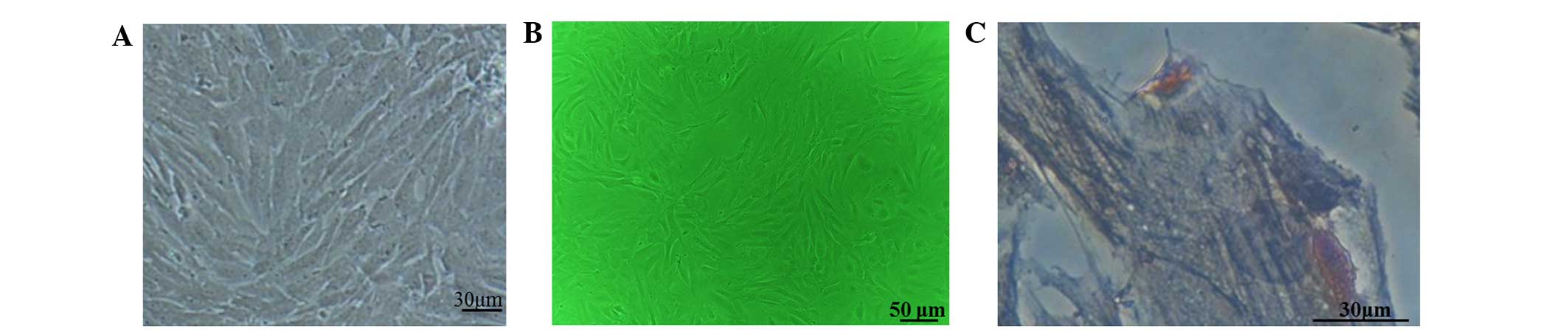
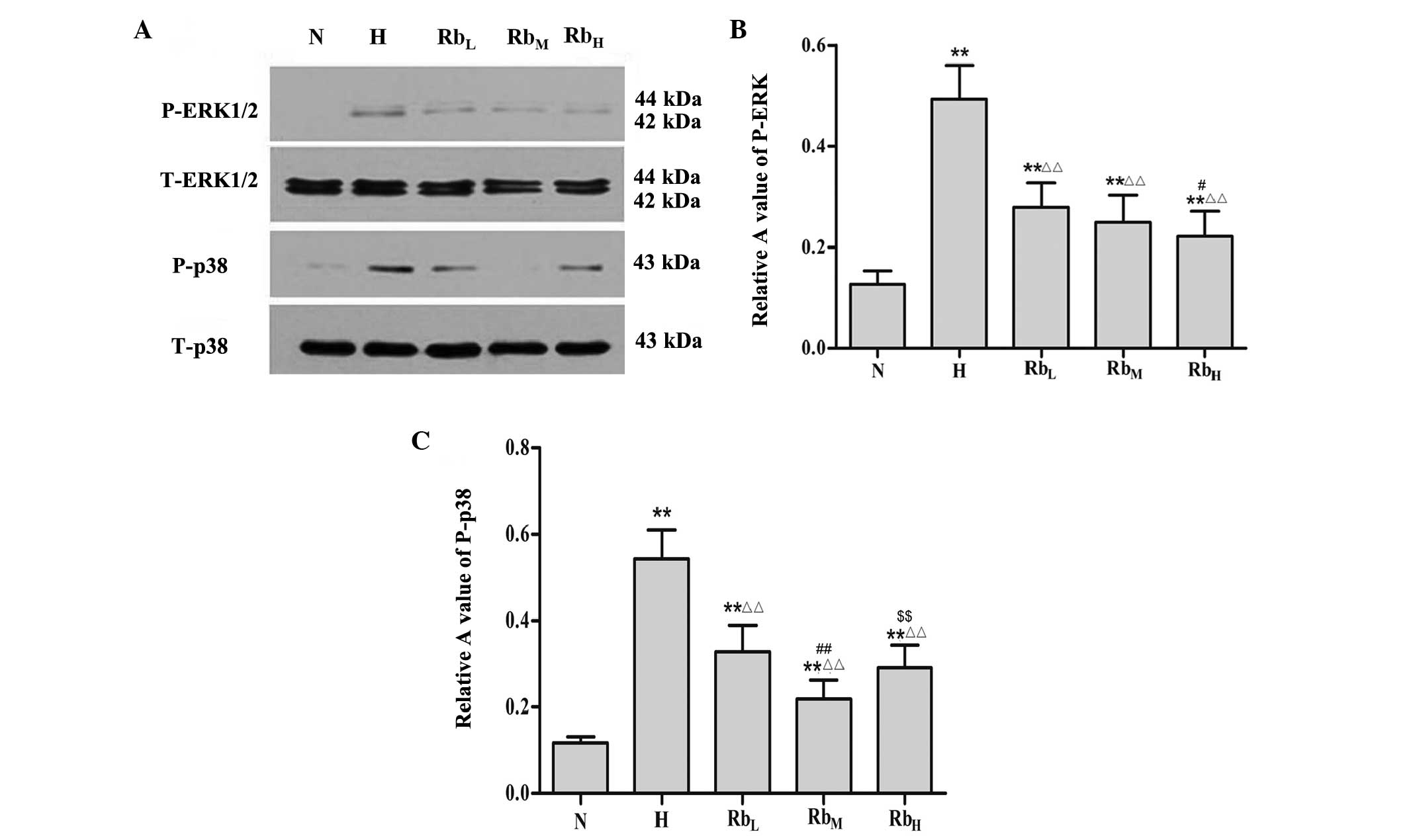
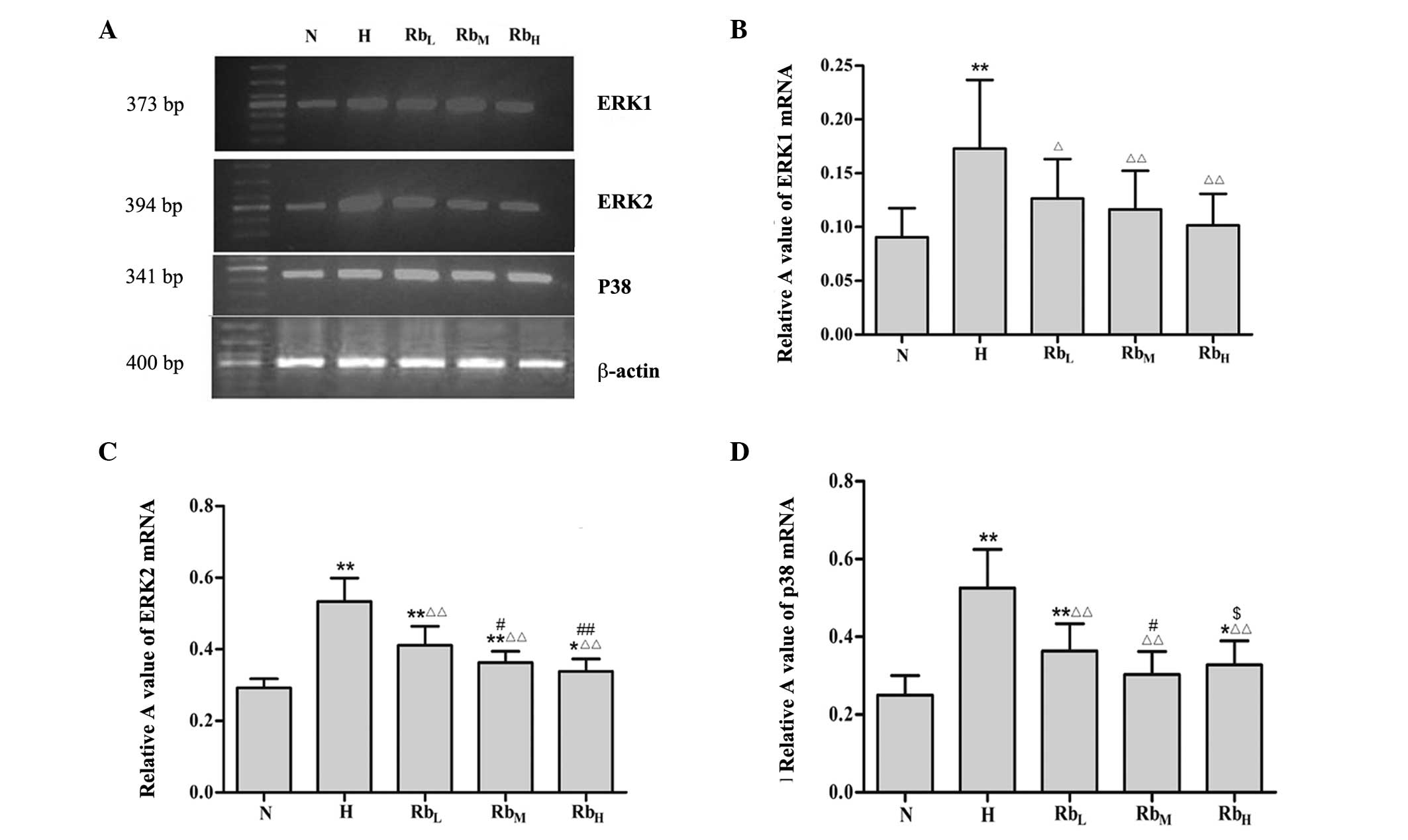
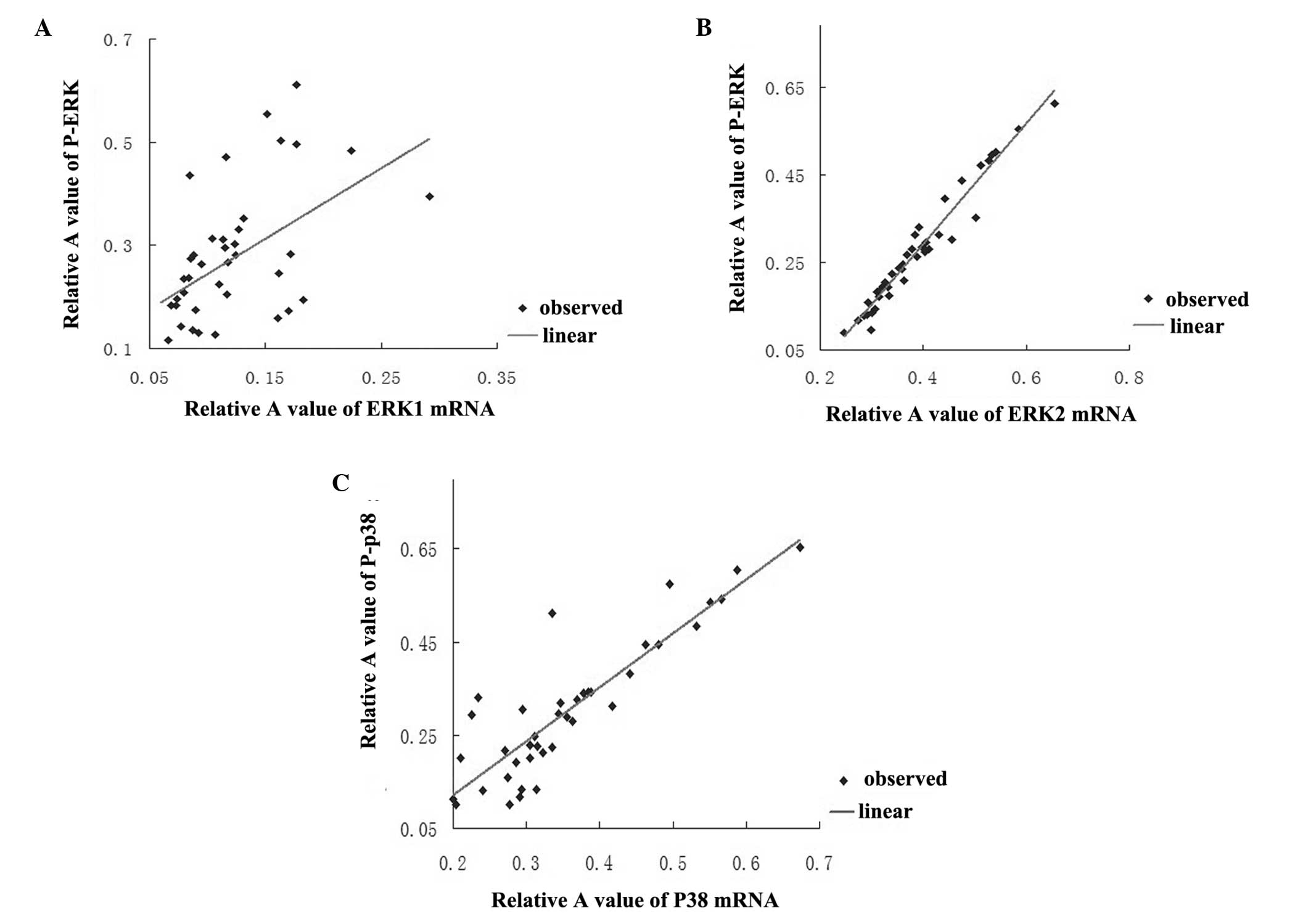
|
1
|
World Health Organization: The top 10
causes of death, 2000 and 2012. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/Updated.
May;2014.
|
|
2
|
Burney P, Jithoo A, Kato B, Janson C,
Mannino D, Nizankowska-Mogilnicka E, Studnicka M, Tan W, Bateman E,
Koçabas A, et al: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease mortality
and prevalence: The associations with smoking and poverty-a BOLD
analysis. Thorax. 69:465–473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pauwels RA, Buist AS, Calverley PM,
Jenkins CR and Hurd SS: GOLD Scientific Committee: Global strategy
for the diagnosis, management and prevention of chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease. NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic
Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Workshop summary. Am J Resp Crit
Care. 163:1256–1276. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kennedy TP, Michael JR, Huang CK, Kallman
CH, Zahka K, Schlott W and Summer W: Nifedipine inhibits hypoxic
pulmonary vasoconstriction during rest and exercise in patients
with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A controlled
double-blind study. Am Rev Res Dis. 129:544–551. 1984.
|
|
5
|
Seemungal T, Harper-Owen R, Bhowmik A,
Moric I, Sanderson G, Message S, Maccallum P, Meade TW, Jeffries
DJ, Johnston SL and Wedzicha JA: Respiratory viruses, symptoms and
inflammatory markers in acute exacerbations and stable chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Resp Crit Care Med.
164:1618–1623. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chaouat A, Naeije R and Weitzenblum E:
Pulmonary hypertension in COPD. Eur Respir J. 32:1371–1385. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu J, Wang Y, Qiu L, Yu Y and Wang C:
Saponins of Panax notoginseng: Chemistry, cellular targets
and therapeutic opportunities in cardiovascular diseases. Expert
Opin Investig Drugs. 23:523–539. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Zhang HG, Jia Y and Li XH: Panax
notoginseng saponins attenuate atherogenesis accelerated by
zymosan in rabbits. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:1324–1330. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fan JS, Liu DN, Huang G, Xu ZZ, Jia Y,
Zhang HG, Li XH and He FT: Panax notoginseng saponins
attenuate atherosclerosis via reciprocal regulation of lipid
metabolism and inflammation by inducing liver X receptor alpha
expression. J Ethnopharmacol. 142:732–738. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu L, Zhang W, Tang YH, Li H, Chen BY,
Zhang GM and Deng CQ: Effect of total saponins of ‘Panax
notoginseng root’ on aortic intimal hyperplasia and the
expressions of cell cycle protein and extracellular matrix in rats.
Phytomedicine. 17:233–240. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gan J, Li P, Wang Z, Chen J, Liang X, Liu
M, Xie W, Yin R and Huang F: Rosuvastatin suppresses
platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle
cell proliferation and migration via the MAPK signaling pathway.
Exp Ther Med. 6:899–903. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D808–D815, database issue. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu Y, Lin L, Tang L, Zheng M, Ma Y, Huang
L, Meng W and Wang W: Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates hypoxia and
hypercapnia-induced vasoconstriction in isolated rat pulmonary
arterial rings by reducing the expression of ERK. Am J Chinese Med.
42:799–816. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li X, Lu W, Fu X, Zhang Y, Yang K, Zhong
N, Ran P and Wang J: BMP4 increases canonical transient receptor
potential protein expression by activating p38 MAPK and ERK1/2
signaling pathways in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J
Resp Cell Mol Biol. 49:212–220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wen FQ and He B: Interpretation of Global
Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Chronic
Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (GOLD) (revised 2011). Zhonghua Yi
Xue Za Zhi. 92:939–940. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Roux PP and Blenis J: ERK and p38
MAPK-activated protein kinases: A family of protein kinases with
diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 68:320–344.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Pathological roles of
MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1802:396–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Waseem T, Duxbury M, Ashley SW and
Robinson MK: Ghrelin promotes intestinal epithelial cell
proliferation through PI3K/Akt pathway and EGFR trans-activation
both converging to ERK 1/2 phosphorylation. Peptides. 52:113–121.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee SM, Lee CT, Kim YW, Han SK, Shim YS
and Yoo CG: Hypoxia confers protection against apoptosis via
PI3K/Akt and ERK pathways in lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
242:231–238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jin N, Hatton N, Swartz DR, Xia Xl,
Harrington MA, Larsen SH and Rhoades RA: Hypoxia activates
jun-N-terminal kinase, extracellular signal-regulated protein
kinase and p38 kinase in pulmonary arteries. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 23:593–601. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Welch LC, Lecuona E, Briva A, Trejo HE,
Dada LA and Sznajder JI: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
(ERK) participates in the hypercapnia-induced Na, K-ATPase
downregulation. FEBS Lett. 584:3985–3989. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
O'Toole D, Hassett P, Contreras M, Higgins
BD, McKeown ST, McAuley DF, O'Brien T and Laffey JG: Hypercapnic
acidosis attenuates pulmonary epithelial wound repair by an
NF-kappaB dependent mechanism. Thorax. 64:976–982. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dou L, Lu Y, Shen T, Huang X, Man Y, Wang
S and Li J: Panax notogingseng saponins suppress RAGE/MAPK
signaling and NF-kappaB activation in apolipoprotein-E-deficient
atherosclerosis-prone mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 29:875–882. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ge KL, Chen WF, Xie JX and Wong MS:
Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against 6-OHDA-induced toxicity in MES23.
5 cells via Akt and ERK signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol.
127:118–123. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang HS and Wang SQ: Notoginsenoside R1
inhibits TNF-alpha-induced fibronectin production in smooth muscle
cells via the ROS/ERK pathway. Free Radical Bio Med. 40:1664–1674.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Penumatsa KC, Toksoz D, Warburton RR,
Hilmer AJ, Liu T, Khosla C, Comhair SA and Fanburg BL: Role of
hypoxia-induced transglutaminase 2 in pulmonary artery smooth
muscle cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
307:L576–L585. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shan R, Chen L, Li X, Wu H, Liang Q and
Tang X: Hypoxia promotes rabbit pulmonary artery smooth muscle
cells proliferation through a 15-LOX-2 product
15(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent
Fatty Acids. 86:85–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wei L, Yu X, Shi H, Zhang B, Lian M, Li J,
Shen T, Xing Y and Zhu D: 15-PGDH/15-KETE plays a role in
hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling through
ERK1/2-dependent PAR-2 pathway. Cell Signal. 26:1476–1488. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hutchison MR: BDNF alters ERK/p38 MAPK
activity ratios to promote differentiation in growth plate
chondrocytes. Mol Endocrinol. 26:1406–1416. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ge C, Yang Q, Zhao G, Yu H, Kirkwood KL
and Franceschi RT: Interactions between extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and P38 Map kinase pathways in the
control of RUNX2 phosphorylation and transcriptional activity. J
Bone Miner Res. 27:538–551. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
de Araújo Herculano B, Vandresen-Filho S,
Martins WC, Boeck CR and Tasca CI: NMDA preconditioning protects
against quinolinic acid-induced seizures via PKA, PI3K and MAPK/ERK
signaling pathways. Behav Brain Res. 219:92–97. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hirota Y, Tsukazaki T, Yonekura A,
Miyazaki Y, Osaki M, Shindo H and Yamashita S: Activation of
specific MEK-ERK cascade is necessary for TGFβ signaling and
crosstalk with PKA and PKC pathways in cultured rat articular
chondrocytes. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 8:241–247. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhou D, Liu Y, Zhang X, Gu X, Wang H, Luo
X, Zhang J, Zou H and Guan M: Functional polymorphisms of the ABCG2
gene are associated with gout disease in the Chinese Han male
population. Int J Mol Sci. 15:9149–9159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|