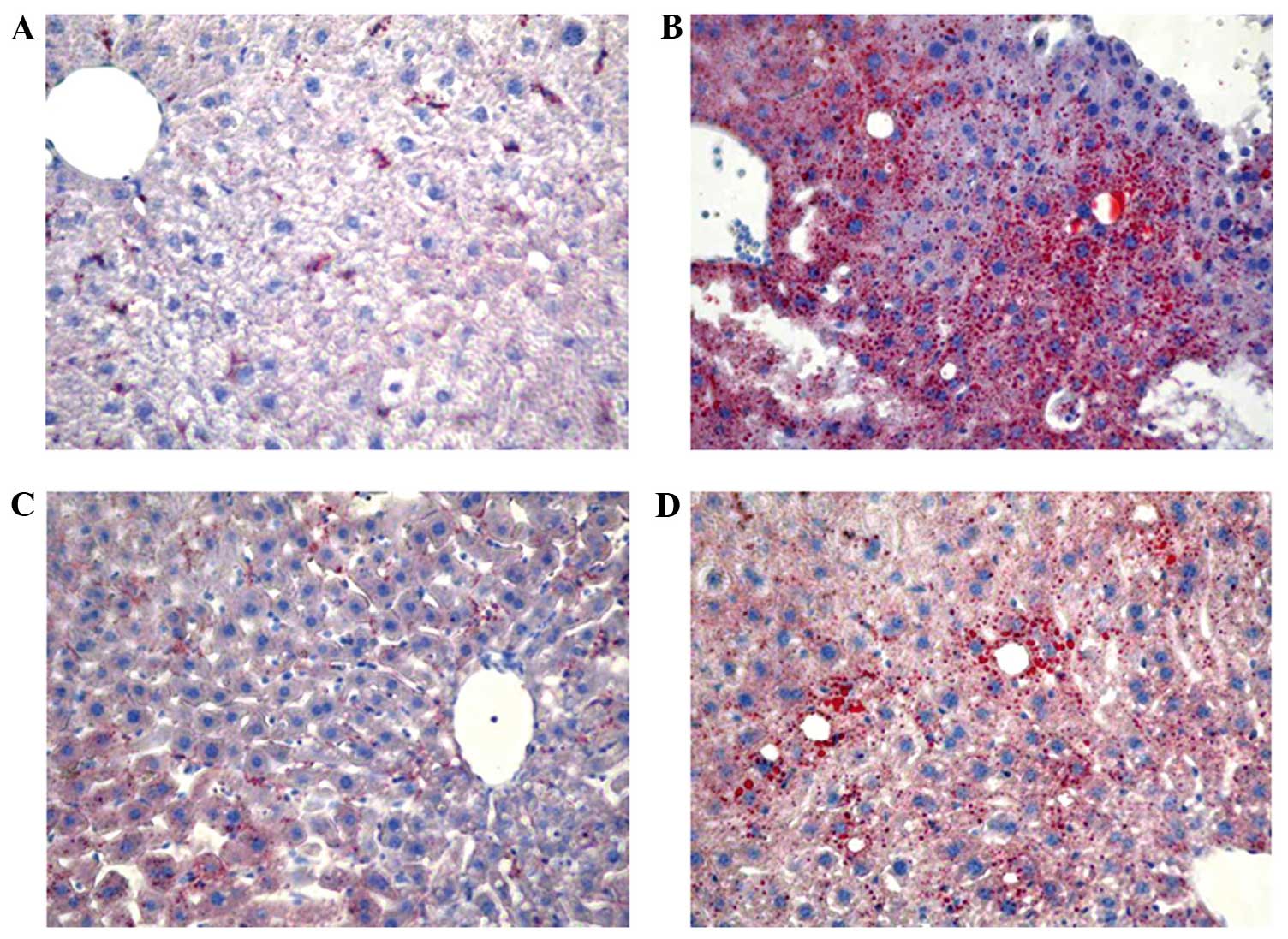
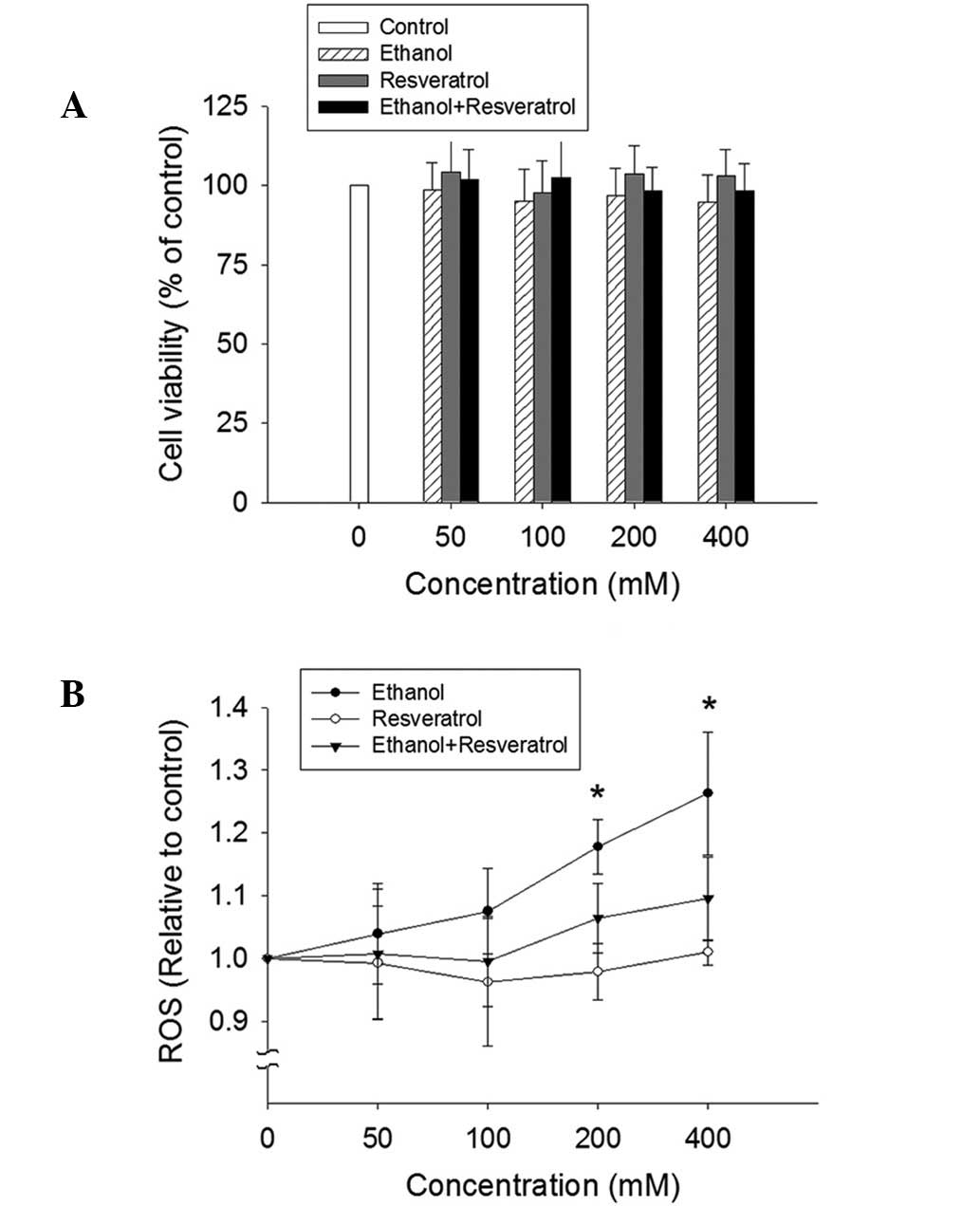
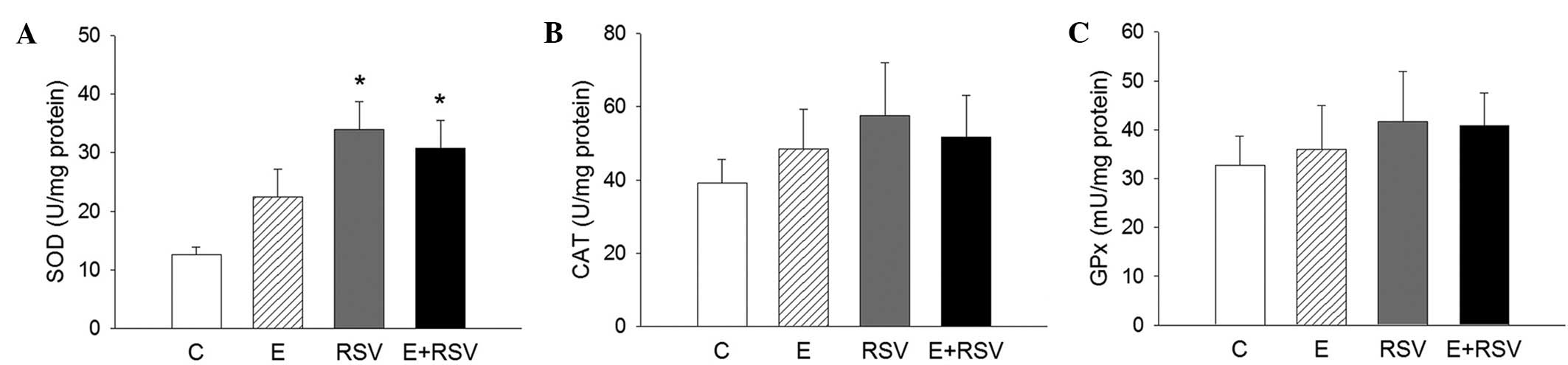
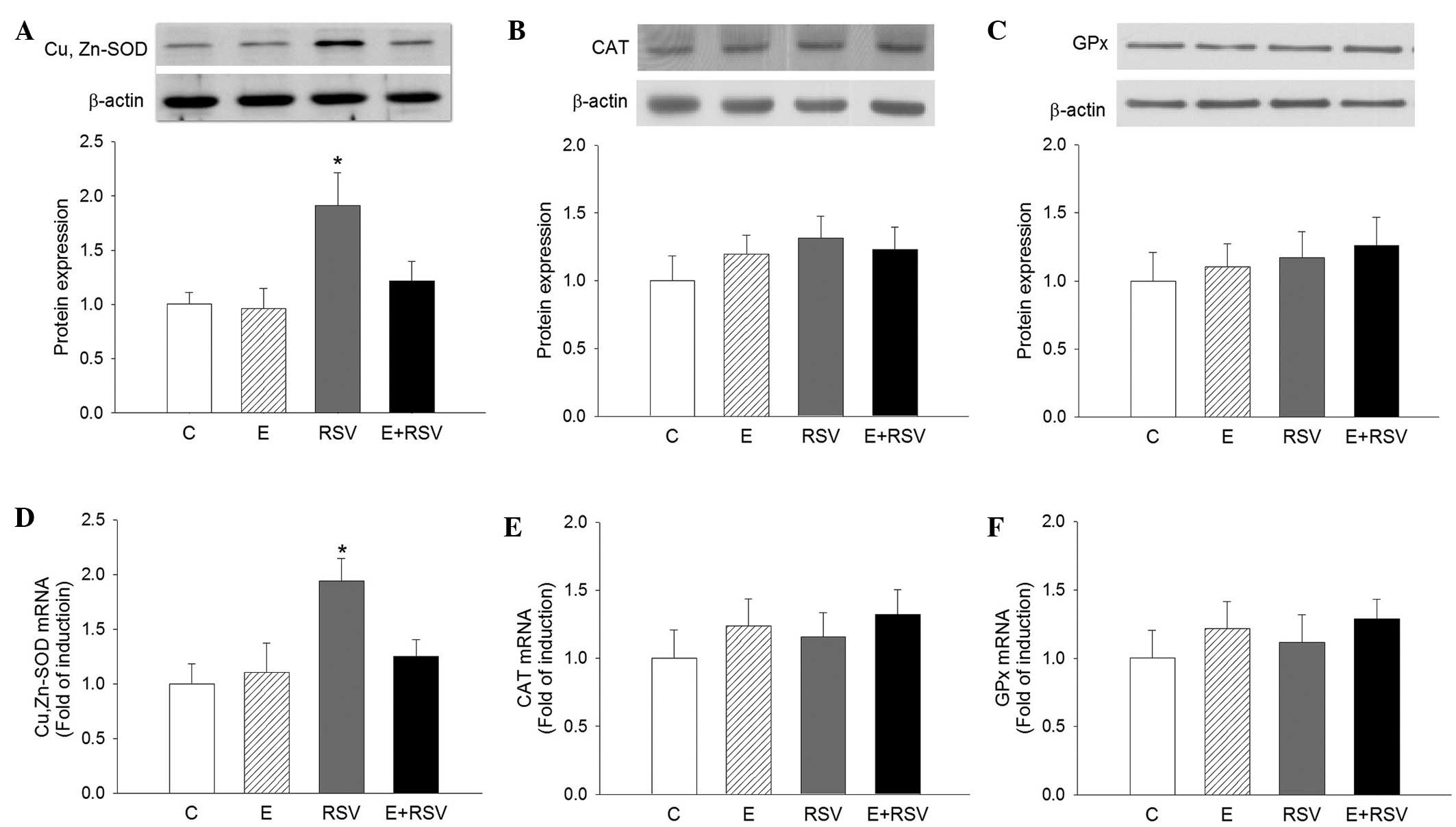
|
1
|
Pirola L and Fröjdö S: Resveratrol: One
molecule, many targets. IUBMB Life. 60:323–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shakibaei M, Harikumar KB and Aggarwal BB:
Resveratrol addiction: To die or not to die. Mol Nutr Food Res.
53:115–128. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leonard SS, Xia C, Jiang BH, Stinefelt B,
Klandorf H, Harris GK and Shi X: Resveratrol scavenges reactive
oxygen species and effects radical-induced cellular responses.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 309:1017–1026. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lasa A, Schweiger M, Kotzbeck P, Churruca
I, Simón E, Zechner R and Portillo MP: Resveratrol regulates
lipolysis via adipose triglyceride lipase. J Nutr Biochem.
23:379–384. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mikuła-Pietrasik J, Kuczmarska A, Rubiś B,
Filas V, Murias M, Zieliński P, Piwocka K and Książek K:
Resveratrol delays replicative senescence of human mesothelial
cells via mobilization of antioxidative and DNA repair mechanisms.
Free Radic Biol Med. 52:2234–2245. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park DW, Kim JS, Chin BR and Baek SH:
Resveratrol inhibits inflammation induced by heat-killed
Listeria monocytogenes. J Med Food. 15:788–794. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Voloshyna I, Hussaini SM and Reiss AB:
Resveratrol in cholesterol metabolism and atherosclerosis. J Med
Food. 15:763–773. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bhatt JK, Thomas S and Nanjan MJ:
Resveratrol supplementation improves glycemic control in type 2
diabetes mellitus. Nutr Res. 32:537–541. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chang CC, Chang CY, Huang JP and Hung LM:
Effect of resveratrol on oxidative and inflammatory stress in liver
and spleen of streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic rats. Chin J
Physiol. 55:192–201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sadruddin S and Arora R: Resveratrol:
Biologic and therapeutic implications. J Cardiometab Syndr.
4:102–106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tomé-Carneiro J, Gonzálvez M, Larrosa M,
García-Almagro FJ, Avilés-Plaza F, Parra S, Yáñez-Gascón MJ,
Ruiz-Ros JA, García-Conesa MT, Tomás-Barberán FA and Espín JC:
Consumption of a grape extract supplement containing resveratrol
decreases oxidized LDL and ApoB in patients undergoing primary
prevention of cardiovascular disease: A triple-blind, 6-month
follow-up, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Mol Nutr Food Res.
56:810–821. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cesaratto L, Vascotto C, Calligaris S and
Tell G: The importance of redox state in liver damage. Ann Hepatol.
3:86–92. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Room R, Babor T and Rehm J: Alcohol and
public health. Lancet. 365:519–530. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cahill A, Cunningham CC, Adachi M, Ishii
H, Bailey SM, Fromenty B and Davies A: Effects of alcohol and
oxidative stress on liver pathology: The role of the mitochondrion.
Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 26:907–915. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hoek JB and Pastorino JG: Cellular
signaling mechanisms in alcohol-induced liver damage. Semin Liver
Dis. 24:257–272. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu KC, Liu J and Klaassen CD: Role of Nrf2
in preventing ethanol-induced oxidative stress and lipid
accumulation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 262:321–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
de Alwis NM and Day CP: Non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease: The mist gradually clears. J Hepatol. 48(Suppl
1): S104–S112. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mann RE, Smart RG and Govoni R: The
epidemiology of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Res Health.
27:209–219. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kumar M, Sharma VL, Sehgal A and Jain M:
Protective effects of green and white tea against benzo(a)pyrene
induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in murine model. Nutr
Cancer. 64:300–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pigeolet E, Corbisier P, Houbion A,
Lambert D, Michiels C, Raes M, Zachary MD and Remacle J:
Glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase
inactivation by peroxides and oxygen derived free radicals. Mech
Ageing Dev. 3:283–297. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jonker JW, Suh JM, Atkins AR, Ahmadian M,
Li P, Whyte J, He M, Juguilon H, Yin YQ, Phillips CT, et al: A
PPARγ-FGF1 axis is required for adaptive adipose remodelling and
metabolic homeostasis. Nature. 485:391–394. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kidani Y and Bensinger SJ: Liver X
receptor and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor as
integrators of lipid homeostasis and immunity. Immunol Rev.
249:72–83. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Berger J and Moller DE: The mechanisms of
action of PPARs. Annu Rev Med. 53:409–435. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang J, Jia Y, Fu T, Viswakarma N, Bai L,
Rao MS, Zhu Y, Borensztajn J and Reddy JK: Sustained activation of
PPARα by endogenous ligands increases hepatic fatty acid oxidation
and prevents obesity in ob/ob mice. FASEB J. 26:628–638. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takahashi N, Senda M, Lin S, Goto T, Yano
M, Sasaki T, Murakami S and Kawada T: Auraptene regulates gene
expression involved in lipid metabolism through PPARα activation in
diabetic obese mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:1791–1797. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chong HC, Tan MJ, Philippe V, Tan SH, Tan
CK, Ku CW, Goh YY, Wahli W, Michalik L and Tan NS: Regulation of
epithelial-mesenchymal IL-1 signaling by PPARbeta/delta is
essential for skin homeostasis and wound healing. J Cell Biol.
184:817–831. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Man MQ, Barish GD, Schmuth M, Crumrine D,
Barak Y, Chang S, Jiang Y, Evans RM, Elias PM and Feingold KR:
Deficiency of PPARbeta/delta in the epidermis results in defective
cutaneous permeability barrier homeostasis and increased
inflammation. J Invest Dermatol. 128:370–377. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Müller R, Rieck M and Müller-Brüsselbach
S: Regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation by PPARβ/δ.
PPAR Res. 2008:6148522008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoo HY, Chang MS and Rho HM: Induction of
the rat Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene through the peroxisome
proliferator-responsive element by arachidonic acid. Gene.
234:87–91. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Girnun GD, Domann FE, Moore SA and Robbins
ME: Identification of a functional peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor response element in the rat
catalase promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 16:2793–2801. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jung KH, Chu K, Lee ST, Kim SJ, Song EC,
Kim EH, Park DK, Sinn DI, Kim JM, Kim M and Roh JK: Blockade of AT1
receptor reduces apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress in
normotensive rats with intracerebral hemorrhage. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 322:1051–1058. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
National Research Council (US) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research: Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US).
1996.
|
|
33
|
Lin KY, Chen YL, Shih CC, Pan JP, Chan WE
and Chiang AN: Contribution of HDL-apolipoproteins to the
inhibition of low density lipoprotein oxidation and lipid
accumulation in macrophages. J Cell Biochem. 86:258–267. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cui W, Chen SL and Hu KQ: Quantification
and mechanisms of oleic acid-induced steatosis in HepG2 cells. Am J
Transl Res. 2:95–104. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Carmichael J, DeGraff WG, Gazdar AF, Minna
JD and Mitchell JB: Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated
colorimetric assay: Assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer
Res. 47:936–942. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
LeBel CP, Ischiropoulos H and Bondy SC:
Evaluation of the probe 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin as an indicator of
reactive oxygen species formation and oxidative stress. Chem Res
Toxicol. 5:227–231. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Oyanagui Y: Reevaluation of assay methods
and establishment of kit for superoxide dismutase activity. Anal
Biochem. 142:290–296. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen J, Rogers SC and Kavdia M: Analysis
of kinetics of dihydroethidium fluorescence with superoxide using
xanthine oxidase and hypoxanthine assay. Ann Biomed Eng.
41:327–337. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Aebi H: Catalase in vitro. Methods
Enzymol. 105:121–126. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Flohé L and Günzler WA: Assays of
glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol. 105:114–121. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bradford MM: A Rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu CL, Wang YZ, Guo J, Liu JX and Feng J:
Comparison of age-related differences in expression of antioxidant
enzyme mRNA and activity in various tissues of pigs. Comp Biochem
Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 147:445–451. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Patel DN, King CA, Bailey SR, Holt JW,
Venkatachalam K, Agrawal A, Valente AJ and Chandrasekar B:
Interleukin-17 stimulates C-reactive protein expression in
hepatocytes and smooth muscle cells via p38 MAPK and
ERK1/2-dependent NF-kappaB and C/EBPbeta activation. J Biol Chem.
282:27229–27238. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Young DC, Kingsley SD, Ryan KA and Dutko
FJ: Selective inactivation of eukaryotic β-galactosidase in assays
for inhibitors of HIV-1 TAT using bacterial β-galactosidase as a
reporter enzyme. Anal Biochem. 215:24–30. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pochareddy S and Edenberg HJ: Chronic
alcohol exposure alters gene expression in HepG2 cells. Alcohol
Clin Exp Res. 36:1021–1033. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tsukamoto H and Lu SC: Current concepts in
the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver injury. FASEB J. 15:1335–1349.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Comporti M, Signorini C, Leoncini S, Gardi
C, Ciccoli L, Giardini A, Vecchio D and Arezzini B: Ethanol-induced
oxidative stress: Basic knowledge. Genes Nutr. 2:101–109. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Park DW, Baek K, Kim JR, Lee JJ, Ryu SH,
Chin BR and Baek SH: Resveratrol inhibits foam cell formation via
NADPH oxidase 1-mediated reactive oxygen species and monocyte
chemotactic protein-1. Exp Mol Med. 41:171–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Matés JM, Pérez-Gómez C and de Núñez
Castro I: Antioxidant enzymes and human diseases. Clin Biochem.
32:595–603. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kasdallah-Grissa A, Mornagui B, Aouani E,
Hammami M, El May M, Gharbi N, Kamoun A and El-Fazaâ S:
Resveratrol, a red wine polyphenol, attenuates ethanol-induced
oxidative stress in rat liver. Life Sci. 80:1033–1039. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cheng G, Zhang X, Gao D, Jiang X and Dong
W: Resveratrol inhibits MMP-9 expression by up-regulating PPAR
alpha expression in an oxygen glucose deprivation-exposed neuron
model. Neurosci Lett. 451:105–108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kennedy A, Overman A, Lapoint K, Hopkins
R, West T, Chuang CC, Martinez K, Bell D and McIntosh M: Conjugated
linoleic acid-mediated inflammation and insulin resistance in human
adipocytes are attenuated by resveratrol. J Lipid Res. 50:225–232.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|