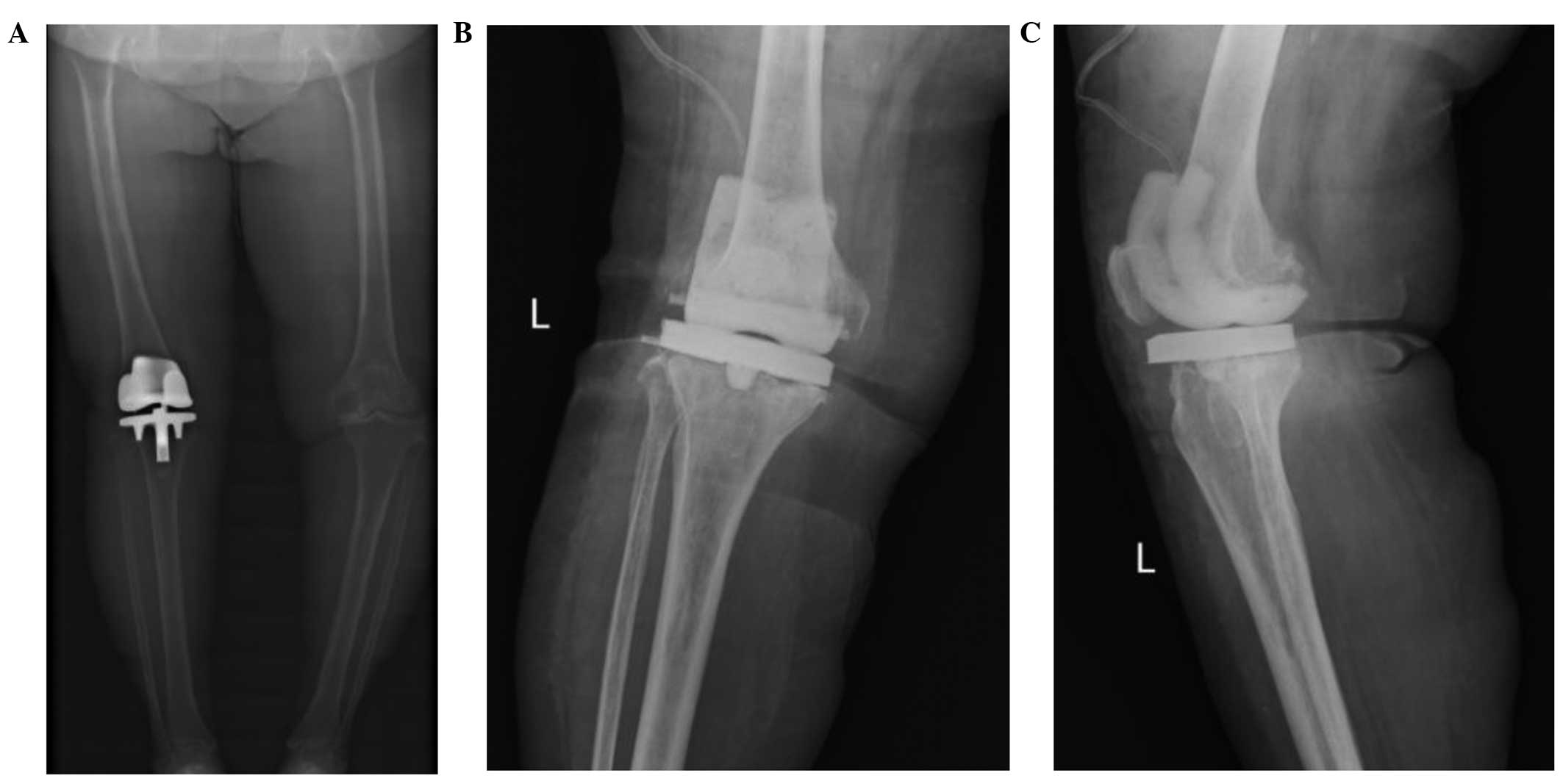
|
1
|
Vahedian-Ardakani M, Mortazavi S and
Farzan M: Total knee arthroplasty: Does the tibial medial side
defect affect outcome? Acta Med Iran. 8:462–465. 2015.
|
|
2
|
Soriano A, Bori G, García-Ramiro S,
Martinez-Pastor JC, Miana T, Codina C, Maculé F, Basora M, Martínez
JA, Riba J, et al: Timing of antibiotic prophylaxis for primary
total knee arthroplasty performed during ischemia. Clin Infect Dis.
46:1009–1014. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martínez-Pastor JC, Maculé-Beneyto F and
Suso-Vergara S: Acute infection in total knee arthroplasty:
Diagnosis and treatment. Open Orthop J. 7:197–204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Otto M: Molecular basis of
Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. Semin Immunopathol.
34:201–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peersman G, Laskin R, Davis J and Peterson
M: Infection in total knee replacement: A retrospective review of
6489 total knee replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 392:15–23.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Joshy S, Gogi N, Thomas B, Mahale A and
Singh BK: Delayed onset of deep infection after total knee
arthroplasty: Comparison based on the infecting organism. J Orthop
Surg (Hong Kong). 15:154–158. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kilgus DJ, Howe DJ and Strang A: Results
of periprosthetic hip and knee infections caused by resistant
bacteria. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 404:116–124. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee JH, Lee JH, Shin YR, Lee JS, Kim WK,
Chi HS, Park CJ and Lee KH: Spontaneous remission of aplastic
anemia: A retrospective analysis. Haematologica. 86:928–933.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yan ZS, Zhang L, Wang HJ, Zhou K, Li JP,
Huang ZD, Wan L, Shang L, Bao XL and Zhang FK: Acute arrest of
hemopoiesis mimics aplastic anemia: 23 cases report. Zhonghua Xue
Ye Xue Za Zhi. 28:750–753. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marty FM and Koo S: Med Mycol. Role of
(1->3)-beta-D-glucan in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis.
Med Mycol 47 Suppl. 1:S233–S240. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Borsato ML, Bruniera P, Cusato MP, Spewien
KE, Durigon EL and Toporovski J: Aplastic crisis in sickle cell
anemia induced by parvovírus B19. J Pediatr (Rio J). 76:458–460.
2000.(In Portuguese). View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ilesanmi OO: Pathological basis of
symptoms and crises in sickle cell disorder: Implications for
counseling and psychotherapy. Hematol Rep. 26:e22010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cauff BE and Quinn CT: Transient
parvovirus-associated hypoplasia of multiple peripheral blood cell
lines in children with chronichemolytic anemia. Pediatr Blood
Cancer. 50:861–864. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Carzavec D, Gaćina P, Vasilj A and Katović
SK: Aplastic crisis induced by human parvovirus B19 as an initial
presentation of hereditary spherocytosis. Coll Antropol.
34:619–621. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Al-Abdwani RM, Khamis FA, Balkhair A,
Sacharia M and Wali YA: A child with human parvovirus B19 infection
induced aplastic anemia and acute hepatitis: Effectiveness of
immunosuppressive therapy. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 25:699–703. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kaptan K, Beyan C, Ural AU, Ustün C, Cetin
T, Avcu F, Kubar A, Aliş M and Yalçin A: Successful treatment of
severe aplastic anemia associated with human parvovirus B19 and
Epstein-Barr virus in a healthy subject with allo-BMT. Am J
Hematol. 67:252–255. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Leoz Gordillo I and Suárez Pérez E:
Aplastic crisis due to Parvovirus B19 and Epstein-Barr virus in a
patient with hereditary spherocytosis. An Pediatr (Barc).
82:e102–e107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rajput R, Sehgal A, Jain D, Sen R and
Gupta A: Acute parvovirus B19 infection leading to severe aplastic
anemia in a previously healthy adult female. Indian J Hematol Blood
Transfus. 28:123–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou Yan and Zhu Shuqing: Acute arrest of
hematopoiesis due to oral methotrexate in a patient with uremia.
Adverse Drug Reactions J. 12:351–352. 2010.
|
|
20
|
Alijanipour P and Parvizi J: Infection
post-total knee replacement: Current concepts. Curr Rev
Musculoskelet Med. 7:96–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bjerke-Kroll BT, Christ AB, McLawhorn AS,
Sculco PK, Jules-Elysée KM and Sculco TP: Periprosthetic joint
infections treated with two-stage revision over 14 years: An
evolving microbiology profile. J Arthroplasty. 29:877–882. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aggarwal VK, Bakhshi H, Ecker NU, Parvizi
J, Gehrke T and Kendoff D: Organism profile in periprosthetic joint
infection: Pathogens differ at two arthroplasty infection referral
centers in Europe and in the United States. J Knee Surg.
27:399–406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Drago L, Signori V, De Vecchi E, Vassena
C, Palazzi E, Cappelletti L, Romanò D and Romanò CL: Use of
dithiothreitol to improve the diagnosis of prosthetic joint
infections. J Orthop Res. 31:1694–1699. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rak M, Barlič-Maganja D, Kavčič M, Trebše
R and Cőr A: Comparison of molecular and culture method in
diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. FEMS Microbiol Lett.
343:42–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu C, Qu X, Liu F, Li H, Mao Y and Zhu Z:
Risk factors for periprosthetic joint infection after total hip ar
oplasty and total knee arthroplasty in Chinese patients. PLoS One.
9:e953002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|