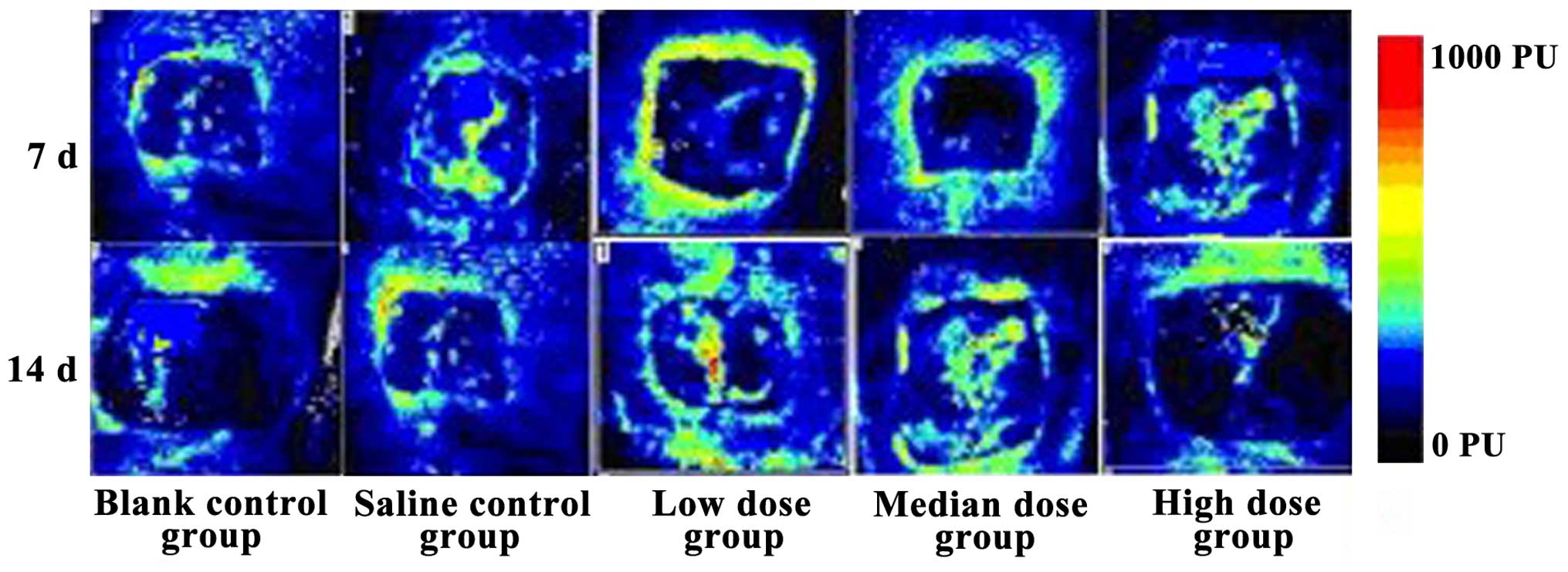
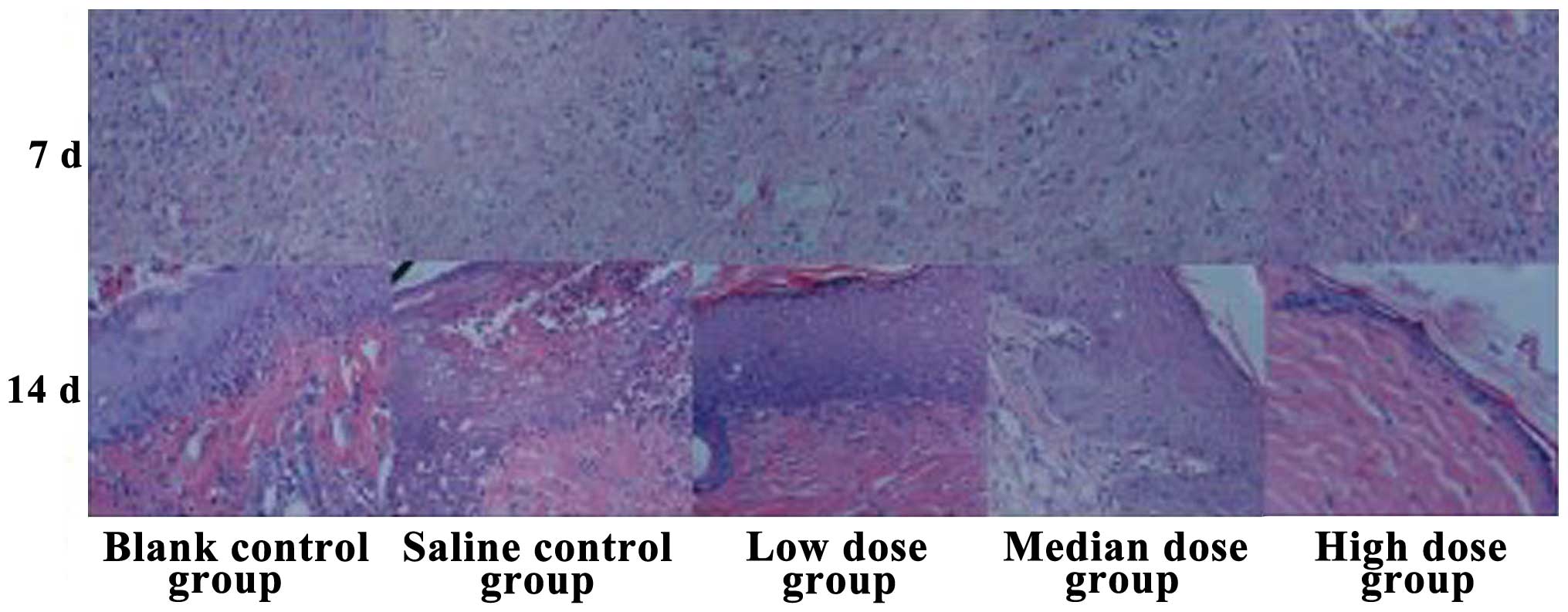
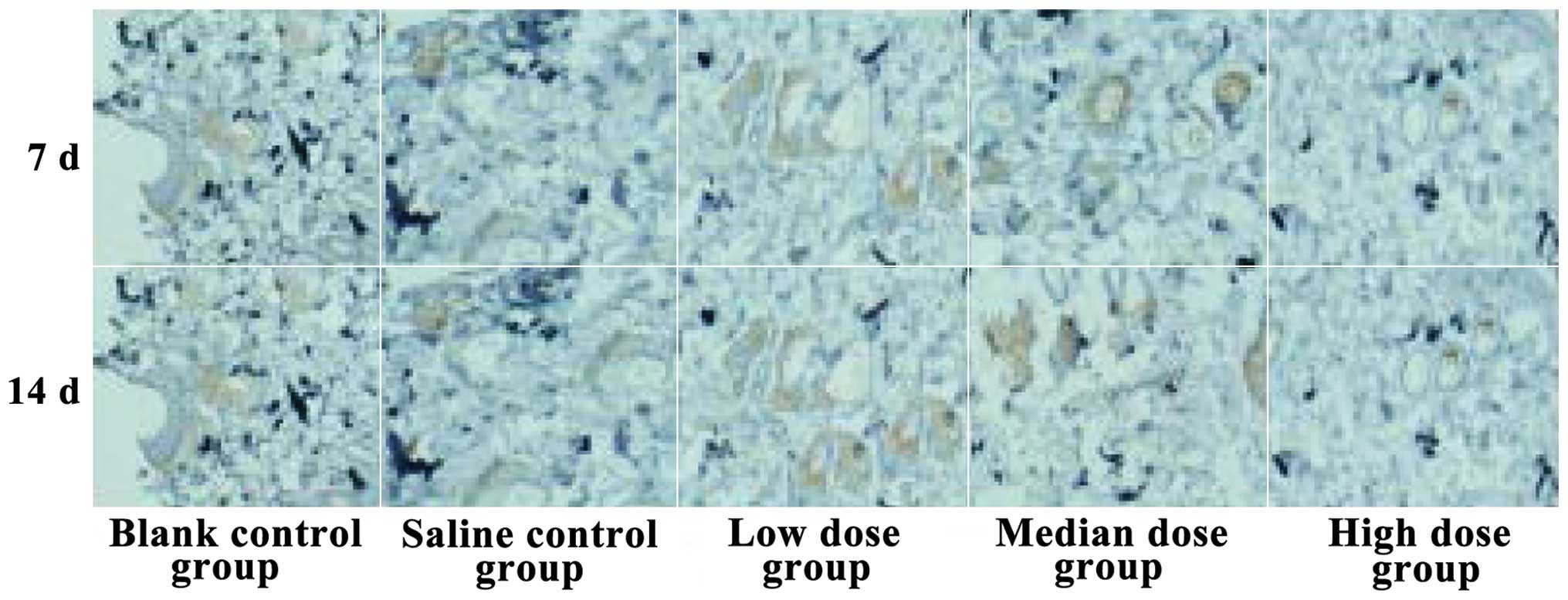
|
1
|
Yu G, Ye L, Tan W, Zhu X, Li Y and Jiang
D: A novel dermal matrix generated from burned skin as a promising
substitute for deep degree burns therapy. Mol Med Rep. 4:23–25.
2016.
|
|
2
|
Lei J, Hou C, Duan P, Hao Z, Zhai Y and
Meng Y: Clinical application of modified skin soft tissue expansion
in early repair of devastating wound on the head due to electrical
burn. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 31:406–409. 2015.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chi Y, Chai J, Xu C, Luo H and Zhang Q:
Apelin inhibits the activation of the nucleotide-binding domain and
the leucine-rich, repeat-containing family, pyrin-containing 3
(NLRP3) inflammasome and ameliorates insulin resistance in severely
burned rats. Surgery. 157:1142–1152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang M, Xue X, Xie P and Zhang J: Effects
of nerve growth factor-insulin composite gel on deep second degree
scald wound healing in diabetic rats. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian
Wai Ke Za Zhi. 27:182–188. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bircher A, de Boer EM, Agner T, Wahlberg
JE and Serup J: Guidelines for measurement of cutaneous blood flow
by laser Doppler flowmetry. A report from the Standardization Group
of the European Society of Contact Dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis.
30:65–72. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dong J, Tang Q, Li W and Tian F: Our
preliminary experiences in topical administration of insulin in
addition to vacuum assisted closure for wound healing in diabetic
patients. Minerva Chir. 70:389–391. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim SM, Kim YH, Jun YJ, Yoo G and Rhie JW:
The effect of diabetes on the wound healing potential of
adipose-tissue derived stem cells. Int Wound J. 13(Suppl 1): 33–41.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Salazar JJ, Ennis WJ and Koh TJ: Diabetes
medications: Impact on inflammation and wound healing. J Diabetes
Complications. 30:746–752. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dhall S, Silva JP, Liu Y, Hrynyk M, Garcia
M, Chan A, Lyubovitsky J, Neufeld RJ and Martins-Green M: Release
of insulin from PLGA-alginate dressing stimulates regenerative
healing of burn wounds in rats. Clin Sci (Lond). 129:1115–1129.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Azevedo F, Pessoa A, Moreira G, Santos MD,
Liberti E, Araujo E, Carvalho C, Saad M and Lima MH: Effect of
topical insulin on second-degree burns in diabetic rats. Biol Res
Nurs. 18:181–192. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Attia EA, Belal DM, El Samahy MH and El
Hamamsy MH: A pilot trial using topical regular crystalline insulin
vs. aqueous zinc solution for uncomplicated cutaneous wound
healing: Impact on quality of life. Wound Repair Regen. 22:52–57.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang XJ, Meng C, Chinkes DL and Herndon
DN: Beneficial effects of insulin on cell proliferation and protein
metabolism in skin donor site wound. J Surg Res. 168:e155–e161.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang XJ, Wu X, Wolf SE, Hawkins HK,
Chinkes DL and Wolfe RR: Local insulin-zinc injection accelerates
skin donor site wound healing. J Surg Res. 142:90–96. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Woodley DT, Wysong A, DeClerck B, Chen M
and Li W: Keratinocyte migration and a hypothetical new role for
extracellular heat shock protein 90 alpha in orchestrating skin
wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 4:203–212. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Puddu A, Sanguineti R, Traverso CE,
Viviani GL and Nicolò M: Response to anti-VEGF-A treatment of
endothelial cells in vitro. Exp Eye Res. 146:128–136. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kryger ZB, Sisco M, Roy NK, Lu L,
Rosenberg D and Mustoe TA: Temporal expression of the transforming
growth factor-Beta pathway in the rabbit ear model of wound healing
and scarring. J Am Coll Surg. 205:78–88. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
von Sydow A Koskela, Janbaz C, Kardeby C,
Repsilber D and Ivarsson M: IL-1α counteract TGF-β regulated genes
and pathways in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 117:1622–1632.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|