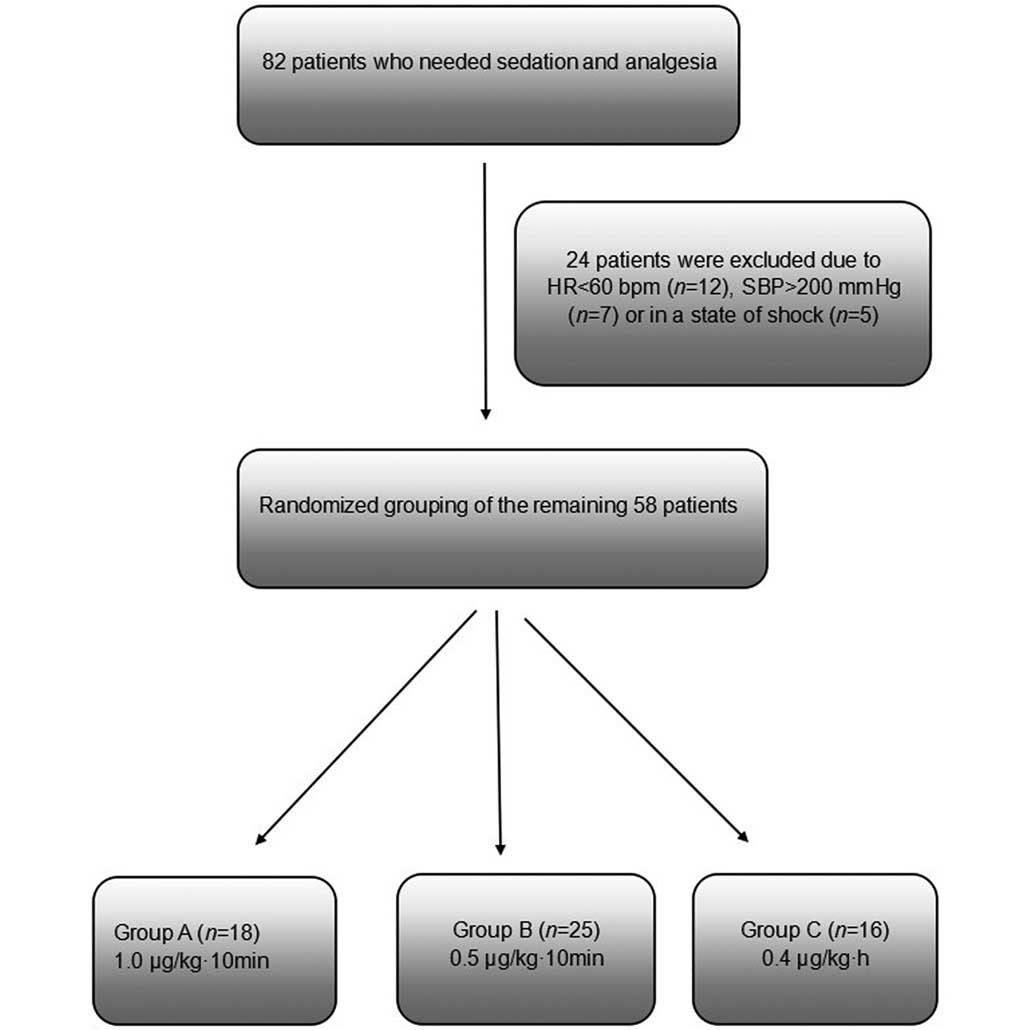
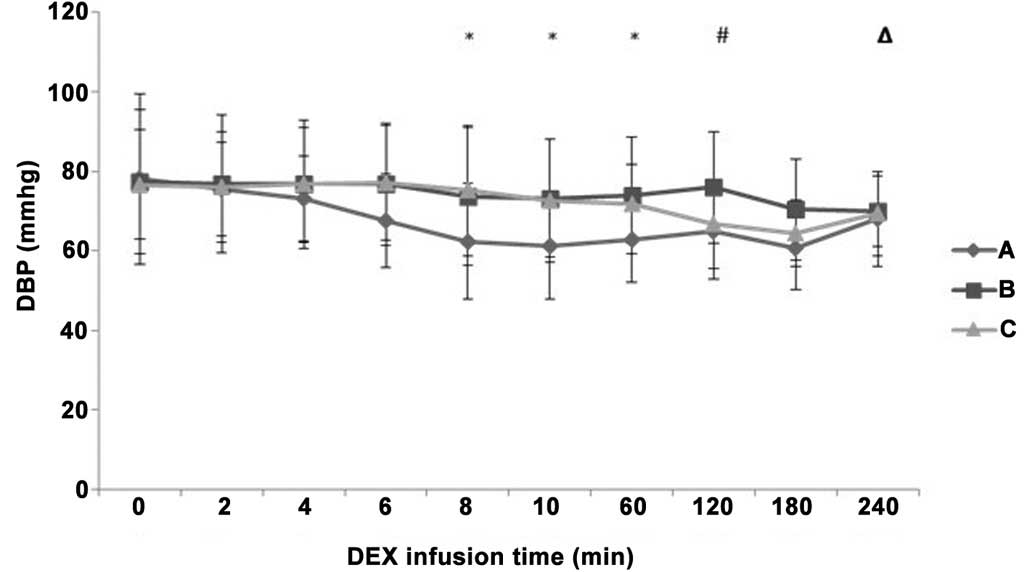
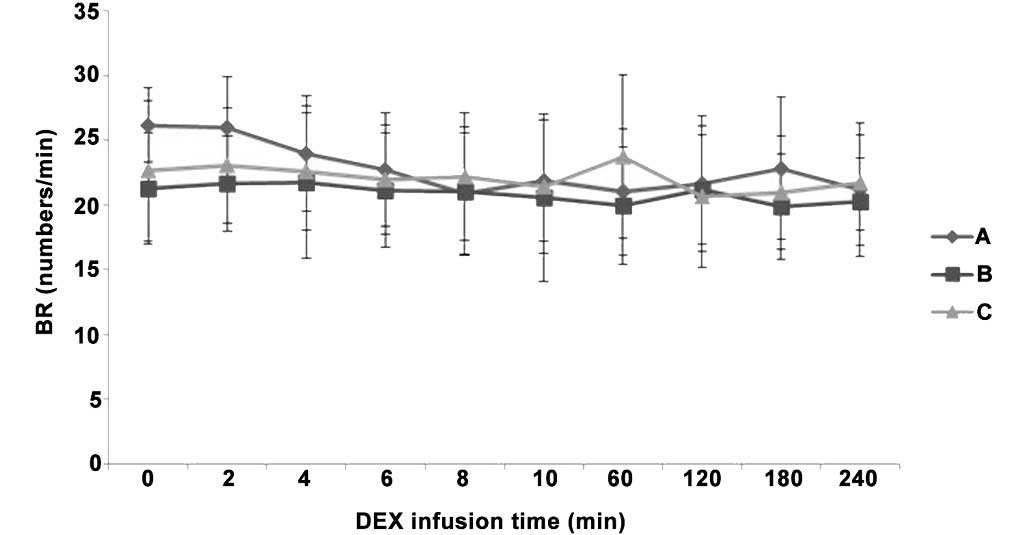
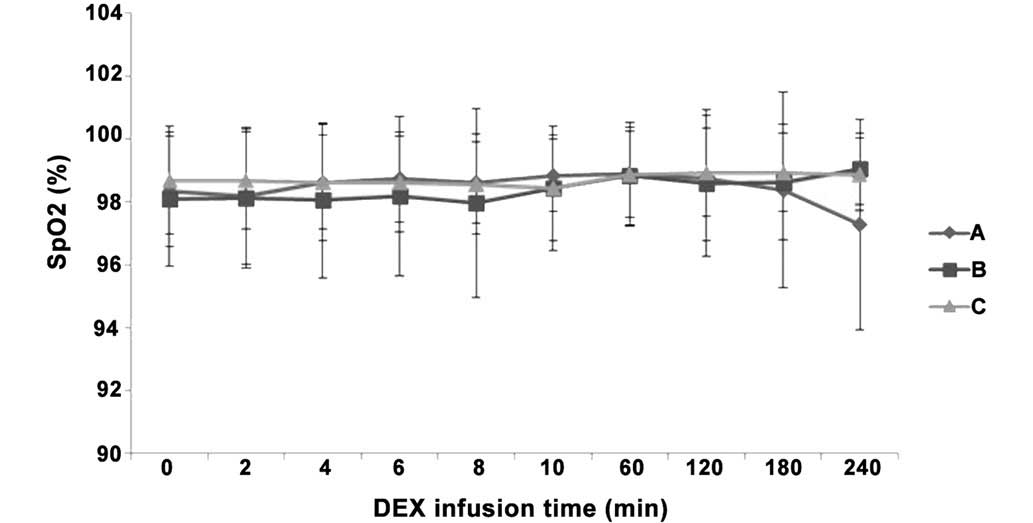
|
1
|
Oldham M and Pisani MA: Sedation in
critically ill patients. Crit Care Clin. 31:563–87. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Genta PR, Eckert DJ, Gregorio MG, Danzi
NJ, Moriya HT, Malhotra A and Lorenzi-Filho G: Critical closing
pressure during midazolam-induced sleep. J Appl Physiol (1985).
111:1315–1322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Perrier ND, Baerga-Varela Y and Murray MJ:
Death related to propofol use in an adult patient. Crit Care Med.
28:3071–3074. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pichot C, Ghignone M and Quintin L:
Dexmedetomidine and clonidine: From second- to first-line sedative
agents in the critical care setting? J Intensive Care Med.
27:219–237. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rayner SG, Weinert CR, Peng H, Jepsen S
and Broccard AF: Study Institution: Dexmedetomidine as adjunct
treatment for severe alcohol withdrawal in the ICU. Ann Intensive
Care. 23:122012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yang L, Xu JM, Jiang X, Ruan W, Cui Y and
He L: Effect of dexmedetomidine on plasma brain-derived
neurotrophic factor: A double-blind, randomized and
placebo-controlled study. Ups J Med Sci. 118:235–239. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chrysostomou CI, Beerman L, Shiderly D,
Berry D, Morell VO and Munoz R: Dexmedetomidine: A novel drug for
the treatment of atrial and junctional tachyarrhythmias during the
perioperative period for congenital cardiac surgery: A preliminary
study. Anesth Analg. 107:1514–1522. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jalowiecki P, Rudner R, Gonciarz M,
Kawecki P, Petelenz M and Dziurdzik P: Sole use of dexmedetomidine
has limited utility for conscious sedation during outpatient
colonoscopy. Anesthesiology. 103:269–273. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Giovannitti JA Jr, Thoms SM and Crawford
JJ: Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists: A review of current
clinical applications. Anesth Prog. 62:31–39. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Longrois D, Conti G, Mantz J, Faltlhauser
A, Aantaa R and Tonner P: Sedation in non-invasive ventilation: Do
we know what to do (and why)? Multidiscip Respir Med. 9:562014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nishizawa T, Suzuki H, Sagara S, Kanai T
and Yahagi N: Dexmedetomidine versus midazolam for gastrointestinal
endoscopy: A meta-analysis. Dig Endosc. 27:8–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Goodwin HE, Gill RS, Murakami PN, Thompson
CB, Lewin JJ 3rd and Mirski MA: Dexmedetomidine preserves
attention/calculation when used for cooperative and short-term
intensive care unit sedation. J Crit Care. 28:1113.e7–1113.e10.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ludtke KA, Stanley KS, Yount NL and Gerkin
RD: Retrospective review of critically ill patients experiencing
alcohol withdrawal: Dexmedetomidine versus propofol and/or
lorazepam continuous infusions. Hosp Pharm. 50:208–213. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bhana N, Goa KL and McClellan KJ:
Dexmedetomidine. Drugs. 59:263–270. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bassett R, Adams KM, Danesh V, Groat PM,
Haugen A, Kiewel A, Small C, Van-Leuven M, Venus S and Ely EW:
Rethinking critical care: Decreasing sedation, increasing delirium
monitoring, and increasing patient mobility. Jt Comm J Qual Patient
Saf. 41:62–74. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Del Bufalo C, Morelli A, Bassein L, Fasano
L, Quarta CC, Pacilli AM and Gunella G: Severity scores in
respiratory intensive care: APACHE II predicted mortality better
than SAPS II. Respir Care. 40:1042–1047. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maraboto E: ABCDEs of ICU: Choice of
sedative. Crit Care Nurs Q. 36:157–162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Devabhakthuni S, Armahizer MJ, Dasta JF
and Kane-Gill SL: Analgosedation: A paradigm shift in intensive
care unit sedation practice. Ann Pharmacother. 46:530–540. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gudmundsson G, Ulrik CS, Gislason T,
Lindberg E, Brøndum E, Bakke P and Janson C: Long-term survival in
patients hospitalized for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A
prospective observational study in the Nordic countries. Int J
Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 7:571–576. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ai-Ping C, Lee KH and Lim TK: In-hospital
and 5-year mortality of patients treated in the ICU for acute
exacerbation of COPD: A retrospective study. Chest. 128:518–524.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Andreas S, Haarmann H, Klarner S,
Hasenfuss G and Raupach T: Increased sympathetic nerve activity in
COPD is associated with morbidity and mortality. Lung. 192:235–241.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gerlach AT and Dasta JF: Dexmedetomidine:
An updated review. Ann Pharmacother. 41:245–252. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Riker RR, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, Ceraso D,
Wisemandle W, Koura F, Whitten P, Margolis BD, Byrne DW, Ely EW and
Rocha MG: SEDCOM (Safety and Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine Compared
With Midazolam) Study Group: Dexmedetomidine vs. midazolam for
sedation of critically ill patients: A randomized trial. JAMA.
301:489–499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pandharipande PP, Pun BT, Herr DL, Maze M,
Girard TD, Miller RR, Shintani AK, Thompson JL, Jackson JC, Deppen
SA, et al: Effect of sedation with dexmedetomidine vs lorazepam on
acute brain dysfunction in mechanically ventilated patients: The
MENDS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 298:2644–2653. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maldonado JR, Wysong A, van der Starre PJ,
Block T, Miller C and Reitz BA: Dexmedetomidine and the reduction
of postoperative delirium after cardiac surgery. Psychosomatics.
50:206–217. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ozaki M, Takeda J, Tanaka K, Shiokawa Y,
Nishi S, Matsuda K, Doi M, Kakihana Y, Fujino Y, Takinami M and
Kawai M: Safety and efficacy of dexmedetomidine for long-term
sedation in critically ill patients. J Anesth. 28:38–50. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Takata K, Adachi YU, Suzuki K, Obata Y,
Sato S and Nishiwaki K: Dexmedetomidine-induced atrioventricular
block followed by cardiac arrest during atrial pacing: A case
report and review of the literature. J Anesth. 28:116–120. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bharati S, Pal A, Biswas C and Biswas R:
Incidence of cardiac arrest increases with the indiscriminate use
of dexmedetomidine: A case series and review of published case
reports. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 49:165–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sakamaki F, Satoh T, Nagaya N, Kyotani S,
Nakanishi N and Ishida Y: Abnormality of left ventricular
sympathetic nervous function assessed by (123)
I-metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging in patients with COPD. Chest.
116:1575–1581. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Victor RG and Shafiq MM: Sympathetic
neural mechanisms in human hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep.
10:241–247. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brown SJ, Raman A, Barnes MJ and Mundel T:
Autonomic cardiovascular response to acute hypoxia and passive
head-up tilting in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol. 113:1731–1736. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vincent JL, Baron JF, Reinhart K,
Gattinoni L, Thijs L, Webb A, Meier-Hellmann A, Nollet G and
Peres-Bota D: ABC (Anemia and Blood Transfusion in Critical Care)
Investigators: Anemia and blood transfusion in critically ill
patients. JAMA. 288:1499–1507. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dünser MW and Hasibeder WR: Sympathetic
overstimulation during critical illness: Adverse effects of
adrenergic stress. J Intensive Care Med. 24:293–316. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Franchitto N, Despas F, Labrunée M,
Roncalli J, Boveda S, Galinier M, Senard JM and Pathak A: Tonic
chemoreflex activation contributes to increased sympathetic nerve
activity in heart failure-related anemia. Hypertension.
55:1012–1017. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|