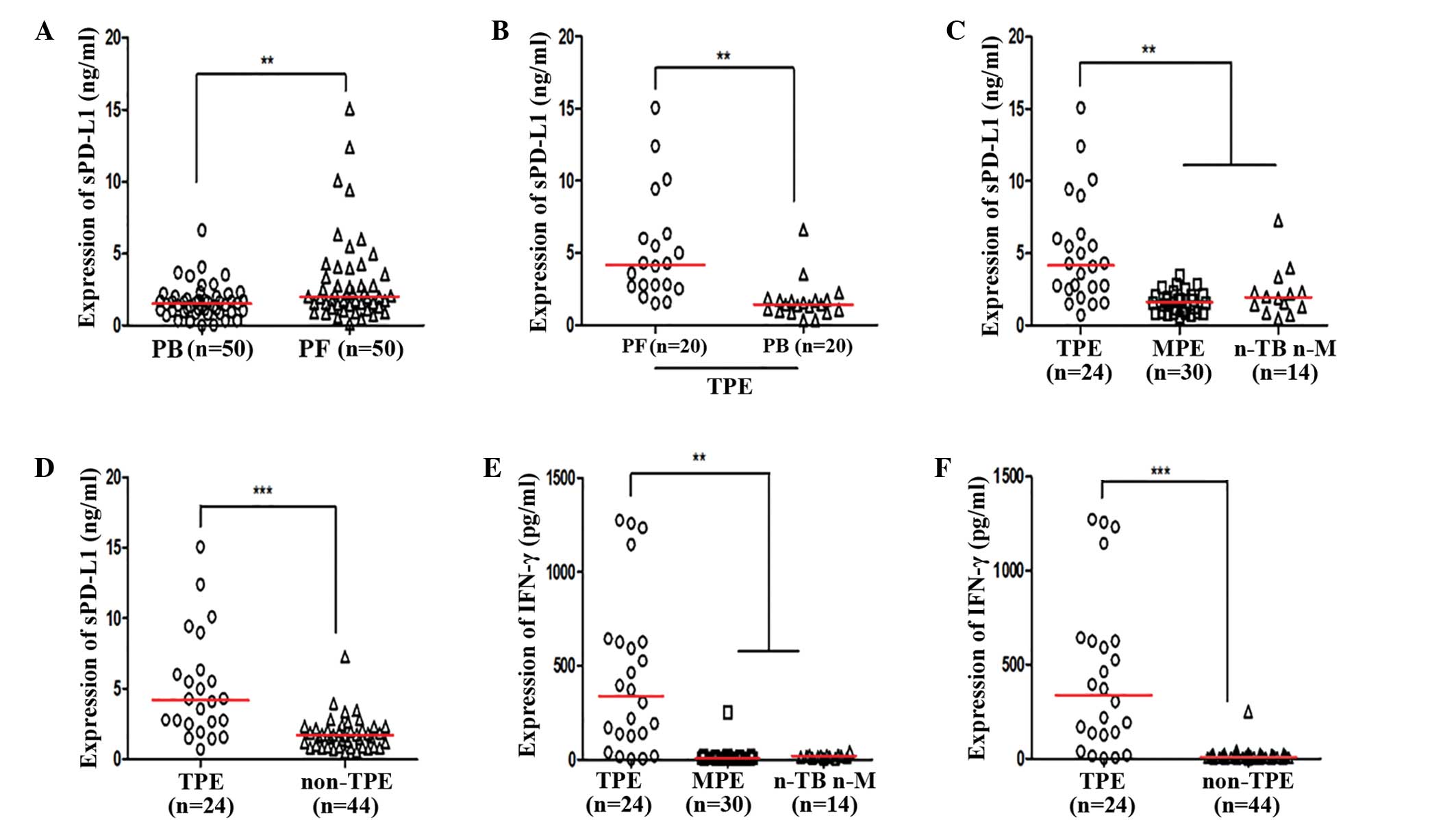
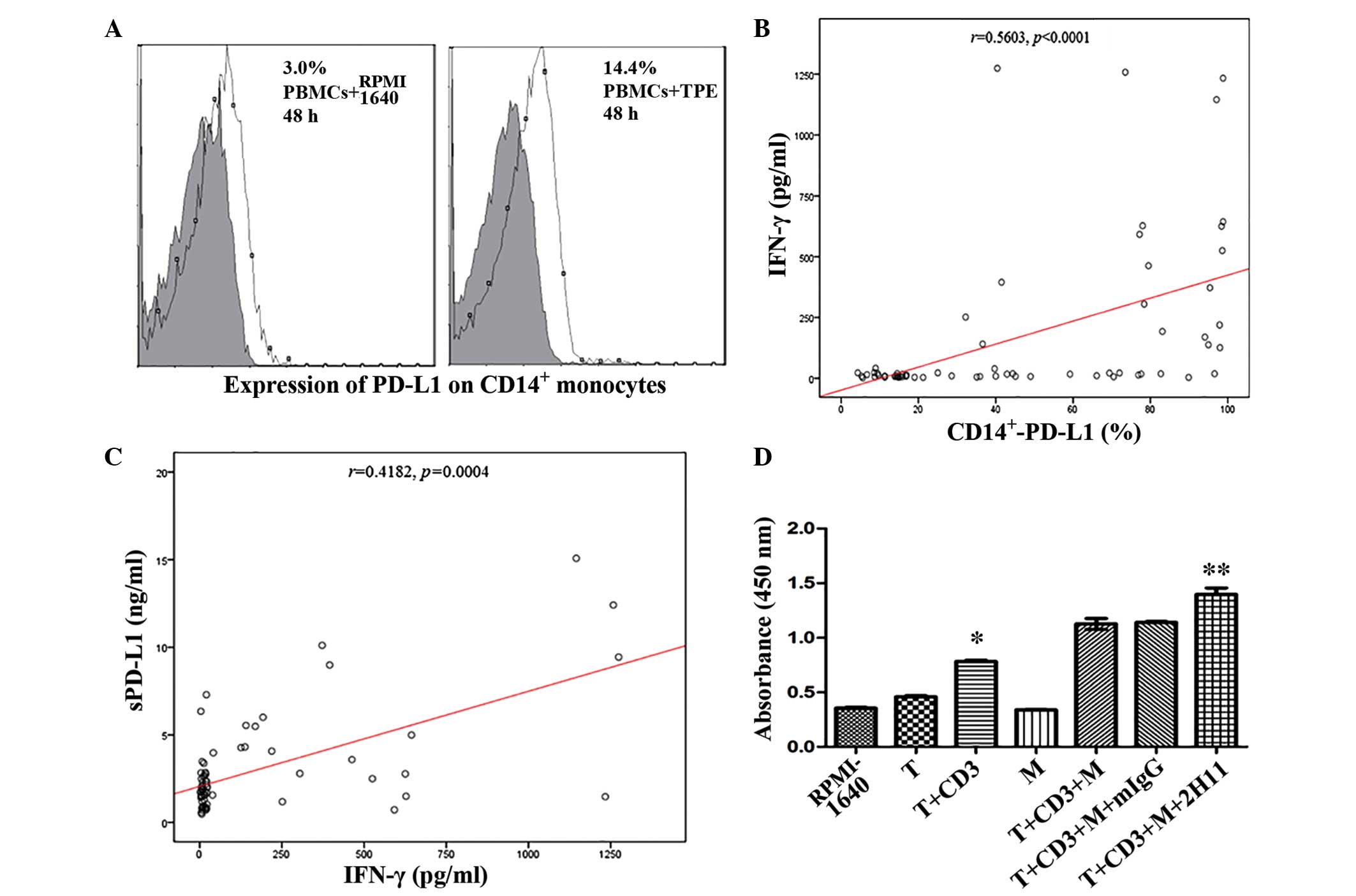
|
1
|
WHO global tuberculosis report. 2015,
https://www.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/191102/1/9789241565059_eng.pdf?ua=1
|
|
2
|
Porcel JM: Tuberculous pleural effusion.
Lung. 187:263–270. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Valdés L, Pose A, San José E and Vázquez
JM Martínez: Tuberculous pleural effusions. Eur J Intern Med.
14:77–88. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khan FY, Hamza M, Omran AH, Saleh M,
Lingawi M, Alnaqdy A, Rahman MO, Ahmedullah HS, Hamza A, Ani AA, et
al: Diagnostic value of pleural fluid interferon-gamma and
adenosine deaminase in patients with pleural tuberculosis in Qatar.
Int J Gen Med. 6:13–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Azimi Q, Rezadoost B, Nadoushan M Jalali
and Davati A: Evaluation of serum cyfra21-1 in patients with
pleural effusion. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 14:613–616.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K and Chen L: B7-H1,
a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation
and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 5:1365–1369. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liang SC, Greenwald RJ, Latchman YE, Rosas
L, Satoskar A, Freeman GJ and Sharpe AH: PD-L1 and PD-L2 have
distinct roles in regulating host immunity to cutaneous
leishmaniasis. Eur J Immunol. 36:58–64. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ye ZJ, Zhou Q, Yin W, Yuan ML, Yang WB,
Xiang F, Zhang JC, Xin JB, Xiong XZ and Shi HZ: Interleukin
22-producing CD4+ T cells in malignant pleural effusion.
Cancer Lett. 326:23–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen Y, Wang Q, Shi B, Xu P, Hu Z, Bai L
and Zhang X: Development of a sandwich ELISA for evaluating soluble
PD-L1 (CD274) in human sera of different ages as well as
supernatants of PD-L1+ cell lines. Cytokine. 56:231–238.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu DM, Yan JC, Wang CP, Chen GH, Ding S,
Liu PJ and Du RZ: The clinical implications of increased OX40
ligand expression in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Clin
Chim Acta. 397:22–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiang J, Jiang J, Liu C, Zhang G, Gao L,
Chen Y, Zhu R, Wang T, Wang F, Zhang X and Xue Q: Enhancement of
membrane B7-H3 costimulatory molecule but reduction of its soluble
form in multiple sclerosis. J Clin Immunol. 33:118–126. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xing YF, Zhang ZL, Shi MH, Ma Y and Chen
YJ: The level of soluble programmed death-1 in peripheral blood of
patients with lung cancer and its clinical implications. Zhonghua
Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 35:102–106. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Frigola X, Inman BA, Lohse CM, Krco CJ,
Cheville JC, Thompson RH, Leibovich B, Blute ML, Dong H and Kwon
ED: Identification of a soluble form of B7-H1 that retains
immunosuppressive activity and is associated with aggressive renal
cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1915–1923. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Muenst S, Soysal SD, Gao F, Obermann EC,
Oertli D and Gillanders WE: The presence of programmed death 1
(PD-1)-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with
poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
139:667–676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
de Paus RA, van Wengen A, Schmidt I,
Visser M, Verdegaal EM, van Dissel JT and van de Vosse E:
Inhibition of the type I immune responses of human monocytes by
IFN-α and IFN-β. Cytokine. 61:645–655. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi B, Du X, Wang Q, Chen Y and Zhang X:
Increased PD-1 on CD4(+)CD28(−) T cell and soluble PD-1 ligand-1 in
patients with T2DM: Association with atherosclerotic macrovascular
diseases. Metabolism. 62:778–785. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Infante-Duarte C and Kamradt T: Th1/Th2
balance in infection. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 21:317–338.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang WB, Liang QL, Ye ZJ, Niu CM, Ma WL,
Xiong XZ, Du RH, Zhou Q, Zhang JC and Shi HZ: Cell origins and
diagnostic accuracy of interleukin 27 in pleural effusions. PLoS
One. 7:e404502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Light RW, Macgregor MI, Luchsinger PC and
Ball WC Jr: Pleural effusions: The diagnostic separation of
transudates and exudates. Ann Intern Med. 77:507–513. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kastelik JA: Management of malignant
pleural effusion. Lung. 191:165–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT,
McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, Schaller JG, Talal N and Winchester RJ:
The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus
erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 25:1271–1277. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Niederman MS, Mandell LA, Anzueto A, Bass
JB, Broughton WA, Campbell GD, Dean N, File T, Fine MJ, Gross PA,
et al: Guidelines for the management of adults with
community-acquired pneumonia. Diagnosis, assessment of severity,
antimicrobial therapy, and prevention. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
163:1730–1754. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jurado JO, Alvarez IB, Pasquinelli V,
Martínez GJ, Quiroga MF, Abbate E, Musella RM, Chuluyan HE and
García VE: Programmed death (PD)-1: PD-ligand1/PD-ligand 2 pathway
inhibits T cell effector functions during human tuberculosis. J
Immunol. 181:116–125. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Reiley WW, Shafiani S, Wittmer ST,
Tucker-Heard G, Moon JJ, Jenkins MK, Urdahl KB, Winslow GM and
Woodland DL: Distinct functions of antigen-specific CD4 T cells
during murine Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 107:19408–19413. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yin W, Tong ZH, Cui A, Zhang JC, Ye ZJ,
Yuan ML, Zhou Q and Shi HZ: PD-1/PD-Ls pathways between CD4(+) T
cells and pleural mesothelial cells in human uberculous pleurisy.
Tuberculosis (Edinb). 94:131–139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Porcel JM: Tuberculous pleural effusion.
Lung. 187:263–270. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xia H, Ye ZJ, Zhou Q, You WJ, Cui A, Wang
XJ, Zhai K, Jin XG, Tong ZH and Shi HZ: IL-27 and IL-27-producing
CD4+ T cells in human tuberculous pleural effusion. Tuberculosis
(Edinb). 94:579–588. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qama D, Choi WI and Kwon KY: Immune
responses in the lungs of patients with tuberculous pleural
effusion without pulmonary tuberculosis. BMC Immunol. 13:452012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Amarnath S, Costanzo CM, Mariotti J,
Ullman JL, Telford WG, Kapoor V, Riley JL, Levine BL, June CH, Fong
T, et al: Regulatory T cells and human myeloid dendritic cells
promote tolerance via programmed death ligand-1. PLoS Biol.
8:e10003022010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Trinath J, Maddur MS, Kaveri SV, Balaji KN
and Bayry J: Mycobacterium tuberculosis promotes regulatory T-cell
expansion via induction of programmed death-1 ligand 1 (PD-L1,
CD274) on dendritic cells. J Infect Dis. 205:694–696. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Frigola X, Inman BA, Krco CJ, Liu X,
Harrington SM, Bulur PA, Dietz AB, Dong H and Kwon ED: Soluble
B7-H1: Differences in production between dendritic cells and T
cells. Immunol Lett. 142:78–82. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
He XH, Xu LH and Liu Y: Identification of
a novel splice variant of human PD-L1 mRNA encoding an
isoform-lacking Igv-like domain. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 26:462–468.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang J, Shi HZ, Liang QL, Qin SM and Qin
XJ: Diagnostic value of interferon-gamma in tuberculous pleurisy: A
metaanalysis. Chest. 131:1133–1141. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee SJ, Jang BC, Lee SW, Yang YI, Suh SI,
Park YM, Oh S, Shin JG, Yao S, Chen L and Choi IH: Interferon
regulatory factor-1 is prerequisite to the constitutive expression
and IFN-gamma-induced up-regulation of B7-H1 (CD274). FEBS Lett.
580:755–762. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ma J, Yang B, Yu S, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Lao
S, Chen X, Li B and Wu C: Tuberculosis antigen-induced expression
of IFN-α in tuberculosis patients inhibits production of IL-1β.
FASEB J. 28:3238–3248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sutherland JS, Garba D, Fombah AE,
Mendy-Gomez A, Mendy FS, Antonio M, Townend J, Ideh RC, Corrah T
and Ota MO: Highly accurate diagnosis of pleural tuberculosis by
immunological analysis of the pleural effusion. PLoS One.
7:e303242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang T, Lv M, Qian Q, Nie Y, Yu L and Hou
Y: Increased frequencies of T helper type 17 cells in tuberculous
pleural effusion. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 91:231–237. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Budak F, Uzaslan EK, Cangür S, Göral G and
Oral HB: Increased pleural soluble Fas Ligand (sFasL) levels in
tuberculosis pleurisy and its relation with T-helper type 1
cytokines. Lung. 186:337–343. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu YC, Lee S Shin-Jung, Chen YS, Tu HZ,
Chen BC and Huang TS: Differential diagnosis of tuberculous and
malignant pleurisy using pleural fluid adenosine deaminase and
interferon gamma in Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 44:88–94.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ibrahim L, Salah M, Abd El Rahman A,
Zeidan A and Ragb M: Crucial role of
CD4+CD25+ FOXP3+ T regulatory
cell, interferon-γ and interleukin-16 in malignant and tuberculous
pleural effusions. Immunol Invest. 42:122–136. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|