Introduction
Lung cancer is a disease that severely threatens
human health and its incidence shows yearly increases (1). Lung cancer accounts for the highest
number of cancer-associated mortalities in women and men worldwide
(2). Metastasis and recurrence are
the primary cause of death in patients with lung cancer, and almost
90% of lung cancer patients succumb to tumor metastasis (3). Unrestricted proliferation of cancer
cells leads to tumor enlargement and subsequent compression on
peripheral organs. Inhibition of tumor cells is an effective
measure of treating malignant tumors. Although chemotherapy is an
important component of the first-line therapies for lung
adenocarcinoma (LAD), chemoresistance represents a predominant
obstacle towards chemotherapeutic treatment of LAD. Induction of
apoptosis has been found to be an effective means of treating
cancer, including non-small-cell lung cancer (4). Therefore, in-depth study of the
molecular mechanisms of lung cancer cell proliferation and
apoptosis is necessary.
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9
(PCSK9) belongs to the family of PCs and encodes a neural
apoptosis-regulated convertase 1 (5). PCSK9 was recently discovered to have
two major biological functions: Maintenance of plasma lipid
homeostasis by regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptors and
regulation of neuronal apoptosis (6–8). Gain-
and loss-of-function mutations in the PCSK9 gene are associated
with hyper- and hypocholesterolemia, respectively (9–11).
Therefore, PCSK9 inhibition is used as a promising therapy to treat
hypercholesterolemia (12). PCSK9 is
also involved in numerous biological processes. Microarray studies
showed that overexpression of PCSK9 leads to the dysregulation of
numerous pathways, including those regulating the cell cycle,
apoptosis and inflammation (13,14).
In vivo studies also suggested that PCSK9 is implicated in
these processes (15,16). Sun et al (17) demonstrated that PCSK9 deficiency
reduced liver metastasis by its ability to lower cholesterol levels
and possibly by enhancing tumor necrosis factor α-mediated
apoptosis.
As biological processes such as cell cycle and
proliferation are modified in cancer, the present study
hypothesized that PCSK9 may regulate cancer cell apoptosis. To the
best of our knowledge, no studies regarding the possible role of
PCSK9 in the development of lung cancer are available. The aim of
the present study was to identify the function of PCSK9 during
apoptosis of lung cancer cells. It was found that PCSK9 small
interfering (si)RNA significantly increased the apoptosis of A549
cells. The results suggested that inhibition of PCSK9 induces
apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of LAD cells.
Materials and methods
Reagents and antibodies
Rabbit anti-human cleaved (c)-caspase-3 (cat. no.
25546-1-AP, 1:2,000), B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2; cat. no.
12789-1-AP; 1:2,000), Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax; cat. no.
23931-1-AP; 1:2,000), 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78; cat.
no. 11587-1-AP; 1:2,000), GRP94 (cat. no. 14700-1-AP; 1:2,000),
protein kinase R-like ER kinase (PERK; cat. no. 24390-1-AP,
1:2,000), cytochrome c oxidase (COX) IV (cat. no. 11242-1-AP;
1:2,000), X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP; cat. no.
10037, 1:2,000) and survivin (cat. no. 10508-1-AP; 1:2,000)
antibodies, as well as mouse anti-GAPDH (cat. no. 60004; 1:2,000)
antibody were purchased from Proteintech (Wuhan, China). Rabbit
anti-human PCSK9 (cat. no. ab181142; 1:3,000) and cytochrome c
(cat. no. ab133504; 1:3,000) antibodies were purchased from Abcam
(Cambridge, UK). Rabbit anti-human phosphorylated (p)-PERK (cat.
no. #5683; 1:3,000), eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 2α (cat.
no. #5169; 1:3,000) and p-eIF2α (cat. no. 3398; 1:3,000) antibodies
were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (Danvers, MA,
USA). Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit
immunoglobulin G (cat. no. 10285-1-AP; 1:2,000) or mouse
immunoglobulin G (cat. no. 16402; 1:2,000) were purchased from
Proteintech. Cell Counting Kit (CCK)-8 and Hoechst 33258 were
purchased from Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology (Haimen, China).
Other reagents were of analytical grade.
Cell culture and RNA interference
The A549 human LAD cell line was obtained from the
American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). Cells were
routinely grown in RPMI-1640 medium (Hyclone; GE Healthcare,
Chalfont, UK) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Hyclone), 100
U/ml penicillin (Sigma-Aldrich, Merck-Millipore, Darmstadt,
Germany) and 100 µg/ml streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich) at 37°C in a
humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. The medium was
replaced every 2–3 days and upon reaching 80% confluence, they were
passaged at a 1:2 ratio.
A549 cells were transfected with 100 nM PCSK9 siRNA
(cat. no. sc-45482; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX,
USA; Genbank ID for PCSK9: NM_174936) or control siRNA (scrambled
siRNA, a universal negative control; cat. no. sc-37007; Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX, USA) with GeneSilencer siRNA
transfection reagent (Genlantis, San Diego, CA, USA), according to
the manufacturer's instructions. At 48 h after transfection, the
efficiency of siRNA-mediated PCSK9 knockdown was determined by
western blot analysis.
Cell proliferation assay
A549 cells were seeded into each well of a 96-well
plate at a density of 5×103 cells/well in culture
medium. After 24 h incubation, cells were transfected with PCSK9
siRNA or control siRNA for 12, 24, 36 and 48 h as described above,
followed by the addition of 10 µl CCK-8 solution. The cells were
then incubated for 3 h at 37°C. Absorbance was measured at 450 and
650 nm using a spectrophotometer (Nanodrop 2000 UV-VIS; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc., Wilmington, DE, USA). The experiments were
performed in triplicate.
Morphological analysis following
Hoechst 33258 staining
A549 cells were seeded in 24-well plates
(6×104 cells/well) overnight and transfected with PCSK9
siRNA or control siRNA for 48 h. The cells were then fixed and
stained with Hoechst 33258 in the dark at 4°C overnight. Apoptotic
cells were visualized using a fluorescence microscope (DM 6000;
Leica microsystems GmbH, Wetzler, Germany).
Preparation of mitochondria and
cytosol
A mitochondria/cytosol kit (Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology) was used to isolate mitochondria and cytosol
according to the manufacturer's instructions. Following the
aforementioned protocol of transfection, 5×107 cells
were collected by centrifugation at 600 × g for 5 min at 4°C,
washed twice with ice-cold PBS and then resuspended in 500 µl
isolation buffer containing protease inhibitors for 10 min on ice.
The cells were mechanically homogenized with a Dunce grinder. The
unbroken cells, debris and nuclei were discarded by centrifugation
at 800 × g for 10 min at 4°C. The supernatants were centrifuged at
12,000 × g for 15 min at 4°C. The supernatant containing the
cytosol was collected and the pellet fraction containing the
mitochondria was dissolved in 50 µl lysis buffer.
Western blot analysis
A549 cells were transfected as described above.
Cells were harvested and lysed for 10 min in ice-cold lysis buffer
[50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 140 mM NaCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2 and
0.5% Nonidet P-40 with complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche,
Mannheim, Germany)]. The lysates were further centrifuged at 12,000
× g for 15 min at 4°C and the supernatants were then collected in
new tubes. The protein concentration was measured using a
bicinchoninic acid protein assay kit (Dingguo, Beijing, China).
Protein samples were boiled for 5 min in the presence of 5X
SDS-PAGE loading buffer. Equal amounts of proteins were subjected
to 12% SDS-PAGE and then electrotransferred onto PVDF membranes
(Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The membranes were blocked for 1 h
in Tris-buffered saline (25 mM Tris at pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl and
0.05% Tween-20) containing 5% nonfat milk powder, and incubated
overnight at 4°C with the indicated antibodies. After washing,
blots were incubated for 1 h at 37°C with HRP-conjugated
anti-rabbit or anti-mouse secondary antibodies. Following further
washing, the blots were revealed using the ECL Plus detection
system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) under conditions
recommended by the manufacturer. Images were captured directly by
the Gel 3100 chemiluminescent and fluorescent imaging system (Sage
Creation Science Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). Quantification of band
densities was performed using Quantity One software version 2.0
(Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) with normalization
to the GAPDH signal. The level of proteins of interest in the siRNA
group was expressed relative to that in the control siRNA
group.
Statistical analysis
Values are expressed as the mean ± standard
deviation. Differences were analyzed using Student's t-test and
one-way analysis of variance to determine the level of
significance. P<0.05 or 0.001 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference. Statistical analysis was
performed using SPSS 19.0 software (IBM SPSS, Armonk, NY, USA).
Results
Effect of PCSK9 on A549 cell
proliferation
A549 cell proliferation was examined using a CCK-8
assay performed subsequent to transfection with PCSK9 siRNA or
control siRNA. As shown in Fig. 1A,
PCSK9 siRNA attenuated the increase in cell proliferation that
occurred in the control siRNA-treated group. Furthermore, the cell
proliferation at 48 h after transfection with PCSK9 siRNA was
significantly reduced compared with that in the control siRNA group
(P<0.05; Fig. 1A). Additionally,
results from western blotting indicated that PCSK9 expression was
significantly decreased compared with the control siRNA group
(P<0.001; Fig. 1B). These data
imply that PCSK9 siRNA inhibits the proliferation of A549
cells.
PCSK9 siRNA induces apoptosis in A549
cells
In order to evaluate whether the inhibition of A549
cell proliferation by PCSK9 siRNA was associated with apoptosis,
characteristic morphological changes were observed by Hoechst 33258
staining (Fig. 2). A549 cells were
transfected with PCSK9 siRNA for 48 h and morphological changes
associated with apoptosis compared with the control group were
observed. In the control siRNA group, nuclei of A549 cells were
round and homogeneously stained (Fig.
2A). However, PCSK9 siRNA-transfected cells exhibited evident
characteristics of apoptosis, including membrane integrity loss or
deformation, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation and chromatin
compaction of late apoptotic appearance (Fig. 2A). Counting of cells with apoptotic
features revealed that the percentage of apoptotic cells was
significantly increased in the PCSK9 siRNA-transfected group, as
compared to that in the group transfected with negative control
siRNA (P<0.05; Fig. 2B).
Together, these results indicated that PCSK9 siRNA induces
apoptosis in A549 cells.
PCSK9 siRNA induces apoptosis via the
caspase-dependent mitochondrial apoptotic pathway
To further assess the role of PCSK9 in A549 cell
apoptosis, the expression of apoptosis-associated proteins was
assessed. These included pro-apoptotic c-caspase-3, anti-apoptotic
XIAP and survivin. Western blot analysis revealed that PCSK9 siRNA
increased the levels of c-caspase-3 by ~17-fold (P<0.001).
Conversely, the levels of XIAP and survivin were decreased by
~2.5-fold (P<0.05) and 16-fold (P<0.001), respectively,
following PCSK9 siRNA transfection (Fig.
3).
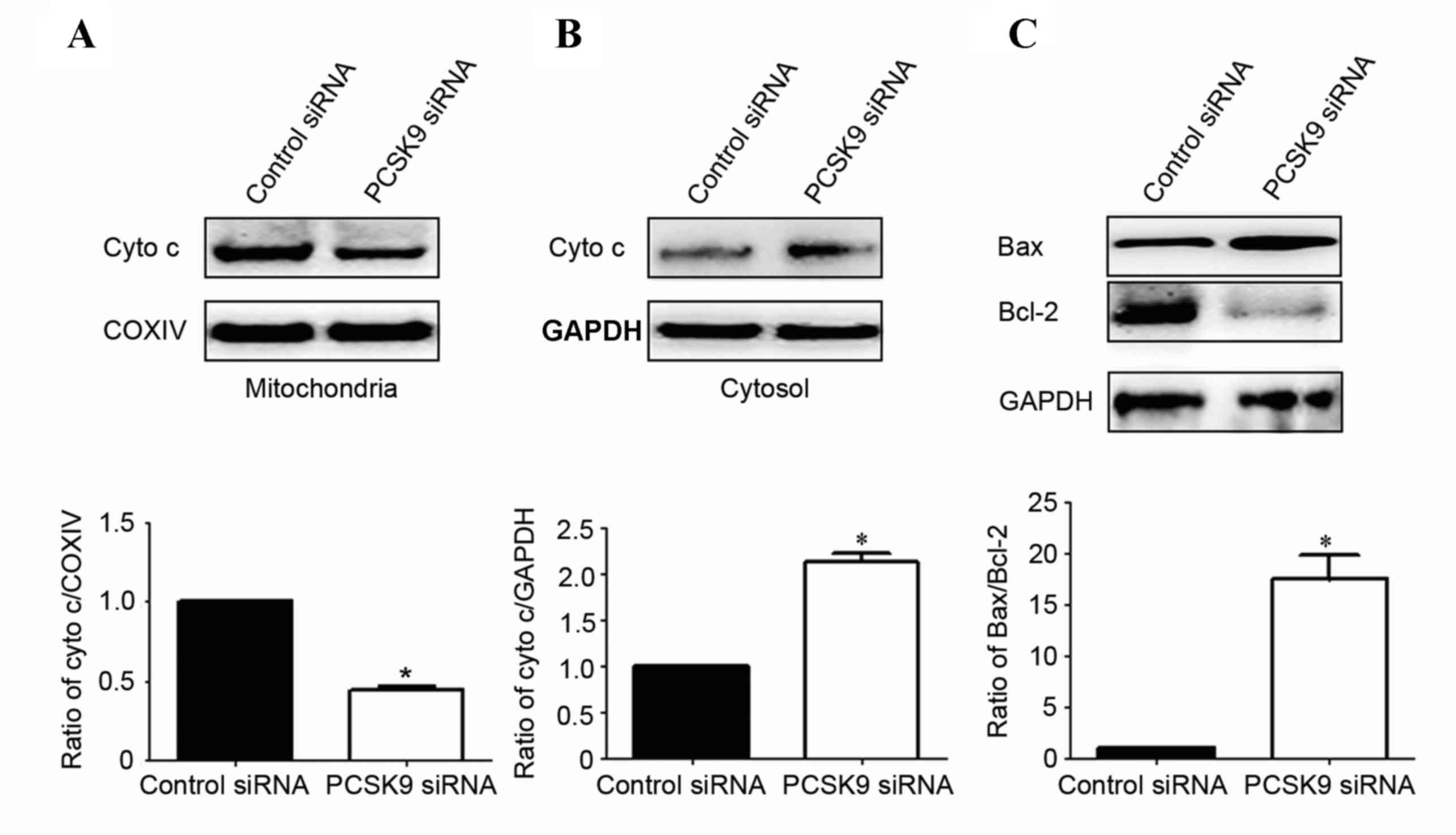
In order to better understand the molecular
mechanisms by which PCSK9 siRNA exerts its pro-apoptotic effects,
the protein expression of mediators of the mitochondrial signaling
pathway was assessed. It was determined whether PCSK9 siRNA
stimulates the release of cytochrome c into the cytosolic
fraction in A549 cells. As expected, cytochrome c was
re-distributed following PCSK9 siRNA transfection. The level of
cytochrome c in mitochondria was significantly decreased by
50% (P<0.05, Fig. 4A).
Correspondingly, the levels of cytochrome c in cytosol were
increased by 190% (P<0.05, Fig.
4B).
Since the Bcl-2 family proteins have a critical role
in regulating the release of cytochrome c, the present study
then investigated the possible involvement of Bax and Bcl-2 in the
process of PCSK9 siRNA-mediated A549 cell apoptosis. As shown in
Fig. 4C, the level of Bax was
significantly increased and Bcl-2 was markedly decreased in PCSK9
siRNA-transfected cells. Statistical analysis showed that PCSK9
siRNA increased the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 by ~17.5-fold
(P<0.05).
PCSK9 siRNA induces the activation of
the ER stress pathway
Since little is known regarding the effect of PCSK9
on ER stress in cultured LAD cells, the present study determined
whether PCSK9 siRNA transfection induces ER stress. The protein
levels of p-PERK and p-eIF2α, which are considered characteristic
markers of ER stress, were assessed (18). As shown in Fig. 5, compared with those in the control
siRNA group, the levels of p-PERK and p-eIF2α were significantly
increased in PCSK9 siRNA-transfected cells, while total PERK and
eIF2α were unchanged. The expression of GRP78 and GRP94, which
serve as gatekeepers for the activation of ER stress transducers,
was then assessed (18). It was
determined that the expression of GRP78 and GRP94 was significantly
increased by PCSK9 siRNA transfection (P<0.05; Fig. 5). These results demonstrated that ER
stress is at least partially involved in PCSK9 siRNA-induced
apoptosis.
Discussion
The PCSK9 gene is a member of the PC family and
encodes the PCSK9 protein, also known as neural apoptosis-regulated
convertase 1 (NARC1), which is involved in regulating apoptosis
(5,19). A microarray study showed that
overexpression of PCSK9D347Y downregulated certain
pro-apoptotic genes in HepG2 cells (14). In addition, the lack of PCSK9
enhanced apoptosis during liver regeneration (15). However, the exact role of PCSK9
during LAD cell apoptosis has remained elusive. The results of the
present study indicated that PCSK9 siRNA inhibits the proliferation
of A549 cells. Based on the results of Hoechst 33258 staining and
western blot analysis, it was concluded that PCSK9 siRNA induces
apoptosis in A549 cells. Thus, the present study provided the first
evidence that PCSK9 has an anti-apoptotic effect in lung cancer
cells.
At present, induction of apoptosis is pursued as a
strategy for killing cancer cells. Members of the IAP family,
survivin and XIAP, contribute to apoptosis resistance of cancer
cells (20). Thus, the present study
investigated whether these apoptosis-associated proteins were
involved in PCSK9 siRNA-induced apoptosis. The results confirmed
the regulatory role of PCSK9 in the apoptosis of A549 cells based
on the following lines of evidence: PCSK9 siRNA increased the
apoptosis of A549 cells by regulating the apoptosis-associated
factors c-caspase-3, XIAP and survivin. The inactivation of XIAP
and survivin by PCSK9 siRNA may prevent the development and
progression of cancers.
It has been well documented that Bcl-2 family
proteins regulate apoptosis through a variety of pathways,
primarily the mitochondrial ones (21). Bcl-2 and its homologs prevent
mitochondrial membrane disruption and cytochrome c release, while
Bax promotes these events. The Bax/Bcl-2 ratio is regarded as a
determinant of the apoptotic status (22). The results of the present study
demonstrated that in mitochondria, the level of cytochrome c
was significantly decreased, while it was increased in the cytosol,
indicating the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria
into the cytoplasm through mitochondrial membrane permeability
increases or rupture. Furthermore, PCSK9 siRNA increased the level
of Bax and decreased the level of Bcl-2, leading to an increase in
the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. These results indicated that PCSK9 siRNA
affects mitochondrial membrane stability. Taken together, these
results demonstrated that PCSK9 siRNA may exert its anti-tumor
activity through the mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathway
(intrinsic apoptotic pathway) in LAD cells.
Another pathway mediating apoptosis is the ER stress
pathway, which may be triggered by a variety of toxic insults and
ultimately leads to apoptosis (23).
ER stress has been reported to induce apoptosis in various cell
types via the upregulation of protein translation mediated through
the PERK-eIF2α pathway (24–27). For instance, upon ER stress, the ER
chaperone GRP78 dissociates from the PERK and initiates
transphosphorylation with subsequent activation of the kinase
(28). The activated PERK then leads
to phosphorylation of eIF2α and subsequent expression of activating
transcription factor 4 protein, which is essential for ER
stress-induced apoptosis (29). The
western blot results of the present study showed that PCSK9 siRNA
increased the levels of GRP94, GRP78, p-PERK and p-eIF2α, which are
vital features of the unfolded protein response and indicate that
PCSK9 siRNA induced apoptosis through the ER stress signaling
pathway.
In conclusion, the present study supported a role of
PCSK9 in regulating apoptosis A549 cells. Further study is
warranted to define the exact mechanisms by which PCSK9 regulates
the apoptosis and proliferation of A549 cells. Even though the
present study focused on lung cancer, a PCSK9 inhibitor, initially
developed to treat hypercholesterolemia (12), may be useful in therapies directed
against various types of cancer and possibly metastasis.
References
|
1
|
Liang R, Chen TX, Wang ZQ, Jin KW, Zhang
LY, Yan QN, Zhang HH and Wang WP: A respective analysis of the
clinicopathological characteristics of large cell carcinoma of
lung. Exp Ther Med. 9:197–202. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mrazek AA and Chao C: Surviving cutaneous
melanoma: A clinical review of follow-up practices, surveillance,
and management of recurrence. Surg Clin North Am. 94:989–1002,
vii-viii. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Singhal S, Vachani A, Antin-Ozerkis D,
Kaiser LR and Albelda SM: Prognostic implications of cell cycle,
apoptosis, and angiogenesis biomarkers in non-small cell lung
cancer: A review. Clin Cancer Res. 11:3974–3986. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Horton JD, Cohen JC and Hobbs HH:
Molecular biology of PCSK9: Its role in LDL metabolism. Trends
Biochem Sci. 32:71–77. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park SW, Moon YA and Horton JD:
Post-transcriptional regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor
protein by proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9a in mouse
liver. J Biol Chem. 279:50630–50638. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Benjannet S, Rhainds D, Essalmani R, Mayne
J, Wickham L, Jin W, Asselin MC, Hamelin J, Varret M and Allard D:
NARC-1/PCSK9 and its natu-ral mutants: Zymogen cleavage and effects
on the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor and LDL cholesterol.
J Biol Chem. 279:48865–48875. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peterson AS, Fong LG and Young SG: PCSK9
function and physiology. J Lipid Res. 49:1595–1599. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abifadel M, Varret M, Rabès JP, Allard D,
Ouguerram K, Devillers M, Cruaud C, Benjannet S, Wickham L, Erlich
D, et al: Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant
hypercholesterolemia. Nat Genet. 34:154–156. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cohen J, Pertsemlidis A, Kotowski IK,
Graham R, Garcia CK and Hobbs HH: Low LDL holesterol in individuals
of African descent resulting from frequent nonsense mutations in
PCSK9. Nat Genet. 37:161–165. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cohen JC, Boerwinkle E, Mosley TH Jr and
Hobbs HH: Sequence variations in PCSK9, low LDL, and protection
against coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 354:1264–1272. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Seidah NG and Prat A: The biology and
therapeutic targeting of the proprotein convertases. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 11:367–383. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lan H, Pang L, Smith MM, Levitan D, Ding
W, Liu L, Shan L, Shah VV, Laverty M, Arreaza G, et al: Proprotein
convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) affects gene expression
pathways beyond cholesterol metabolism in liver cells. J Cell
Physiol. 224:273–281. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ranheim T, Mattingsdal M, Lindvall JM,
Holla OL, Berge KE, Kulseth MA and Leren TP: Genome-wide expression
analysis of cells expressing gain of function mutant D374Y-PCSK9. J
Cell Physiol. 217:459–467. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zaid A, Roubtsova A, Essalmani R,
Marcinkiewicz J, Chamberland A, Hamellin J, Tremblay M, Jacques H,
Jin W, Davignon J, et al: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin
type 9 (PCSK9): Hepatocyte-specific low-density lipoprotein
receptor degradation and critical role in mouse liver regeneration.
Hepatology. 48:646–654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mbikay M, Sirois F, Mayne J, Wang GS, Chen
A, Dewpura T, Prat A, Seidah NG, Chretien M and Scott FW:
PCSK9-deficient mice exhibit impaired glucose tolerance and
pancreatic islet abnormalities. FEBS Lett. 584:701–706. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun XW, Essalmani R, Day R, Khatib AM,
Seidah NG and Prat A: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9
deficiency reduces melanoma metastasis in liver. Neoplasia.
14:1122–1131. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Faitova J, Krekac D, Hrstka R and Vojtesek
B: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
11:488–505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chiang LW, Grenier JM, Ettwiller L,
Jenkins LP, Ficenec D, Martin J, Jin F, DiStefano PS and Wood A: An
orchestrated gene expression component of neuronal programmed cell
death revealed by cDNA array analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:2814–2819. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
LaCasse EC, Mahoney DJ, Cheung HH,
Plenchette S, Baird S and Korneluk RG: IAP-targeted therapies for
cancer. Oncogene. 27:6252–6275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pettersson F, Dalgleish AG, Bissonnette RP
and Colston KW: Retinoids cause apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
cells via activation of RAR-gamma and altered expression of
Bcl-2/Bax. Br J Cancer. 87:555–561. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dufey E, Sepulveda D, Rojas-Rivera D and
Hetz C: Cellular mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum stress
signaling in health and disease. 1. An overview. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 307:C582–C594. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan T, Luo BL, Wei TH, Zhang L, He BM and
Niu RC: Salubrinal protects against cigarette smoke extract-induced
HBEpC apoptosis likely via regulating the activity of PERK-eIF2α
signaling pathway. Arch Med Res. 43:522–529. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stockwell SR, Platt G, Barrie SE,
Zoumpoulidou G, Te Poele RH, Aherne GW, Wilson SC, Sheldrake P,
McDonald E, Venet M, et al: Mechanism-based screen for G1/S
checkpoint activators identifies a selective activator of
EIF2AK3/PERK signalling. PLoS One. 7:e285682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Duan Z, Zhao J, Fan X, Tang C, Liang L,
Nie X, Liu J, Wu Q and Xu G: The PERK-eIF2α signaling pathway is
involved in TCDD-induced ER stress in PC12 cells. Neurotoxicology.
44:149–159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang Q, Li F, Shi K, Wu P, An J, Yang Y
and Xu C: Involvement of p38 in signal switching from autophagy to
apoptosis via the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 axis in selenite-treated NB4
cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e12702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu CY, Schroder M and Kaufman RJ:
Ligand-independent dimerization activates the stress response
kinases IRE1 and PERK in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. J
Biol Chem. 275:24881–24885. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM and Samali
A: Mediators of endoplas-mic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.
EMBO Rep. 7:880–885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|