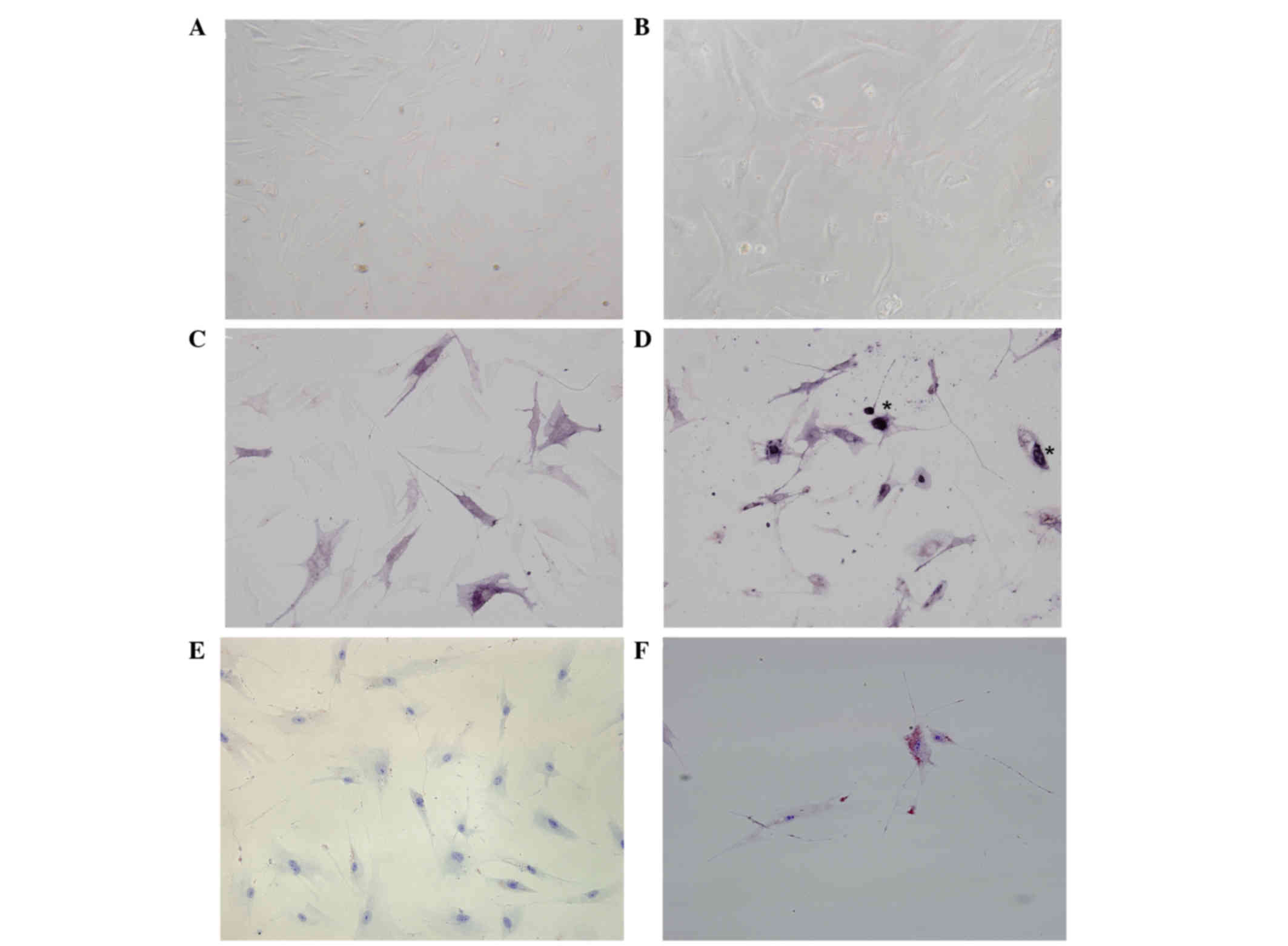
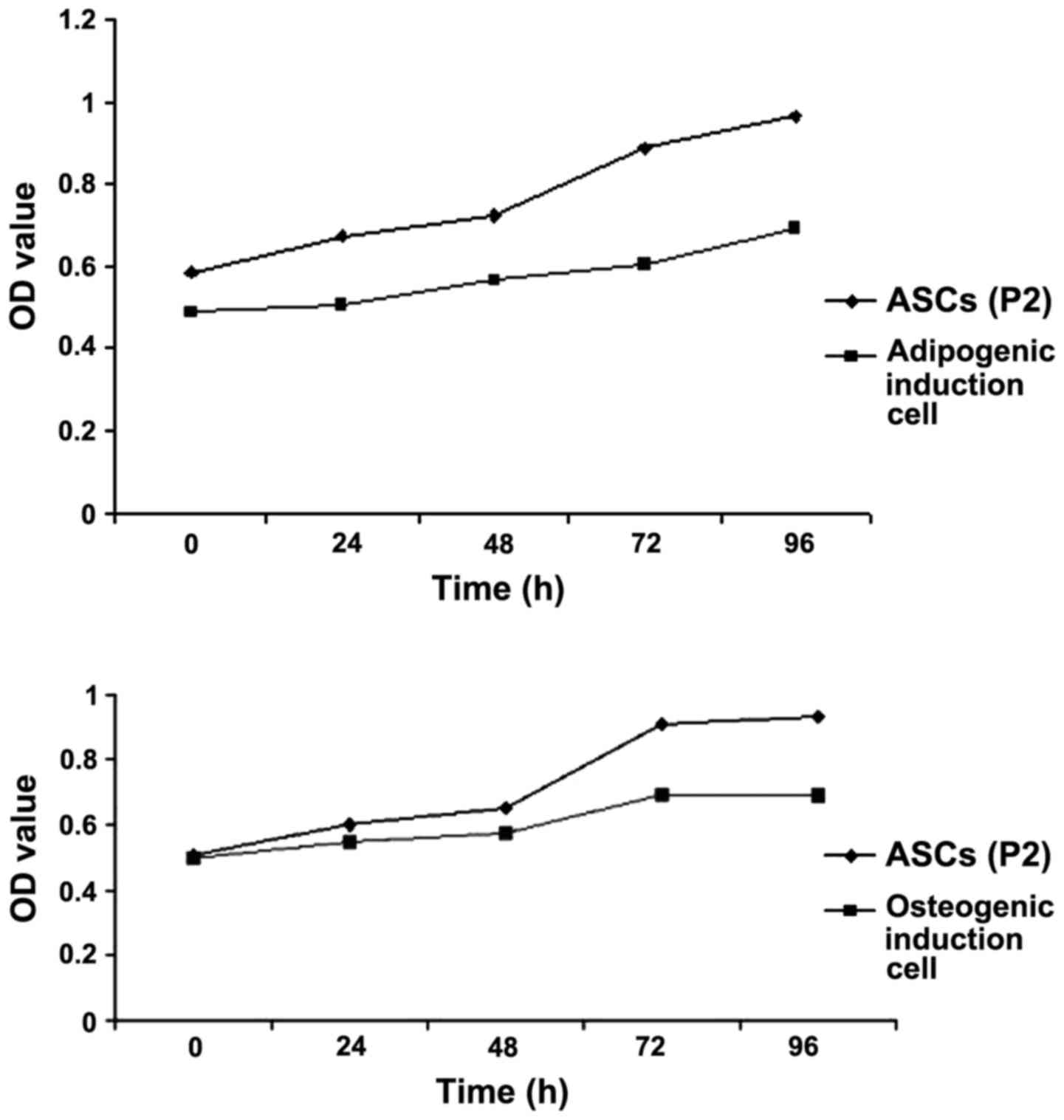
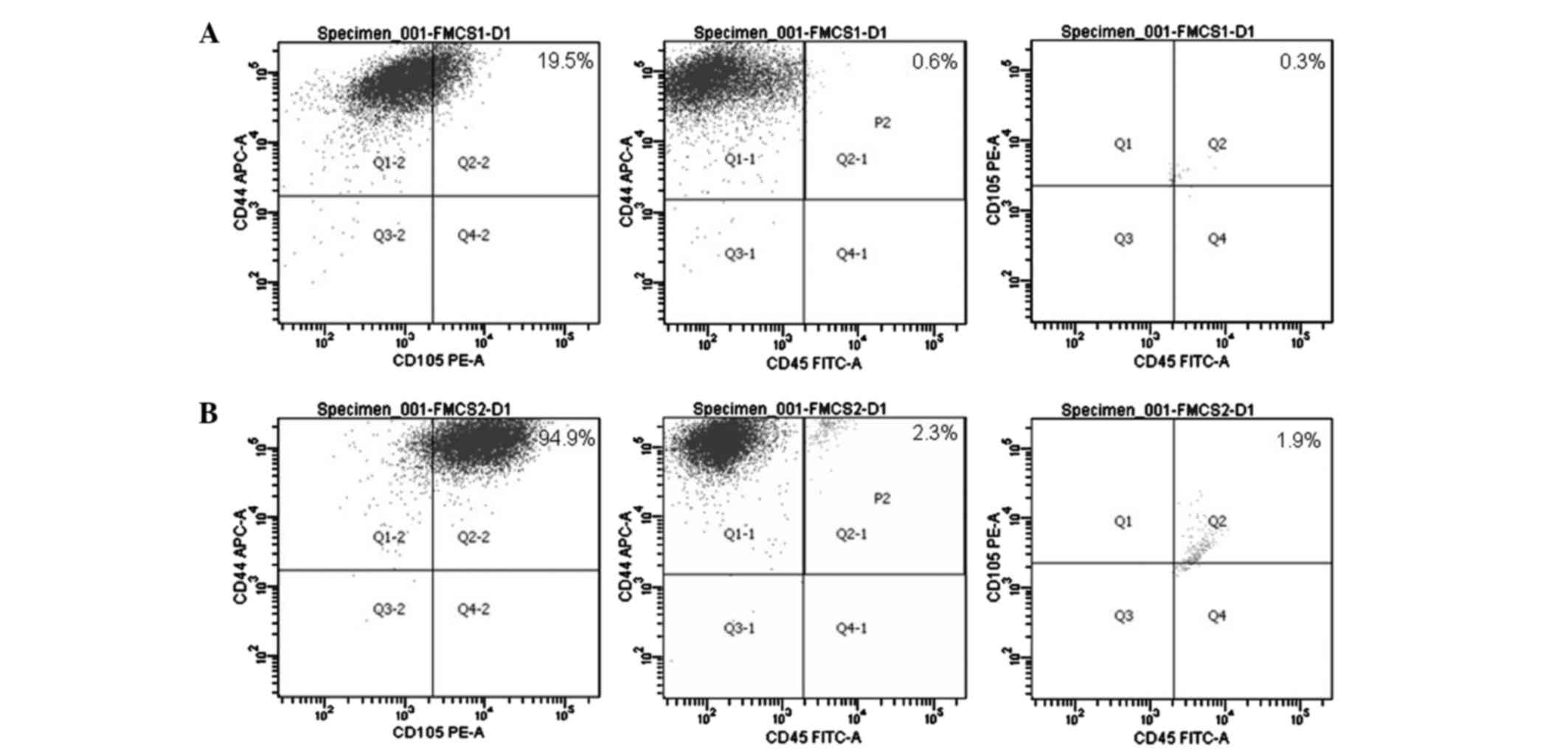
|
1
|
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, Huang J, Futrell
JW, Katz AJ, Benhaim P, Lorenz HP and Hedrick MH: Multilineage
cells from human adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based
therapies. Tissue Eng. 7:211–228. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
LapPar DJ, Kron IL and Yang Z: Stem cell
therapy for ischemic heart disease: Where are we? Curr Opin Organ
Transplant. 14:79–84. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang Z, Hao J and Hu ZM: MicroRNA
expression profiles in human adipose-derived stem cells during
chondrogenic differentiation. Int J Mol Med. 35:579–586.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Laflamme MA and Murry CE: Heart
regeneration. Nature. 473:326–335. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Singh D, Nayak V and Kumar A:
Proliferation of myoblast skeletal cells on three-dimensional
supermacroporous cryogels. Int J Biol Sci. 6:371–381. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Panfilov IA, de Jong R, Takashima S and
Duckers HJ: Clinical study using adipose-derived mesenchymal-like
stem cells in acute myocardial infarction and heart failure.
Methods Mol Biol. 1036:207–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miyahara Y, Nagaya N, Kataoka M, Yanagawa
B, Tanaka K, Hao H, Ishino K, Ishida H, Shimizu T, Kangawa K, et
al: Monolayered mesenchymal stem cells repair scarred myocardium
after myocardial infarction. Nat Med. 12:459–465. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Planat-Bénard V, Menard C, André M, Puceat
M, Perez A, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Pénicaud L and Casteilla L:
Spontaneous cardiomyocyte differentiation from adipose tissue
stromal cells. Circ Res. 94:223–229. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McIntosh K, Zvonic S, Garrett S, Mitchell
JB, Floyd ZE, Hammill L, Kloster A, Di Halvorsen Y, Ting JP, Storms
RW, et al: The immunogenicity of human adipose-derived cells:
Temporal changes in vitro. Stem Cells. 24:1246–1253. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Puissant B, Barreau C, Bourin P, Clavel C,
Corre J, Bousquet C, Taureau C, Cousin B, Abbal M, Laharrague P, et
al: Immunomodulatory effect of human adipose tissue-derived adult
stem cells: Comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Br
J Haematol. 129:118–129. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han ZM, Huang HM and Wang FF:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene-modified bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 9:519–522. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Di C and Zhao Y: Multiple drug resistance
due to resistance to stem cells and stem cell treatment progress in
cancer (Review). Exp Ther Med. 9:289–293. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aust L, Devlin B, Foster SJ, Halvorsen YD,
Hicok K, du Laney T, Sen A, Willingmyre GD and Gimble JM: Yield of
human adipose-derived adult stem cells from liposuction aspirates.
Cytotherapy. 6:7–14. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu G, Wu X, Dietrich MA, Polk P, Scott LK,
Ptitsyn AA and Gimble JM: Yield and characterization of
subcutaneous human adipose-derived stem cells by flow cytometric
and adipogenic mRNA analyzes. Cytotherapy. 12:538–546. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin J, Jeong SI, Shin YM, Lim KS, Shin Hs,
Lee YM, Koh HC and Kim KS: Transplantation of mesenchymal stem
cells within a poly(lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone) scaffold
improves cardiac function in a rat myocardial infarction model. Eur
J Heart Fail. 11:147–153. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oedayrajsingh-Varma MJ, van Ham SM,
Knippenberg M, Helder MN, Klein-Nulend J, Schouten TE, Ritt MJ and
van Milligen FJ: Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell yield
and growth characteristics are affected by the tissue-harvesting
procedure. Cytotherapy. 8:166–177. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang S, Han J, Song SY, Kim WS, Shin S,
Kim JH, Ahn H, Jeong JH, Hwang SJ and Sung JH: Lysophosphatidic
acid increases the proliferation and migration of adipose-derived
stem cells via the generation of reactive oxygen species. Mol Med
Rep. 12:145–149. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Pan F, Liao N, Zheng Y, Wang Y, Gao Y,
Wang S, Jiang Y and Liu X: Intrahepatic transplantation of
adipose-derived stem cells attenuates the progression of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Mol Med Rep.
26:3725–3733. 2015.
|
|
19
|
Lee RH, Kim B, Choi I, Kim H, Choi HS, Suh
K, Bae YC and Jung JS: Characterization and expression analysis of
mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow and adipose tissue.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 14:311–324. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boquest AC, Shahdadfar A, Brinehmann JE
and Collas P: Isolation of stromal stem cells from human adipose
tissue. Methods Mol Biol. 325:35–46. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bourin P, Bunnell BA, Casteilla L,
Dominici M, Katz AJ, March KL, Redl H, Rubin JP, Yoshimura K and
Gimble JM: Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal
vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived
stromal/stem cells: A joint statement of the international
federation for adipose therapeutics and science (IFATS) and the
international society for cellular therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy.
15:641–648. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park HS, Kim JH, Sun BK, Song SU, Suh W
and Sung JH: Hypoxia induces glucose uptake and metabolism of
adipose-derived stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 14:4706–4714.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gimble JM, Katz AJ and Bunnell BA:
Adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine. Circ Res.
100:1249–1260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, De Ugarte DA,
Huang JI, Mizuno H, Alfonso ZC, Fraser JK, Benhaim P and Hedrick
MH: Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol
Biol Cell. 13:4279–4295. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fu X, Tong Z, Li Q, Niu Q, Zhang Z, Tong
X, Tong L and Zhang X: Induction of adipose-derived stem cells into
Schwann-like cells and observation of Schwann-like cell
proliferation. Mol Med Rep. 14:1187–1193. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|