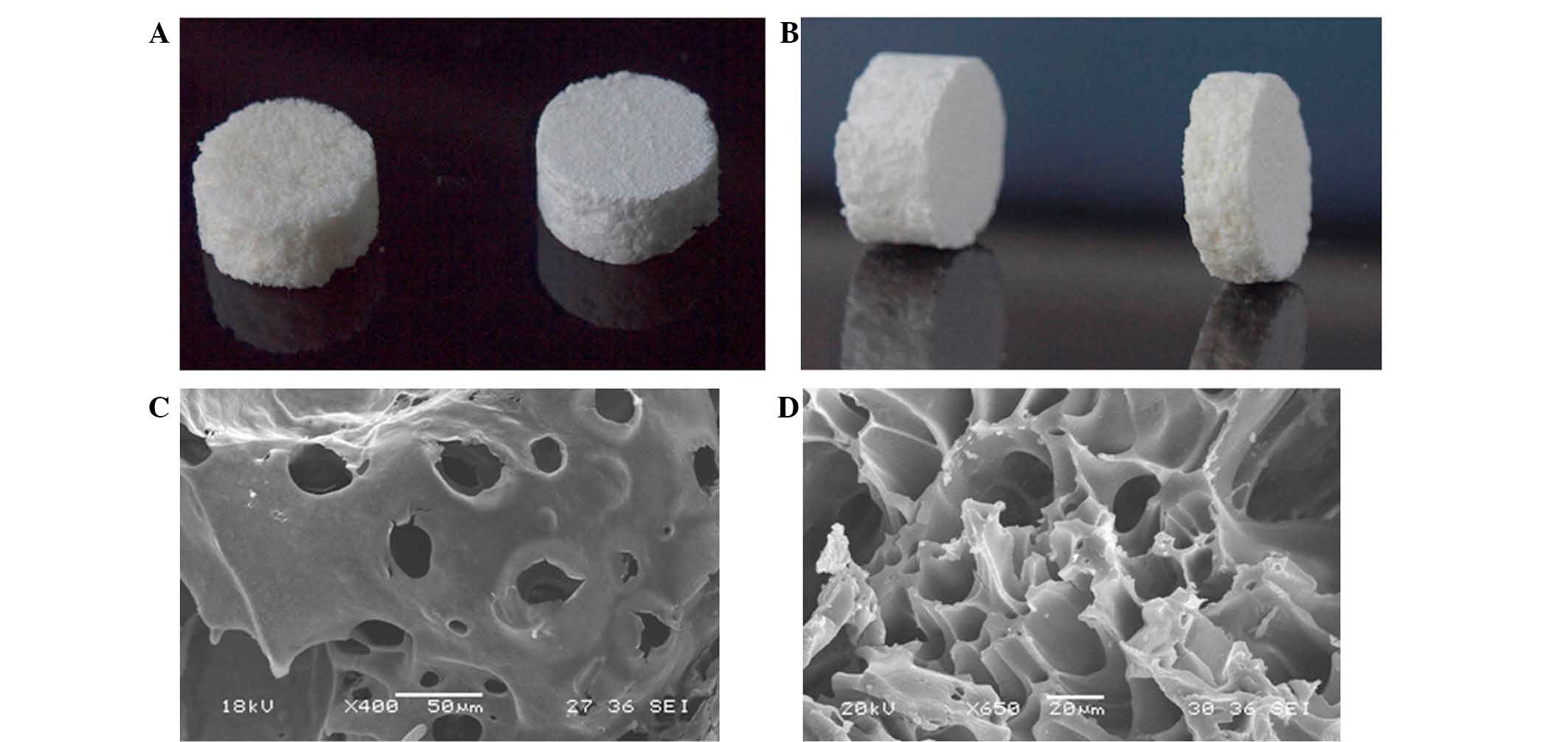
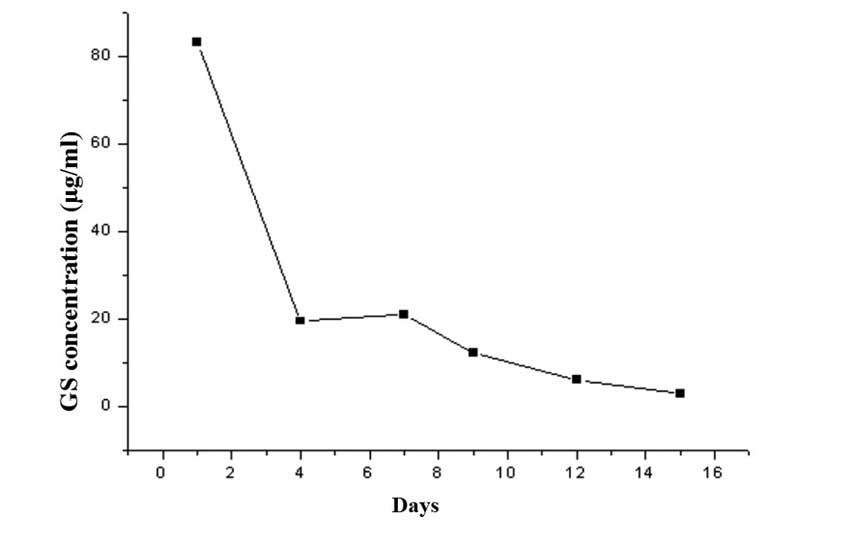
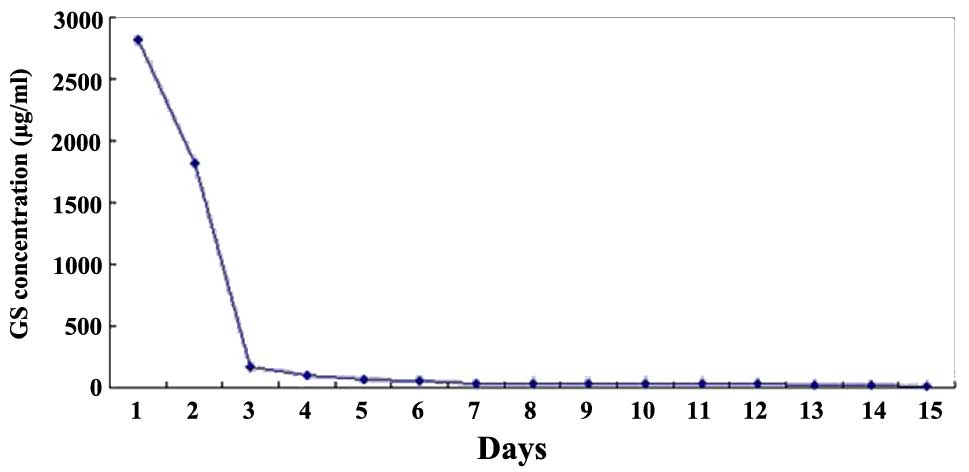
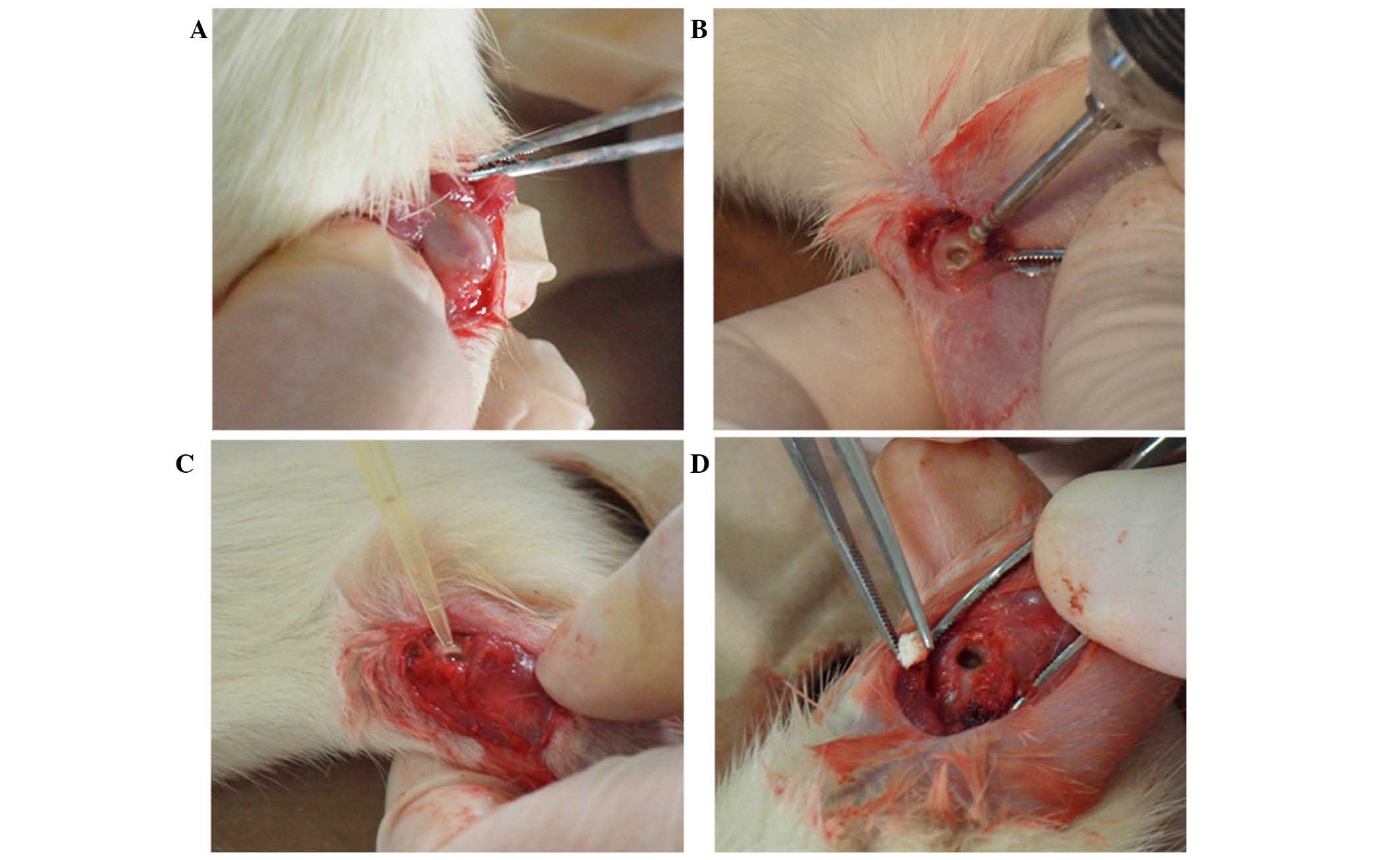
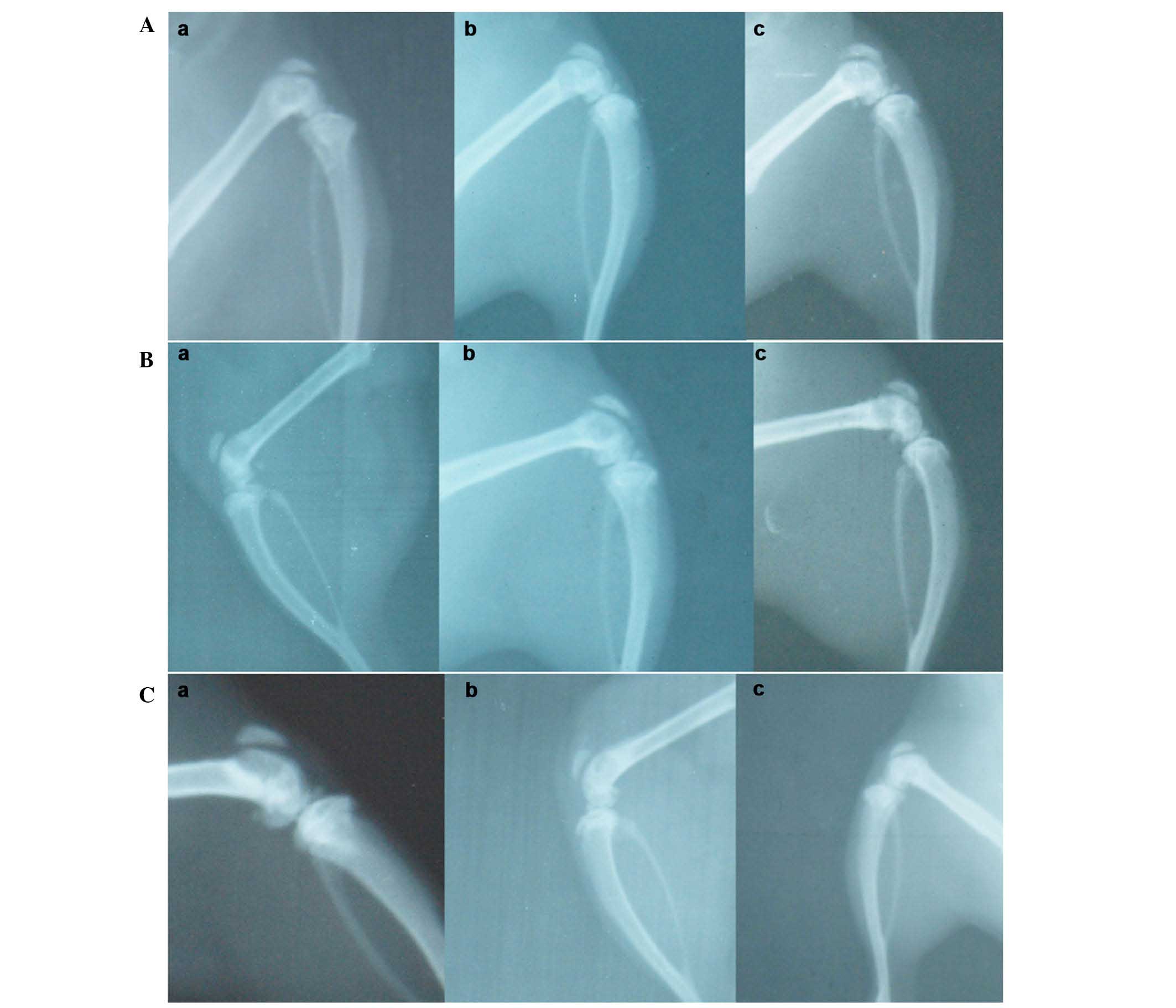
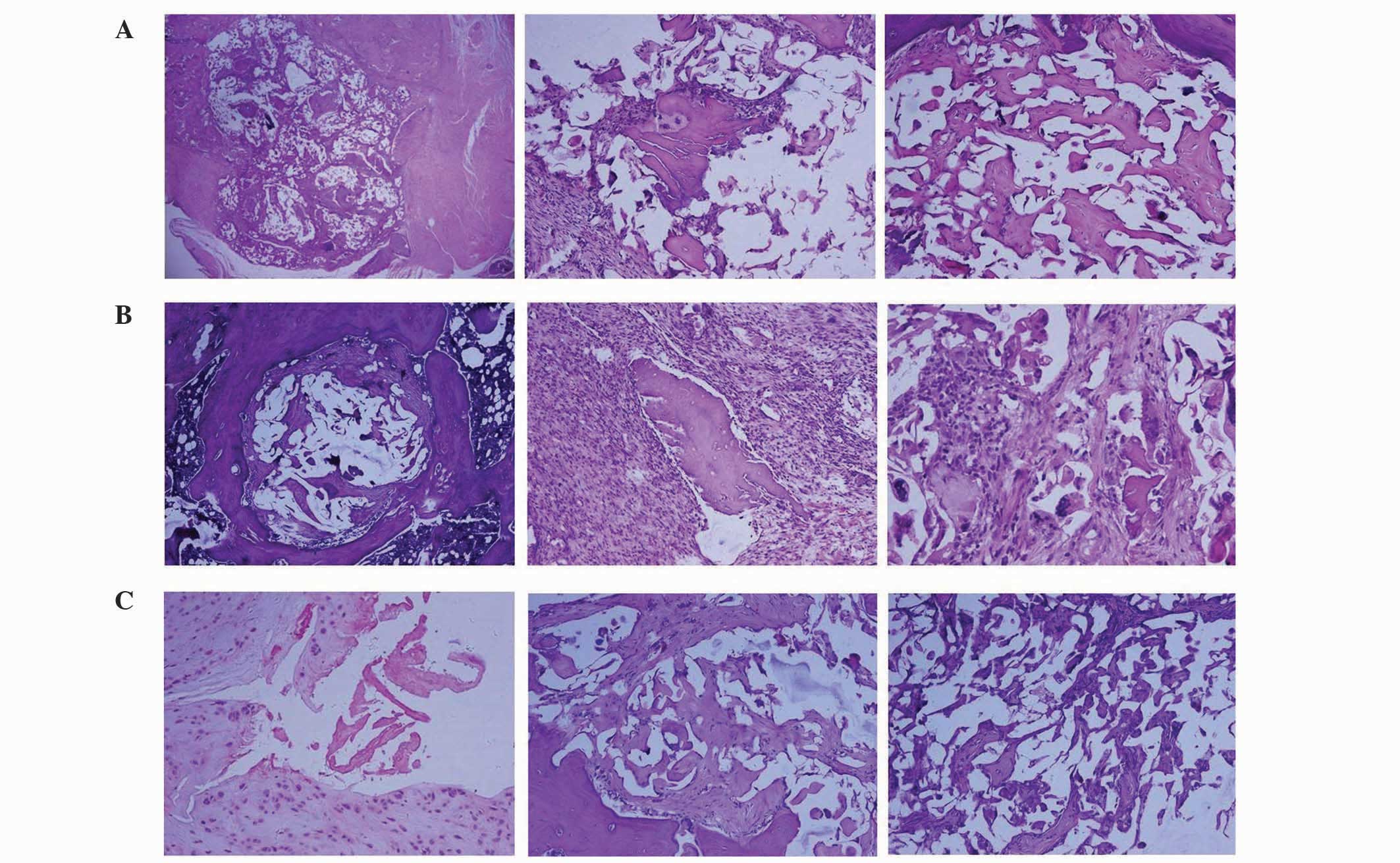
|
1
|
Roberts TT and Rosenbaum AJ: Bone grafts,
bone substitutes and orthobiologics: The bridge between basic
science and clinical advancements in fracture healing.
Organogenesis. 8:114–124. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Crane GM, Ishaug SL and Mikos AG: Bone
tissue engineering. Nat Med. 1:1322–1324. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Won YH, Kim SG, Oh JS and Lim SC: Clinical
evaluation of demineralized bone allograft for sinus lifts in
humans: A clinical and histologic study. Implant Dent. 20:460–464.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lima CE, Calixto JC and Anbinder AL:
Influence of the association between simvastatin and demineralized
bovine bone matrix on bone repair in rats. Braz Oral Res. 25:42–48.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang HY, Luo JB, Zhou M, Zhang Y and
Huang YL: Biotribological properties at the stem-cement interface
lubricated with different media. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.
20:209–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang H, Zhang S, Luo J, Liu Y, Qian S,
Liang F and Huang Y: Investigation of protein adsorption mechanism
and biotribological properties at simulated stem-cement interface.
J Tribol. 135:0323012013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu H, Zhang L, Shi P, Zou Q, Zuo Y and Li
Y: Hydroxyapatite/polyurethane scaffold incorporated with
drug-loaded ethyl cellulose microspheres for bone regeneration. J
Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 95:36–46. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu C, Su P, Wang Y, Chen X, Meng Y, Liu C,
Yu X, Yang X, Yu W, Zhang X, et al: A novel biomimetic composite
scaffold hybridized with mesenchymal stem cells in repair of rat
bone defects models. J Biomed Mater Res A. 95:495–503. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thomas DB, Brooks DE, Bice TG, DeJong ES,
Lonergan KT and Wenke JC: Tobramycin-impregnated calcium sulfate
prevents infection in contaminated wounds. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
441:366–371. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Agarwal A, Goyal RK and Pruthi KK: Fate of
calcium hydroxyapatite blocks with cortico-cancellous autogenous
bone grafting in gap non-union of long bones along with LCP. J Clin
Orthop Trauma. 6:72–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ajiboye RM, Hamamoto JT, Eckardt MA and
Wang JC: Clinical and radiographic outcomes of concentrated bone
marrow aspirate with allograft and demineralized bone matrix for
posterolateral and interbody lumbar fusion in elderly patients. Eur
Spine J. 24:2567–2572. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tavakol S, Khoshzaban A, Azami M, Kashani
IR, Tavakol H, Yazdanifar M and Sorkhabadi SM: The effect of
carrier type on bone regeneration of demineralized bone matrix
in vivo. J Craniofac Surg. 24:2135–2140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Turner TM, Urban RM, Hall DJ, Chye PC,
Segreti J and Gitelis S: Local and systemic levels of tobramycin
delivered from calcium sulfate bone graft substitute pellets. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 437:97–104. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bakhshalian N, Hooshmand S, Campbell SC,
Kim JS, Brummel-Smith K and Arjmandi BH: Biocompatibility and
microstructural analysis of osteopromotive property of allogenic
demineralized dentin matrix. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.
28:1655–1662. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jimi E, Hirata S, Osawa K, Terashita M,
Kitamura C and Fukushima H: The current and future therapies of
bone regeneration to repair bone defects. Int J Dentistry.
1482612012.
|
|
16
|
Chen ZW, Liu H and Zhai WL and Zhai WL:
Treatment of infected bone defect with one stage open cancellous
bone grafting. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 21:377–378. 2008.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
García-Gareta E, Coathup MJ and Blunn GW:
Osteoinduction of bone grafting materials for bone repair and
regeneration. Bone. 81:112–121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li XD and Hu YY: The treatment of
osteomyelitis with gentamicin-reconstituted bone
xenograft-composite. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 83:1063–1068. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hautamäki MP, Aho AJ, Alander P, Rekola J,
Gunn J, Strandberg N and Vallittu PK: Repair of bone segment
defects with surface porous fiber-reinforced polymethyl
methacrylate (PMMA) composite prosthesis: Histomorphometric
incorporation model and characterization by SEM. Acta Orthop.
79:555–564. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zheng J, Su Q, Wang C, Cheng G, Zhu R, Shi
J and Yao K: Synthesis and biological evaluation of PMMA/MMT
nanocomposite as denture base material. J Mater Sci Mater Med.
22:1063–1071. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Z, Kawamura K, Kawashita M, Kudo TA,
Kanetaka H and Hiraoka M: In vitro assessment of
poly(methylmethacrylate)-based bone cement containing magnetite
nanoparticles for hyperthermia treatment of bone tumor. J Biomed
Mater Res A. 100:2537–2545. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fong N, Poole-Warren LA and Simmons A:
Development of sustained-release antibacterial urinary biomaterials
through using an antimicrobial as an organic modifier in
polyurethane nanocomposites. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.
101:310–319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Quaglino P, Nardò T, Fierro MT, Massaia M,
Orsucci L, Fava P, Marenco F, Marra E, Savoia P, Vitolo U, et al:
Clinicopathologic spectrum of cutaneous diseases in patients with
hematologic malignancies with or without allogeneic bone marrow
transplantation: An observational cohort study in 101 patients. G
Ital Dermatol Venereol. 148:453–463. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Anal AK and Stevens WF: Chitosan-alginate
multilayer beads for controlled release of ampicillin. Int J Pharm.
290:45–54. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Buranapanitkit B, Srinilta V, Ingviga N,
Oungbho K, Geater A and Ovatlarnporn C: The efficacy of a
hydroxyapatite composite as a biodegradable antibiotic delivery
system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 424:244–252. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Silverman LD, Lukashova L, Herman OT, Lane
JM and Boskey AL: Release of gentamicin from a tricalcium phosphate
bone implant. J Orthop Res. 25:23–29. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pandey M, Amin M, Ahmad N and Abeer MM:
Rapid synthesis of superabsorbent smart-swelling bacterial
cellulose/acrylamide-based hydrogels for drug delivery. Int J Polym
Sci. 9054712013.
|
|
28
|
Corden TJ, Jones IA, Rudd CD, Christian P,
Downes S and McDougall KE: Physical and biocompatibility properties
of poly-epsilon-caprolactone produced using in situ polymerisation:
A novel manufacturing technique for long-fibre composite materials.
Biomaterials. 21:713–724. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ambrose CG, Clyburn TA, Louden K, Joseph
J, Wright J, Gulati P, Gogola GR and Mikos AG: Effective treatment
of osteomyelitis with biodegradable microspheres in a rabbit model.
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 421:293–299. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mäkinen TJ, Veiranto M, Lankinen P, Moritz
N, Jalava J, Törmälä P and Aro HT: In vitro and in
vivo release of ciprofloxacin from osteoconductive bone defect
filler. J Antimicrob Chemother. 56:1063–1068. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stiller M, Kluk E, Bohner M, Lopez-Heredia
MA, Muller-Mai C and Knabe C: Performance of β-tricalcium phosphate
granules and putty, bone grafting materials after bilateral sinus
floor augmentation in humans. Biomaterials. 35:3154–3163. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yoshikawa T, Ohgushi H, Uemura T, Nakajima
H, Ichijima K, Tamai S and Tateisi T: Human marrow cells-derived
cultured bone in porous ceramics. Biomed Mater Eng. 8:311–320.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hile DD, Amirpour ML, Akgerman A and
Pishko MV: Active growth factor delivery from
poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) foams prepared in supercritical
CO(2). J Control Release. 66:177–185. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang YM, Li BX, Li J, Ma HQ, Zhao YP and
Yuan L: Preparation of porous polylactic-acid/ bone matrix gelatin
composite as scaffold materials for bone-tissue engineering. Nan
Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 26:1745–1748. 2006.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Link DP, van den Dolder J, Jurgens WJ,
Wolke JG and Jansen JA: Mechanical evaluation of implanted calcium
phosphate cement incorporated with PLGA microparticles.
Biomaterials. 27:4941–4947. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yandrapu SK, Upadhyay AK, Petrash JM and
Kompella UB: Nanoparticles in porous microparticles prepared by
supercritical infusion and pressure quench technology for sustained
delivery of bevacizumab. Mol Pharm. 10:4676–4686. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nofar M, Tabatabaei A and Park CB: Effects
of nano-/micro-sized additives on the crystallization behaviors of
PLA and PLA/CO2 mixtures. Polymer. 54:2382–2391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li Z, Ramay HR, Hauch KD, Xiao D and Zhang
M: Chitosan-alginate hybrid scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.
Biomaterials. 26:3919–3928. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bucholz RW: Nonallograft osteoconductive
bone graft substitutes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 395:44–52. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Porter NL, Pilliar RM and Grynpas MD:
Fabrication of porous calcium polyphosphate implants by solid
freeform fabrication: A study of processing parameters and in
vitro degradation characteristics. J Biomed Mater Res.
56:504–515. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|