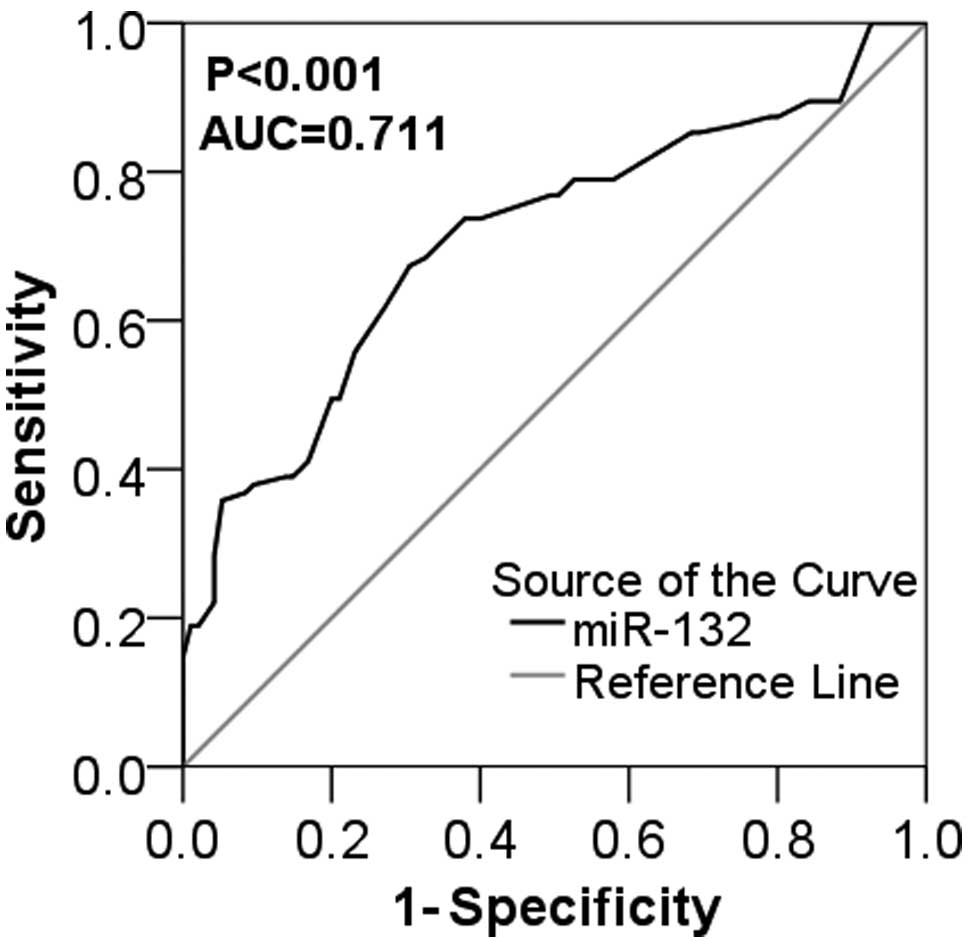
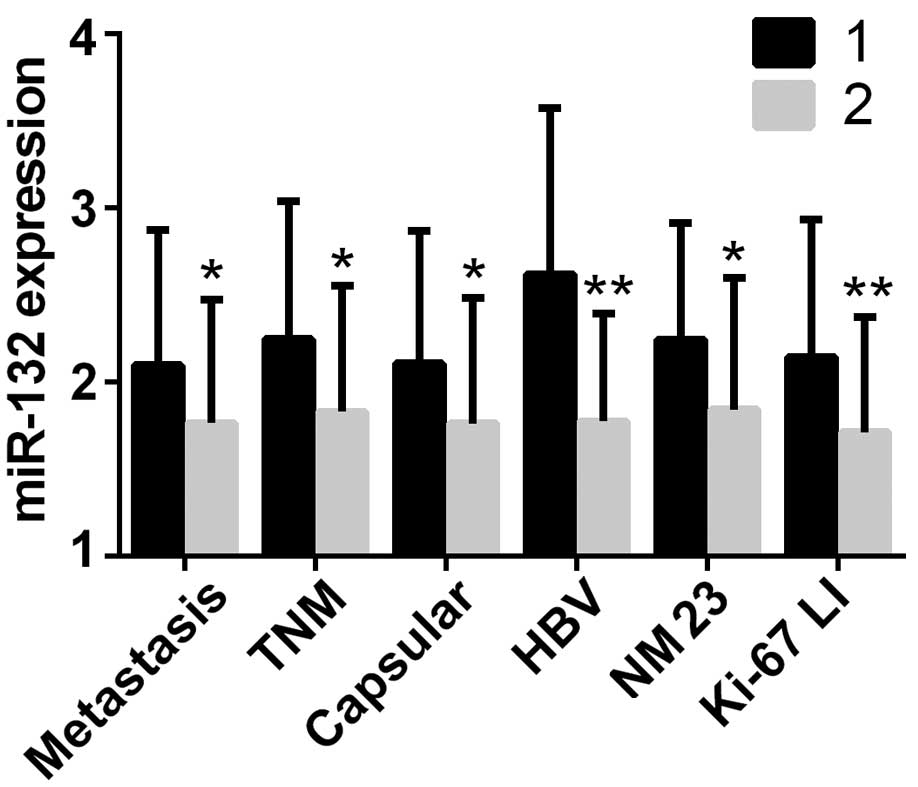
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schwartz M, Roayaie S and Konstadoulakis
M: Strategies for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat
Clin Pract Oncol. 4:424–432. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L and
Reddy KR: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 134:1752–1763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Blum HE: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Therapy
and prevention. World J Gastroenterol. 11:7391–7400.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cho WC: OncomiRs: The discovery and
progress of microRNAs in cancers. Mol Cancer. 6:602007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kent OA and Mendell JT: A small piece in
the cancer puzzle: microRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes.
Oncogene. 25:6188–6196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li G, Shen Q, Li C, Li D, Chen J and He M:
Identification of circulating MicroRNAs as novel potential
biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma detection: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Clin Transl Oncol. 17:684–693. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang K, Zhang Y, Liu C, Xiong Y and Zhang
J: MicroRNAs in the diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer and
their therapeutic potential (review). Int J Oncol. 45:950–958.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Usó M, Jantus-Lewintre E, Sirera R,
Bremnes RM and Camps C: miRNA detection methods and clinical
implications in lung cancer. Future Oncol. 10:2279–2292. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Budhu A, Jia HL, Forgues M, Liu CG,
Goldstein D, Lam A, Zanetti KA, Ye QH, Qin LX, Croce CM, et al:
Identification of metastasis-related microRNAs in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 47:897–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng YB, Luo HP, Shi Q, Hao ZN, Ding Y,
Wang QS, Li SB, Xiao GC and Tong SL: miR-132 inhibits colorectal
cancer invasion and metastasis via directly targeting ZEB2. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:6515–6522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Salendo J, Spitzner M, Kramer F, Zhang X,
Jo P, Wolff HA, Kitz J, Kaulfuß S, Beißbarth T, Dobbelstein M, et
al: Identification of a microRNA expression signature for
chemoradiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells, involving
miRNAs-320a, −224, −132 and let7g. Radiother Oncol. 108:451–457.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang ZG, Chen WX, Wu YH, Liang HF and
Zhang BX: MiR-132 prohibits proliferation, invasion, migration, and
metastasis in breast cancer by targeting HN1. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 454:109–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li S, Meng H, Zhou F, Zhai L, Zhang L, Gu
F, Fan Y, Lang R, Fu L, Gu L and Qi L: MicroRNA-132 is frequently
down-regulated in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) of breast and
acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cell proliferation. Pathol
Res Pract. 209:179–183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang S, Hao J, Xie F, Hu X, Liu C, Tong
J, Zhou J, Wu J and Shao C: Downregulation of miR-132 by promoter
methylation contributes to pancreatic cancer development.
Carcinogenesis. 32:1183–1189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Park JK, Henry JC, Jiang J, Esau C, Gusev
Y, Lerner MR, Postier RG, Brackett DJ and Schmittgen TD: miR-132
and miR-212 are increased in pancreatic cancer and target the
retinoblastoma tumor suppressor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
406:518–523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo G, Long J, Cui X, Xiao Z, Liu Z, Shi
S, Liu L, Liu C, Xu J, Li M and Yu X: Highly lymphatic metastatic
pancreatic cancer cells possess stem cell-like properties. Int J
Oncol. 42:979–984. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cote GA, Gore AJ, McElyea SD, Heathers LE,
Xu H, Sherman S and Korc M: A pilot study to develop a diagnostic
test for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on differential
expression of select miRNA in plasma and bile. Am J Gastroenterol.
109:1942–1952. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Formosa A, Lena AM, Markert EK, Cortelli
S, Miano R, Mauriello A, Croce N, Vandesompele J, Mestdagh P,
Finazzi-Agrò E, et al: DNA methylation silences miR-132 in prostate
cancer. Oncogene. 32:127–134. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu X, Yu H, Cai H and Wang Y: The
expression and clinical significance of miR-132 in gastric cancer
patients. Diagn Pathol. 9:572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu Q, Liao F, Wu H, Cai T, Yang L, Wang
ZF and Zou R: Upregulation of miR-132 expression in glioma and its
clinical significance. Tumour Biol. 35:12299–12304. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lages E, Guttin A, El Atifi M, Ramus C,
Ipas H, Dupré I, Rolland D, Salon C, Godfraind C, de Fraipont F, et
al: MicroRNA and target protein patterns reveal physiopathological
features of glioma subtypes. PLoS One. 6:e206002011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wei X, Tan C, Tang C, Ren G, Xiang T, Qiu
Z, Liu R and Wu Z: Epigenetic repression of miR-132 expression by
the hepatitis B virus × protein in hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Signal. 25:1037–1043. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gan TQ, Tang RX, He RQ, Dang YW, Xie Y and
Chen G: Upregulated MiR-1269 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its
clinical significance. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:714–721.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pan L, Huang S, He R, Rong M, Dang Y and
Chen G: Decreased expression and clinical significance of miR-148a
in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Eur J Med Res. 19:682014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rong M, He R, Dang Y and Chen G:
Expression and clinicopathological significance of miR-146a in
hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Ups J Med Sci. 119:19–24. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rong M, Chen G and Dang Y: Increased
miR-221 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and its role
in enhancing cell growth and inhibiting apoptosis in vitro. BMC
Cancer. 13:212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang J, Xu G, Shen F and Kang Y: miR-132
targeting cyclin E1 suppresses cell proliferation in osteosarcoma
cells. Tumour Biol. 35:4859–4865. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Renjie W and Haiqian L: MiR-132, miR-15a
and miR-16 synergistically inhibit pituitary tumor cell
proliferation, invasion and migration by targeting Sox5. Cancer
Lett. 356:568–578. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
You J, Li Y, Fang N, Liu B, Zu L, Chang R,
Li X and Zhou Q: MiR-132 suppresses the migration and invasion of
lung cancer cells via targeting the EMT regulator ZEB2. PLoS One.
9:e918272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang B, Lu L and Zhang X, Ye W, Wu J, Xi
Q and Zhang X: Hsa-miR-132 regulates apoptosis in non-small cell
lung cancer independent of acetylcholinesterase. J Mol Neurosci.
53:335–344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Parker NR, Correia N, Crossley B, Buckland
ME, Howell VM and Wheeler HR: Correlation of MicroRNA 132
Up-regulation with an unfavorable clinical outcome in patients with
primary glioblastoma multiforme treated with radiotherapy plus
concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide chemotherapy. Transl Oncol.
6:742–748. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang J, Gao T, Tang J, Cai H, Lin L and Fu
S: Loss of microRNA-132 predicts poor prognosis in patients with
primary osteosarcoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 381:9–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chung YW, Bae HS, Song JY, Lee JK, Lee NW,
Kim T and Lee KW: Detection of microRNA as novel biomarkers of
epithelial ovarian cancer from the serum of ovarian cancer
patients. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 23:673–679. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kumar M, Kumar R, Hissar SS, Saraswat MK,
Sharma BC, Sakhuja P and Sarin SK: Risk factors analysis for
hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with and without cirrhosis: A
case-control study of 213 hepatocellular carcinoma patients from
India. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:1104–1111. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Takada S and Koike K: Trans-activation
function of a 3′truncated X gene-cell fusion product from
integrated hepatitis B virus DNA in chronic hepatitis tissues. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:5628–5632. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Koskinas J, Petraki K, Kavantzas N, Rapti
I, Kountouras D and Hadziyannis S: Hepatic expression of the
proliferative marker Ki-67 and p53 protein in HBV or HCV cirrhosis
in relation to dysplastic liver cell changes and hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Viral Hepat. 12:635–641. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|