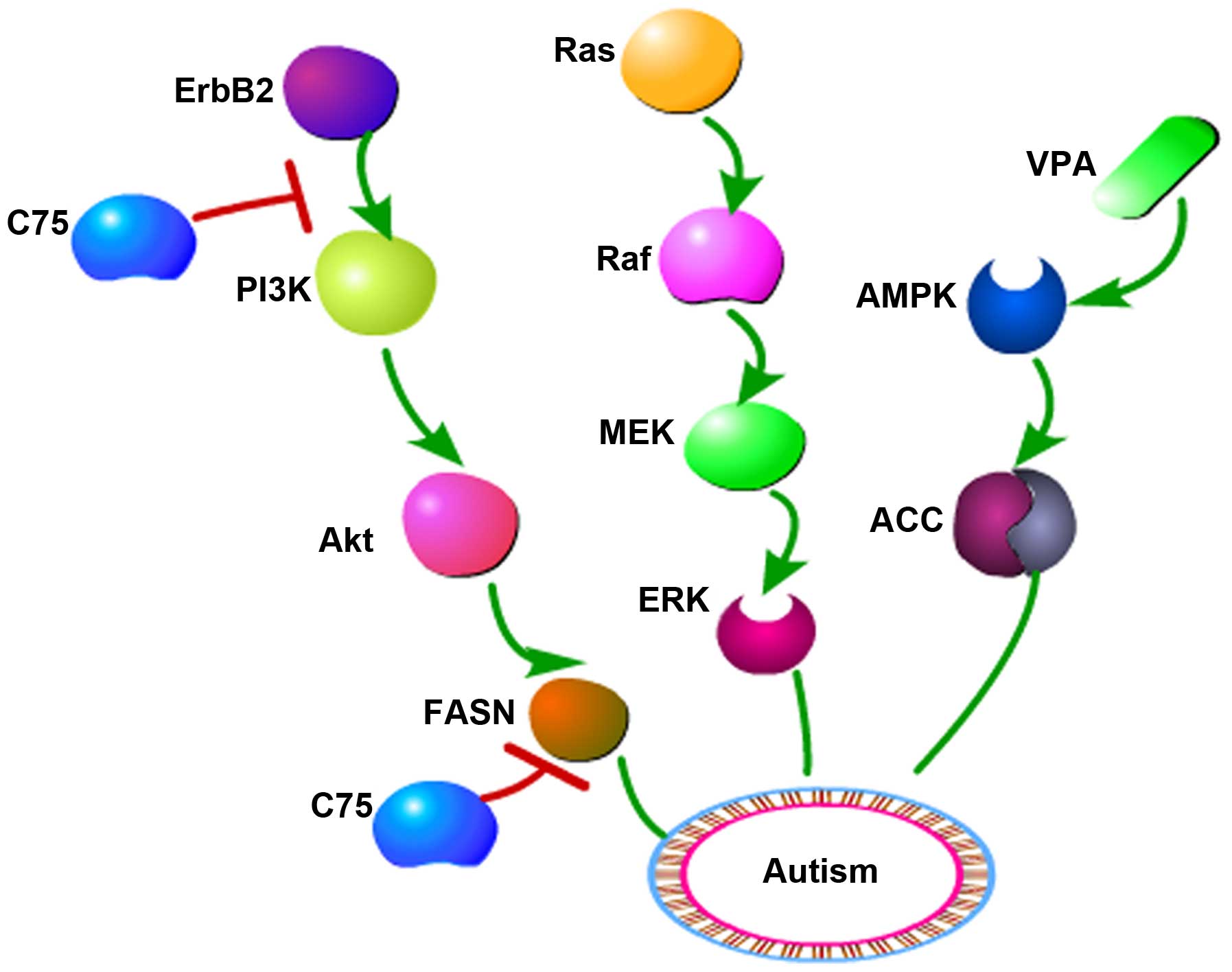
|
1
|
American Psychiatric Association:
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5)
(5th). American Psychiatric Publishing. Arlington, VA: 2013.
|
|
2
|
Ornoy A: Valproic acid in pregnancy: How
much are we endangering the embryo and fetus? Reprod Toxicol.
28:1–10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rodier PM, Ingram JL, Tisdale B and Croog
VJ: Linking etiologies in humans and animal models: Studies of
autism. Reprod Toxicol. 11:417–422. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chomiak T and Hu B: Alterations of
neocortical development and maturation in autism: Insight from
valproic acid exposure and animal models of autism. Neurotoxicol
Teratol. 36:57–66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Foley AG, Gannon S, Rombach-Mullan N,
Prendergast A, Barry C, Cassidy AW and Regan CM: Class I histone
deacetylase inhibition ameliorates social cognition and cell
adhesion molecule plasticity deficits in a rodent model of autism
spectrum disorder. Neuropharmacology. 63:750–760. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bauman ML: Microscopic neuroanatomic
abnormalities in autism. Pediatrics. 87:791–796. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao G, Gao J, Liang S, Wang X, Sun C, Xia
W, Hao Y, Li X, Cao Y and Wu L: Study of the serum levels of
polyunsaturated fatty acids and the expression of related liver
metabolic enzymes in a rat valproate-induced autism model. Int J
Dev Neurosci. 44:14–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brigandi SA, Shao H, Qian SY, Shen Y, Wu
BL and Kang JX: Autistic children exhibit decreased levels of
essential fatty acids in red blood cells. Int J Mol Sci.
16:10061–10076. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Saito M, Chakraborty G, Mao RF and Vadasz
C: Developmental profiles of lipogenic enzymes and their regulators
in the neonatal mouse brain. Neurochem Res. 34:1945–1954. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Spencer EB, Bianchi A, Widmer J and
Witters LA: Brain acetyl-CoA carboxylase: Isozymic identification
and studies of its regulation during development and altered
nutrition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 192:820–825. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schneider T and Przewłocki R: Behavioral
alterations in rats prenatally exposed to valproic acid: Animal
model of autism. Neuropsychopharmacology. 30:80–89. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ha J, Daniel S, Broyles SS and Kim KH:
Critical phosphorylation sites for acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity.
J Biol Chem. 269:22162–22168. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schultz ST, Klonoff-Cohen HS, Wingard DL,
Akshoomoff NA, Macera CA, Ji M and Bacher C: Breastfeeding, infant
formula supplementation and autistic disorder: The results of a
parent survey. Int Breastfeed J. 1:162006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meguid NA, Atta HM, Gouda AS and Khalil
RO: Role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the management of
Egyptian children with autism. Clin Biochem. 41:1044–1048. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lea W, Abbas AS, Sprecher H, Vockley J and
Schulz H: Long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is a key enzyme in the
mitochondrial beta-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1485:121–128. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cox KB, Hamm DA, Millington DS, Matern D,
Vockley J, Rinaldo P, Pinkert CA, Rhead WJ, Lindsey JR and Wood PA:
Gestational, pathologic and biochemical differences between very
long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency and long-chain
acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency in the mouse. Hum Mol Genet.
10:2069–2077. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Clark-Taylor T and Clark-Taylor BE: Is
autism a disorder of fatty acid metabolism? Possible dysfunction of
mitochondrial beta-oxidation by long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase.
Med Hypotheses. 62:970–975. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Persson B, Kallberg Y, Bray JE, Bruford E,
Dellaporta SL, Favia AD, Duarte RG, Jörnvall H, Kavanagh KL,
Kedishvili N, et al: The SDR (short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase
and related enzymes) nomenclature initiative. Chem Biol Interact.
178:94–98. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Veigel D, Wagner R, Stübiger G, Wuczkowski
M, Filipits M, Horvat R, Benhamú B, López-Rodríguez ML, Leisser A,
Valent P, et al: Fatty acid synthase is a metabolic marker of cell
proliferation rather than malignancy in ovarian cancer and its
precursor cells. Int J Cancer. 136:2078–2090. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pucilowska J, Vithayathil J, Tavares EJ,
Kelly C, Karlo JC and Landreth GE: The 16p11.2 deletion mouse model
of autism exhibits altered cortical progenitor proliferation and
brain cytoarchitecture linked to the ERK MAPK pathway. J Neurosci.
35:3190–3200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang K, Cao F, Sheikh AM, Malik M, Wen G,
Wei H, Brown WT and Li X: Up-regulation of Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling
impairs cultured neuronal cell migration, neurogenesis, synapse
formation, and dendritic spine development. Brain Struct Funct.
218:669–682. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cao FJ, Zhang X, Liu T, Li XW, Malik M and
Feng SQ: Up-regulation of Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling in the spinal
cord impairs neural cell migration, neurogenesis, synapse
formation, and dendritic spine development. Chin Med J (Engl).
126:3879–3885. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Grunt TW, Wagner R, Grusch M, Berger W,
Singer CF, Marian B, Zielinski CC and Lupu R: Interaction between
fatty acid synthase- and ErbB-systems in ovarian cancer cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 385:454–459. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Long XH, Zhang GM, Peng AF, Luo QF, Zhang
L, Wen HC, Zhou RP, Gao S, Zhou Y and Liu ZL: Lapatinib alters the
malignant phenotype of osteosarcoma cells via downregulation of the
activity of the HER2-PI3K/AKT-FASN axis in vitro. Oncol Rep.
31:328–334. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen J, Alberts I and Li X: Dysregulation
of the IGF-I/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in autism spectrum
disorders. Int J Dev Neurosci. 35:35–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Abu-Elheiga L, Matzuk MM, Abo-Hashema KA
and Wakil SJ: Continuous fatty acid oxidation and reduced fat
storage in mice lacking acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2. Science.
291:2613–2616. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nelson DL and Cox MM: Lehninger Principles
of Biochemistry (5th). W. H. Freeman and Company. London:
8062008.
|
|
29
|
Giulivi C, Zhang YF, Omanska-Klusek A,
Ross-Inta C, Wong S, Hertz-Picciotto I, Tassone F and Pessah IN:
Mitochondrial dysfunction in autism. JAMA. 304:2389–2396. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Frye RE, Melnyk S and Macfabe DF: Unique
acyl-carnitine profiles are potential biomarkers for acquired
mitochondrial disease in autism spectrum disorder. Transl
Psychiatry. 3:e2202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Thomas RH, Foley KA, Mepham JR, Tichenoff
LJ, Possmayer F and MacFabe DF: Altered brain phospholipid and
acylcarnitine profiles in propionic acid infused rodents: Further
development of a potential model of autism spectrum disorders. J
Neurochem. 113:515–529. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Avery LB and Bumpus NN: Valproic acid is a
novel activator of AMP-activated protein kinase and decreases liver
mass, hepatic fat accumulation and serum glucose in obese mice. Mol
Pharmacol. 85:1–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wen JP, Liu CE, Hu YT, Chen G and Lin LX:
Globular adiponectin regulates energy homeostasis through
AMP-activated protein kinase-acetyl-CoA carboxylase (AMPK/ACC)
pathway in the hypothalamus. Mol Cell Biochem. 344:109–115. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ahn Y, Narous M, Tobias R, Rho JM and
Mychasiuk R: The ketogenic diet modifies social and metabolic
alterations identified in the prenatal valproic acid model of
autism spectrum disorder. Dev Neurosci. 36:371–380. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jeon BT, Lee DH, Kim KH, Kim HJ, Kang SS,
Cho GJ, Choi WS and Roh GS: Ketogenic diet attenuates kainic
acid-induced hippocampal cell death by decreasing AMPK/ACC pathway
activity and HSP70. Neurosci Lett. 453:49–53. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|