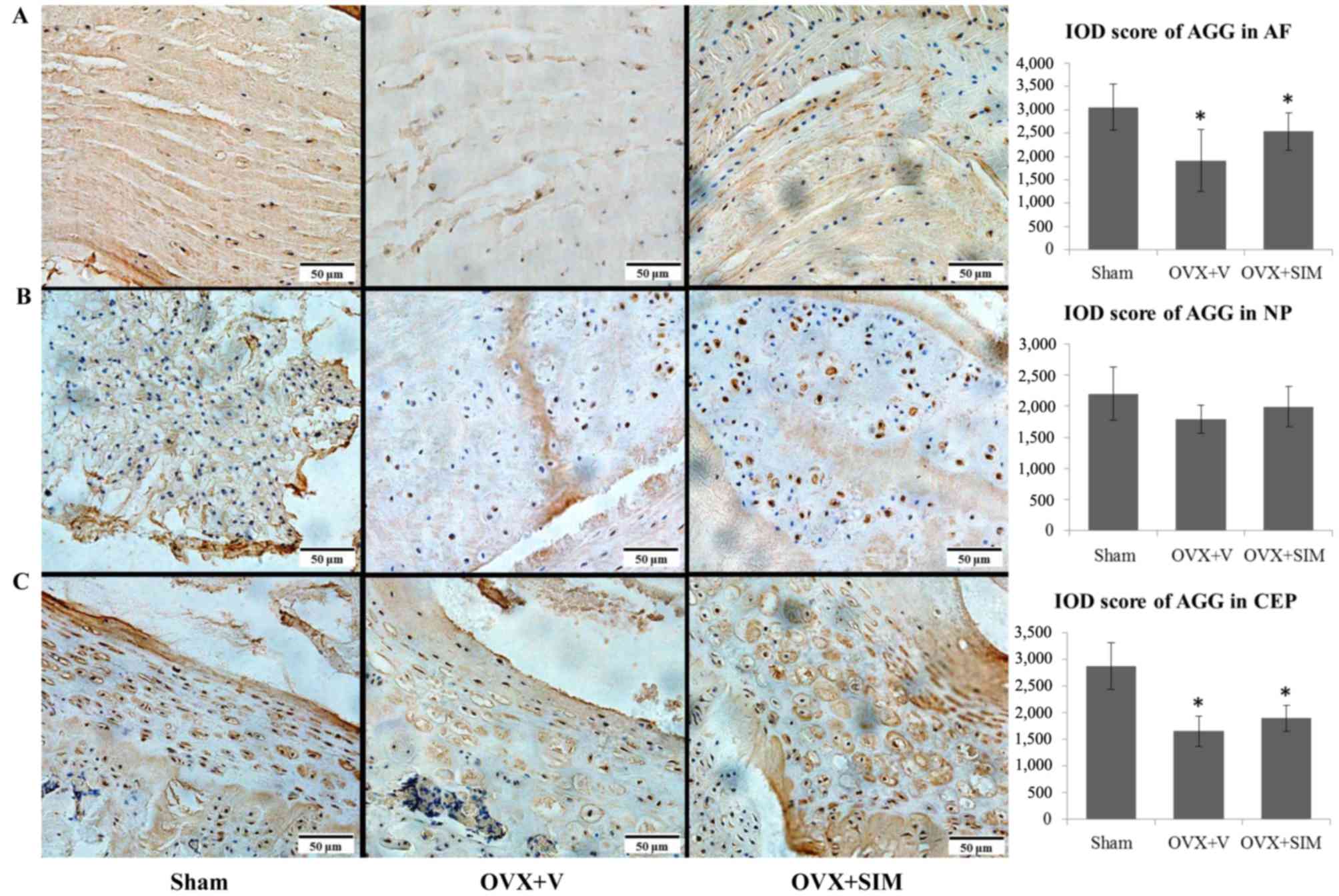
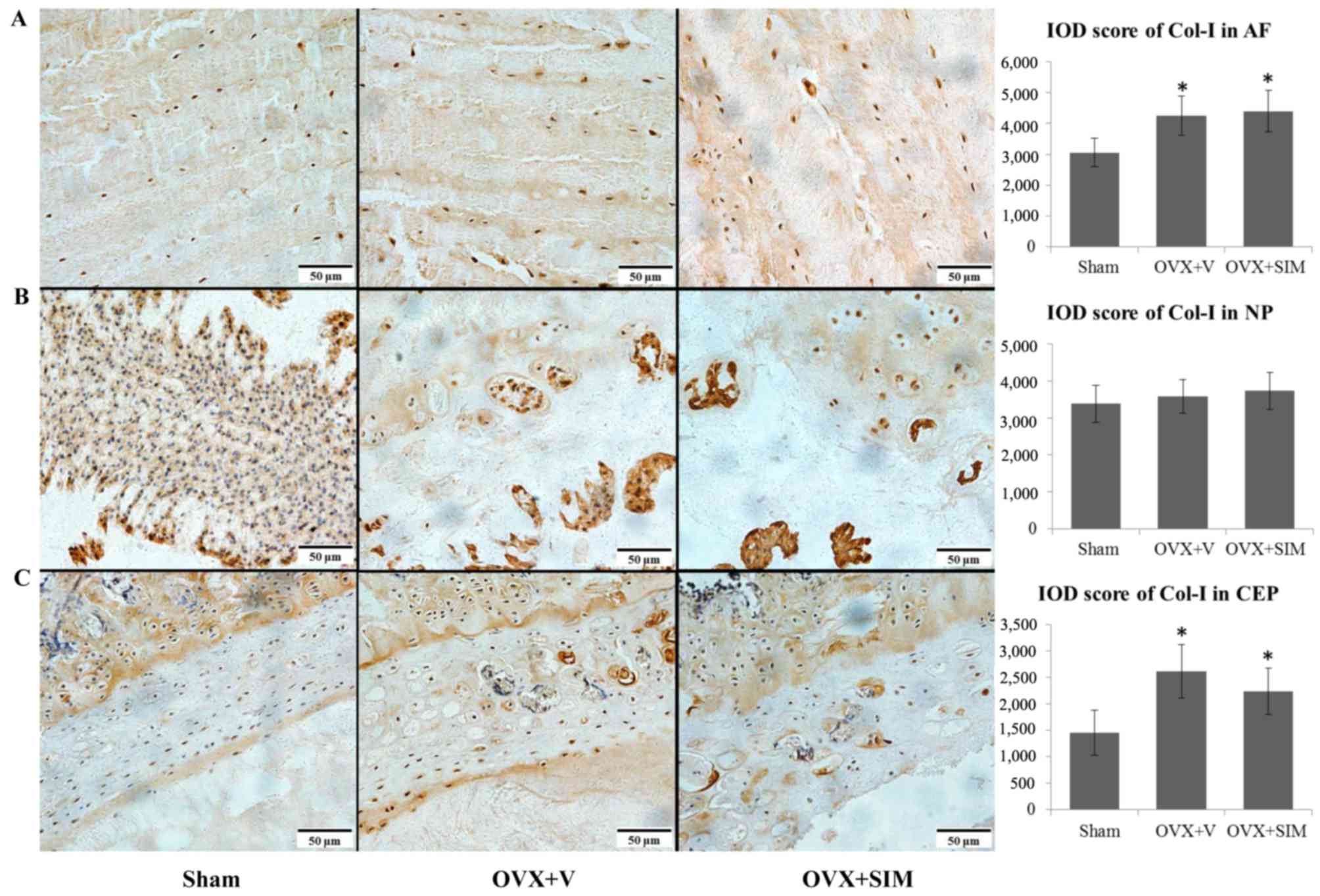
|
1
|
Manek NJ and MacGregor AJ: Epidemiology of
back disorders: Prevalence, risk factors, and prognosis. Curr Opin
Rheumatol. 17:134–140. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Masuda K and An HS: Prevention of disc
degeneration with growth factors. Eur Spine J. 15:(Suppl 3).
S422–S432. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Andersson GB: Epidemiological features of
chronic low-back pain. Lancet. 354:581–585. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Feng C, Liu H, Yang Y, Huang B and Zhou Y:
Growth and differentiation factor-5 contributes to the structural
and functional maintenance of the intervertebral disc. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 35:1–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hadjipavlou AG, Tzermiadianos MN, Bogduk N
and Zindrick MR: The pathophysiology of disc degeneration: A
critical review. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 90:1261–1270. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fabreguet I, Fechtenbaum J, Briot K,
Paternotte S and Roux C: Lumbar disc degeneration in osteoporotic
men: Prevalence and assessment of the relation with presence of
vertebral fracture. J Rheumatol. 40:1183–1190. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang YX and Griffith JF: Effect of
menopause on lumbar disc degeneration: Potential etiology.
Radiology. 257:318–320. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang T, Zhang L, Huang C, Cheng AG and
Dang GT: Relationship between osteopenia and lumbar intervertebral
disc degeneration in ovariectomized rats. Calcif Tissue Int.
75:205–213. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luo Y, Zhang L, Wang WY, Hu QF, Song HP,
Su YL and Zhang YZ: Alendronate retards the progression of lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration in ovariectomized rats. Bone.
55:439–448. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tian FM, Yang K, Wang WY, Luo Y, Li SY,
Song HP, Zhang YZ, Shen Y and Zhang L: Calcitonin suppresses
intervertebral disk degeneration and preserves lumbar vertebral
bone mineral density and bone strength in ovariectomized rats.
Osteoporos Int. 26:2853–2861. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chuengsamarn S, Rattanamongkoulgul S,
Suwanwalaikorn S, Wattanasirichaigoon S and Kaufman L: Effects of
statins vs. Non-statin lipid-lowering therapy on bone formation and
bone mineral density biomarkers in patients with hyperlipidemia.
Bone. 46:1011–1015. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang N, Cui Y, Tan J, Fu X, Han X, Leng H
and Song C: Local injection of a single dose of simvastatin
augments osteoporotic bone mass in ovariectomized rats. J Bone
Miner Metab. 32:252–260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hernández JL, Olmos JM, Romaña G, Martinez
J, Castillo J, Yezerska I, Pinedo G and González-Macías J: Bone
mineral density in statin users: A population-based analysis from a
Spanish cohort. J Bone Miner Metab. 32:184–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan J, Yang N, Fu X, Cui Y, Guo Q, Ma T,
Yin X, Leng H and Song C: Single-dose local simvastatin injection
improves implant fixation via increased angiogenesis and bone
formation in an ovariectomized rat model. Med Sci Monit.
21:1428–1439. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Oxlund H and Andreassen TT: Simvastatin
treatment partially prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss while
increasing cortical bone formation. Bone. 34:609–618. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Than KD, Rahman SU, Wang L, Khan A, Kyere
KA, Than TT, Miyata Y, Park YS, La Marca F, Kim HM, et al:
Intradiscal injection of simvastatin results in radiologic,
histologic, and genetic evidence of disc regeneration in a rat
model of degenerative disc disease. Spine J. 14:1017–1028. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mosekilde L, Danielsen CC and Knudsen UB:
The effect of aging and ovariectomy on the vertebral bone mass and
biomechanical properties of mature rats. Bone. 14:1–6. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sehmisch S, Galal R, Kolios L, Tezval M,
Dullin C, Zimmer S, Stuermer KM and Stuermer EK: Effects of
low-magnitude, high-frequency mechanical stimulation in the rat
osteopenia model. Osteoporos Int. 20:1999–2008. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Khan K, Sharan K, Swarnkar G, Chakravarti
B, Mittal M, Barbhuyan TK, China SP, Khan MP, Nagar GK, Yadav D, et
al: Positive skeletal effects of cladrin, a naturally occurring
dimethoxydaidzein, in osteopenic rats that were maintained after
treatment discontinuation. Osteoporos Int. 24:1455–1470. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Oliver RA, Yu Y, Yee G, Low AK, Diwan AD
and Walsh WR: Poor histological healing of a femoral fracture
following 12 months of oestrogen deficiency in rats. Osteoporos
Int. 24:2581–2589. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roberts S, Evans H, Trivedi J and Menage
J: Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 88:(Suppl 2). S10–S14. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Le Maitre CL, Pockert A, Buttle DJ,
Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA: Matrix synthesis and degradation in
human intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochem Soc Trans.
35:652–655. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang H and Lin CY: Simvastatin stimulates
chondrogenic phenotype of intervertebral disc cells partially
through BMP-2 pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 33:E525–E531. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi S, Wang C, Yuan W, Wang X and Zhou X:
Potential prevention: Orally administered statins may retard the
pathologic process of disc degeneration. Med Hypotheses.
76:125–127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Corsino A, Bellosta S, Baetta R, Fumagalli
R, Paoletti R and Bernini F: New insights into the pharmacodynamic
and pharmacokinetic properties of statins. Pharmacol Ther.
84:413–428. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Reinoso RF, SánchezNavarro A, García MJ
and Prous JR: Preclinical pharmacokinetics of statins. Methods Find
Exp Clin Pharmacol. 24:593–613. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
William D and Feely J:
Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic drug interaction with HMG-CoA
reductase inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet. 41:343–370. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Soukane DM, Shirazi-Adl A and Urban JP:
Computation of coupled diffusion of oxygen, glucose and lactic acid
in an intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 40:2645–2654. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kaleağasıoğlu F, Olcay E and Olgaç V:
Statin-induced calcific Achilles tendinopathy in rats: Comparison
of biomechanical and histopathological effects of simvastatin,
atorvastatin and rosuvastatin. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.
2015.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Miyazawa A, Matsuno T, Asano K, Tabata Y
and Satoh T: Controlled release of simvastatin from biodegradable
hydrogels promotes odontoblastic differentiation. Dent Mater J.
34:466–474. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Oryan A, Kamali A and Moshiri A: Potential
mechanisms and applications of statins on osteogenesis: Current
modalities, conflicts and future directions. J Control Release.
215:12–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|