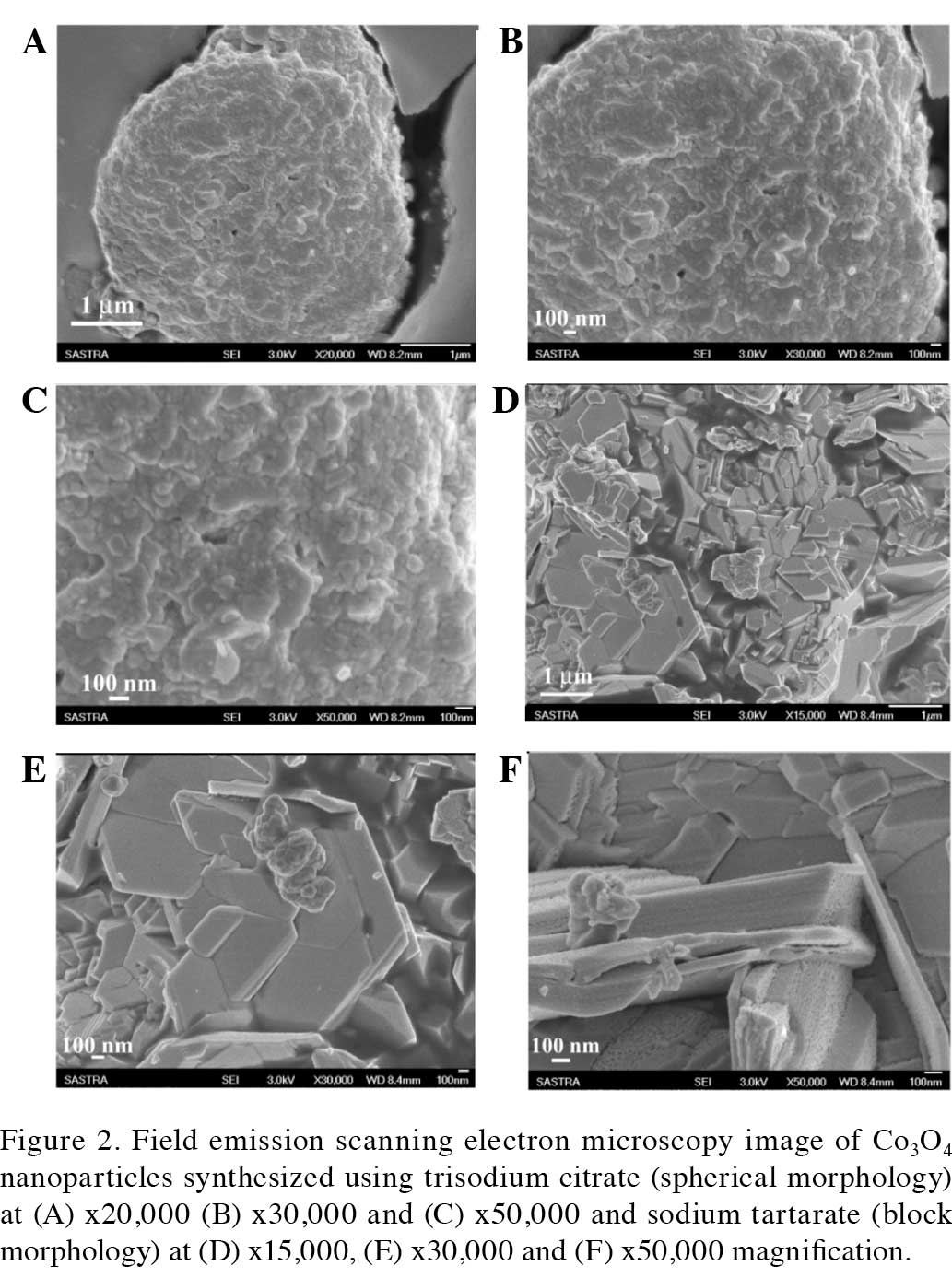
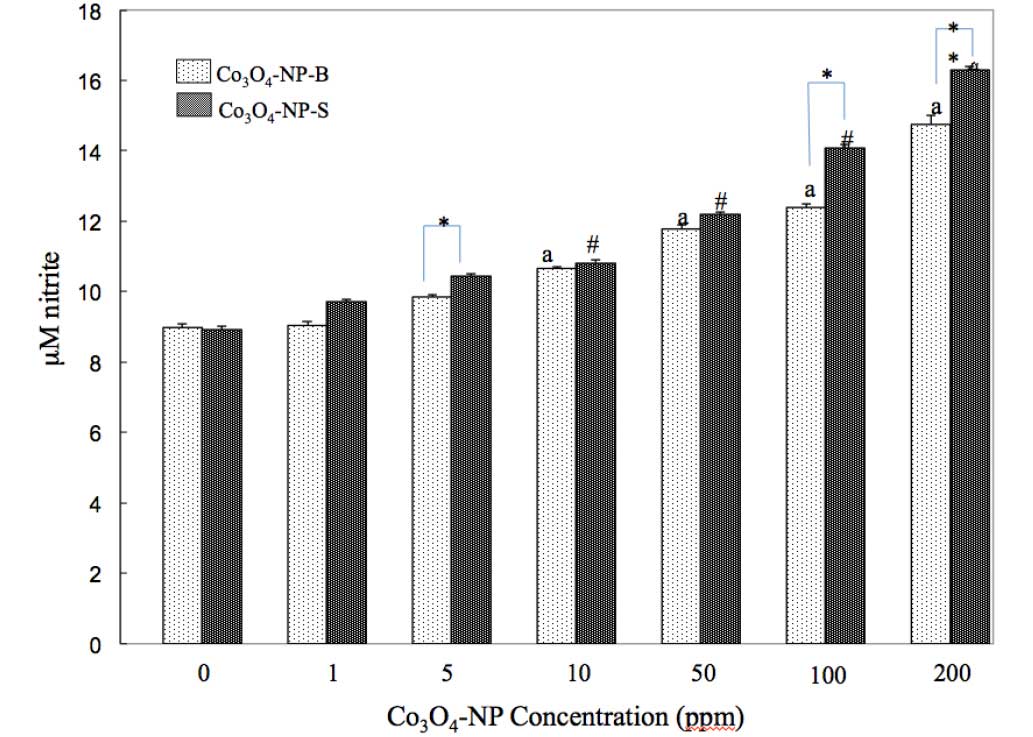
|
1
|
Ando M, Kobayashi T, Iijima S and Haruta
M: Optical recognition of CO and H2 by use of gas-sensitive
Au-Co3O4 composite films. J Mater Chem. 7:1779–1783. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li WY, Xu LN and Chen J: Co3O4
nanomaterials in lithium-ion batteries and gas sensors. Adv Funct
Mater. 15:851–857. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ghosh M, Sampathkumaran EV and Rao CNR:
Synthesis and magnetic properties of CoO nanoparticles. Chem Mater.
17:2348–2352. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang RM, Liu CM, Zhang HZ, Chen CP, Guo L,
Xu HB and Yang SH: Porous nanotubes of Co3O4: Synthesis,
characterization, and magnetic properties. Appl Phys Lett.
85:2080–2082. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang X, Chen XY, Gao LS, Zheng HG, Zhang Z
and Qian YT: One-Dimensional arrays of Co3O4 nanoparticles:
Synthesis, characterization, and optical and electrochemical
properties. J Phys Chem B. 108:16401–16404. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yang R, Wang Z, Liu J and Chen L: Nano
Co3O4 particles embedded in porous hard carbon spherules as anode
material for Li-ion batteries. Electrochem Solid-State Lett.
7:A496–A499. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Im Y, Lee C, Vasquez RP, Bangar MA, Myung
NV, Menke EJ, Penner RM and Yun M: Investigation of a single Pd
nanowire for use as a hydrogen sensor. Small. 2:356–358. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang X, Zhuang J, Peng Q and Li Y: A
general strategy for nanocrystal synthesis. Nature. 437:121–124.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lou XWD, Archer LA and Yang Z: Hollow
Micro-/Nanostructures: Synthesis and Applications. Adv Mater.
20:3987–4019. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Tan B and Wu Y: Mesoporous Co3O4
nanowire arrays for lithium ion batteries with high capacity and
rate capability. Nano Lett. 8:265–270. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
García-Pacheco G, Cabañas-Moreno JG,
Yee-Madeira H and Cruz-Gandarilla F: Co3O4 nanoparticles produced
by mechanochemical reactions. Nanotechnology. 17:2528–2535. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He T, Chen D, Jiao X and Wang Y: Co3O4
Nanoboxes: Surfactant-templated fabrication and microstructure
characterization. Adv Mater. 18:1078–1082. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang ZH, Chen XY, Zhang M and Qian YT:
Synthesis of Co3O4 nanorod bunches from a single precursor
Co(CO3)0.35Cl0.20(OH)1.10. Solid State Sci. 7:13–15. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Salabaş EL, Rumplecker A, Kleitz F, Radu F
and Schüth F: Exchange anisotropy in nanocasted Co3O4 nanowires.
Nano Lett. 6:2977–2981. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li T, Yang S, Huang L, Gu B and Du Y: A
novel process from cobalt nanowire to Co3O4 nanotube.
Nanotechnology. 15:1479–1482. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yu T, Zhu YW, Xu XJ, Shen ZX, Chen P, Lim
CT, Thong JTL and Sow CH: Controlled growth and field-emission
properties of cobalt oxide nanowalls. Adv Mater. 17:1595–1599.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bhattacharya K, Cramer H, Albrecht C,
Schins R, Rahman Q, Zimmermann U and Dopp E: Vanadium
pentoxide-coated ultrafine titanium dioxide particles induce
cellular damage and micronucleus formation in V79 cells. J Toxicol
Environ Health A. 71:976–980. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lison D, Lauwerys R, Demedts M and Nemery
B: Experimental research into the pathogenesis of cobalt/hard metal
lung disease. Eur Respir J. 9:1024–1028. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lison D, De Boeck M, Verougstraete V and
Kirsch-Volders M: Update on the genotoxicity and carcinogenicity of
cobalt compounds. Occup Environ Med. 58:619–625. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Domingo JL: Metal-induced developmental
toxicity in mammals: A review. J Toxicol Environ Health.
42:123–141. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Magaye R, Zhao J, Bowman L and Ding M:
Genotoxicity and carcinogenicity of cobalt-, nickel- and
copper-based nanoparticles. Exp Ther Med. 4:551–561.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kuo CY, Wong RH, Lin JY, Lai JC and Lee H:
Accumulation of chromium and nickel metals in lung tumors from lung
cancer patients in Taiwan. J Toxicol Environ Health A.
69:1337–1344. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
De Boeck M, Kirsch-Volders M and Lison D:
Cobalt and antimony, Genotoxicity and carcinogenicity. Mutat Res.
533:135–152. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Beyersmann D and Hartwig A: The genetic
toxicology of cobalt. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 115:137–145. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ponti J, Sabbioni E, Munaro B, Broggi F,
Marmorato P, Franchini F, Colognato R and Rossi F: Genotoxicity and
morphological transformation induced by cobalt nanoparticles and
cobalt chloride, An in vitro study in Balb/3T3 mouse fibroblasts.
Mutagenesis. 24:439–445. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Colognato R, Bonelli A, Ponti J, Farina M,
Bergamaschi E, Sabbioni E and Migliore L: Comparative genotoxicity
of cobalt nanoparticles and ions on human peripheral leukocytes in
vitro. Mutagenesis. 23:377–382. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Papageorgiou I, Brown C, Schins R, Singh
S, Newson R, Davis S, Fisher J, Ingham E and Case CP: The effect of
nano- and micron-sized particles of cobalt-chromium alloy on human
fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials. 28:2946–2958. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Aker WG, Hwang HM, Yedjou CG, Yu H
and Tchounwou PB: A study of the mechanism of in vitro cytotoxicity
of metal oxide nanoparticles using catfish primary hepatocytes and
human HepG2 cells. Sci Total Environ. 409:4753–4762. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guildford AL, Poletti T, Osbourne LH, Di
Cerbo A, Gatti AM and Santin M: Nanoparticles of a different source
induce different patterns of activation in key biochemical and
cellular components of the host response. J R Soc Interface.
6:1213–1221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Papis E, Rossi F, Raspanti M, Dalle-Donne
I, Colombo G, Milzani A, Bernardini G and Gornati R: Engineered
cobalt oxide nanoparticles readily enter cells. Toxicol Lett.
189:253–259. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Anard D, Kirsch-Volders M, Elhajouji A,
Belpaeme K and Lison D: In vitro genotoxic effects of hard metal
particles assessed by alkaline single cell gel and elution assays.
Carcinogenesis. 18:177–184. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ding M, Kisin ER, Zhao J, Bowman L, Lu Y,
Jiang B, Leonard S, Vallyathan V, Castranova V and Murray AR:
Size-dependent effects of tungsten carbide-cobalt particles on
oxygen radical production and activation of cell signaling pathways
in murine epidermal cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 241:260–268.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pershina AG, Sazonov AE, Novikov DV,
Knyazev AS, Izaak TI, Itin VI, Naiden EP, Magaeva AA and Terechova
OG: Study of DNA interaction with cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J
Nanosci Nanotechnol. 11:2673–2677. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rebello V, Shaikh S and Desai PV: Toxicity
of cobalt oxide nanoparticles on microalgae (Navicula sp. and
Chetoceros sp.) and Bivalve (Meritrix meritrix) cells. 2010
International Conference on Environmental Engineering and
Applications. Singapore. 195–199. 2010.http://toc.proceedings.com/09360webtoc.pdf
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ghodake G, Seo YD and Lee DS: Hazardous
phytotoxic nature of cobalt and zinc oxide nanoparticles assessed
using Allium cepa. J Hazard Mater. 186:952–955. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Falfushynska H, Gnatyshyna L, Turta O,
Stoliar O, Mitina N, Zaichenko A and Stoika R: Responses of hepatic
metallothioneins and apoptotic activity in Carassius auratus
gibelio witness a release of cobalt and zinc from waterborne
nanoscale composites. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol.
160:66–74. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu Z, Zhang B and Yan B: Regulation of
enzyme activity through interactions with nanoparticles. Int J Mol
Sci. 10:4198–4209. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Manikandan R, Thiagarajan R, Beulaja S,
Sudhandiran G and Arumugam M: Effect of curcumin on
selenite-induced cataractogenesis in Wistar rat pups. Curr Eye Res.
35:122–129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Manikandan R, Thiagarajan R, Beulaja S,
Sudhandiran G and Arumugam M: Curcumin prevents free
radical-mediated cataractogenesis through modulations in lens
calcium. Free Radic Biol Med. 48:483–492. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr and
Feather-Stone RM: A new and rapid colorimetric determination of
acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 7:88–95. 1961.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Matzapetakis M, Dakanali M, Raptopoulou
CP, Tangoulis V, Terzis A, Moon N, Giapintzakis J and Salifoglou A:
Synthesis, spectroscopic, and structural characterization of the
first aqueous cobalt(II)-citrate complex, Toward a potentially
bioavailable form of cobalt in biologically relevant fluids. J Biol
Inorg Chem. 5:469–474. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Haines RA, Kipp EB and Reimer M:
Cobalt(III) complexes containing optically active tartaric acid.
Inorg Chem. 13:2473–2476. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Theja GS, Lowrence RC, Ravi V, Nagarajan S
and Anthony SP: Synthesis of Cu2O micro/nanocrystals with tunable
morphologies using coordinating ligands as structure controlling
agents and antimicrobial studies. CrystEngComm. 16:9866–9872. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lou XW, Deng D, Lee JY, Feng J and Archer
LA: Self-supported formation of needlelike Co3O4 nanotubes and
their application as lithium-ion battery electrodes. Adv Mater.
20:258–262. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Diamond JM, Winchester EL, Mackler DG,
Rasnake WJ, Fanelli JK and Gruber D: Toxicity of cobalt to
fresh-water indicator species as a function of water hardness.
Aquat Toxicol. 22:163–179. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Gibbs RJ: Metals in the sediments along
the Hudson River estuary. Environ Int. 20:507–516. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gambardella C, Aluigi MG, Ferrando S,
Gallus L, Ramoino P, Gatti AM, Rottigni M and Falugi C:
Developmental abnormalities and changes in cholinesterase activity
in sea urchin embryos and larvae from sperm exposed to engineered
nanoparticles. Aquat Toxicol 130-131. 77–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Gambardella C, Ferrando S, Morgana S,
Gallus L, Ramoino P, Ravera S, Bramini M, Diaspro A, Faimali M and
Falugi C: Exposure of Paracentrotus lividus male gametes to
engineered nanoparticles affects skeletal bio-mineralization
processes and larval plasticity. Aquat Toxicol. 158:181–191. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cavallo D, Ciervo A, Fresegna AM, Maiello
R, Tassone P, Buresti G, Casciardi S, Iavicoli S and Ursini CL:
Investigation on cobalt-oxide nanoparticles cyto-genotoxicity and
inflammatory response in two types of respiratory cells. J Appl
Toxicol. 35:1102–1113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang H, Liu C, Yang D, Zhang H and Xi Z:
Comparative study of cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and
genotoxicity induced by four typical nanomaterials, The role of
particle size, shape and composition. J Appl Toxicol. 29:69–78.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hansen T, Clermont G, Alves A, Eloy R,
Brochhausen C, Boutrand JP, Gatti AM and Kirkpatrick CJ: Biological
tolerance of different materials in bulk and nanoparticulate form
in a rat model, Sarcoma development by nanoparticles. J R Soc
Interface. 3:767–775. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Vertegel AA, Siegel RW and Dordick JS:
Silica nanoparticle size influences the structure and enzymatic
activity of adsorbed lysozyme. Langmuir. 20:6800–6807. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Asuri P, Bale SS, Pangule RC, Shah DA,
Kane RS and Dordick JS: Structure, function, and stability of
enzymes covalently attached to single-walled carbon nanotubes.
Langmuir. 23:12318–12321. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Asuri P, Karajanagi SS, Vertegel AA,
Dordick JS and Kane RS: Enhanced stability of enzymes adsorbed onto
nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 7:1675–1678. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shang W, Nuffer JH, Dordick JS and Siegel
RW: Unfolding of ribonuclease A on silica nanoparticle surfaces.
Nano Lett. 7:1991–1995. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lundqvist M, Sethson I and Jonsson BH:
Protein adsorption onto silica nanoparticles, Conformational
changes depend on the particles' curvature and the protein
stability. Langmuir. 20:10639–10647. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Fischer NO, 5 CM, Simard JM and Rotello
VM: Inhibition of chymotrypsin through surface binding using
nanoparticle-based receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:5018–5023.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang Z, Zhao J, Li F, Gao D and Xing B:
Adsorption and inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by different
nanoparticles. Chemosphere. 77:67–73. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gagner JE, Lopez MD, Dordick JS and Siegel
RW: Effect of gold nanoparticle morphology on adsorbed protein
structure and function. Biomaterials. 32:7241–7252. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sanford J and Venkatapathy R: State of the
Science Literature Review: Everything Nanosilver and More.
Scientific Technical, Research, Engineering, and Modeling Support
Final Report. Varner K: (Washington, DC). U. S. Environmental
Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development. 1–197.
2010.
|
|
62
|
Saptarshi SR, Duschl A and Lopata AL:
Interaction of nanoparticles with proteins, Relation to
bio-reactivity of the nanoparticle. J Nanobiotechnology. 11:262013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Schafer FQ and Buettner GR: Redox
environment of the cell as viewed through the redox state of the
glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple. Free Radic Biol Med.
30:1191–1212. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gilbert HF: Redox control of enzyme
activities by thiol/disulfide exchange. Methods Enzymol.
107:330–351. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Klatt P and Lamas S: Regulation of protein
function by S-glutathiolation in response to oxidative and
nitrosative stress. Eur J Biochem. 267:4928–4944. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|