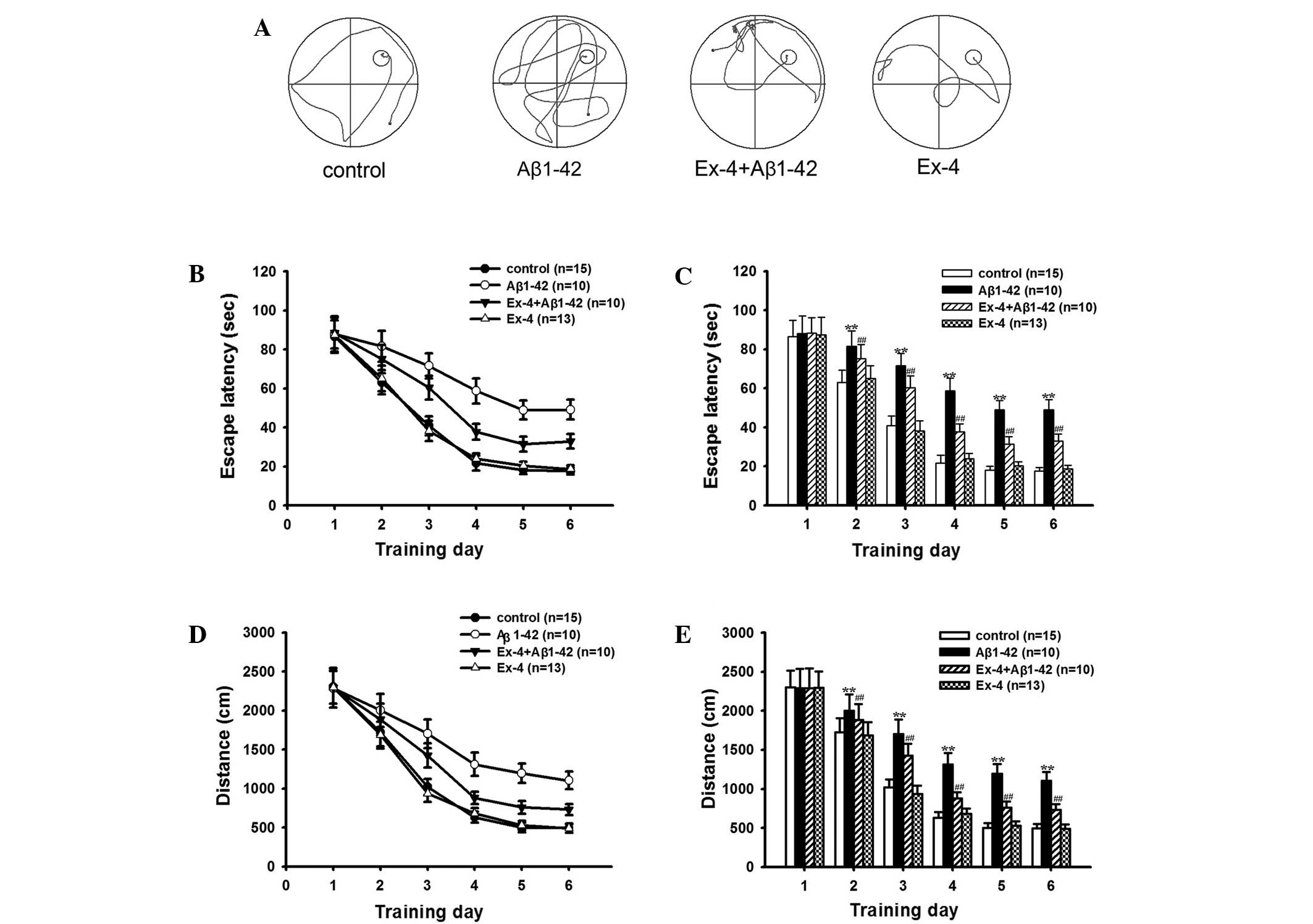
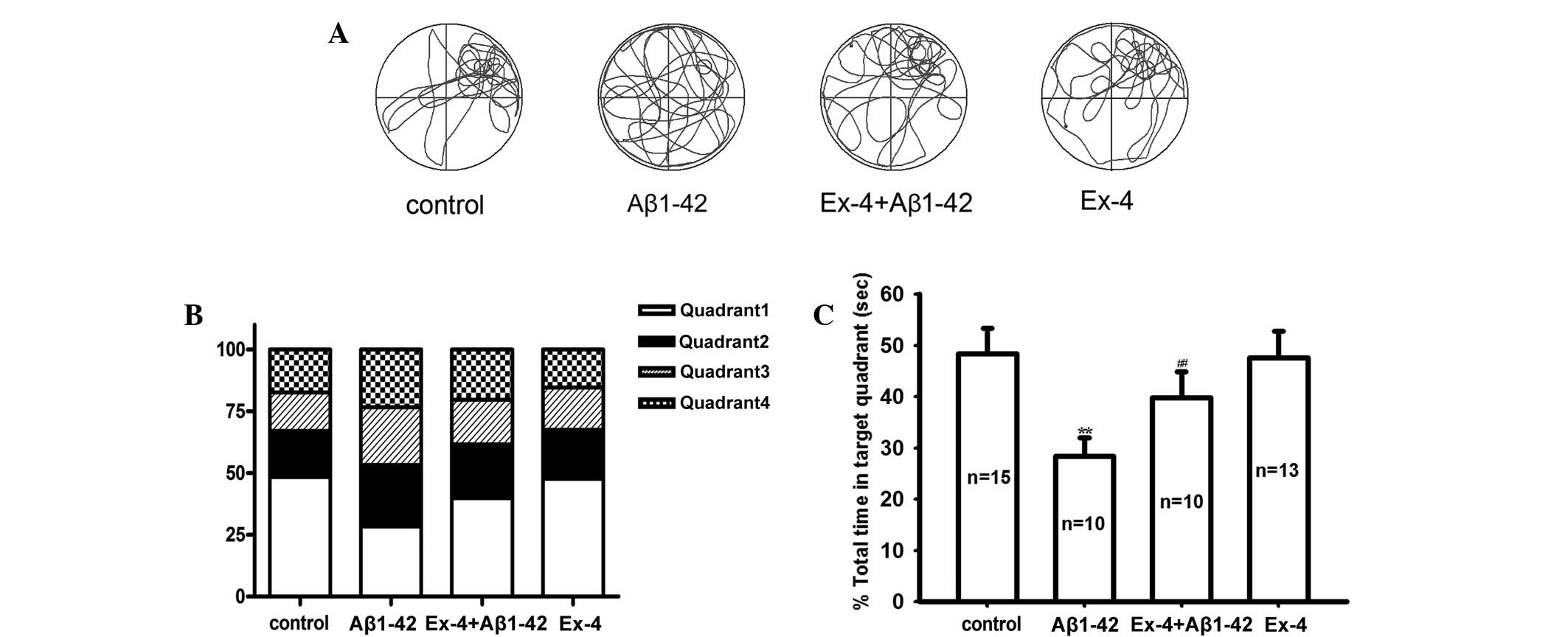
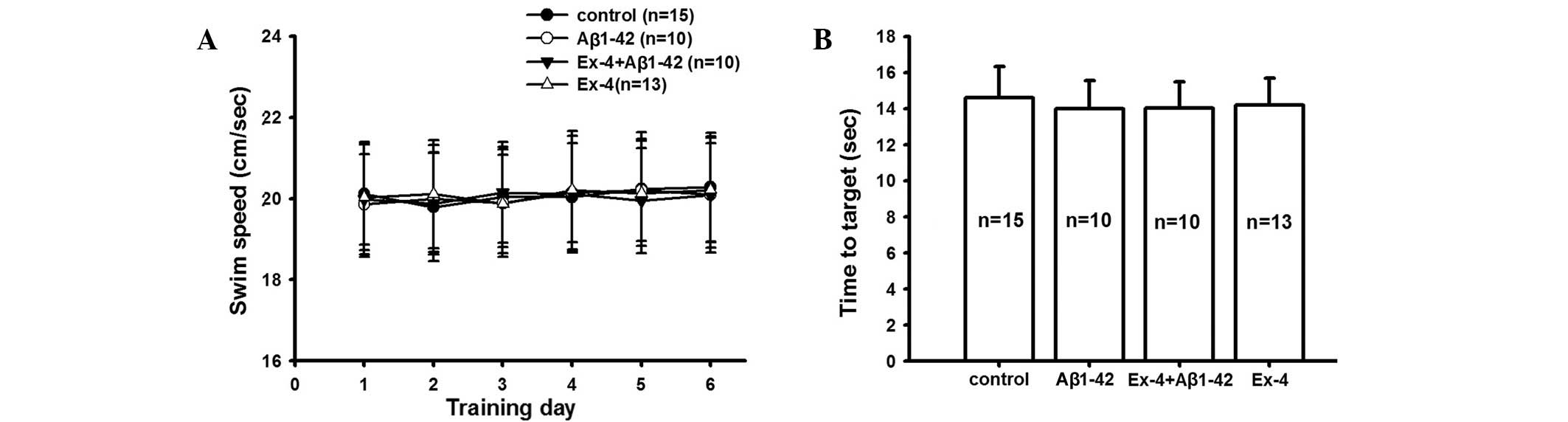
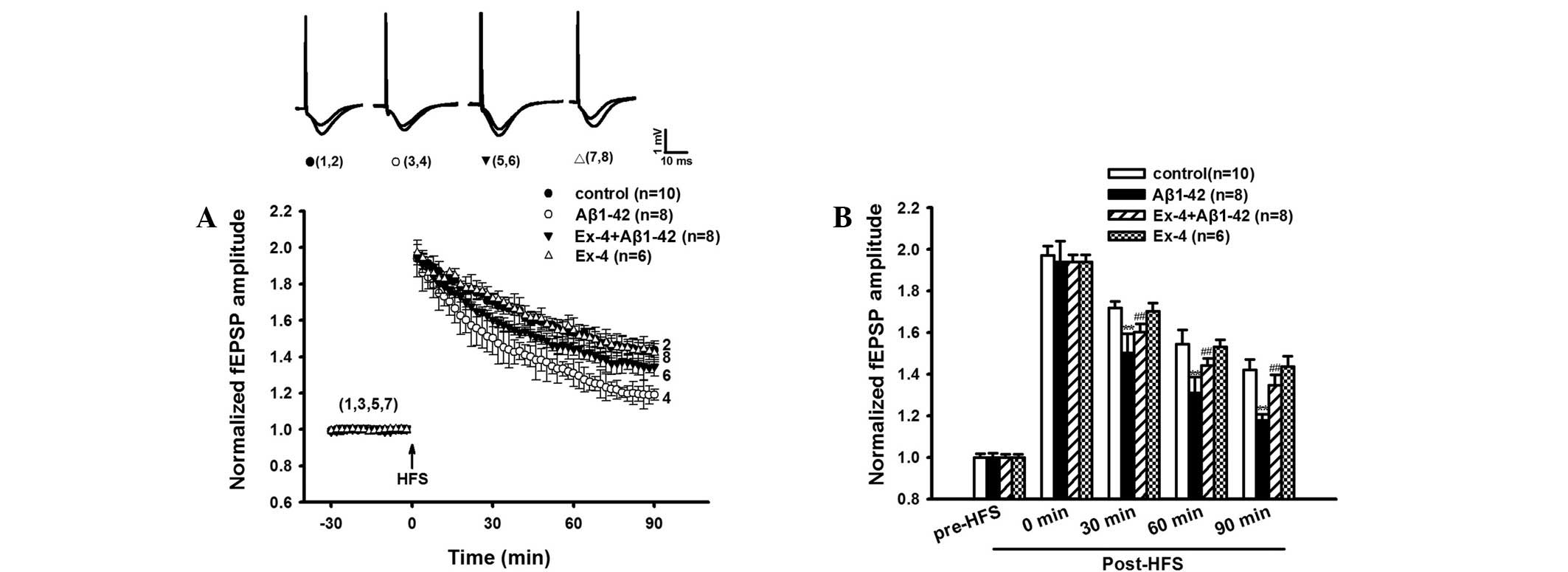
|
1
|
Cummings JL: Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J
Med. 351:56–67. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hardy J and Allsop D: Amyloid deposition
as the central event in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 12:383–388. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hoenicka J: Genes in Alzheimer's disease.
Rev Neurol. 42:302–305. 2006.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bohm C, Chen F, Sevalle J, Qamar S, Dodd
R, Li Y, Schmitt-Ulms G, Fraser PE and St George-Hyslop PH: Current
and future implications of basic and translational research on
amyloid-β peptide production and removal pathways. Mol Cell
Neurosci. 66:3–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ohtake N, Saito M, Eto M and Seki K:
Exendin-4 promotes the membrane trafficking of the AMPA receptor
GluR1 subunit and ADAM10 in the mouse neocortex. Regul Pept
190–191. 1–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Vilsbøll T, Agersø H, Krarup T and Holst
JJ: Similar elimination rates of glucagon-like peptide-1 in obese
type 2 diabetic patients and healthy subjects. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 88:220–224. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lupi R, Mancarella R, Del Guerra S,
Bugliani M, Del Prato S, Boggi U, Mosca F, Filipponi F and
Marchetti P: Effects of exendin-4 on islets from type 2 diabetes
patients. Diabetes Obes Metab. 10:515–519. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bassil F, Fernagut PO, Bezard E and
Meissner WG: Insulin, IGF-1 and GLP-1 signaling in
neurodegenerative disorders: targets for disease modification? Prog
Neurobiol. 118:1–18. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calsolaro V and Edison P: Novel GLP-1
(glucagon-like peptide-1) analogues and insulin in the treatment
for Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. CNS
Drugs. 29:1023–1039. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang XH, Li L, Hölscher C, Pan YF, Chen XR
and Qi JS: Val8-glucagon-like peptide-1 protects against
Aβ1-40-induced impairment of hippocampal late-phase long-term
potentiation and spatial learning in rats. Neuroscience.
170:1239–1248. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang XH, Yang W, Hölscher C, Wang ZJ, Cai
HY, Li QS and Qi JS: Val8-GLP-1 remodels synaptic
activity and intracellular calcium homeostasis impaired by amyloid
β peptide in rats. J Neurosci Res. 91:568–577. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gengler S, McClean PL, McCurtin R, Gault
VA and Hölscher C: Val (8)GLP-1 rescues synaptic plasticity and
reduces dense core plaques in APP/PS1 mice. Neurobiol Aging.
33:265–276. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xie Z and Xu Z: General anesthetics and
β-amyloid protein. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry.
47:140–146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
O'Hare E, Weldon DT, Mantyh PW, Ghilardi
JR, Finke MP, Kuskowski MA, Maggio JE, Shephard RA and Cleary J:
Delayed behavioral effects following intrahippocampal injection of
aggregated A beta (1–42). Brain Res. 815:1–10. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Querfurth HW and LaFerla FM: Alzheimer's
disease. N Engl J Med. 362:329–344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chiu MJ, Chen TF, Yip PK, Hua MS and Tang
LY: Behavioral and psychologic symptoms in different types of
dementia. J Formos Med Assoc. 105:556–562. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sorrentino G and Bonavita V:
Neurodegeneration and Alzheimer's disease: The lesson from
tauopathies. Neurol Sci. 28:63–71. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Blennow K, de Leon MJ and Zetterberg H:
Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 368:387–403. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nitta A, Fukuta T, Hasegawa T and
Nabeshima T: Continuous infusion of beta-amyloid protein into the
rat cerebral ventricle induces learning impairment and neuronal and
morphological degeneration. Jpn J Pharmacol. 73:51–57. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Robbins TW, McAlonan G, Muir JL and
Everitt BJ: Cognitive enhancers in theory and practice: Studies of
the cholinergic hypothesis of cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's
disease. Behav Brain Res. 83:15–23. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shankar GM, Li S, Mehta TH, Garcia-Munoz
A, Shepardson NE, Smith I, Brett FM, Farrell MA, Rowan MJ, Lemere
CA, et al: Amyloid-beta protein dimers isolated directly from
Alzheimer's brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med.
14:837–842. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Glenner GG and Wong CW: Alzheimer's
disease: Initial report of the purification and characterization of
a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 120:885–890. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guan ZZ: Cross-talk between oxidative
stress and modifications of cholinergic and glutaminergic receptors
in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
29:773–780. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chakroborty S, Kim J, Schneider C,
Jacobson C, Molgó J and Stutzmann GE: Early presynaptic and
postsynaptic calcium signaling abnormalities mask underlying
synaptic depression in presymptomatic Alzheimer's disease mice. J
Neurosci. 32:8341–8353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Clementi ME, Marini S, Coletta M, Orsini
F, Giardina B and Misiti F: Abeta(31–35) and Abeta(25–35) fragments
of amyloid beta-protein induce cellular death through apoptotic
signals: Role of the redox state of methionine-35. FEBS Lett.
579:2913–2918. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kanai M, Matsubara E, Isoe K, Urakami K,
Nakashima K, Arai H, Sasaki H, Abe K, Iwatsubo T, Kosaka T, et al:
Longitudinal study of cerebrospinal fluid levels of tau, A
beta1-40, and A beta1-42(43) in Alzheimer's disease: a study in
Japan. Ann Neurol. 44:17–26. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lambert MP, Barlow AK, Chromy BA, Edwards
C, Freed R, Liosatos M, Morgan TE, Rozovsky I, Trommer B, Viola KL,
et al: Diffusible, nonfibrillar ligands derived from Abeta1-42 are
potent central nervous system neurotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:6448–6453. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bernardi A, Frozza RL, Meneghetti A, Hoppe
JB, Battastini AM, Pohlmann AR, Guterres SS and Salbego CG:
Indomethacin-loaded lipid-core nanocapsules reduce the damage
triggered by Aβ1-42 in Alzheimer's disease models. Int J
Nanomedicine. 7:4927–4942. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yamada K, Tanaka T, Han D, Senzaki K,
Kameyama T and Nabeshima T: Protective effects of idebenone and
alpha-tocopherol on beta-amyloid-(1–42)-induced learning and memory
deficits in rats: implication of oxidative stress in
beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in vivo. Eur J Neurosci.
11:83–90. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kheirbakhsh R, Chinisaz M, Khodayari S,
Amanpour S, Dehpour AR, Muhammadnejad A, Larijani B and
Ebrahim-Habibi A: Injection of insulin amyloid fibrils in the
hippocampus of male Wistar rats: Report on memory impairment and
formation of amyloid plaques. Neurol Sci. 36:1411–1416. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garcia-Osta A and Alberini CM: Amyloid
beta mediates memory formation. Learn Mem. 16:267–272. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nalivaeva NN, Beckett C, Belyaev ND and
Turner AJ: Are amyloid-degrading enzymes viable therapeutic targets
in Alzheimer's disease? J Neurochem. 120:(Suppl 1). S167–S185.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Soininen H and Hiltunen M: Targeting
ApoE4/ApoE receptor LRP1 in Alzheimer's disease. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 17:781–794. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jones A, Kulozik P, Ostertag A and Herzig
S: Common pathological processes and transcriptional pathways in
Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes. J Alzheimers Dis.
16:787–808. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leibson CL, Rocca WA, Hanson VA, Cha R,
Kokmen E, O'Brien PC and Palumbo PJ: Risk of dementia among persons
with diabetes mellitus: A population-based cohort study. Am J
Epidemiol. 145:301–308. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Janson J, Laedtke T, Parisi JE, O'Brien P,
Petersen RC and Butler PC: Increased risk of type 2 diabetes in
Alzheimer disease. Diabetes. 53:474–481. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Alafuzoff I, Aho L, Helisalmi S, Mannermaa
A and Soininen H: Beta-amyloid deposition in brains of subjects
with diabetes. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 35:60–68. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Accardi G, Caruso C, Colonna-Romano G,
Camarda C, Monastero R and Candore G: Can Alzheimer disease be a
form of type 3 diabetes? Rejuvenation Res. 15:217–221. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley
L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, Eckman CB, Tanzi RE, Selkoe DJ and
Guenette S: Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of
insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor
protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci.
100:4162–4167. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Frank-Cannon TC, Alto LT, McAlpine FE and
Tansey MG: Does neuroinflammation fan the flame in
neurodegenerative diseases? Mol Neurodegener. 4:472009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kahn SE, Hull RL and Utzschneider KM:
Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2
diabetes. Nature. 444:840–846. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nadkarni P, Chepurny OG and Holz GG:
Regulation of glucose homeostasis by GLP-1. Prog Mol Biol Transl
Sci. 121:23–65. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Baggio LL and Drucker DJ: Biology of
incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology. 132:2131–2157. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Manandhar B and Ahn JM: Glucagon-like
peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs: Recent advances, new possibilities, and
therapeutic implications. J Med Chem. 58:1020–1037. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hunter K and Hölscher C: Drugs developed
to treat diabetes, liraglutide and lixisenatide, cross the blood
brain barrier and enhance neurogenesis. BMC Neurosci. 13:332012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shirazi RH, Dickson SL and Skibicka KP:
Gut peptide GLP-1 and its analogue, Exendin-4, decrease alcohol
intake and reward. PLoS One. 8:e619652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kiesewetter DO, Gao H, Ma Y, Niu G, Quan
Q, Guo N and Chen X: 18F-radiolabeled analogs of exendin-4 for PET
imaging of GLP-1 in insulinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
39:463–473. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Eakin K, Li Y, Chiang YH, Hoffer BJ,
Rosenheim H, Greig NH and Miller JP: Exendin-4 ameliorates
traumatic brain injury-induced cognitive impairment in rats. PLoS
One. 8:e820162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Baudry M, Zhu G, Liu Y, Wang Y, Briz V and
Bi X: Multiple cellular cascades participate in long-term
potentiation and in hippocampus-dependent learning. Brain Res.
1621:73–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li YF, Cheng YF, Huang Y, Conti M, Wilson
SP, O'Donnell JM and Zhang HT: Phosphodiesterase-4D knock-out and
RNA interference-mediated knock-down enhance memory and increase
hippocampal neurogenesis via increased cAMP signaling. J Neurosci.
31:172–183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Brightwell JJ, Smith CA, Neve RL and
Colombo PJ: Long-term memory for place learning is facilitated by
expression of cAMP response element-binding protein in the dorsal
hippocampus. Learn Mem. 14:195–199. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gonzalez GA and Montminy MR: Cyclic AMP
stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of
CREB at serine 133. Cell. 59:675–680. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xiong WX, Zhou GX, Wang B, Xue ZG, Wang L,
Sun HC and Ge SJ: Impaired spatial learning and memory after
sevoflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia in aged rats is associated
with down-regulated cAMP/CREB signaling. PLoS One. 8:e794082013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Luo J, Phan TX, Yang Y, Garelick MG and
Storm DR: Increases in cAMP, MAPK activity and CREB phosphorylation
during REM sleep: Implications for REM sleep and memory
consolidation. J Neurosci. 33:6460–6468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang C, Yang XM, Zhuo YY, Zhou H, Lin HB,
Cheng YF, Xu JP and Zhang HT: The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor
rolipram reverses Aβ-induced cognitive impairment and
neuroinflammatory and apoptotic responses in rats. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 15:749–766. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|