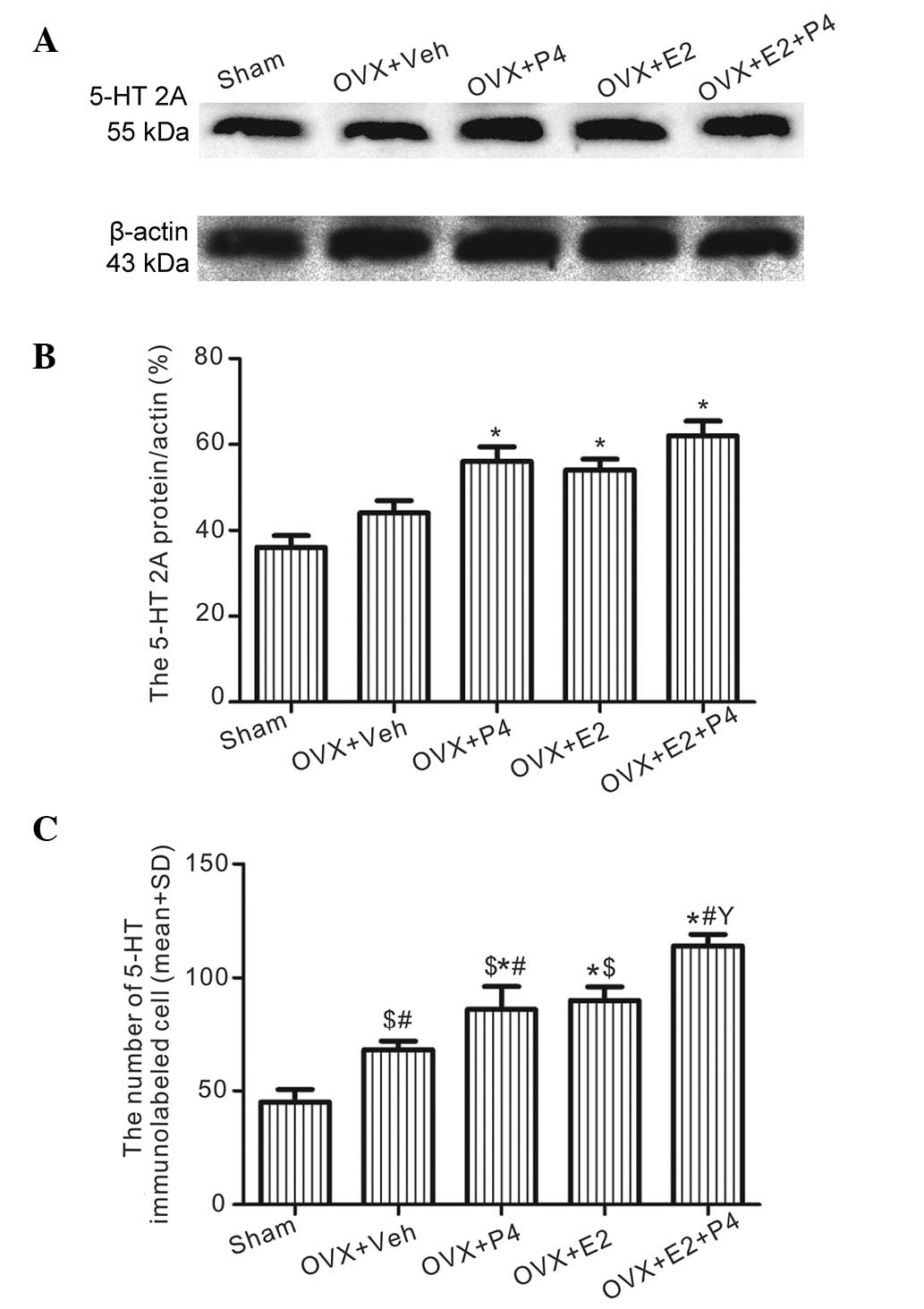
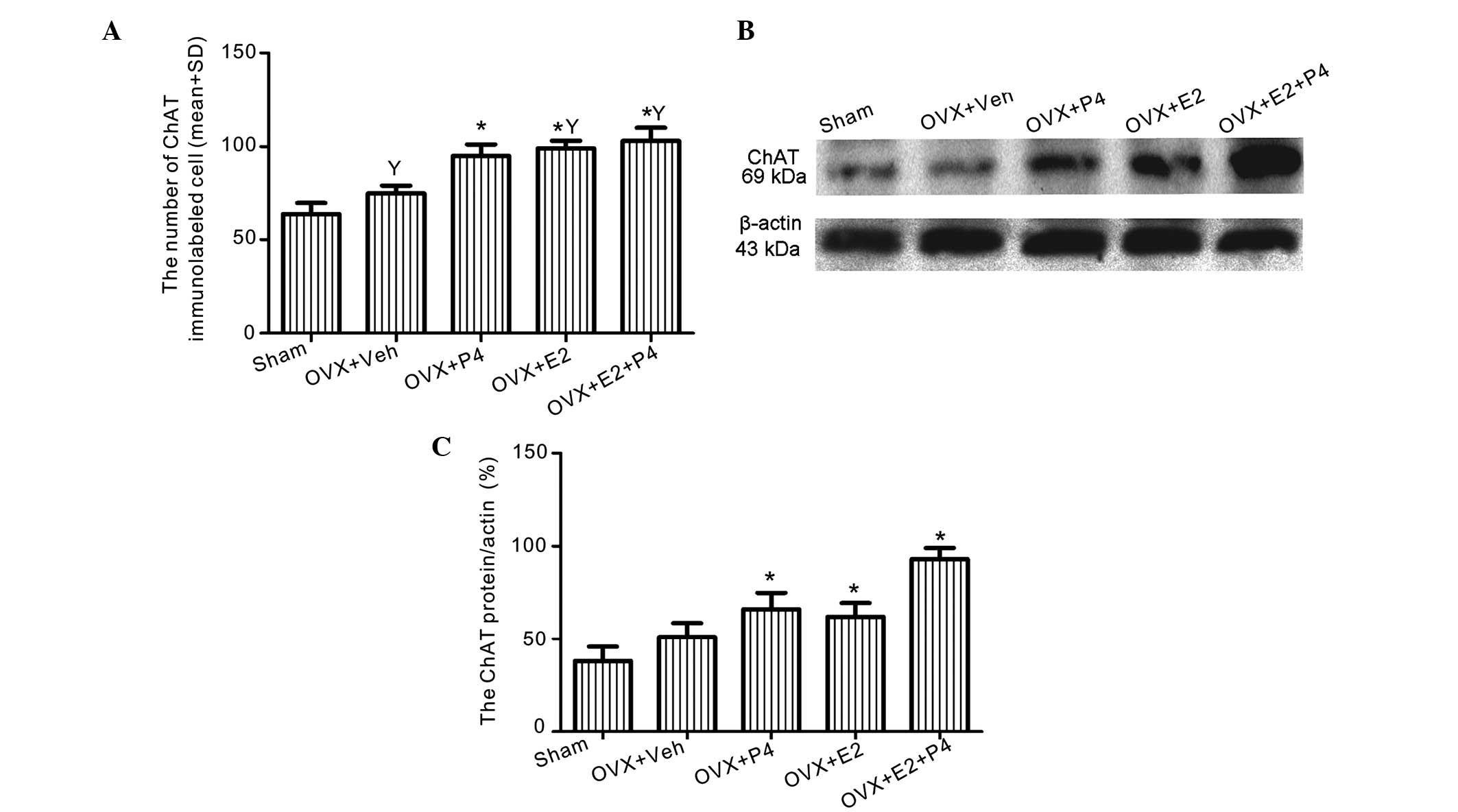
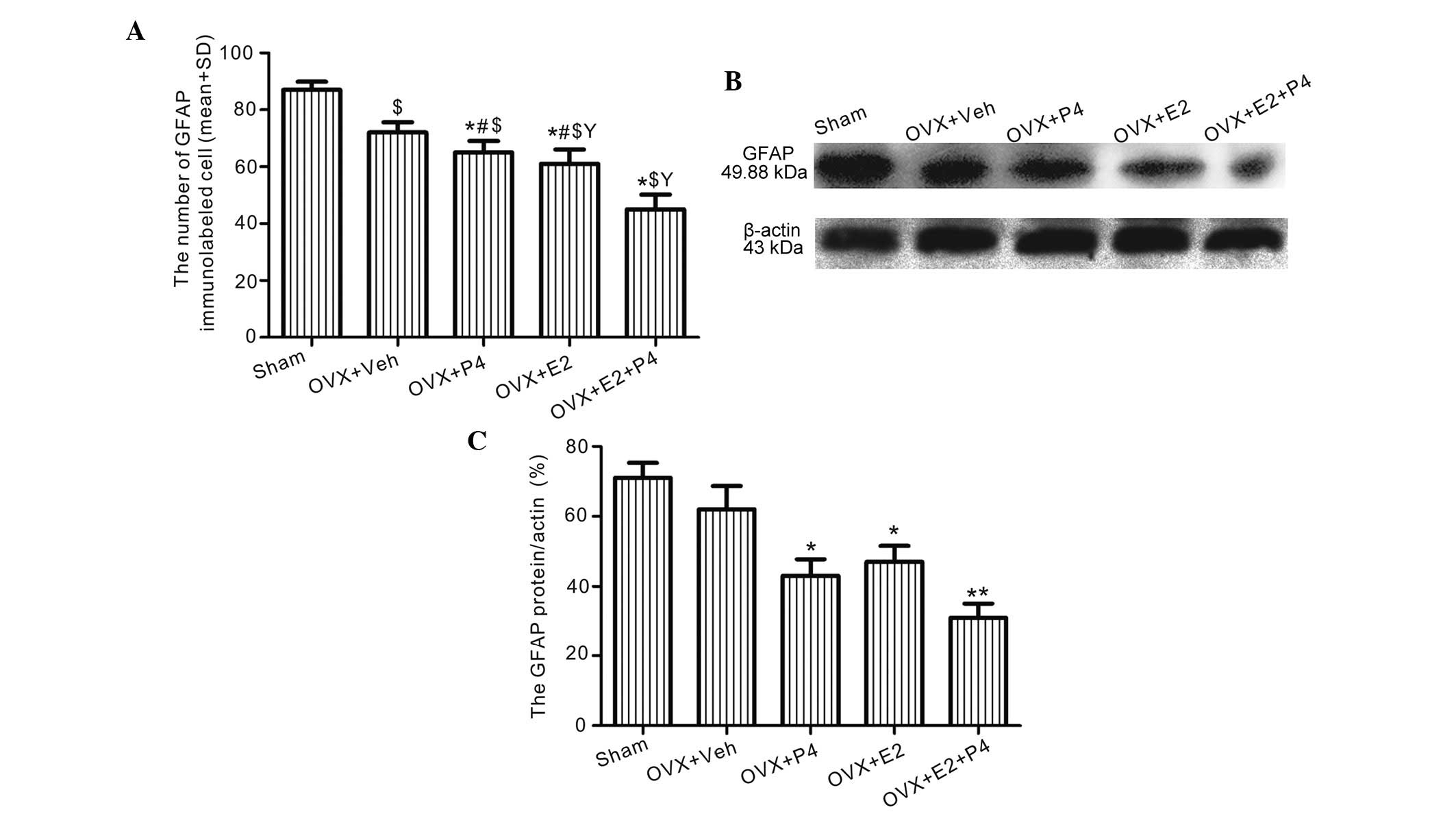
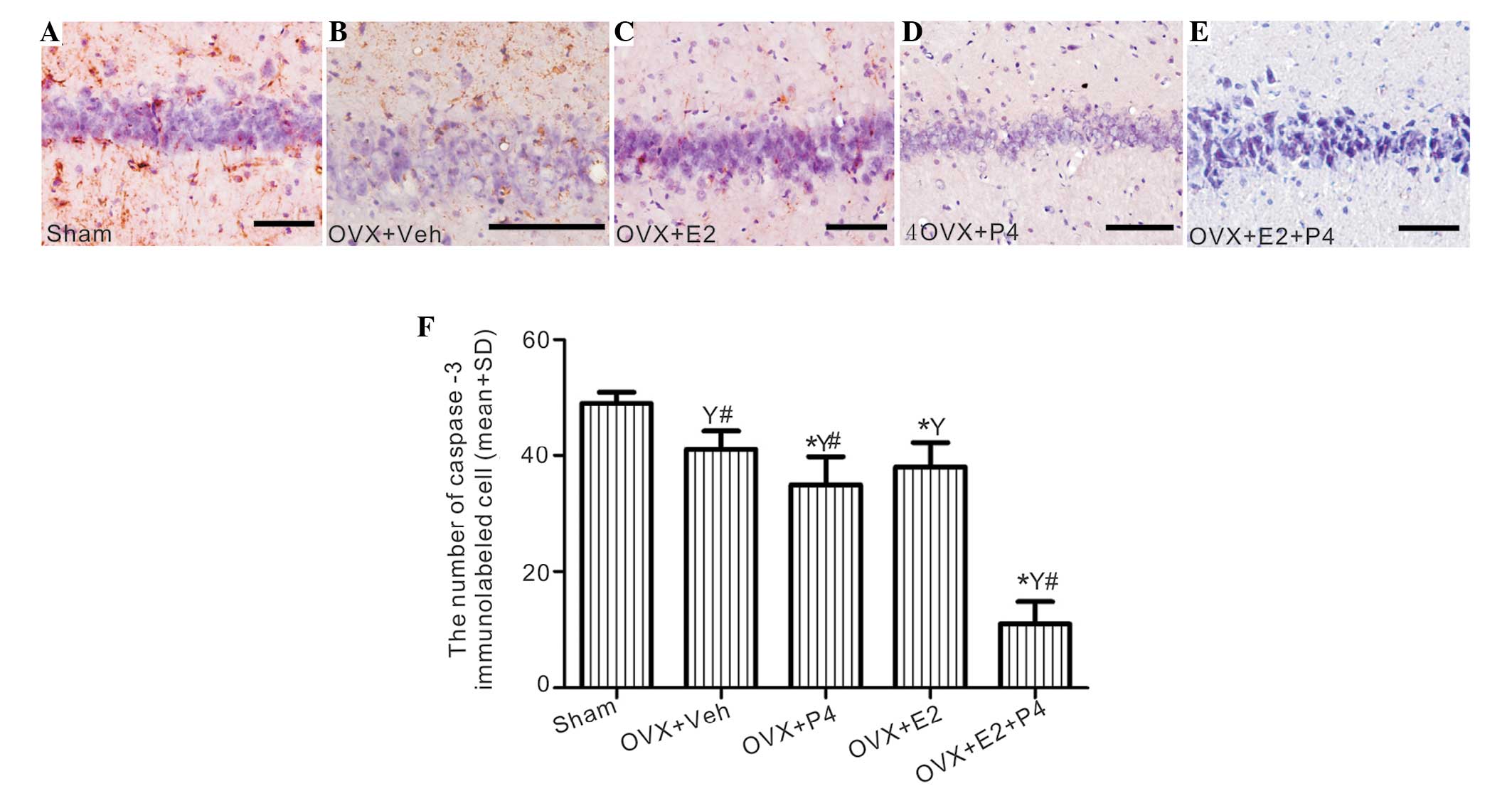
|
1
|
Han M, Liu Y, Tan Q, Zhang B, Wang W, Liu
J, Zhang XJ, Wang YY and Zhang JM: Therapeutic efficacy of
stemazole in a beta-amyloid injection rat model of Alzheimer's
disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 657:104–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fang M, Wang J, Han S, Hu Z, Zhan JB, Ling
S, Rudd JA and Geng Y: Protective effects of ω-conotoxin on
amyloid-β-induced damage in PC12 cells. Toxicol Lett. 206:325–338.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He FQ, Qiu BY, Zhang XH, Li TK, Xie Q, Cui
DJ, Huang XL and Gan HT: Tetrandrine attenuates spatial memory
impairment and hippocampal neuroinflammation via inhibiting NF-κB
activation in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease induced by
amyloid-β(1–42). Brain Res. 1384:89–96. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ling S, Zhou J, Rudd JA, Hu Z and Fang M:
The recent updates of therapeutic approaches against aβ for the
treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Anat Rec (Hoboken).
294:1307–1318. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Matsuda Y, Hirano H and Watanabe Y:
Effects of estrogen on acetylcholine release in frontal cortex of
female rats: Involvement of serotonergic neuronal systems. Brain
Res. 937:58–65. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vest RS and Pike CJ: Gender, sex steroid
hormones, and Alzheimer's disease. Horm Behav. 63:301–307. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu Z, Li Y, Fang M, Wai MS and Yew DT:
Exogenous progesterone: A potential therapeutic candidate in CNS
injury and neurodegeneration. Curr Med Chem. 16:1418–1425. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Birzniece V, Johansson IM, Wang MD,
Bäckström T and Olsson T: Ovarian hormone effects on
5-hydroxytryptamine(2A) and 5-hydroxytryptamine(2C) receptor mRNA
expression in the ventral hippocampus and frontal cortex of female
rats. Neurosci Lett. 319:157–161. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McLaughlin KJ, Bimonte-Nelson H,
Neisewander JL and Conrad CD: Assessment of estradiol influence on
spatial tasks and hippocampal CA1 spines: Evidence that the
duration of hormone deprivation after ovariectomy compromises
17beta-estradiol effectiveness in altering CA1 spines. Horm Behav.
54:386–395. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Si D, Li J, Liu J, Wang X, Wei Z, Tian Q,
Wang H and Liu G: Progesterone protects blood-brain barrier
function and improves neurological outcome following traumatic
brain injury in rats. Exp Ther Med. 8:1010–1014. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sandstrom NJ and Williams CL: Spatial
memory retention is enhanced by acute and continuous estradiol
replacement. Horm Behav. 45:128–135. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chisholm NC and Juraska JM: Factors
influencing the cognitive and neural effects of hormone treatment
during aging in a rodent model. Brain Res. 1514:40–49. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang VC, Neese SL, Korol DL and Schantz
SL: Chronic estradiol replacement impairs performance on an operant
delayed spatial alternation task in young, middle-aged, and old
rats. Horm Behav. 56:382–390. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Meng Y, Wang R, Yang F, Ji ZJ, Fang L and
Sheng SL: Amyloid precursor protein 17-mer peptide ameliorates
hippocampal neurodegeneration in ovariectomized rats. Neurosci
Lett. 468:173–177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mittal G, Carswell H, Brett R, Currie S
and Kumar MN: Development and evaluation of polymer nanoparticles
for oral delivery of estradiol to rat brain in a model of
Alzheimer's pathology. J Control Release. 150:220–228. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hruska Z and Dohanich GP: The effects of
chronic estradiol treatment on working memory deficits induced by
combined infusion of beta-amyloid (1–42) and ibotenic acid. Horm
Behav. 52:297–306. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shang XL, Zhao JH, Cao YP and Xue YX:
Effects of synaptic plasticity regulated by 17beta-estradiol on
learning and memory in rats with Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci
Bull. 26:133–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jung JI, Ladd TB, Kukar T, Price AR, Moore
BD, Koo EH, Golde TE and Felsenstein KM: Steroids as γ-secretase
modulators. FASEB J. 27:3775–3785. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Singh M and Su C: Progesterone-induced
neuroprotection: Factors that may predict therapeutic efficacy.
Brain Res. 1514:98–106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singh M: Progesterone-induced
neuroprotection. Endocrine. 29:271–274. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Misra M, Katzman DK, Estella NM, Eddy KT,
Weigel T, Goldstein MA, Miller KK and Klibanski A: Impact of
physiologic estrogen replacement on anxiety symptoms, body shape
perception, and eating attitudes in adolescent girls with anorexia
nervosa: Data from a randomized controlled trial. J Clin
Psychiatry. 74:e765–e771. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bristot G, Ascoli B, Gubert C, Panizzutti
B, Kapczinski F and Rosa AR: Progesterone and its metabolites as
therapeutic targets in psychiatric disorders. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 18:679–690. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Henry JF and Sherwin BB: Hormones and
cognitive functioning during late pregnancy and postpartum: A
longitudinal study. Behav Neurosci. 126:73–85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bojar I, Gujski M, Raczkiewicz D and
Rothenberg KG: Cognitive functions, apolipoprotein E genotype and
hormonal replacement therapy of postmenopausal women. Neuro
Endocrinol Lett. 34:635–642. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brown S: IMS updates its recommendations
on the use of HRT. Menopause Int. 19:105–106. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rocca WA, Grossardt BR and Shuster LT:
Oophorectomy, estrogen, and dementia: A 2014 update. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 389:7–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rasgon NL, Geist CL, Kenna HA, Wroolie TE,
Williams KE and Silverman DH: Prospective randomized trial to
assess effects of continuing hormone therapy on cerebral function
in postmenopausal women at risk for dementia. PLoS One.
9:e890952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Feng Z, Cheng Y and Zhang JT: Long-term
effects of melatonin or 17 beta-estradiol on improving spatial
memory performance in cognitively impaired, ovariectomized adult
rats. J Pineal Res. 37:198–206. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Abel T, Nguyen PV, Barad M, Deuel TA,
Kandel ER and Bourtchouladze R: Genetic demonstration of a role for
PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term
memory. Cell. 88:615–626. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Armstrong RA: What causes alzheimer's
disease? Folia Neuropathol. 51:169–188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hu Z, Rudd JA and Fang M: Development of
the human corpus striatum and the presence of nNOS and 5-HT2A
receptors. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 95:127–131. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
de Quervain DJ, Henke K, Aerni A, Coluccia
D, Wollmer MA, Hock C, Nitsch RM and Papassotiropoulos A: A
functional genetic variation of the 5-HT2a receptor affects human
memory. Nat Neurosci. 6:1141–1142. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Meneses A: 5-HT systems: Emergent targets
for memory formation and memory alterations. Rev Neurosci.
24:629–664. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boulougouris V, Glennon JC and Robbins TW:
Dissociable effects of selective 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor
antagonists on serial spatial reversal learning in rats.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 33:2007–2019. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lorke DE, Lu G, Cho E and Yew DT:
Serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT6 receptors in the prefrontal cortex of
Alzheimer and normal aging patients. BMC Neurosci. 7:362006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Han S, Rudd JA, Hu ZY, Zhang L, Yew DT and
Fang M: Analysis of neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression and
increasing astrogliosis in the brain of
senescence-accelerated-prone 8 mice. Int J Neurosci. 120:602–608.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tomassoni D, Nwankwo IE, Gabrielli MG,
Bhatt S, Muhammad AB, Lokhandwala MF, Tayebati SK and Amenta F:
Astrogliosis in the brain of obese Zucker rat: A model of metabolic
syndrome. Neurosci Lett. 543:136–141. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu Y, Zhang AQ and Yew DT: Age related
changes of various markers of astrocytes in senescence-accelerated
mice hippocampus. Neurochem Int. 46:565–574. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Finch CE: Neurons, glia, and plasticity in
normal brain aging. Adv Gerontol. 10:35–39. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kaur P, Jodhka PK, Underwood WA, Bowles
CA, de Fiebre NC, de Fiebre CM and Singh M: Progesterone increases
brain-derived neuroptrophic factor expression and protects against
glutamate toxicity in a mitogen-activated protein kinase- and
phosphoinositide-3 kinase-dependent manner in cerebral cortical
explants. J Neurosci Res. 85:2441–2449. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu Z, Cai H, Zhang P, Li H, Liu H and Li
Z: Activation of ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt by IGF-1 on GAP-43 expression
in DRG neurons with excitotoxicity induced by glutamate in vitro.
Cell Mol Neurobiol. 32:191–200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nguyen H and Syed V: Progesterone inhibits
growth and induces apoptosis in cancer cells through modulation of
reactive oxygen species. Gynecol Endocrinol. 27:830–836. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|