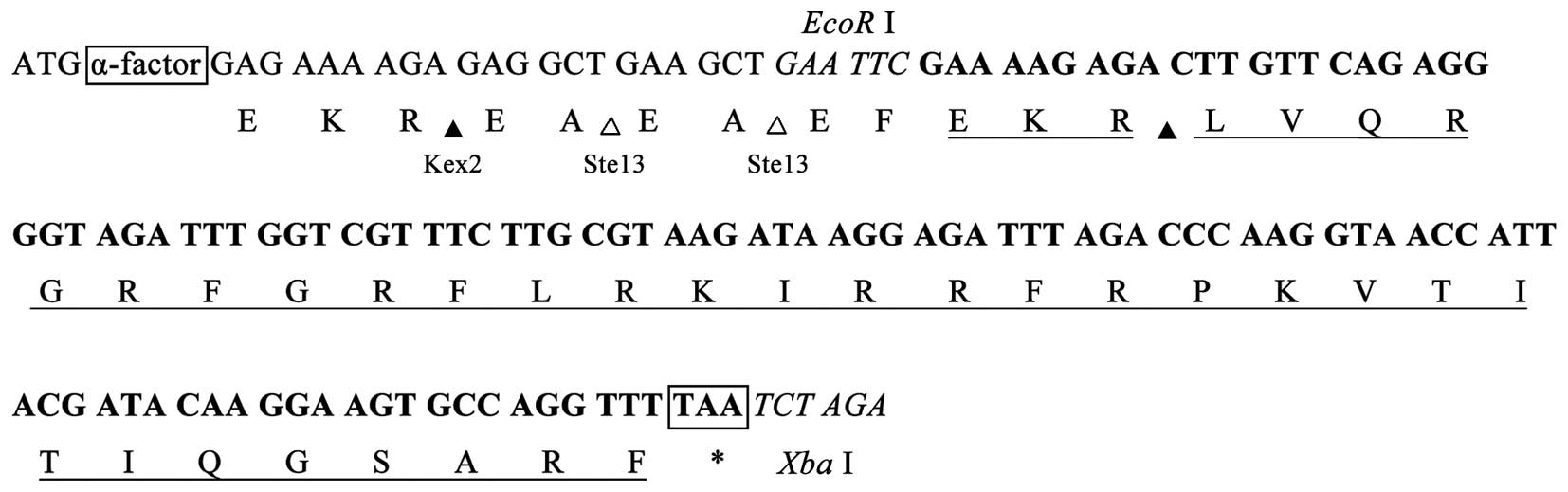
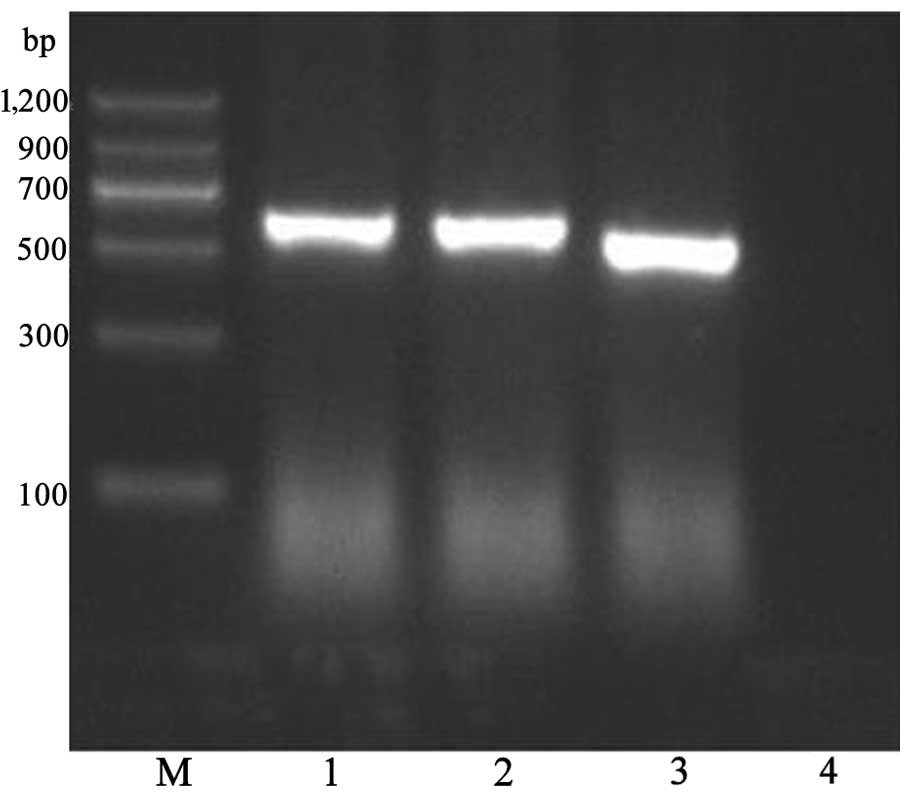
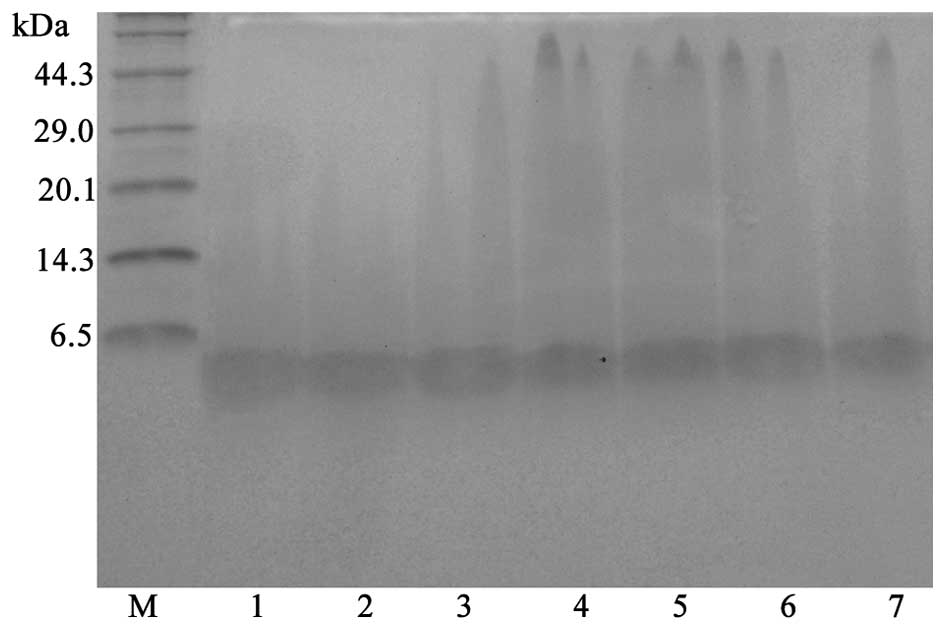
|
1
|
Rai J, Randhawa GK and Kaur M: Recent
advances in antibacterial drugs. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 3:3–10.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Spížek J, Novotná J, Rezanka T and Demain
AL: Do we need new antibiotics? The search for new targets and new
compounds. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 37:1241–1248. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zasloff M: Antimicrobial peptides of
multicellular organisms. Nature. 415:389–395. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hancock RE and Sahl HG: Antimicrobial and
host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies.
Nat Biotechnol. 24:1551–1557. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tomasinsig L and Zanetti M: The
cathelicidins - structure, function and evolution. Curr Protein
Pept Sci. 6:23–34. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zaiou M and Gallo RL: Cathelicidins,
essential gene-encoded mammalian antibiotics. J Mol Med (Berl).
80:549–561. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zaiou M, Nizet V and Gallo RL:
Antimicrobial and protease inhibitory functions of the human
cathelicidin (hCAP18/LL-37) prosequence. J Invest Dermatol.
120:810–816. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiao Y, Cai Y, Bommineni YR, Fernando SC,
Prakash O, Gilliland SE and Zhang G: Identification and functional
characterization of three chicken cathelicidins with potent
antimicrobial activity. J Biol Chem. 281:2858–2867. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xiao Y, Herrera AI, Bommineni YR, Soulages
JL, Prakash O and Zhang G: The central kink region of fowlicidin-2,
an alpha-helical host defense peptide, is critically involved in
bacterial killing and endotoxin neutralization. J Innate Immun.
1:268–280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Parachin NS, Mulder KC, Viana AA, Dias SC
and Franco OL: Expression systems for heterologous production of
antimicrobial peptides. Peptides. 38:446–456. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ahmad M, Hirz M, Pichler H and Schwab H:
Protein expression in Pichia pastoris: Recent achievements and
perspectives for heterologous protein production. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 98:5301–5317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gellissen G, Kunze G, Gaillardin C, Cregg
JM, Berardi E, Veenhuis M and van der Klei I: New yeast expression
platforms based on methylotrophic Hansenula polymorpha and Pichia
pastoris and on dimorphic Arxula adeninivorans and Yarrowia
lipolytica -A comparison. FEMS Yeast Res. 5:1079–1096. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hélène B, Céline L, Patrick C, Fabien R,
Christine V, Yves C and Guy M: High-level secretory production of
recombinant porcine follicle-stimulating hormone by Pichia
pastoris. Process Biochem. 36:907–913. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Feng X, Xu W, Qu P, Li X, Xing L, Liu D,
Jiao J, Wang J, Li Z and Liu C: High-yield recombinant expression
of the chicken antimicrobial peptide fowlicidin-2 in Escherichia
coli. Biotechnol Prog. 31:369–374. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sambrook J, Fristsch EF and Maniatis T:
Molecular cloning: A laboratory manualSambrook J: Science Press;
Beijing: pp. 87–102. 2002, (In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Chen Z, Wang D, Cong Y, Wang J, Zhu J,
Yang J, Hu Z, Hu X, Tan Y, Hu F and Rao X: Recombinant
antimicrobial peptide hPAB-β expressed in Pichia pastoris, a
potential agent active against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 89:281–291. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dean SN, Bishop BM and van Hoek ML:
Natural and synthetic cathelicidin peptides with anti-microbial and
anti-biofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Microbiol.
11:1142011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin MC, Hui CF, Chen JY and Wu JL: The
antimicrobial peptide, shrimp anti-lipopolysaccharide factor
(SALF), inhibits proinflammatory cytokine expressions through the
MAPK and NF-κB pathways in Trichomonas vaginalis adherent to HeLa
cells. Peptides. 38:197–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moellering RC Jr: New approaches to
developing antimicrobials for resistant bacteria. J Infect
Chemother. 9:8–11. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jin F, Xu X, Zhang W and Gu D: Expression
and characterization of a housefly cecropin gene in the
methylotrophic yeast, Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif.
49:39–46. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cereghino JL and Cregg JM: Heterologous
protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris.
FEMS Microbiol Rev. 24:45–66. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang A, Wang S, Shen M, Chen F, Zou Z, Ran
X, Cheng T, Su Y and Wang J: High level expression and purification
of bioactive human alpha-defensin 5 mature peptide in Pichia
pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 84:877–884. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fuller RS, Brake A and Thorner J: Yeast
prohormone processing enzyme (KEX2 gene product) is a
Ca2+-dependent serine protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
86:1434–1438. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Seeboth PG and Heim J: In-vitro processing
of yeast alpha-factor leader fusion proteins using a soluble yscF
(Kex2) variant. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 35:771–776. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li L, Wang JX, Zhao XF, Kang CJ, Liu N,
Xiang JH, Li FH, Sueda S and Kondo H: High level expression,
purification, and characterization of the shrimp antimicrobial
peptide, Ch-penaeidin, in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif.
392:144–151. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wu M and Hancock RE: Interaction of the
cyclic antimicrobial cationic peptide bactenecin with the outer and
cytoplasmic membrane. J Biol Chem. 274:29–35. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang W, Seo J, Willingham SB, Czyzewski
AM, Gonzalgo ML, Weissman IL and Barron AE: Learning from
host-defense peptides: Cationic, amphipathic peptoids with potent
anticancer activity. PLoS One. 9:e903972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang QZ, Wang C, Lang L, Zhou Y, Wang H
and Shang DJ: Design of potent, non-toxic anticancer peptides based
on the structure of the antimicrobial peptide, temporin-1CEa. Arch
Pharm Res. 36:1302–1310. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Büchau AS, Morizane S, Trowbridge J,
Schauber J, Kotol P, Bui JD and Gallo RL: The host defense peptide
cathelicidin is required for NK cell-mediated suppression of tumor
growth. J Immunol. 184:369–378. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kuroda K, Fukuda T, Okumura K, Yoneyama H,
Isogai H, Savage PB and Isogai E: Ceragenin CSA-13 induces cell
cycle arrest and antiproliferative effects in wild-type and p53
null mutant HCT116 colon cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs.
24:826–834. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ren SX, Shen J, Cheng AS, Lu L, Chan RL,
Li ZJ, Wang XJ, Wong CC, Zhang L, Ng SS, et al: FK-16 derived from
the anticancer peptide LL-37 induces caspase-independent apoptosis
and autophagic cell death in colon cancer cells. PLoS One.
8:e636412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Ke M, Tian Y, Wang J, Li B, Wang
Y, Dou J and Zhou C: BF-30 selectively inhibits melanoma cell
proliferation via cytoplasmic membrane permeabilization and
DNA-binding in vitro and in B16F10-bearing mice. Eur J Pharmacol.
707:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Conlon JM, Mechkarska M, Prajeep M, Arafat
K, Zaric M, Lukic ML and Attoub S: Transformation of the naturally
occurring frog skin peptide, alyteserin-2a into a potent, non-toxic
anti-cancer agent. Amino Acids. 44:715–723. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gaspar D, Veiga AS and Castanho MA: From
antimicrobial to anticancer peptides. A review. Front Microbiol.
4:2942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|