvera-Alvarez I, Hale PM,
Zdravkovic M and Bode B: LEAD-3 (Mono) Study Group: Liraglutide
versus glimepiride monotherapy for type 2 diabetes (LEAD-3 Mono): A
randomised, 52-week, phase III, double-blind, parallel-treatment
trial. Lancet. 373:473–481. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zinman B, Gerich J, Buse JB, Lewin A,
Schwartz S, Raskin P, Hale PM, Zdravkovic M and Blonde L: LEAD-4
Study Investigators: Efficacy and safety of the human glucagon-like
peptide-1 analog liraglutide in combination with metformin and
thiazolidinedione in patients with type 2 diabetes (LEAD-4
Met+TZD). Diabetes Care. 32:1224–1230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Russell-Jones D, Vaag A, Schmitz O, Sethi
BK, Lalic N, Antic S, Zdravkovic M, Ravn GM and Simó R: Liraglutide
Effect and Action in Diabetes 5 (LEAD-5) met+SU Study Group:
Liraglutide vs insulin glargine and placebo in combination with
metformin and sulfonylurea therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus
(LEAD-5 met+SU): A randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia.
52:2046–2055. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Özenirler S, Degertekin CK, Erkan G, Elbeğ
Ş, Tuncer C, Kandilc U and Akyol G: Serum liver fatty acid binding
protein shows good correlation with liver histology in NASH.
Hepatogastroenterology. 60:1095–1100. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Higuchi N, Kato M, Tanaka M, Miyazaki M,
Takao S, Kohjima M, Kotoh K, Enjoji M, Nakamuta M and Takayanagi R:
Effects of insulin resistance and hepatic lipid accumulation on
hepatic mRNA expression levels of apoB, MTP and L-FABP in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Exp Ther Med. 2:1077–1081.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jung EJ, Kwon SW, Jung BH, Oh SH and Lee
BH: Role of the AMPK/SREBP-1 pathway in the development of orotic
acid-induced fatty liver. J Lipid Res. 52:1617–1625. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Srivastava RA, Pinkosky SL, Filippov S,
Hanselman JC, Cramer CT and Newton RS: AMP-activated protein
kinase: An emerging drug target to regulate imbalances in lipid and
carbohydrate metabolism to treat cardio-metabolic diseases. J Lipid
Res. 53:2490–2514. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Porstmann T, Santos CR, Griffiths B, Cully
M, Wu M, Leevers S, Griffiths JR, Chung YL and Schulze A: SREBP
activity is regulated by mTORC1 and contributes to Akt-dependent
cell growth. Cell Metab. 8:224–236. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shklyaev S, Aslanidi G, Tennant M, Prima
V, Kohlbrenner E, Kroutov V, Campbell-Thompson M, Crawford J, Shek
EW, Scarpace PJ and Zolotukhin S: Sustained peripheral expression
of transgene adiponectin offsets the development of diet-induced
obesity in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:14217–14222. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
You M, Matsumoto M, Pacold CM, Cho WK and
Crabb DW: The role of AMP-activated protein kinase in the action of
ethanol in the liver. Gastroenterology. 127:1798–1808. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gundewar S, Calvert JW, Jha S,
Toedt-Pingel I, Ji SY, Nunez D, Ramachandran A, Anaya-Cisneros M,
Tian R and Lefer DJ: Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by
metformin improves left ventricular function and survival in heart
failure. Circ Res. 104:403–411. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sasaki H, Asanuma H, Fujita M, Takahama H,
Wakeno M, Ito S, Ogai A, Asakura M, Kim J, Minamino T, et al:
Metformin prevents progression of heart failure in dogs: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase. Circulation. 119:2568–2577. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|