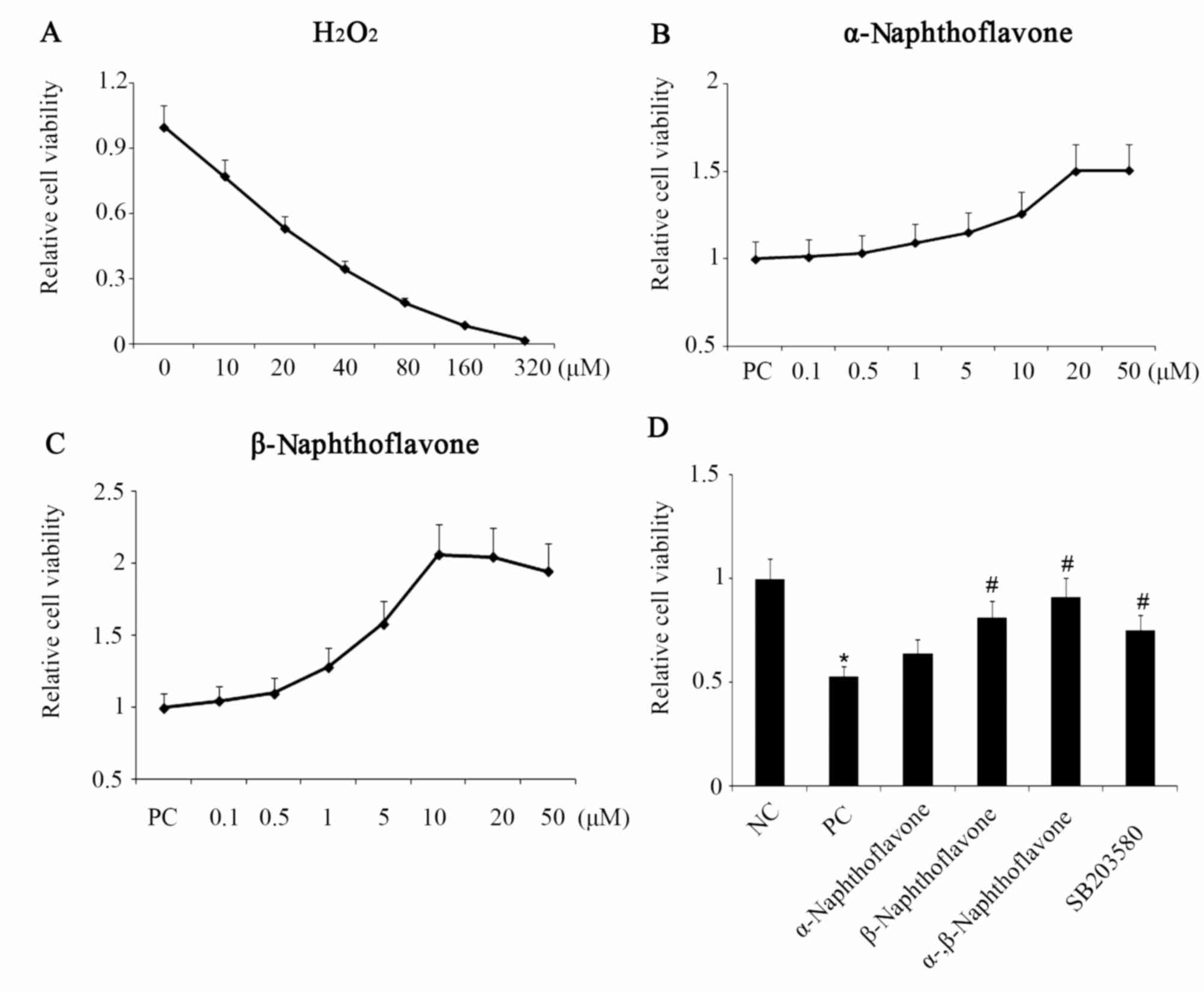
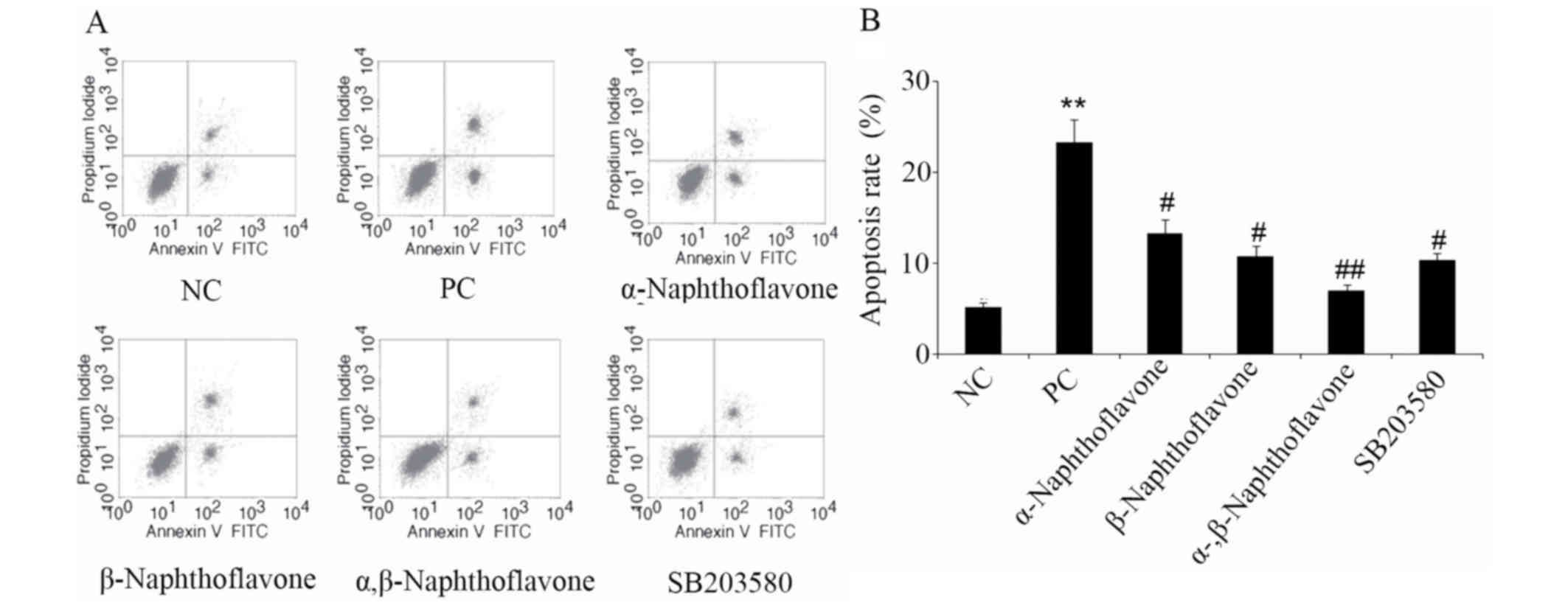
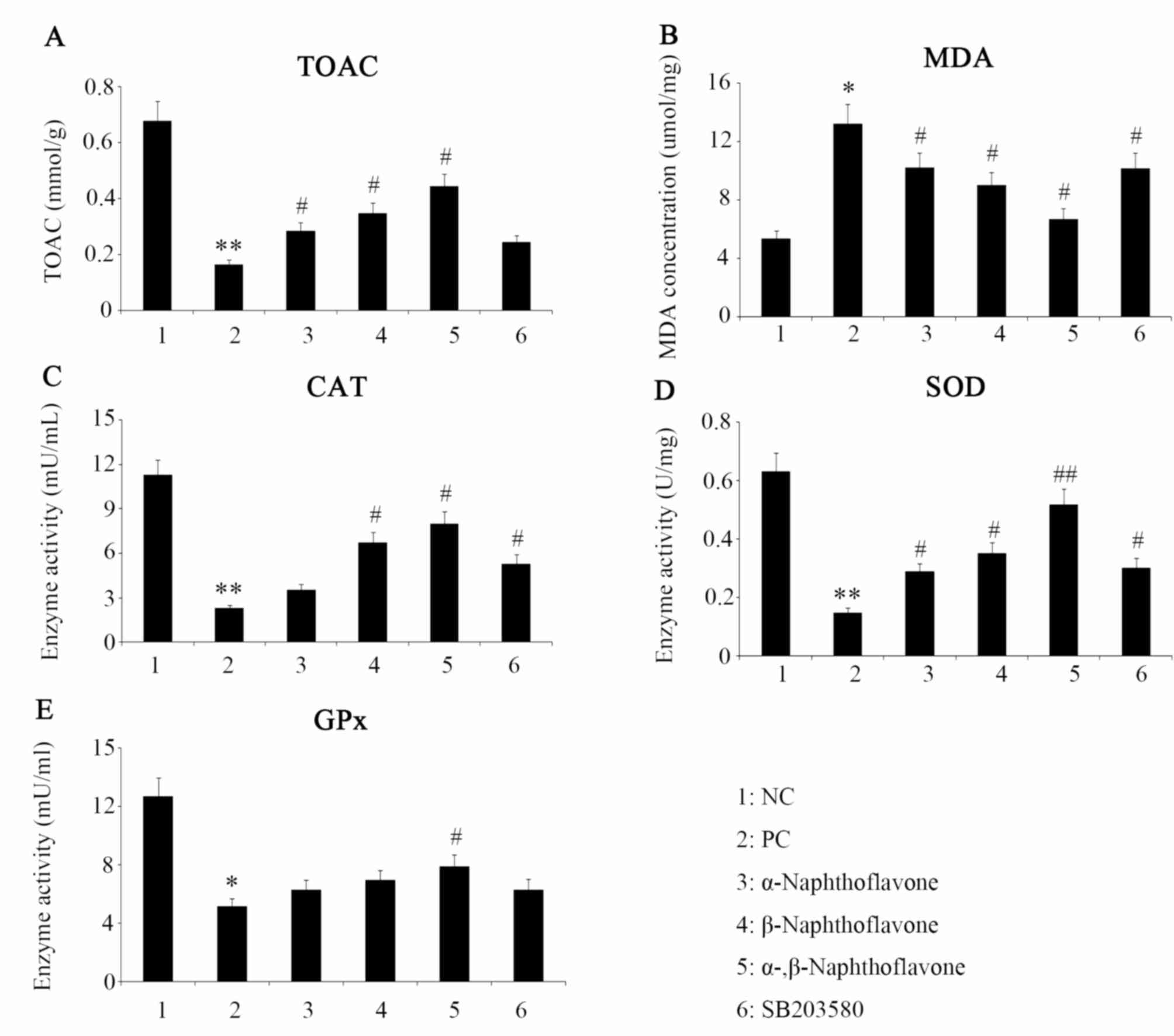
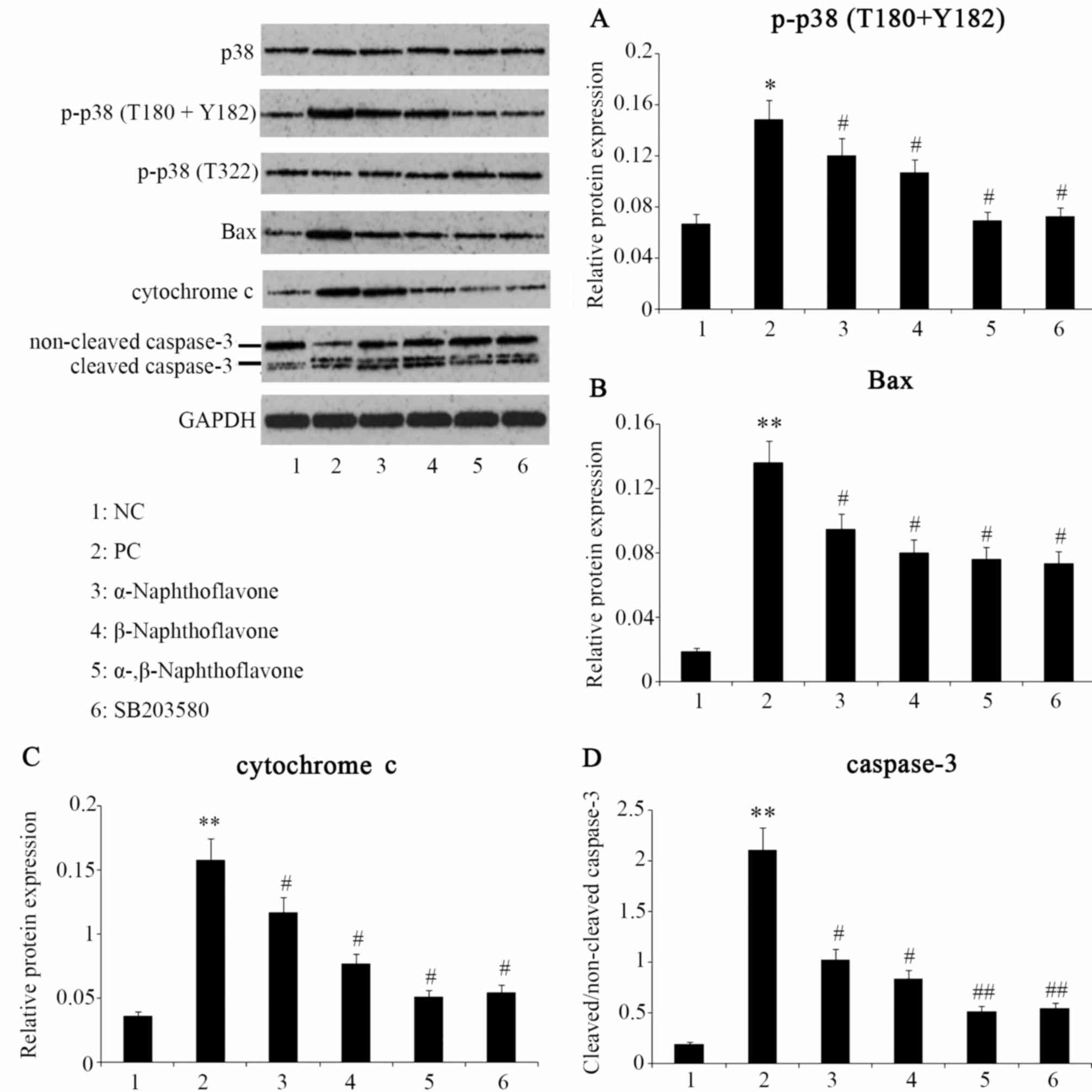
|
1
|
Weaver J and Liu KJ: Does normobaric
hyperoxia increase oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke? A
critical review of the literature. Med Gas Res. 5:112015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Amara F, Berbenni M, Fragni M, Leoni G,
Viggiani S, Ippolito VM, Larocca M, Rossano R, Alberghina L, Riccio
P and Colangelo AM: Neuroprotection by cocktails of dietary
antioxidants under conditions of nerve growth factor deprivation.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:2172582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Choong CJ and Say YH: Neuroprotection of
α-synuclein under acute and chronic rotenone and maneb treatment is
abolished by its familial Parkinson's disease mutations A30P, A53T
and E46K. Neurotoxicology. 32:857–863. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tchantchou F, Graves M, Ortiz D, Rogers E
and Shea TB: Dietary supplementation with apple juice concentrate
alleviates the compensatory increase in glutathione synthase
transcription and activity that accompanies dietary- and
genetically-induced oxidative stress. J Nutr Health Aging.
8:492–496. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Villegas-Rivera G, Román-Pintos LM,
Cardona-Muñoz EG, Arias-Carvajal O, Rodríguez-Carrizalez AD,
Troyo-Sanromán R, Pacheco-Moisés FP, Moreno-Ulloa A and
Miranda-Díaz AG: Effects of ezetimibe/simvastatin and rosuvastatin
on oxidative stress in diabetic neuropathy: A randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2015:7562942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang T, Li X, Zhu W, Chen C, Sun Z, Tan Z
and Kang J: Alteration of antioxidant enzymes and associated genes
induced by grape seed extracts in the primary muscle cells of goats
in vitro. PLoS One. 9:e1076702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Soundararajan R, Wishart AD, Rupasinghe
HP, Arcellana-Panlilio M, Nelson CM, Mayne M and Robertson GS:
Quercetin 3-glucoside protects neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells in
vitro against oxidative damage by inducing sterol regulatory
element-binding protein-2-mediated cholesterol biosynthesis. J Biol
Chem. 283:2231–2245. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu XH, Li GL, Wang BA, Qin Y, Bai SR, Rong
J, Deng T and Li Q: Diallyl trisufide protects against oxygen
glucose deprivation-induced apoptosis by scavenging free radicals
via the PI3K/Akt-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in B35 neural
cells. Brain Res. 1614:38–50. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z, Ji C, Wu L, Qiu J, Li Q, Shao Z
and Chen G: Tert-butylhydroquinone alleviates early brain injury
and cognitive dysfunction after experimental subarachnoid
hemorrhage: Role of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway. PLoS One. 9:e976852014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singh N, Agrawal M and Doré S:
Neuroprotective properties and mechanisms of resveratrol in vitro
and in vivo experimental cerebral stroke models. ACS Chem Neurosci.
4:1151–1162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bournival J, Plouffe M, Renaud J,
Provencher C and Martinoli MG: Quercetin and sesamin protect
dopaminergic cells from MPP+-induced neuroinflammation in a
microglial (N9)-neuronal (PC12) coculture system. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2012:9219412012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mena MA, Casarejos MJ, Solano R,
Rodríguez-Navarro JA, Gómez A, Rodal I, Medina M and de Yebenes JG:
NP7 protects from cell death induced by oxidative stress in
neuronal and glial midbrain cultures from parkin null mice. FEBS
Lett. 583:168–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jazvinšćak Jembrek M, Hof PR and Šimić G:
Ceramides in Alzheimer's disease: Key mediators of neuronal
apoptosis induced by oxidative stress and Aβ accumulation. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2015:3467832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Leonardo CC and Doré S: Dietary flavonoids
are neuroprotective through Nrf2-coordinated induction of
endogenous cytoprotective proteins. Nutr Neurosci. 14:226–236.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin WL, Wang SM, Ho YJ, Kuo HC, Lee YJ and
Tseng TH: Ethyl acetate extract of Wedelia chinensis inhibits
tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced damage in PC12 cells and
D-galactose-induced neuronal cell loss in mice. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 14:4912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu A, Wu Z, Meng J, McGeer PL, Zhu Y,
Nakanishi H and Wu S: The neuroprotective effects of ratanasampil
on oxidative stress-mediated neuronal damage in human neuronal
SH-SY5Y cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:7923422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dhawan K: Drug/substance reversal effects
of a novel tri-substituted benzoflavone moiety (BZF) isolated from
Passiflora incarnata Linn.-a brief perspective. Addict Biol.
8:379–386. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu Q, Yu J, Yang W, Kimatu BM, Fang Y, Ma
N and Pei F: Identification of flavonoids from Flammulina velutipes
and its neuroprotective effect on pheochromocytoma-12 cells. Food
Chem. 204:274–282. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nannelli A, Rossignolo F, Tolando R,
Rossato P, Longo V and Gervasi PG: Effect of beta-naphthoflavone on
AhR-regulated genes (CYP1A1, 1A2, 1B1, 2S1, Nrf2, and GST) and
antioxidant enzymes in various brain regions of pig. Toxicology.
265:69–79. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morrissy S, Strom J, Purdom-Dickinson S
and Chen QM: NAD(P)H: Quinone oxidoreductase 1 is induced by
progesterone in cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 12:108–114.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Higgins LG and Hayes JD: Mechanisms of
induction of cytosolic and microsomal glutathione transferase (GST)
genes by xenobiotics and pro-inflammatory agents. Drug Metab Rev.
43:92–137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reed JR, Cawley GF and Backes WL:
Inhibition of cytochrome P450 1A2-mediated metabolism and
production of reactive oxygen species by heme oxygenase-1 in rat
liver microsomes. Drug Metab Lett. 5:6–16. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hsu SY, Liou JW, Cheng TL, Peng SY, Lin
CC, Chu YY, Luo WC, Huang ZK and Jiang SJ: Beta-Naphthoflavone
protects from peritonitis by reducing TNF-alpha-induced endothelial
cell activation. Pharmacol Res. 102:192–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Milardovic S, Kereković I, Derrico R and
Rumenjak V: A novel method for flow injection analysis of total
antioxidant capacity using enzymatically produced ABTS*+ and
biamperometric detector containing interdigitated electrode.
Talanta. 71:213–220. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsikas D: Assessment of lipid peroxidation
by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological
samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal Biochem. Oct
24–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Park HR, Lee H, Park H, Jeon JW, Cho WK
and Ma JY: Neuroprotective effects of Liriope platyphylla extract
against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in human
neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 15:1712015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liao PL, Li CH, Chang CY, Lu SR, Lin CH,
Tse LS and Cheng YW: Anti-ageing effects of alpha-naphthoflavone on
normal and UVB-irradiated human skin fibroblasts. Exp Dermatol.
21:546–548. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mense SM, Singh B, Remotti F, Liu X and
Bhat HK: Vitamin C and alpha-naphthoflavone prevent
estrogen-induced mammary tumors and decrease oxidative stress in
female ACI rats. Carcinogenesis. 30:1202–1208. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiao Y, Xue X, Wu YF, Xin GZ, Qian Y, Xie
TP, Gong LK and Ren J: Beta-Naphthoflavone protects mice from
aristolochic acid-I-induced acute kidney injury in a CYP1A
dependent mechanism. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:1559–1565. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sinha A, Muthiah K, Jiang W, Couroucli X,
Barrios R and Moorthy B: Attenuation of hyperoxic lung injury by
the CYP1A inducer beta-naphthoflavone. Toxicol Sci. 87:204–212.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kober SL, Meyer-Alert H, Grienitz D,
Hollert H and Frohme M: Intact cell mass spectrometry as a rapid
and specific tool for the differentiation of toxic effects in
cell-based ecotoxicological test systems. Anal Bioanal Chem.
407:7721–7731. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Csepregi K, Neugart S, Schreiner M and
Hideg É: Comparative evaluation of total antioxidant capacities of
plant polyphenols. Molecules. 21:pii.E208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Orozco TJ, Wang JF and Keen CL: Chronic
consumption of a flavanol- and procyanindin-rich diet is associated
with reduced levels of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine in rat testes. J
Nutr Biochem. 14:104–110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Burri SH, Kim CN, Fang G, Chang BS,
Perkins C, Harris W, Davis LW, Thompson CB and Bhalla KN: ‘Loop’
domain deletional mutant of Bcl-xL is as effective as p29Bcl-xL in
inhibiting radiation-induced cytosolic accumulation of cytochrome c
(cyt c), caspase-3 activity and apoptosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 43:423–430. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|