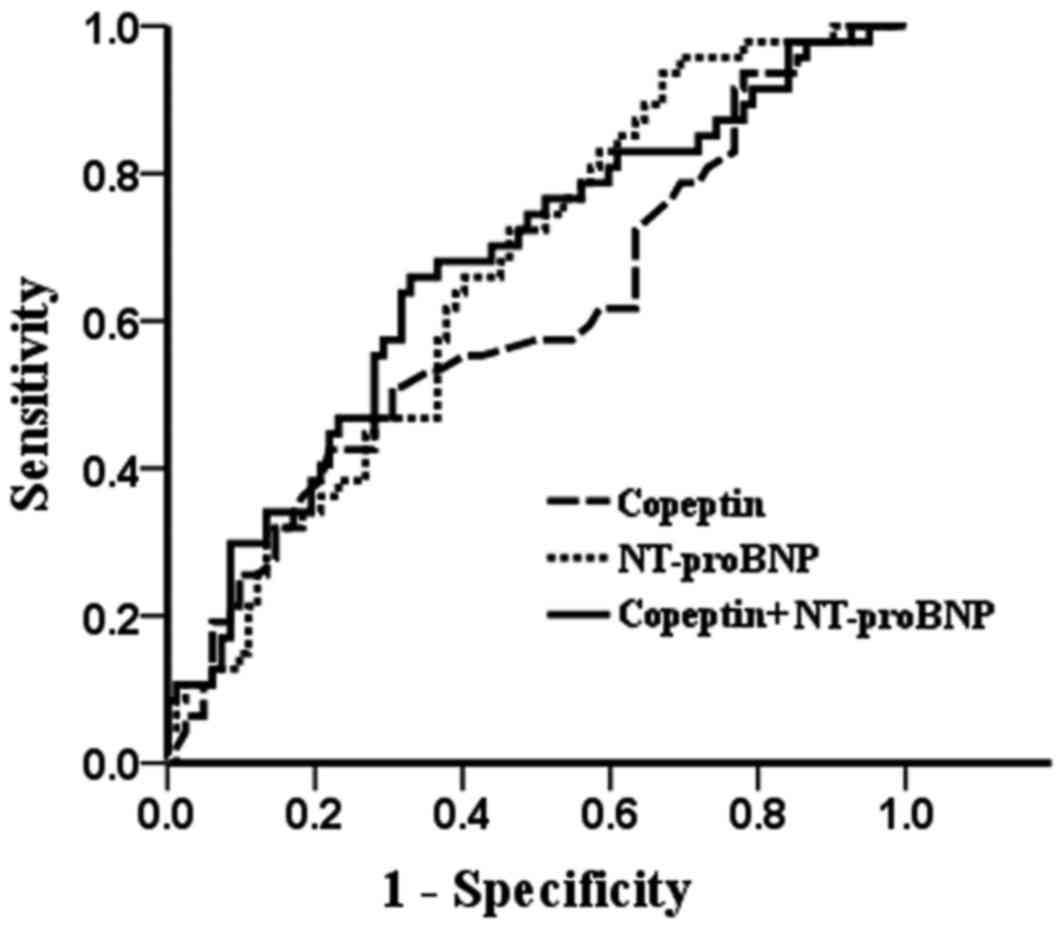
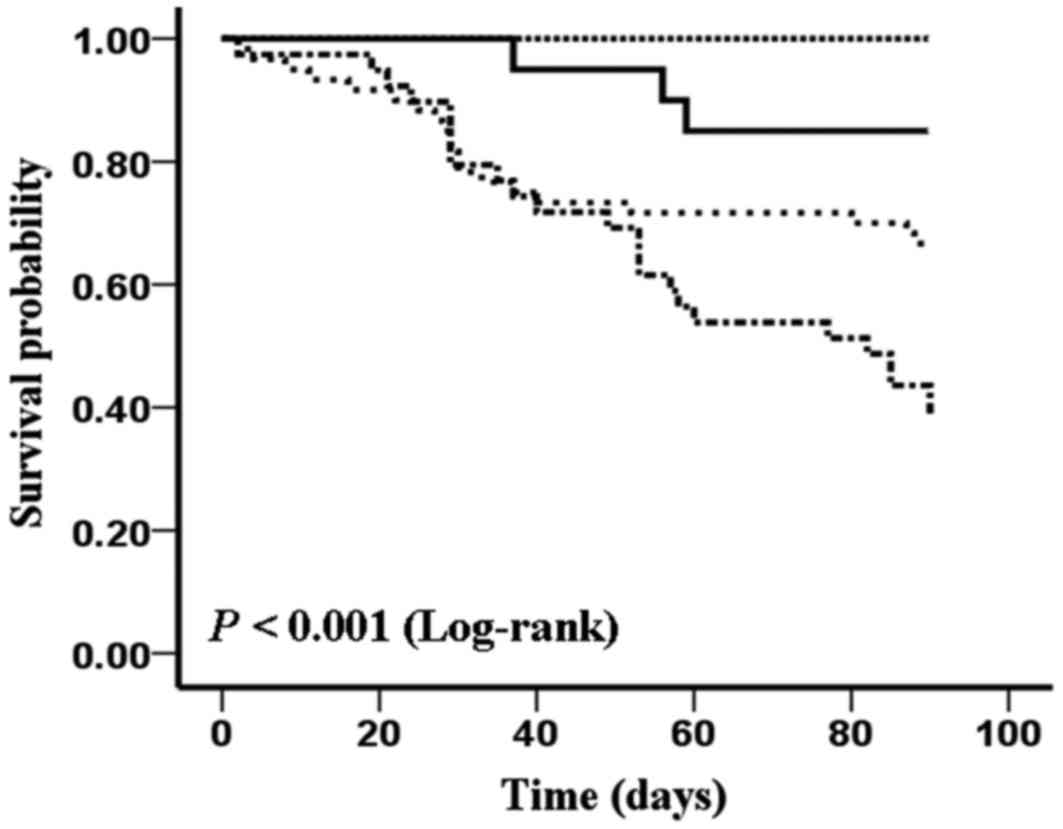
|
1
|
Cowie MR, Mosterd A, Wood DA, Deckers JW,
Poole-Wilson PA, Sutton GC and Grobbee DE: The epidemiology of
heart failure. Eur Heart J. 18:208–225. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsutamoto T, Wada A, Maeda K, Hisanaga T,
Maeda Y, Fukai D, Ohnishi M, Sugimoto Y and Kinoshita M:
Attenuation of compensation of endogenous cardiac natriuretic
peptide system in chronic heart failure: Prognostic role of plasma
brain natriuretic peptide concentration in patients with chronic
symptomatic left ventricular dysfunction. Circulation. 96:509–516.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Januzzi JL, van Kimmenade R, Lainchbury J,
Bayes-Genis A, Ordonez-Llanos J, Santalo-Bel M, Pinto YM and
Richards M: NT-proBNP testing for diagnosis and short-term
prognosis in acute destabilized heart failure: An international
pooled analysis of 1256 patients: The international collaborative
of NT-proBNP study. Eur Heart J. 27:330–337. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moe GW, Howlett J, Januzzi JL and Zowall
H: Canadian Multicenter Improved Management of Patients With
Congestive Heart Failure (IMPROVE-CHF) Study Investigators:
N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide testing improves the
management of patients with suspected acute heart failure: Primary
results of the Canadian prospective randomized multicenter
IMPROVE-CHF study. Circulation. 115:3103–3110. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maisel A, Mueller C, Adams K Jr, Anker SD,
Aspromonte N, Cleland JG, Cohen-Solal A, Dahlstrom U, DeMaria A, Di
Somma S, et al: State of the art: Using natriuretic peptide levels
in clinical practice. Eur J Heart Fail. 10:824–839. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Braunwald E: Biomarkers in heart failure.
N Engl J Med. 358:2148–2159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fiore G, Suppress P, Triggiani V, Resta F
and Sabba C: Neuroimmune activation in chronic heart failure.
Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 13:68–75. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Land H, Schütz G, Schmale H and Richter D:
Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA encoding bovine arginine
vasopressin-neurophysin II precursor. Nature. 295:299–303. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Friedmann AS, Malott KA, Memoli VA, Pai
SI, Yu XM and North WG: Products of vasopressin gene expression in
small-cell carcinoma of the lung. Br J Cancer. 69:260–263. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morgenthaler NG, Müller B, Struck J,
Bergmann A, Redl H and Christ-Crain M: Copeptin, a stable peptide
of the arginine vasopressin precursor, is elevated in hemorrhagic
and septic shock. Shock. 28:219–226. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morgenthaler NG, Struck J, Alonso C and
Bergmann A: Assay for the measurement of copeptin, a stable peptide
derived from the precursor of vasopressin. Clin Chem. 52:112–119.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stoiser B, Mörtl D, Hülsmann M, Berger R,
Struck J, Morgenthaler NG, Bergmann A and Pacher R: Copeptin, a
fragment of the vasopressin precursor, as a novel predictor of
outcome in heart failure. Eur J Clin Invest. 36:771–778. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gegenhuber A, Struck J, Dieplinger B,
Poelz W, Pacher R, Morgenthaler NG, Bergmann A, Haltmayer M and
Mueller T: Comparative evaluation of B-type natriuretic peptide,
mid-regional pro-A-type natriuretic peptide, mid-regional
pro-adrenomedullin, and Copeptin to predict 1-year mortality in
patients with acute destabilized heart failure. J Card Fail.
13:42–49. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Maisel A, Xue Y, Shah K, Mueller C, Nowak
R, Peacock WF, Ponikowski P, Mockel M, Hogan C, Wu AH, et al:
Increased 90-day mortality in patients with acute heart failure
with elevated copeptin: Secondary results from the Biomarkers in
Acute Heart Failure (BACH) study. Circ Heart Fail. 4:613–620. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G,
McMurray JJ, Ponikowski P, Poole-Wilson PA, Strömberg A, van
Veldhuisen DJ, Atar D, Hoes AW, et al: ESC Guidelines for the
diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008 Rhe
Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic
Heart Failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed
in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association of the ESC
(HFA) and endorsed by the European Society of Intensive Care
Medicine (ESICM). Eur Heart J. 29:2388–2442. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Müller B, Morgenthaler N, Stolz D, Schuetz
P, Müller C, Bingisser R, Bergmann A, Tamm M and Christ-Crain M:
Circulating levels of copeptin, a novel biomarker, in lower
respiratory tract infections. Eur J Clin Invest. 37:145–152. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Noveanu M, Breidthardt T, Potocki M,
Reichlin T, Twerenbold R, Uthoff H, Socrates T, Arenja N, Reiter M,
Meissner J, et al: Direct comparison of serial B-type natriuretic
peptide and NT-proBNP levels for prediction of short- and long-term
outcome in acute decompensated heart failure. Critical Care.
15:R12011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Metra M, Nodari S, Parrinello G, Specchia
C, Brentana L, Rocca P, Fracassi F, Bordonali T, Milani P, Danesi
R, et al: The role of plasma biomarkers in acute heart failure.
Serial changes and independent prognostic value of NT-proBNP and
cardiac troponin-T. Eur J Heart Fail. 9:776–786. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hanley JA and McNeil BJ: A method of
comparing the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves
derived from the same cases. Radiology. 148:839–843. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Katan M, Nigro N, Fluri F, Schuetz P,
Morgenthaler NG, Jax F, Meckel S, Gass A, Bingisser R, Steck A, et
al: Stress hormones predict cerebrovascular re-events after
transient ischemic attacks. Neurology. 76:563–566. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Urwyler SA, Schuetz P, Fluri F,
Morgenthaler NG, Zweifel C, Bergmann A, Bingisser R, Kappos L,
Steck A, Engelter S, et al: Prognostic value of copeptin: One-year
outcome in patients with acute stroke. Stroke. 41:1564–1567. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dong XQ, Huang M, Yang SB, Yu WH and Zhang
ZY: Copeptin is associated with mortality in patients with
traumatic brain injury. J Trauma. 71:1194–1198. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Katan M, Morgenthaler N, Widmer I, Puder
JJ, König C, Müller B and Christ-Crain M: Copeptin, a stable
peptide derived from the vasopressin precursor, correlates with the
individual stress level. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 29:341–346.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peacock WF, Nowak R, Christenson R,
DiSomma S, Neath SX, Hartmann O, Mueller C, Ponikowski P, Möckel M,
Hogan C, et al: Short-term mortality risk in emergency department
acute heart failure. Acad Emerg Med. 18:947–958. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nickel CH, Bingisser R and Morgenthaler
NG: The role of copeptin as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker
for risk stratification in the emergency department. BMC Medicine.
10:72012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fonarow GC, Adams KF Jr, Abraham WT, Yancy
CW and Boscardin WJ: ADHERE Scientific Advisory Committee, Study
Group, and Investigators: Risk stratification for in-hospital
mortality in acutely decompensated heart failure: Classification
and regression tree analysis. JAMA. 293:572–580. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|