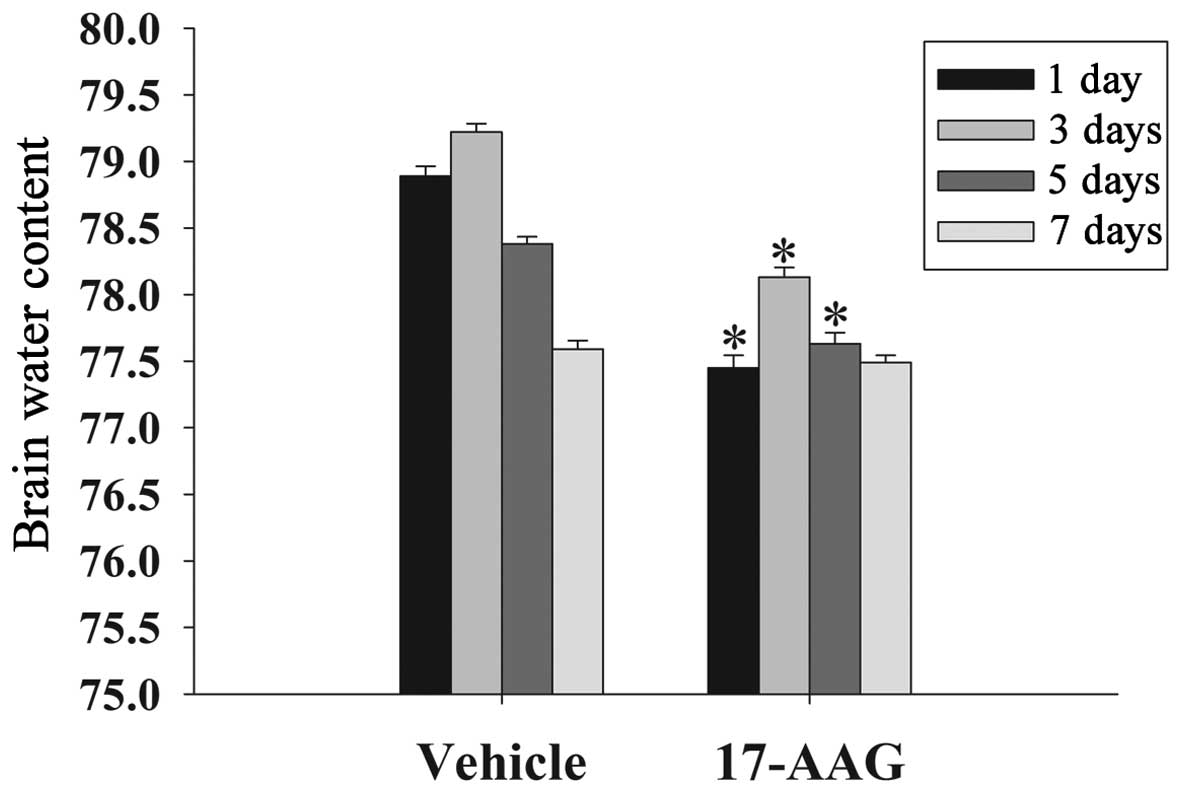
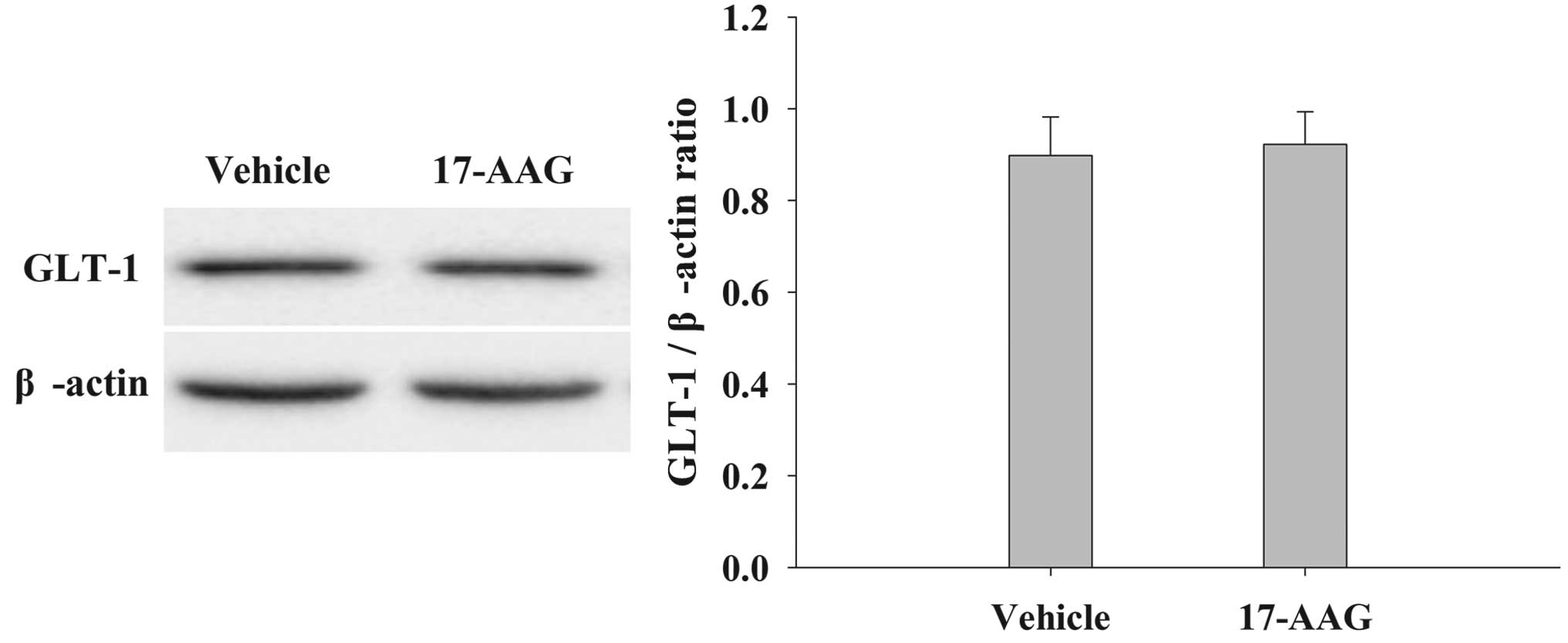
|
1
|
Hyder AA, Wunderlich CA, Puvanachandra P,
Gururaj G and Kobusingye OC: The impact of traumatic brain
injuries: A global perspective. NeuroRehabilitation. 22:341–353.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Johnson VE, Stewart W and Smith DH:
Widespread τ and amyloid-β pathology many years after a single
traumatic brain injury in humans. Brain Pathol. 22:142–149. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Werner C and Engelhard K: Pathophysiology
of traumatic brain injury. Br J Anaesth. 99:4–9. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Loane DJ and Faden AI: Neuroprotection for
traumatic brain injury: Translational challenges and emerging
therapeutic strategies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 31:596–604. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kamm K, Vanderkolk W, Lawrence C, Jonker M
and Davis AT: The effect of traumatic brain injury upon the
concentration and expression of interleukin-1β and interleukin-10
in the rat. J Trauma. 60:152–157. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aibiki M, Maekawa S, Ogura S, Kinoshita Y,
Kawai N and Yokono S: Effect of moderate hypothermia on systemic
and internal jugular plasma IL-6 levels after traumatic brain
injury in humans. J Neurotrauma. 16:225–232. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hang C-H, Shi J-X, Li J-S, Li W-Q and Wu
W: Expressions of intestinal NF-kappaB, TNF-α, and IL-6 following
traumatic brain injury in rats. J Surg Res. 123:188–193. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen G, Shi JX, Hang CH, Xie W, Liu J and
Liu X: Inhibitory effect on cerebral inflammatory agents that
accompany traumatic brain injury in a rat model: A potential
neuroprotective mechanism of recombinant human erythropoietin
(rhEPO). Neurosci let. 425:177–182. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mayer MP and Bukau B: Hsp70 chaperones:
Cellular functions and molecular mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci.
62:670–684. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nowak TS Jr and Jacewicz M: The heat
shock/stress response in focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Pathol.
4:67–76. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kelly S and Yenari MA: Neuroprotection:
Heat shock proteins. Curr Med Res Opin. 18:(Suppl 2). s55–s60.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee S-H, Kim M, Yoon B-W, Kim YJ, Ma SJ,
Roh JK, Lee JS and Seo JS: Targeted hsp70. 1 disruption increases
infarction volume after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke.
32:2905–2912. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim N, Kim JY and Yenari MA:
Anti-inflammatory properties and pharmacological induction of Hsp70
after brain injury. Inflammopharmacology. 20:177–185. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen SF, Hsu CW, Huang WH and Wang JY:
Post-injury baicalein improves histological and functional outcomes
and reduces inflammatory cytokines after experimental traumatic
brain injury. Br J Pharmacol. 155:1279–1296. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cui CM, Gao JL, Cui Y, Sun LQ, Wang YC,
Wang KJ, Li R, Tian YX and Cui JZ: Chloroquine exerts
neuroprotection following traumatic brain injury via suppression of
inflammation and neuronal autophagic death. Mol Med Rep.
12:2323–2328. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wei J, Pan X, Pei Z, Wang W, Qiu W, Shi Z
and Xiao G: The beta-lactam antibiotic, ceftriaxone, provides
neuroprotective potential via anti-excitotoxicity and
anti-inflammation response in a rat model of traumatic brain
injury. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 73:654–660. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ikeda Y and Long DM: The molecular basis
of brain injury and brain edema: The role of oxygen free radicals.
Neurosurgery. 27:1–11. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McKinlay A, Grace RC, Horwood LJ,
Fergusson DM, Ridder EM and MacFarlane MR: Prevalence of traumatic
brain injury among children, adolescents and young adults:
Prospective evidence from a birth cohort. Brain Inj. 22:175–181.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
O'Connor WT, Smyth A and Gilchrist MD:
Animal models of traumatic brain injury: A critical evaluation.
Pharmacol Ther. 130:106–113. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Outeiro TF, Klucken J, Strathearn KE, Liu
F, Nguyen P, Rochet JC, Hyman BT and McLean PJ: Small heat shock
proteins protect against α-synuclein-induced toxicity and
aggregation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 351:631–638. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Adachi H, Katsuno M, Minamiyama M, Sang C,
Pagoulatos G, Angelidis C, Kusakabe M, Yoshiki A, Kobayashi Y, Doyu
M and Sobue G: Heat shock protein 70 chaperone overexpression
ameliorates phenotypes of the spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy
transgenic mouse model by reducing nuclear-localized mutant
androgen receptor protein. J Neurosci. 23:2203–2211.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hollander JM, Martin JL, Belke DD, Scott
BT, Swanson E, Krishnamoorthy V and Dillmann WH: Overexpression of
wild-type heat shock protein 27 and a nonphosphorylatable heat
shock protein 27 mutant protects against ischemia/reperfusion
injury in a transgenic mouse model. Circulation. 110:3544–3552.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hutter JJ, Mestril R, Tam EK, Sievers RE,
Dillmann WH and Wolfe CL: Overexpression of heat shock protein 72
in transgenic mice decreases infarct size in vivo. Circulation.
94:1408–1411. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fumo G, Akin C, Metcalfe DD and Neckers L:
17-Allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG) is effective in
down-regulating mutated, constitutively activated KIT protein in
human mast cells. Blood. 103:1078–1084. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Harrison EM, Sharpe E, Bellamy CO, McNally
SJ, Devey L, Garden OJ, Ross JA and Wigmore SJ: Heat shock protein
90-binding agents protect renal cells from oxidative stress and
reduce kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 295:F397–F405. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Morganti-Kossmann MC, Rancan M, Stahel PF
and Kossmann T: Inflammatory response in acute traumatic brain
injury: A double-edged sword. Curr Opin Crit Care. 8:101–105. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heneka MT, Sharp A, Klockgether T,
Gavrilyuk V and Feinstein DL: The heat shock response inhibits
NF-kappaB activation, nitric oxide synthase type 2 expression, and
macrophage/microglial activation in brain. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 20:800–811. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ding XZ, Fernandez-Prada CM, Bhattacharjee
AK and Hoover DL: Overexpression of hsp-70 inhibits bacterial
lipopolysaccharide-induced production of cytokines in human
monocyte-derived macrophages. Cytokine. 16:210–219. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zheng Z, Kim JY, Ma H, Lee JE and Yenari
MA: Anti-inflammatory effects of the 70 kDa heat shock protein in
experimental stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 28:53–63. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Palmer AM, Marion DW, Botscheller ML,
Swedlow PE, Styren SD and DeKosky ST: Traumatic brain
injury-induced excitotoxicity assessed in a controlled cortical
impact model. J Neurochem. 61:2015–2024. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tanaka K, Watase K, Manabe T, Yamada K,
Watanabe M, Takahashi K, Iwama H, Nishikawa T, Ichihara N, Kikuchi
T, et al: Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking
the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science. 276:1699–1702. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|