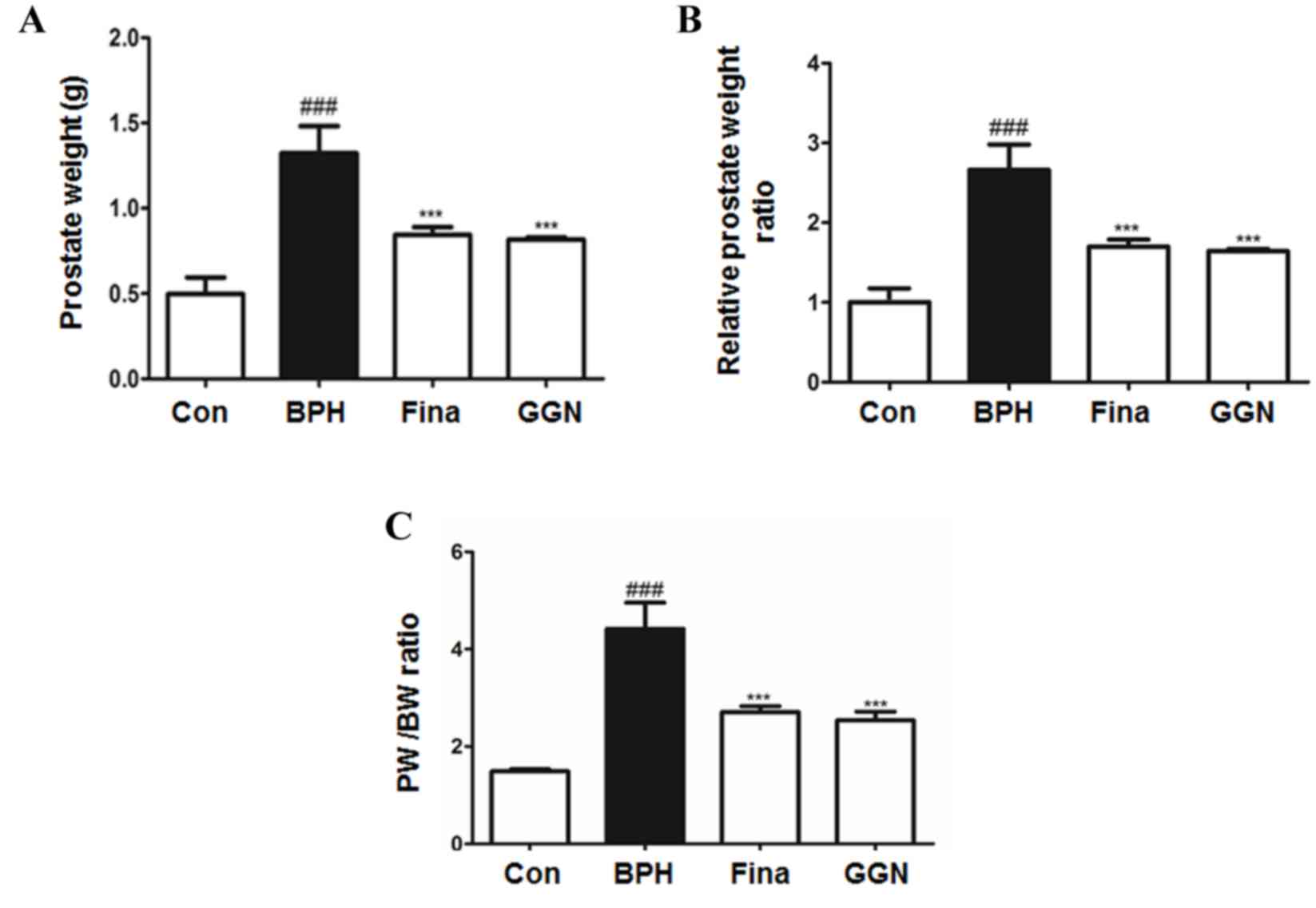
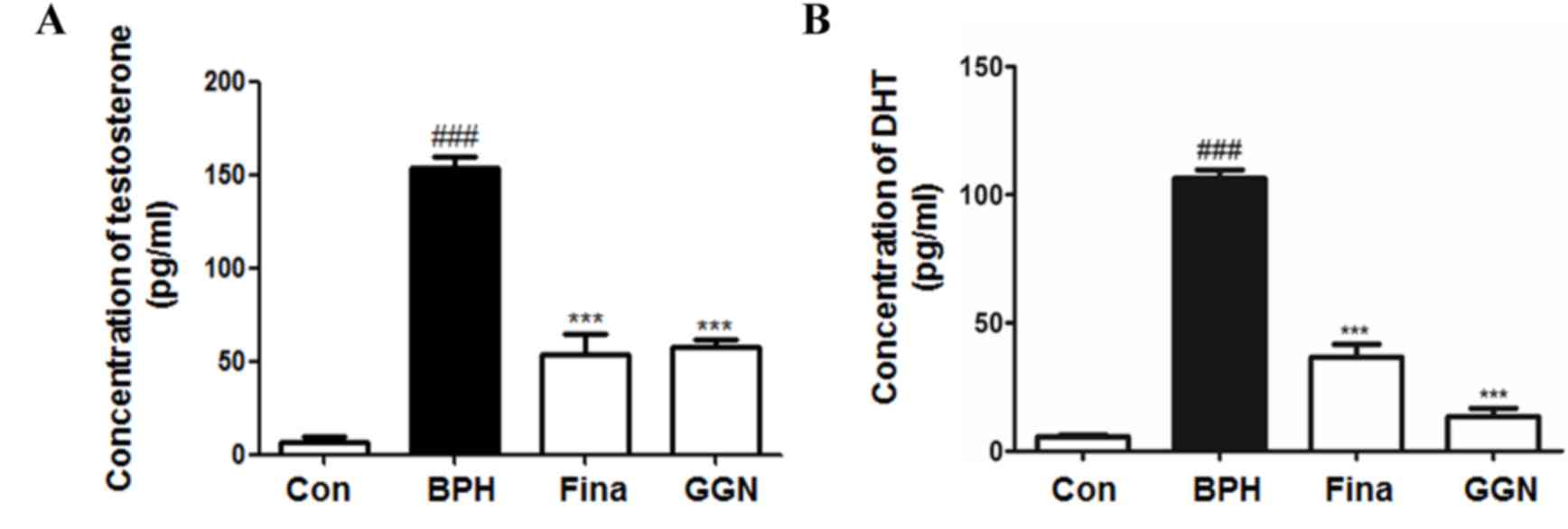
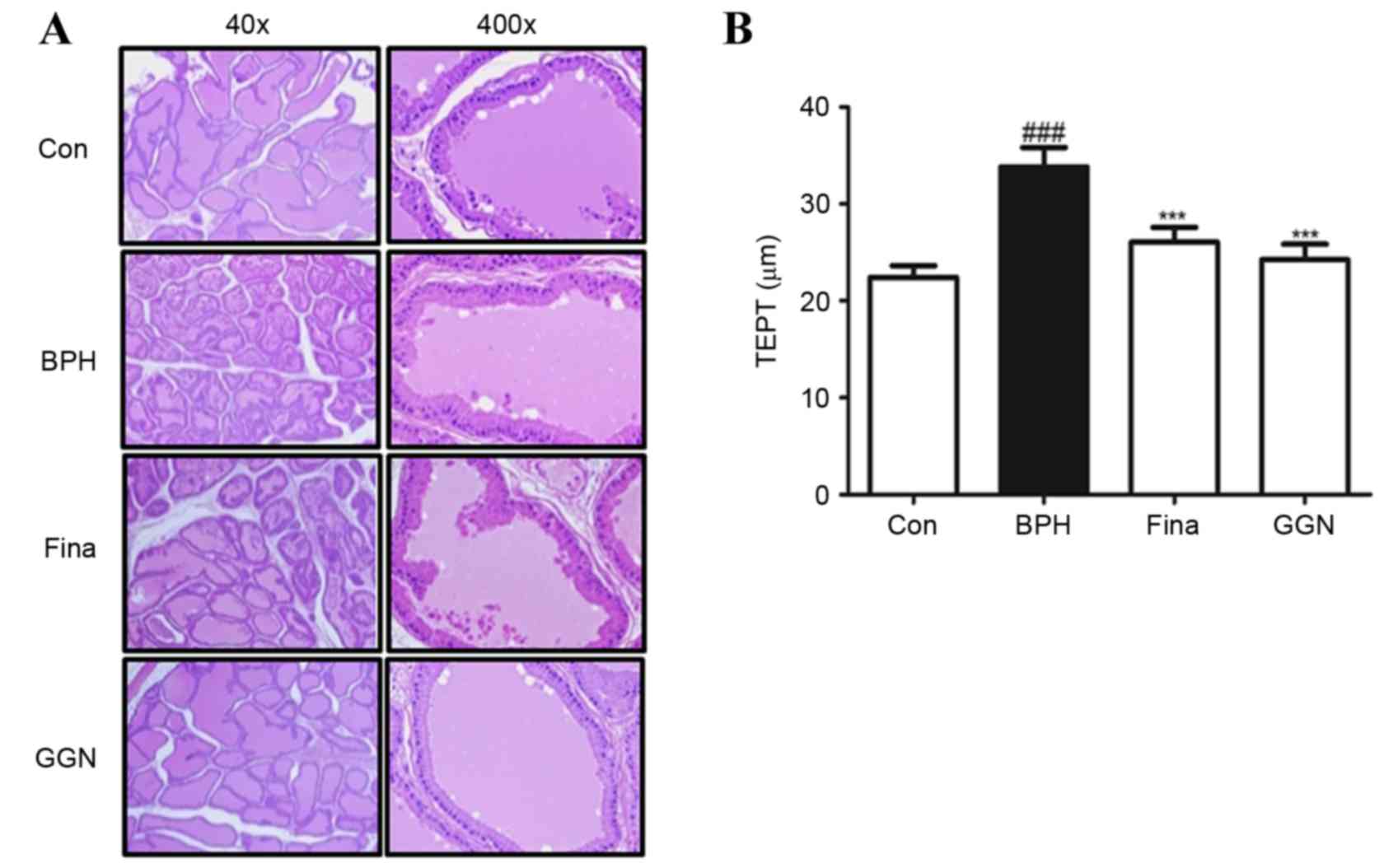
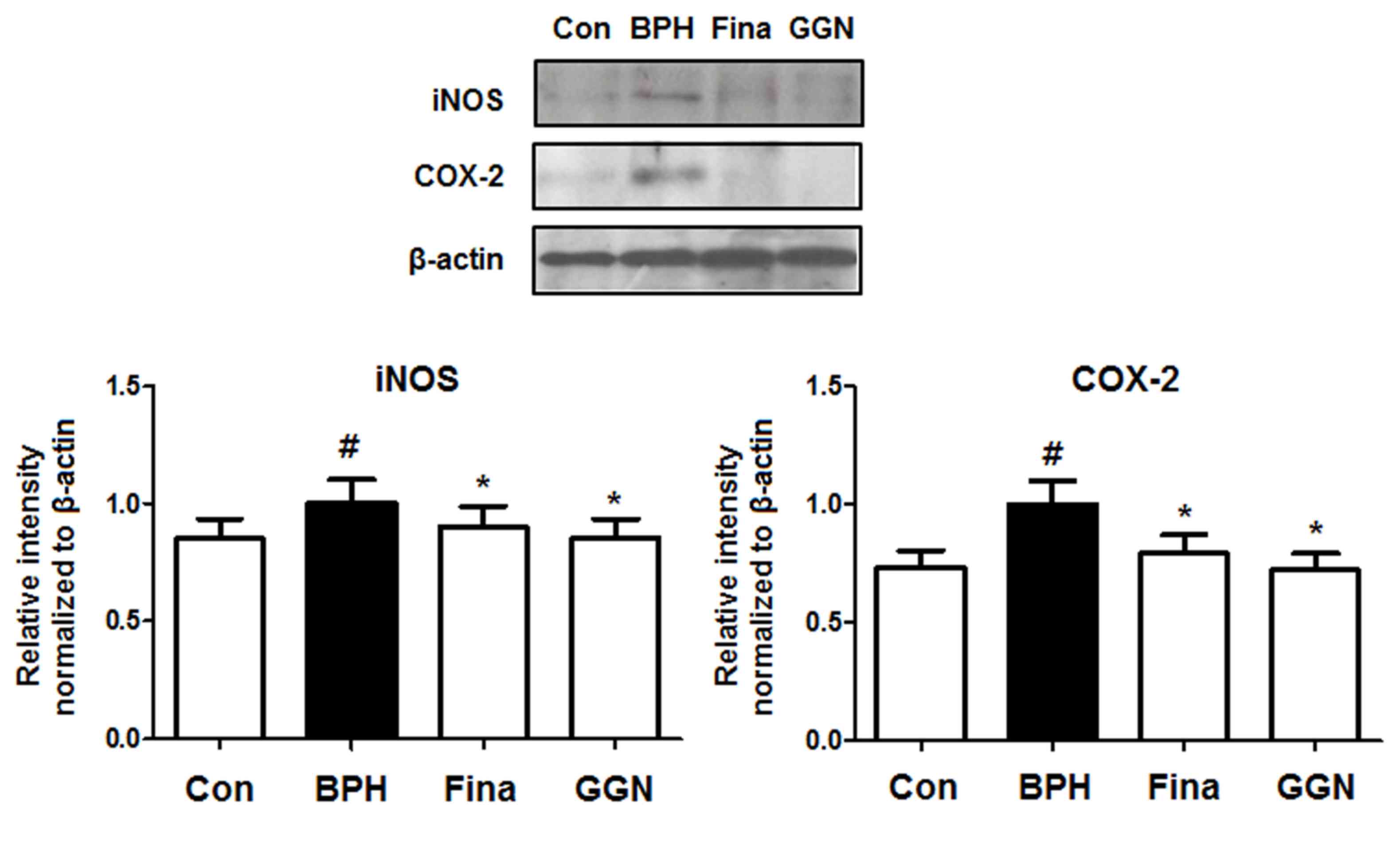
|
1
|
Boyle P, Maisonneuve P and Napalkov P:
Incidence of prostate cancer will double by the year 2030: The
argument for. Eur Urol. 29:(Suppl 2). S3–S9. 1996.
|
|
2
|
McVary KT: BPH: Epidemiology and
comorbidities. Am J Manag Care. 12:(Suppl 5). S122–S128.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sciarra A, Di Silverio F, Salciccia S,
Gomez AM Autran, Gentilucci A and Gentile V: Inflammation and
chronic prostatic diseases: Evidence for a link? Eur Urol.
52:964–972. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sciarra A, Mariotti G, Salciccia S, Gomez
A Autran, Monti S, Toscano V and Di Silverio F: Prostate growth and
inflammation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 108:254–260. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Robert G, Descazeaud A, Nicolaïew N, Terry
S, Sirab N, Vacherot F, Maillé P, Allory Y and de la Taille A:
Inflammation in benign prostatic hyperplasia: A 282 patients'
immunohistochemical analysis. Prostate. 69:1774–1780. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Di Silverio F, Bosman C, Salvatori M,
Albanesi L, Pannunzi L Proietti, Ciccariello M, Cardi A, Salvatori
G and Sciarra A: Combination therapy with rofecoxib and finasteride
in the treatment of men with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS)
and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Eur Urol. 47:72–78;
discussion 78–79. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nicholson TM and Ricke WA: Androgens and
estrogens in benign prostatic hyperplasia: Past, present and
future. Differentiation. 82:184–199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kyprianou N, Tu H and Jacobs SC: Apoptotic
versus proliferative activities in human benign prostatic
hyperplasia. Hum Pathol. 27:668–675. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rittmaster RS: 5alpha-reductase inhibitors
in benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer risk reduction.
Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 22:389–402. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartsch G, Rittmaster RS and Klocker H:
Dihydrotestosterone and the concept of 5alpha-reductase inhibition
in human benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 37:367–380. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tacklind J, Fink HA, Macdonald R, Rutks I
and Wilt TJ: Finasteride for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. CD0060152010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Oelke M, Bachmann A, Descazeaud A,
Emberton M, Gravas S, Michel MC, N'dow J, Nordling J and de la
Rosette JJ: European Association of Urology: EAU guidelines on the
treatment and follow-up of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract
symptoms including benign prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol.
64:118–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kyprianou N: Doxazosin and terazosin
suppress prostate growth by inducing apoptosis: Clinical
significance. J Urol. 169:1520–1525. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Morelli A, Filippi S, Comeglio P,
Sarchielli E, Chavalmane AK, Vignozzi L, Fibbi B, Silvestrini E,
Sandner P, Gacci M, et al: Acute vardenafil administration improves
bladder oxygenation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Sex Med.
7:107–120. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim JKSB, Lee EJ and Kim HK: Study on the
treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in oriental
medicine. The Journal of Korean Oriental Medical Society.
19:211–227. 1998.
|
|
16
|
Kim JH, Kim SS, Han IH, Sim S, Ahn MH and
Ryu JS: Proliferation of prostate stromal cell induced by benign
prostatic hyperplasia epithelial cell stimulated with Trichomonas
vaginalis via crosstalk with mast cell. Prostate. 76:1431–1444.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Heo J: The Treasured Mirror of Eastern
Medicine. 2. 3rd. Yoekang Press; Seoul: 2005
|
|
18
|
Zou W, Liu W, Yang B, Wu L, Yang J, Zou T,
Liu F, Xia L and Zhang D: Quercetin protects against
perfluorooctanoic acid-induced liver injury by attenuating
oxidative stress and inflammatory response in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 28:129–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Devi KP, Malar DS, Nabavi SF, Sureda A,
Xiao J, Nabavi SM and Daglia M: Kaempferol and inflammation: From
chemistry to medicine. Pharmacol Res. 99:1–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zeng KW, Yu Q, Liao LX, Song FJ, Lv HN,
Jiang Y and Tu PF: Anti-neuroinflammatory effect of MC13, a novel
coumarin compound from Condiment Murraya, through inhibiting
lipopolysaccharide-induced TRAF6-TAK1-NF-kB, P38/ERK MAPKS and
Jak2-Stat1/Stat3 pathways. J Cell Biochem. 116:1286–1299. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee HS, Kang P, Kim KY and Seol GH:
Foeniculum vulgare Mill. Protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice through
ERK-dependent NF-kappaB activation. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
19:183–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jeon EJ, Chung KS and An HJ:
Anti-proliferation effects of Cistanches salsa on the progression
of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
94:104–111. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo QL, Ding QL and Wu ZQ: Effect of
baicalein on experimental prostatic hyperplasia in rats and mice.
Biol Pharm Bull. 27:333–337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
De Nunzio C, Kramer G, Marberger M,
Montironi R, Nelson W, Schröder F, Sciarra A and Tubaro A: The
controversial relationship between benign prostatic hyperplasia and
prostate cancer: The role of inflammation. Eur Urol. 60:106–117.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Baltaci S, Orhan D, Gögüs C, Türkölmez K,
Tulunay O and Gögüs O: Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression
in benign prostatic hyperplasia, low- and high-grade prostatic
intraepithelial neoplasia and prostatic carcinoma. BJU Int.
88:100–103. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chiu TH, Lan KY, Yang MD, Lin JJ, Hsia TC,
Wu CT, Yang JS, Chueh FS and Chung JG: Diallyl sulfide promotes
cell-cycle arrest through the p53 expression and triggers induction
of apoptosis via caspase- and mitochondria-dependent signaling
pathways in human cervical cancer Ca Ski cells. Nutr Cancer.
65:505–514. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Petros AM, Olejniczak ET and Fesik SW:
Structural biology of the Bcl-2 family of proteins. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1644:83–94. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Elkahwaji JE: The role of inflammatory
mediators in the development of prostatic hyperplasia and prostate
cancer. Res Rep Urol. 5:1–10. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fibbi B, Penna G, Morelli A, Adorini L and
Maggi M: Chronic inflammation in the pathogenesis of benign
prostatic hyperplasia. Int J Androl. 33:475–488. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chughtai B, Lee R, Te A and Kaplan S: Role
of inflammation in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Rev Urol.
13:147–150. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang W, Bergh A and Damber JE: Chronic
inflammation in benign prostate hyperplasia is associated with
focal upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2, Bcl-2, and cell
proliferation in the glandular epithelium. Prostate. 61:60–72.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sugar LM: Inflammation and prostate
cancer. Can J Urol. 13:(Suppl 1). 46–47. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Strasser A, Jost PJ and Nagata S: The many
roles of FAS receptor signaling in the immune system. Immunity.
30:180–192. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boatright KM, Renatus M, Scott FL,
Sperandio S, Shin H, Pedersen IM, Ricci JE, Edris WA, Sutherlin DP,
Green DR and Salvesen GS: A unified model for apical caspase
activation. Mol Cell. 11:529–541. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Salakou S, Kardamakis D, Tsamandas AC,
Zolota V, Apostolakis E, Tzelepi V, Papathanasopoulos P, Bonikos
DS, Papapetropoulos T, Petsas T and Dougenis D: Increased Bax/Bcl-2
ratio up-regulates caspase-3 and increases apoptosis in the thymus
of patients with myasthenia gravis. In Vivo. 21:123–132.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun Y, Holley AK and St Clair DK: p53
regulation of energy metabolism and mitochondria regulation of p53
in cancer cells: An insight into the role of manganese superoxide
dismutase. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 14:261–273. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Kepp O, Tajeddine
N and Kroemer G: Targeting p53 to mitochondria for cancer therapy.
Cell Cycle. 7:1949–1955. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Teissier S, Ben Khalifa Y, Mori M, Pautier
P, Desaintes C and Thierry F: A new E6/P63 pathway, together with a
strong E7/E2F mitotic pathway, modulates the transcriptome in
cervical cancer cells. J Virol. 81:9368–9376. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|