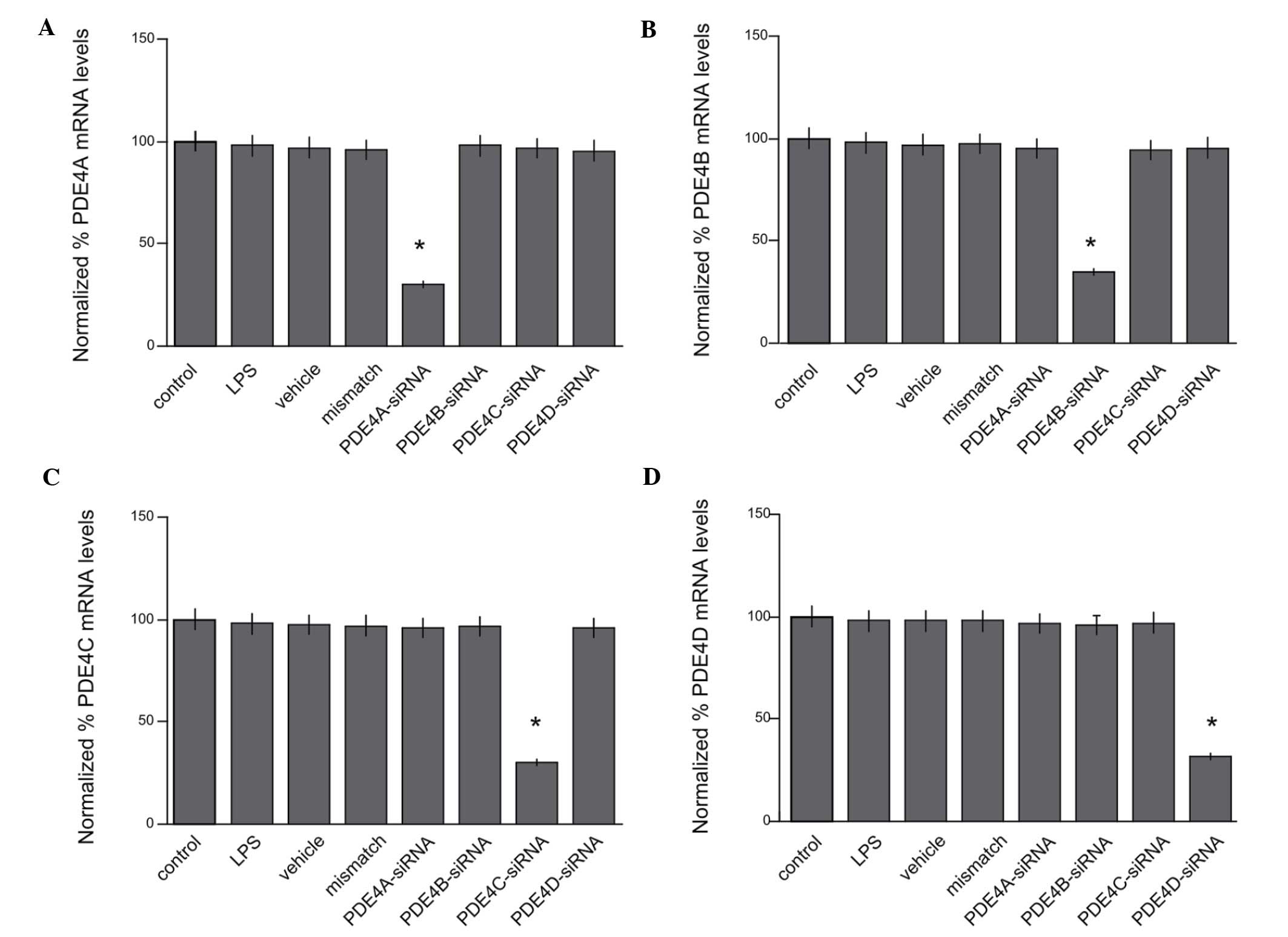
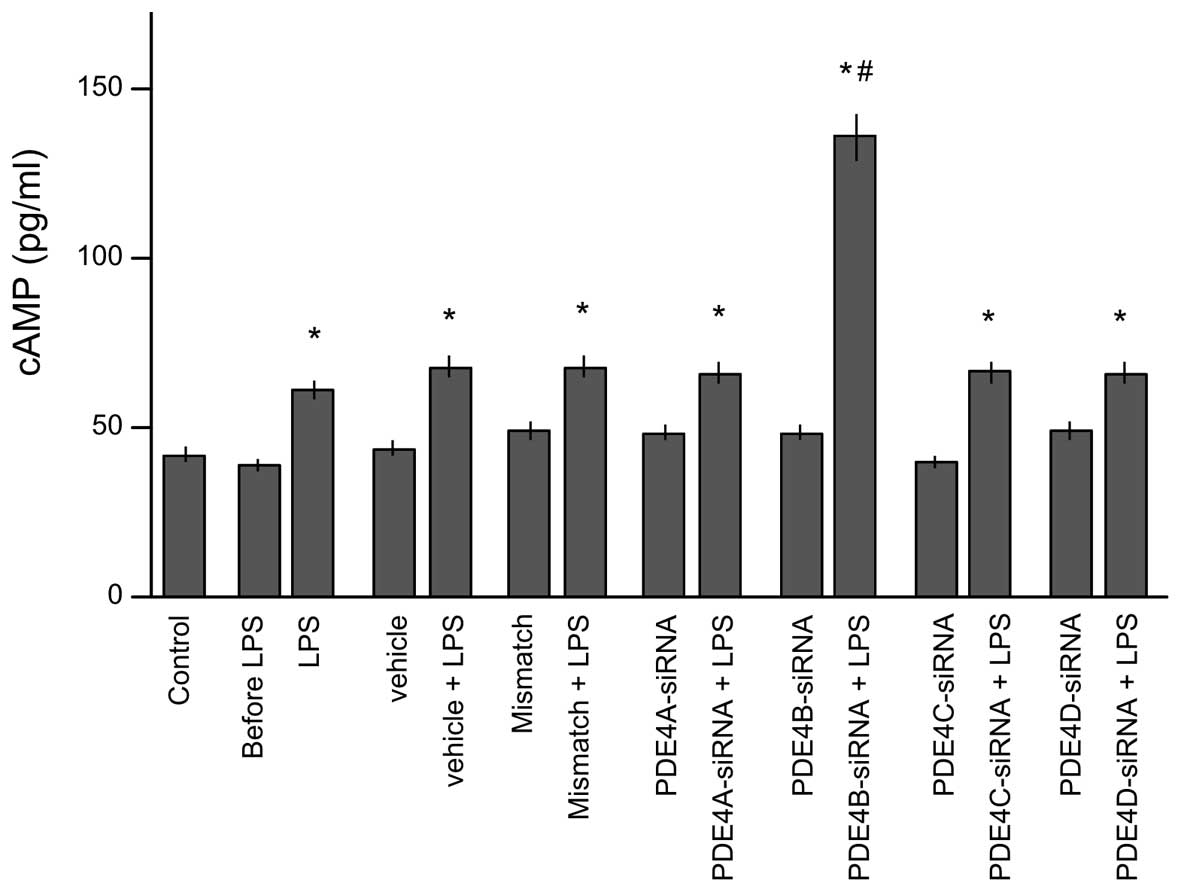
|
1
|
Gremo F, Sogos V, Ennas MG, Meloni A,
Persichini T, Colasanti M and Lauro GM: Features and functions of
human microglia cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 429:79–97. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
WyssCoray T and Rogers J: Inflammation in
Alzheimer disease - a brief review of the basic science and
clinical literature. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
2:a0063462012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Karagkouni A, Alevizos M and Theoharides
TC: Effect of stress on brain inflammation and multiple sclerosis.
Autoimmun Rev. 12:947–953. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Campbell JN and Meyer RA: Mechanisms of
neuropathic pain. Neuron. 52:77–92. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aloisi F: Immune function of microglia.
Glia. 36:165–179. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garden GA and Möller T: Microglia biology
in health and disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 1:127–137. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Buttini M, Mir A, Appel K, Wiederhold KH,
Limonta S, Gebicke Haerter PJ and Boddeke HW: Lipopolysaccharide
induces expression of tumour necrosis factor alpha in rat brain:
Inhibition by methylprednisolone and by rolipram. Br J Pharmacol.
122:1483–1489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tanaka J, Toku K, Matsuda S, Sudo S,
Fujita H, Sakanaka M and Maeda N: Induction of resting microglia in
culture medium devoid of glycine and serine. Glia. 24:198–215.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang B, Yang L, Konishi Y, Maeda N,
Sakanaka M and Tanaka J: Suppressive effects of phosphodiesterase
type IV inhibitors on rat cultured microglial cells: comparison
with other types of cAMP-elevating agents. Neuropharmacology.
42:262–269. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Conti M and Jin SL: The molecular biology
of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol
Biol. 63:1–38. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Houslay MD: Underpinning compartmentalised
cAMP signalling through targeted cAMP breakdown. Trends Biochem
Sci. 35:91–100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jarnagin K, Chanda S, Coronado D,
Ciaravino V, Zane LT, GuttmanYassky E and Lebwohl MG: Crisaborole
topical ointment, 2%: A nonsteroidal, topical, anti-inflammatory
phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor in clinical development for the
treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Drugs Dermatol. 15:390–396.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pearse DD and Hughes ZA: PDE4B as a
microglia target to reduce neuroinflammation. Glia. Apr 1–2016.doi:
10.1002/glia.22986 (Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Flemming S, Schlegel N, Wunder C, Meir M,
Baar W, Wollborn J, Roewer N, Germer CT and Schick MA:
Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition dose dependently stabilizes
microvascular barrier functions and microcirculation in a rodent
model of polymicrobial sepsis. Shock. 41:537–545. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin SL, Ding SL and Lin SC:
Phosphodiesterase 4 and its inhibitors in inflammatory diseases.
Chang Gung Med J. 35:197–210. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA,
Driver SE and Mello CC: Potent and specific genetic interference by
double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 391:806–811.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Doré-Savard L, Roussy G, Dansereau MA,
Collingwood MA, Lennox KA, Rose SD, Beaudet N, Behlke MA and Sarret
P: Central delivery of Dicer-substrate siRNA: A direct application
for pain research. Mol Ther. 16:1331–1339. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Röhl T and Kurreck J: RNA interference in
pain research. J Neurochem. 99:371–380. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang H, Bielekova B, Okazaki H,
ClarenceSmith K, Johnson KP, Bergey G, Martin R and Dhib-Jalbut S:
The effect of vesnarinone on TNF alpha production in human
peripheral blood mononuclear cells and microglia: A preclinical
study for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol.
97:134–145. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xue Y, Wang Y, Feng DC, Xiao BG and Xu LY:
Tetrandrine suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial
activation by inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
29:245–251. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu J, Zhao X, Cao J, Xue Q, Feng X, Liu
X, Zhang F and Yu B: Differential roles of PKA and Epac on the
production of cytokines in the endotoxin-stimulated primary
cultured microglia. J Mol Neurosci. 45:186–193. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choi DC, Lee JY, Lim EJ, Baik HH, Oh TH
and Yune TY: Inhibition of ROS-induced p38MAPK and ERK activation
in microglia by acupuncture relieves neuropathic pain after spinal
cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol. 236:268–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li W, Li Y, Zhu S, Ji Q, Shu Y, Zhang L
and Liu J: Rosuvastatin attenuated the existing morphine tolerance
in rats with L5 spinal nerve transection through inhibiting
activation of astrocytes and phosphorylation of ERK42/44. Neurosci
Lett. 584:314–319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jin SL and Conti M: Induction of the
cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase PDE4B is essential for
LPS-activated TNF-alpha responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:7628–7633. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jin SL, Lan L, Zoudilova M and Conti M:
Specific role of phosphodiesterase 4B in lipopolysaccharide-induced
signaling in mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 175:1523–1531. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Robichaud A, Stamatiou PB, Jin SC,
Lachance N, MacDonald D, Laliberté F, Liu S, Huang Z, Conti M and
Chan CC: Deletion of phosphodiesterase 4D in mice shortens
alpha(2)-adrenoceptor-mediated anesthesia, a behavioral correlate
of emesis. J Clin Invest. 110:1045–1052. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bao F, Fleming JC, Golshani R, Pearse DD,
Kasabov L, Brown A and Weaver LC: A selective phosphodiesterase-4
inhibitor reduces leukocyte infiltration, oxidative processes and
tissue damage after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma.
28:1035–1049. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Erdogan S, Aslantas O, Celik S and Atik E:
The effects of increased cAMP content on inflammation, oxidative
stress and PDE4 transcripts during Brucella melitensis infection.
Res Vet Sci. 84:18–25. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pearse DD, Pereira FC, Marcillo AE, Bates
ML, Berrocal YA, Filbin MT and Bunge MB: cAMP and Schwann cells
promote axonal growth and functional recovery after spinal cord
injury. Nat Med. 10:610–616. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nagasawa SY, Takuwa N, Sugimoto N, Mabuchi
H and Takuwa Y: Inhibition of Rac activation as a mechanism for
negative regulation of actin cytoskeletal reorganization and cell
motility by cAMP. Biochem J. 385:737–744. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sanz MJ, Cortijo J and Morcillo EJ: PDE4
inhibitors as new anti-inflammatory drugs: Effects on cell
trafficking and cell adhesion molecules expression. Pharmacol Ther.
106:269–297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lorenowicz MJ, FernandezBorja M and
Hordijk PL: cAMP signaling in leukocyte transendothelial migration.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 27:1014–1022. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ninković J and Roy S: Morphine decreases
bacterial phagocytosis by inhibiting actin polymerization through
cAMP-, Rac-1- and p38 MAPK-dependent mechanisms. Am J Pathol.
180:1068–1079. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Emery AC and Eiden LE: Signaling through
the neuropeptide GPCR PAC1 induces neuritogenesis via a
single linear cAMP- and ERK-dependent pathway using a novel cAMP
sensor. FASEB J. 26:3199–3211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Enserink JM, Christensen AE, de Rooij J,
van Triest M, Schwede F, Genieser HG, Døskeland SO, Blank JL and
Bos JL: A novel Epac-specific cAMP analogue demonstrates
independent regulation of Rap1 and ERK. Nat Cell Biol. 4:901–906.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhuang ZY, Gerner P, Woolf CJ and Ji RR:
ERK is sequentially activated in neurons, microglia and astrocytes
by spinal nerve ligation and contributes to mechanical allodynia in
this neuropathic pain model. Pain. 114:149–159. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|