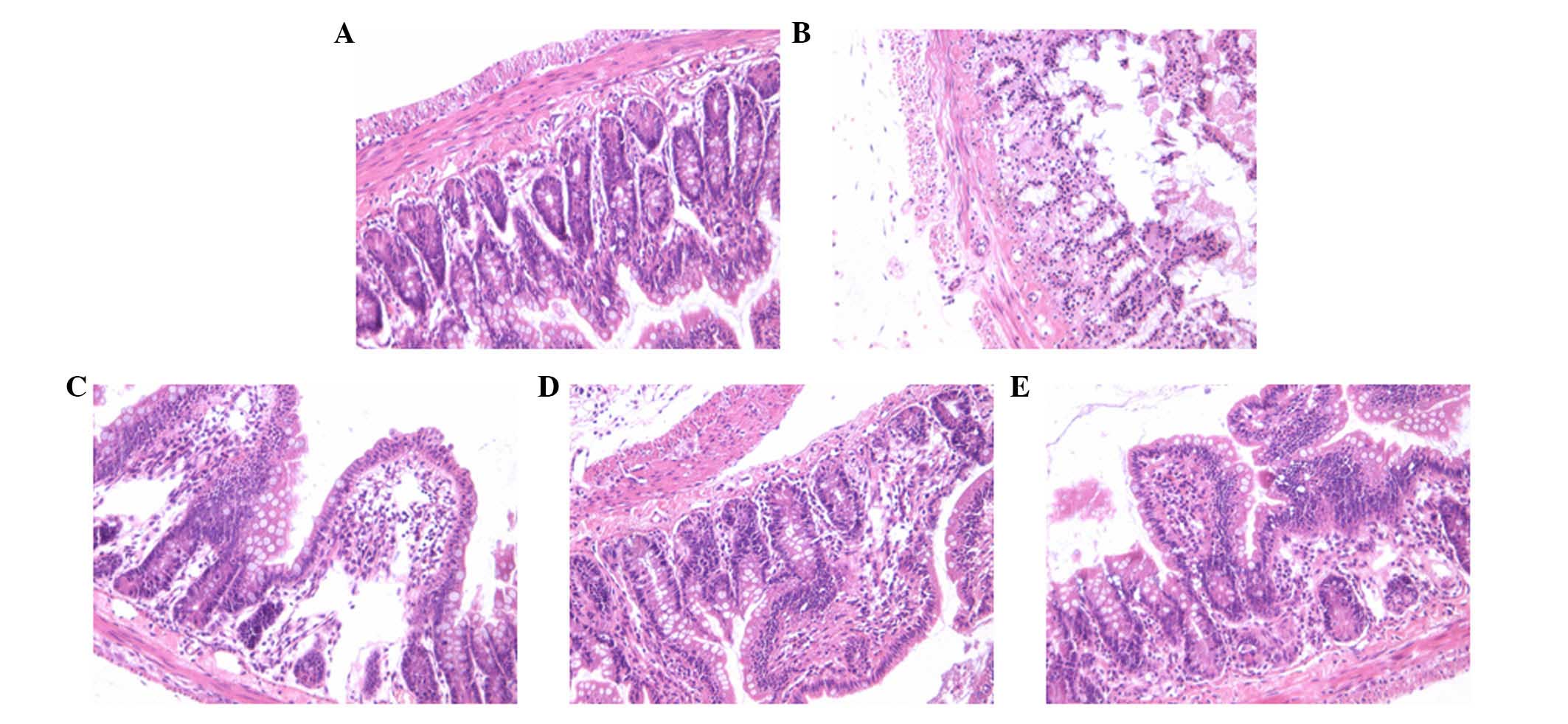
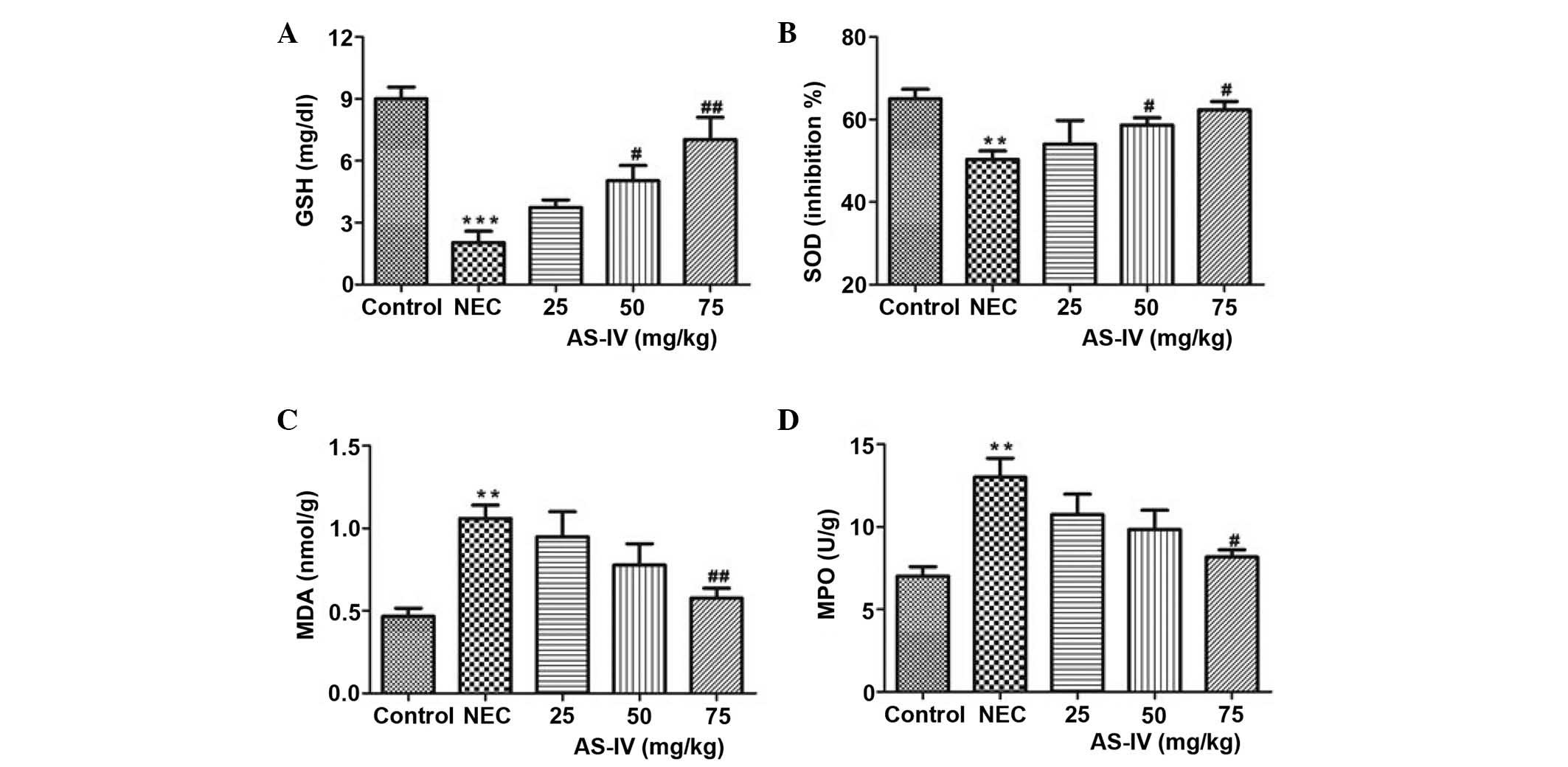
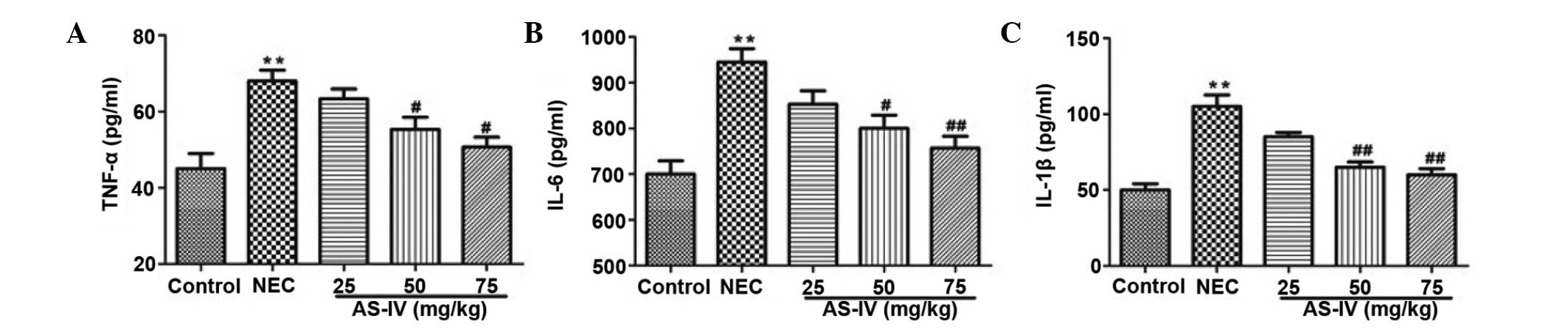
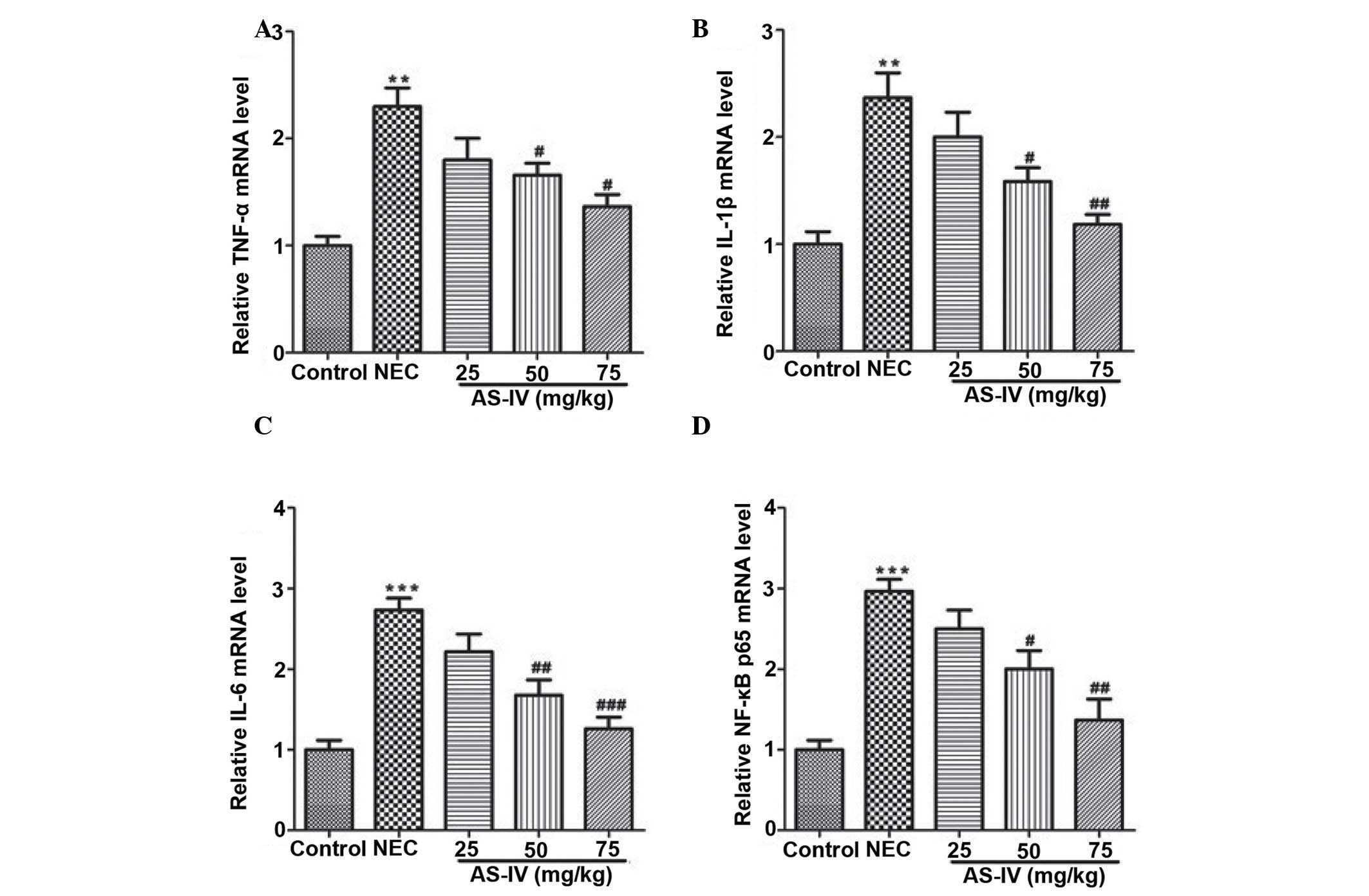
|
1
|
Chen CC and Allan WW: Probiotics and the
mechanism of necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Pediatr Surg.
22:94–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nanthakumar N, Meng D, Goldstein AM, Zhu
W, Lu L, Uauy R, Llanos A, Claud EC and Walker WA: The mechanism of
excessive intestinal inflammation in necrotizing enterocolitis: An
immature innate immune response. PLoS One. 6:e177762011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schnabl KL, Van Aerde JE, Thomson AB and
Clandinin MT: Necrotizing enterocolitis: A multifactorial disease
with no cure. World J Gastroenterol. 14:2142–2161. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chandler JC and Hebra A: Necrotizing
enterocolitis in infants with very low birth weight. Semin Pediatr
Surg. 9:63–72. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chung JW, Jeon JH, Yoon SR and Choi I:
Vitamin D3 upregulated protein 1 (VDUP1) is a regulator for redox
signaling and stress-mediated diseases. J Dermatol. 33:662–669.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pan CL and Dong ZW: Antiasthmatic effects
of eugenol in a mouse model of allergic asthma by regulation of
vitamin D3 upregulated protein 1/NF-κB pathway. Inflammation.
38:1385–1393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim SY, Suh HY, Chuang JW, Yoon SR and
Choi I: Diverse functions of VDUP1 in cell proliferation,
differentiation and diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 4:345–351.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kutuk O and Basaga H: Inflammation meets
oxidation: NF-κB as a mediator of initial lesion development in
atherosclerosis. Trends Mol Med. 9:549–557. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tanner SM, Berryhill TF, Ellenburg JL,
Jilling T, Cleveland DS, Lorenz RG and Martin CA: Pathogenesis of
necrotizing enterocolitis: Modeling the innate immune response. Am
J Pathol. 185:4–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shilan M and Mohammad A: A review on the
role of oxidative stress and inflammation in necrotizing
enterocolitis and benefits of the phosphodiesterase inhibitor
pentoxifylline. International Journal of Pharmacology. 9:245–250.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Frost BL, Jilling T and Caplan MS: The
importance of pro-inflammatory signaling in neonatal necrotizing
enterocolitis. Semin Perinatol. 32:100–106. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cevik M, Karadag CA, Sakiz DE, Tander B
and Embleton DD: The role of nitric oxide in an experimental
necrotising enterocolitis model. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 10:24–28.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He Y, Du M, Gao Y, Liu H, Wang H, Wu X and
Wang Z: Astragaloside IV attenuates experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis of mice by counteracting oxidative stress at
multiple levels. PLoS One. 8:e764952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lai PK, Chan JY, Cheng L, Lau CP, Han SQ,
Leung PC, Fung KP and Lau CB: Isolation of anti-inflammatory
fractions and compounds from the root of Astragalus membranaceus.
Phytother Res. 27:581–587. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren S, Zhang H, Mu Y, Sun M and Liu P:
Pharmacological effects of Astragaloside IV: A literature review. J
Tradit Chin Med. 33:413–416. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Z, Cai Y, Zhang W, Liu X and Liu S:
Astragaloside IV inhibits platelet-derived growth
factor-BB-stimulated proliferation and migration of vascular smooth
muscle cells via the inhibition of p38 MAPK signaling. Exp Ther
Med. 8:1253–1258. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yazıcı S, Akşit H, Korkut O, Sunay B and
Çelik T: Effects of boric acid and 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate on
necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 58:61–67.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li J, Gu T, Fu X and Zhao R: Effect of
salvianolic acid A and C compatibility on inflammatory cytokines in
rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Tradit Chin Med.
35:564–570. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nadler EP, Dickinson E, Knisely A, Zhang
XR, Boyle P, Beer-Stolz D, Watkins SC and Ford HR: Expression of
inducible nitric oxide synthase and interleukin-12 in experimental
necrotizing enterocolitis. J Surg Res. 92:71–77. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hillegass LM, Griswold DE, Brickson B and
Albrightson-Winslow C: Assessment of myeloperoxidase activity in
whole rat kidney. J Pharmacol Methods. 24:285–295. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu HE, Chen Y, Sun XB, Tong B and Fan XH:
Effects of luteolin on retinal oxidative stress and inflammation in
diabetes. RSC Advances. 5:4898–4904. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Williams CM and Coleman JW: Induced
expression of mRNA for IL-5, IL-6, TNF-alpha, MIP-2 and IFN-gamma
in immunologically activated rat peritoneal mast cells: Inhibition
by dexamethasone and cyclosporin A. Immunology. 86:244–249.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lasanianos NG, Kanakaris NK, Dimitriou R,
Pape HC and Giannoudis PV: Second hit phenomenon: Existing evidence
of clinical implications. Injury. 42:617–629. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qi W, Shen Q, Zhang L, Han LP and Wang S:
Study on the inflammatory intervention of erythropoietin on NEC.
Exp Ther Med Jun. 11:2221–2224. 2016.
|
|
26
|
Heida FH, Hulscher JB, Schurink M, van
Vliet MJ, Kooi EM, Kasper DC, Pones M, Bos AF and Benkoe TM:
Bloodstream infections during the onset of necrotizing
enterocolitis and their relation with the pro-inflammatory
response, gut wall integrity and severity of disease in NEC. J
Pediatr Surg. 50:1837–1841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chung CY, Park YL, Kim N, Oh HH, Myung DS,
Kim JS, Cho SB, Lee WS, Kim HS, Ahn BW and Joo YE: Rice prolamin
extract ameliorates acute murine colitis by inhibiting nuclear
factor-kappaB and modulating intestinal apoptosis and cell
proliferation. Clin Exp Immunol. 178:537–547. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Everard A, Geurts L, Caesar R, Van Hul M,
Matamoros S, Duparc T, Denis RG, Cochez P, Pierard F, Castel J, et
al: Intestinal epithelial MyD88 is a sensor switching host
metabolism towards obesity according to nutritional status. Nat
Commun. 5:56482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lu M, Tang F, Zhang J, Luan A, Mei M, Xu
C, Zhang S, Wang H and Maslov LN: Astragaloside IV attenuates
injury caused by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in rats via
regulation of toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB signaling
pathway. Phytother Res. 29:599–606. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|