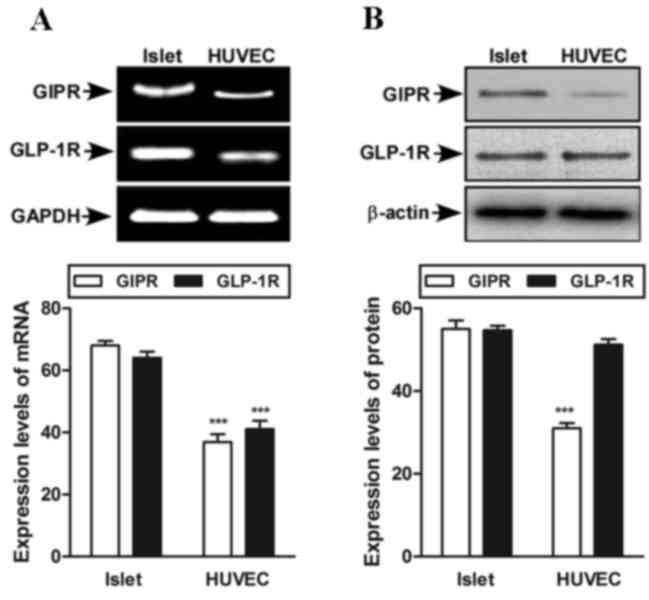
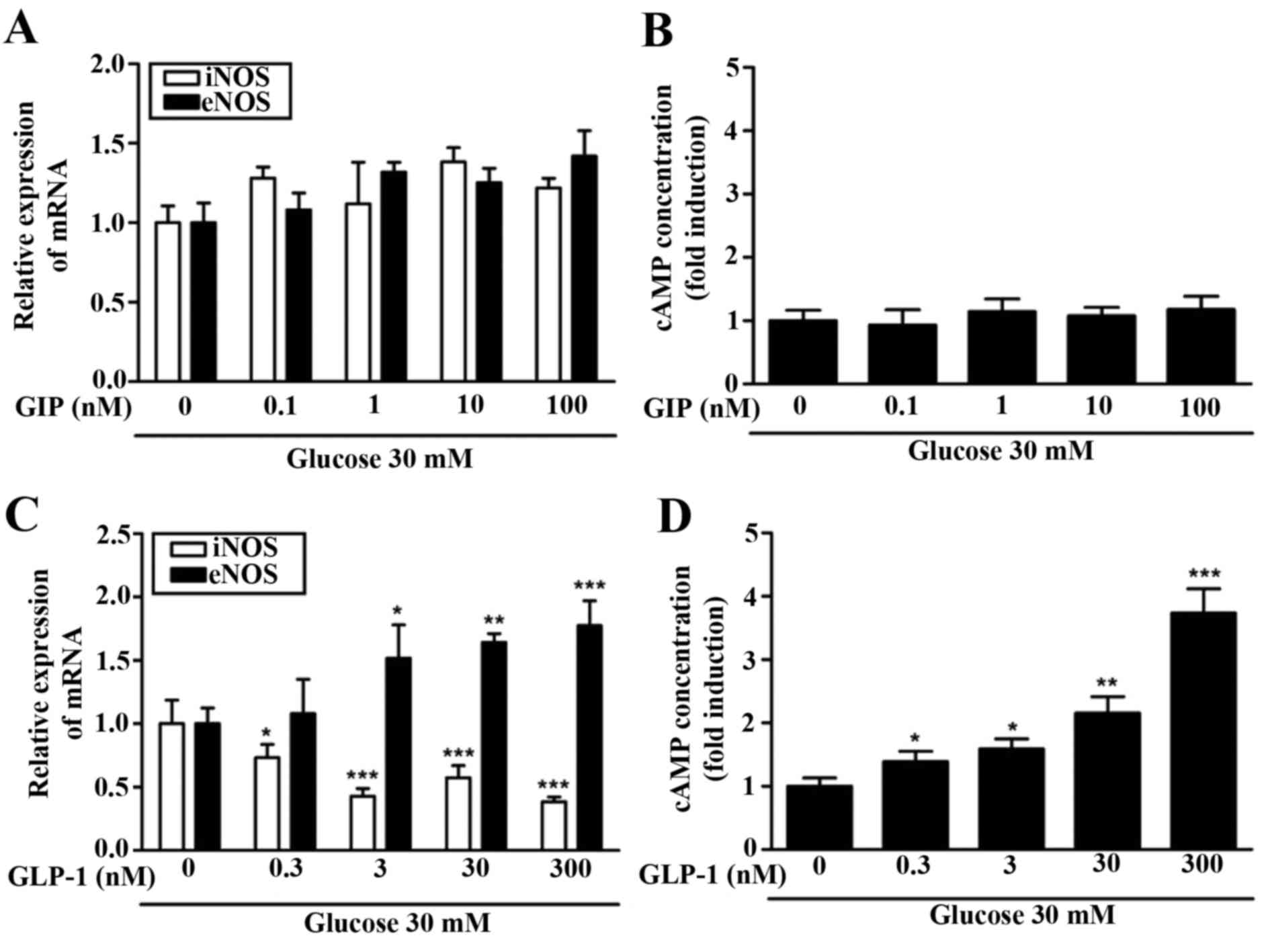
|
1
|
Rask-Madsen C and King GL: Mechanisms of
disease: Endothelial dysfunction in insulin resistance and
diabetes. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 3:46–56. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
ACCORD Study Group, ; Gerstein HC, Miller
ME, Genuth S, Ismail-Beigi F, Buse JB, Goff DC Jr..Probstfield JL,
Cushman WC, Ginsberg HN, et al: Long-term effects of intensive
glucose lowering on cardiovascular outcomes. N Engl J Med.
364:818–828. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Förstermann U, Closs EI, Pollock JS,
Nakane M, Schwarz P, Gath I and Kleinert H: Nitric oxide synthase
isozymes: Characterization, purification, molecular cloning and
functions. Hypertension. 23:1121–1131. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wright E Jr..Scism-Bacon JL and Glass LC:
Oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes: The role of fasting and
postprandial glycaemia. Int J Clin Pract. 60:308–314. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schäfer A and Bauersachs J: Endothelial
dysfunction, impaired endogenous platelet inhibition and platelet
activation in diabetes and atherosclerosis. Curr Vasc Pharmacol.
6:52–60. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davignon J and Ganz P: Role of endothelial
dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 109(23 Suppl 1):
III27–III32. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vilsbøll T, Krarup T, Madsbad S and Holst
JJ: Both GLP-1 and GIP are insulinotropic at basal and postprandial
glucose levels and contribute nearly equally to the incretin effect
of a meal in healthy subjects. Regul Pept. 114:115–121. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim W and Egan JM: The role of incretins
in glucose homeostasis and diabetes treatment. Pharmacol Rev.
60:470–512. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kogire M, Inoue K, Sumi S, Doi R, Yun M,
Kaji H and Tobe T: Effects of gastric inhibitory polypeptide and
glucagon on portal venous and hepatic arterial flow in conscious
dogs. Dig Dis Sci. 37:1666–1670. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ojima A, Matsui T, Maeda S, Takeuchi M and
Yamagishi S: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIp)
inhibits signaling pathways of advanced glycation end products
(AGEs) in endothelial cells via its antioxidative properties. Horm
Metab Res. 44:501–505. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Forst T, Weber MM and Pfützner A:
Cardiovascular benefits of GLP-1-based therapies in patients with
diabetes mellitus type 2: Effects on endothelial and vascular
dysfunction beyond glycemic control. Exp Diabetes Res.
2012:6354722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Holst JJ: The physiology of glucagon-like
peptide 1. Physiol Rev. 87:1409–1439. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hansotia T, Maida A, Flock G, Yamada Y,
Tsukiyama K, Seino Y and Drucker DJ: Extrapancreatic incretin
receptors modulate glucose homeostasis, body weight and energy
expenditure. J Clin Invest. 117:143–152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hong JY, Park KY, Kim BJ, Hwang WM, Kim DH
and Lim DM: Effects of short-term exenatide treatment on regional
fat distribution, glycated hemoglobin levels and aortic pulse wave
velocity of obese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Endocrinol
Metab (Seoul). 31:80–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nichols WW: Clinical measurement of
arterial stiffness obtained from noninvasive pressure waveforms. Am
J Hypertens. 18:3S–10S. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Anderson TJ: Arterial stiffness or
endothelial dysfunction as a surrogate marker of vascular risk. Can
J Cardiol. 22 Suppl B:72B–80B. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ding L and Zhang J: Glucagon-like
peptide-1 activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 33:75–81.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
MacDonald PE, El-Kholy W, Riedel MJ,
Salapatek AM, Light PE and Wheeler MB: The multiple actions of
GLP-1 on the process of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.
Diabetes. 51 Suppl 3:S434–S442. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhong Q, Bollag RJ, Dransfield DT,
Gasalla-Herraiz J, Ding KH, Min L and Isales CM: Glucose-dependent
insulinotropic peptide signaling pathways in endothelial cells.
Peptides. 21:1427–1432. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
D'Angelo G, Lee H and Weiner RI:
CAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits the mitogenic action of
vascular endothelial growth factor and fibroblast growth factor in
capillary endothelial cells by blocking raf activation. J Cell
Biochem. 67:353–366. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ding KH, Zhong Q and Isales CM:
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide stimulates thymidine
incorporation in endothelial cells: Role of endothelin-1. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 285:E390–E396. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eriksson L, Saxelin R, Röhl S, Roy J,
Caidahl K, Nyström T, Hedin U and Razuvaev A: Glucagon like
peptide-1 receptor activation does not affect re-endothelization
but reduces intimal hyperplasia via direct effects on smooth muscle
cells in a nondiabetic model of arterial injury. J Vasc Res.
52:41–52. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ge GH, Dou HJ, Yang SS, Ma JW, Cheng WB,
Qiao ZY, Hou YM and Fang WY: Glucagon-like peptide-1 protects
against cardiac microvascular endothelial cells injured by high
glucose. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 8:73–78. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang D, Luo P, Wang Y, Li W, Wang C, Sun
D, Zhang R, Su T, Ma X, Zeng C, et al: Glucagon-like peptide-1
protects against cardiac microvascular injury in diabetes via a
cAMP/PKA/Rho-dependent mechanism. Diabetes. 62:1697–1708. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lüscher TF and Barton M: Biology of the
endothelium. Clin Cardiol. 20(11 Suppl 2): II3–II10. 1997.
|
|
27
|
Forbes JM and Cooper ME: Mechanisms of
diabetic complications. Physiol Rev. 93:137–188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Deanfield JE, Halcox JP and Rabelink TJ:
Endothelial function and dysfunction: Testing and clinical
relevance. Circulation. 115:1285–1295. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Belz GG and Mohr-Kahaly S: Cacoa and dark
chocolate in cardiovascular prevention? Dtsch Med Wochenschr.
136:2657–2663. 2011.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|