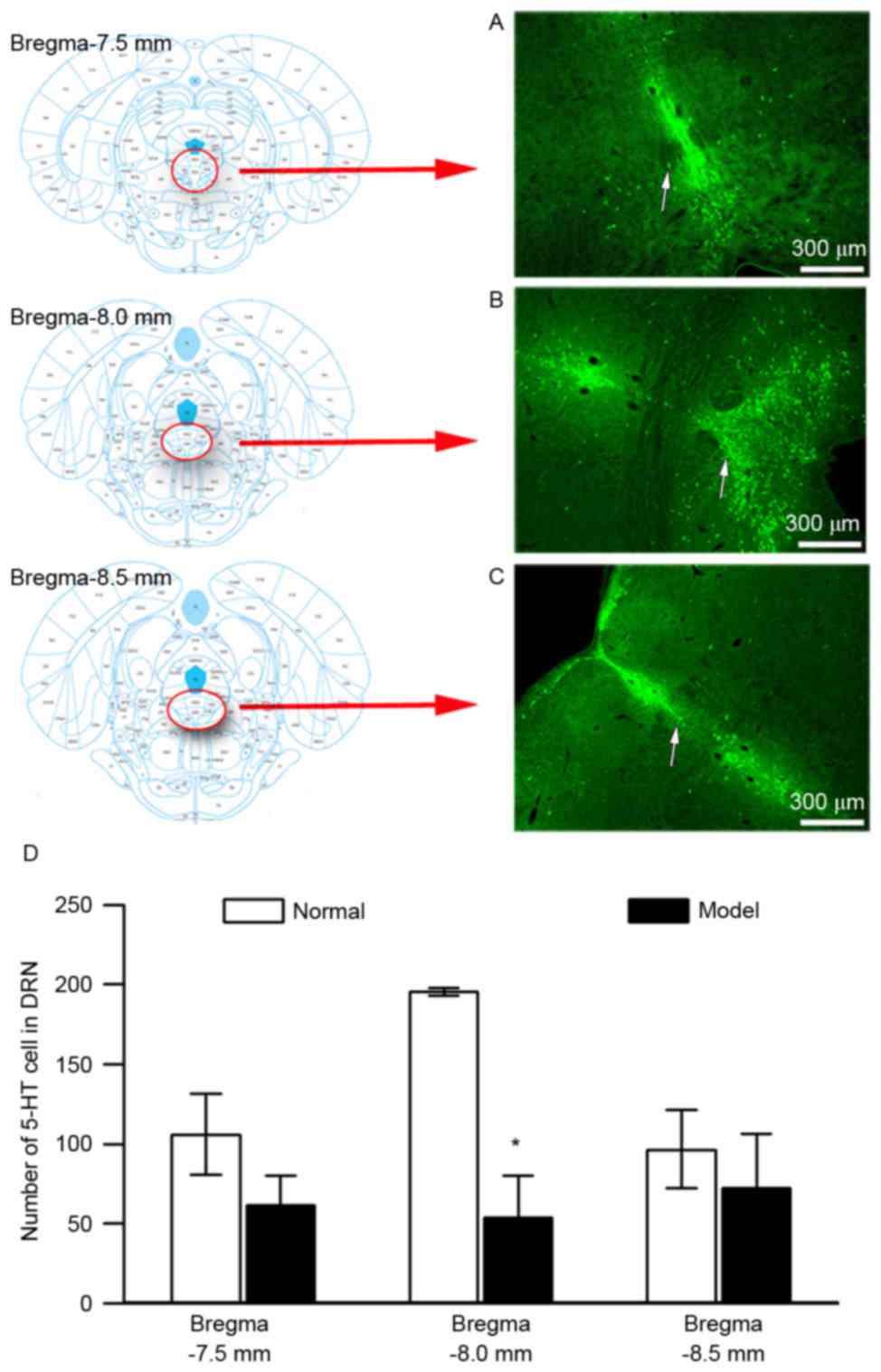
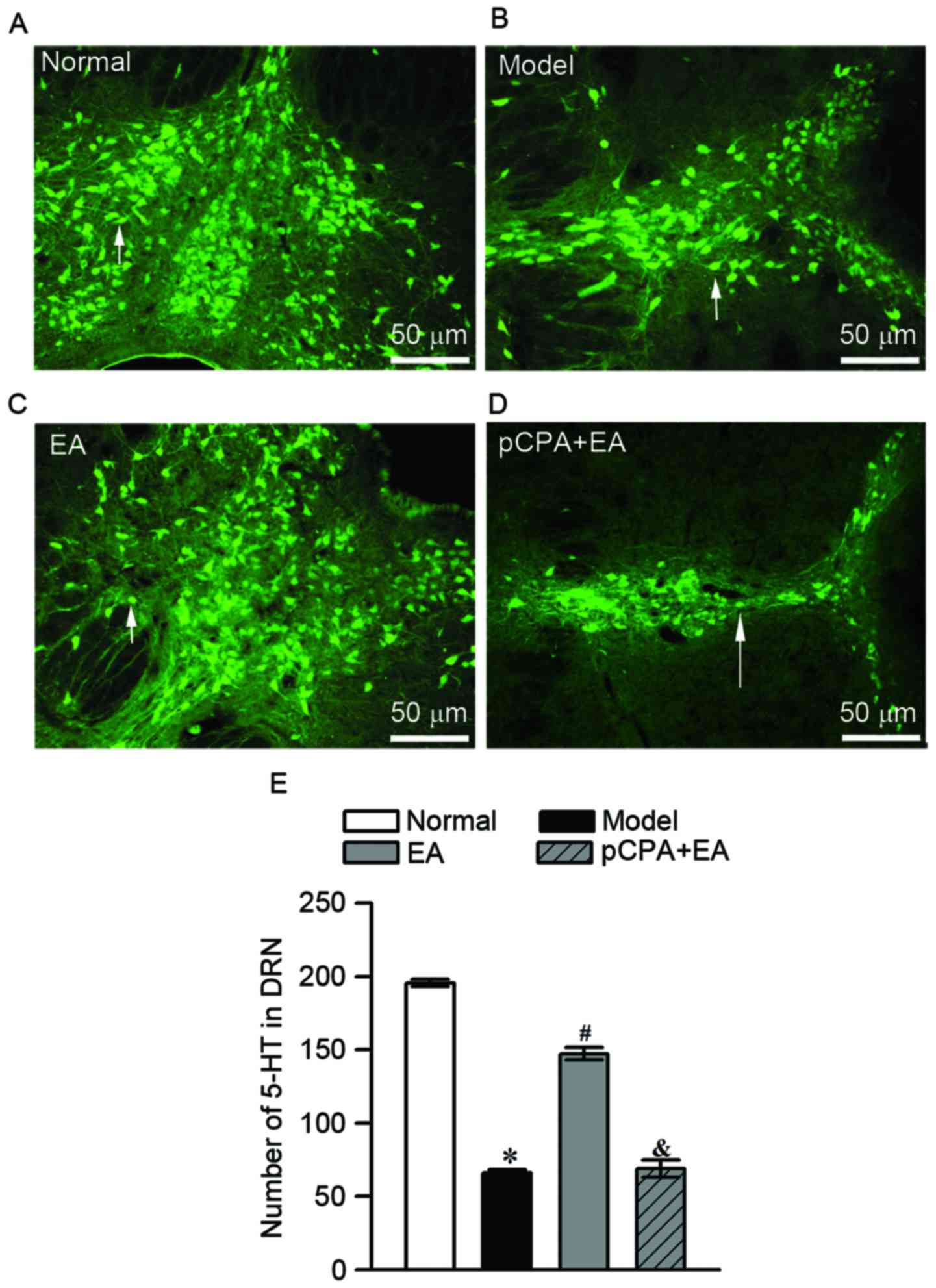
|
1
|
Goldenberg DL: Pain/depression dyad: A key
to a better understanding and treatment of functional somatic
syndromes. Am J Med. 123:675–682. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ohayon MM and Schatzberg AF: Using chronic
pain to predict depressive morbidity in the general population.
Arch Gen Psychiatry. 60:39–47. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Minami M: Neuronal mechanisms underlying
pain-induced negative emotions. Brain nerve. 64:1241–1247. 2012.(In
Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wieser MJ, Gerdes AB, Reicherts P and
Pauli P: Mutual influences of pain and emotional face processing.
Front Psychol. 5:11602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Keefe FJ, Lumley M, Anderson T, Lynch T,
Studts JL and Carson KL: Pain and emotion: New research directions.
J Clin Psychol. 57:587–607. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bellato E, Marini E, Castoldi F,
Barbasetti N, Mattei L, Bonasia DE and Blonna D: Fibromyalgia
syndrome: Etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Pain
Res Treat. 2012:4261302012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Berman BM, Langevin HM, Witt CM and Dubner
R: Acupuncture for chronic low back pain. N Engl J Med.
363:454–461. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin JG, Lo MW, Wen YR, Hsieh CL, Tsai SK
and Sun WZ: The effect of high and low frequency electroacupuncture
in pain after lower abdominal surgery. Pain. 99:509–514. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weber A, Werneck L, Paiva E and Gans P:
Effects of music in combination with vibration in acupuncture
points on the treatment of fibromyalgia. J Altern Complement Med.
21:77–82. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Andersson SA and Holmgren E: Pain
threshold effects of peripheral conditioning stimulationAdvances in
Pain Research Therapy. 1. Raven Press; New York, NY: pp. 761–768.
1976
|
|
11
|
Youn JI, Sung KK, Song BK, Kim M and Lee
S: Effects of electro-acupuncture therapy on post-stroke depression
in patients with different degrees of motor function impairments: A
pilot study. J Phys Ther Sci. 25:725–728. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lumley MA, Cohen JL, Borszcz GS, Cano A,
Radcliffe AM, Porter LS, Schubiner H and Keefe FJ: Pain and
emotion: A biopsychosocial review of recent research. J Clin
Psychol. 67:942–968. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu YY, Jiang YL, He XF, Zhao XY, Shao XM,
Du JY and Fang JQ: Effects of electroacupuncture with dominant
frequency at SP 6 and ST 36 based on meridian theory on
pain-depression dyad in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2015:7328452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ossipov MH, Dussor GO and Porreca F:
Central modulation of pain. J Clin Invest. 120:3779–3787. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Freitas RL, Bassi GS, de Oliveira AM and
Coimbra NC: Serotonergic neurotransmission in the dorsal raphe
nucleus recruits in situ 5-HT (2A/2C) receptors to modulate the
post-ictal antinociception. Exp Neurol. 213:410–418. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lowry CA, Johnson PL, Hay-Schmidt A,
Mikkelsen J and Shekhar A: Modulation of anxiety circuits by
serotonergic systems. Stress. 8:233–246. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lowry CA, Hollis JH, De Vries A, Pan B,
Brunet LR, Hunt JR, Paton JF, van Kampen E, Knight DM, Evans AK, et
al: Identification of an immune-responsive mesolimbocortical
serotonergic system: Potential role in regulation of emotional
behavior. Neuroscience. 146:756–772. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu SF: Pain and analgesiaNeurology. Wei L:
1. 2nd. Fudan University Press; Shanghai: pp. 330–349. 1999, (In
Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Yano T, Kato B, Fukuda F, Shinbara H,
Yoshimoto K, Ozaki A and Kuriyama K: Alterations in the function of
cerebral dopaminergic and serotonergic systems following
electroacupuncture and moxibustion applications: Possible
correlates with their antistress and psychosomatic actions.
Neurochem Res. 29:283–293. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bertholomey ML, Henderson AN, Badia-Elder
NE and Stewart RB: Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-induced reductions in
alcohol intake during continuous access and following alcohol
deprivation are not altered by restraint stress in
alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 97:453–461.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Paxinos G and Watson C: The rat brain in
stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press; San Diego, CA: 1986
|
|
22
|
Thibault K, Calvino B, Rivals I, Marchand
F, Dubacq S, McMahon SB and Pezet S: Molecular mechanisms
underlying the enhanced analgesic effect of oxycodone compared to
morphine in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. PLoS One.
9:e912972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thibault K, Elisabeth B, Sophie D, Claude
FZ, Bernard R and Bernard C: Antinociceptive and anti-allodynic
effects of oral PL37, a complete inhibitor of
enkephalin-catabolizing enzymes, in a rat model of peripheral
neuropathic pain induced by vincristine. Eur J Pharmacol.
600:71–77. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shepherd JK, Grewal SS, Fletcher A, Bill
DJ and Dourish CT: Behavioural and pharmacological characterisation
of the elevated ‘zero-maze’ as an animal model of anxiety.
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 116:56–64. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gould TD, Dao DT and Kovacsics CE: The
open field testMood and anxiety related phenotypes in mice. Gould
TD: Humana Press; Totowa, NJ: pp. 1–20. 2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Singer S, Rossi S, Verzosa S, Hashim A,
Lonow R, Cooper T, Sershen H and Lajtha A: Nicotine-induced changes
in neurotransmitter levels in brain areas associated with cognitive
function. Neurochem Res. 29:1779–1792. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pani AK, Jiao Y, Sample KJ and Smeyne RJ:
Neurochemical measurement of adenosine in discrete brain regions of
five strains of inbred mice. PLoS One. 9:e924222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fukui M, Rodriguiz RM, Zhou J, Jiang SX,
Phillips LE, Caron MG and Wetsel WC: Vmat2 heterozygous mutant mice
display a depressive-like phenotype. J Neurosci. 27:10520–10529.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
de Vry J, Vanmierlo T, Martínez-Martínez
P, Losen M, Temel Y, Boere J, Kenis G, Steckler T, Steinbusch HW,
De Baets M and Prickaerts J: TrkB in the hippocampus and nucleus
accumbens differentially modulates depression-like behavior in
mice. Behav Brain Res. 296:15–25. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bair MJ, Robinson RL, Katon W and Kroenke
K: Depression and pain comorbidity: A literature review. Arch
Intern Med. 163:2433–2445. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Alba-Delgado C, Llorca-Torralba M,
Horrillo I, Ortega JE, Mico JA, Sánchez-Blázquez P, Meana JJ and
Berrocoso E: Chronic pain leads to concomitant noradrenergic
impairment and mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 73:54–62. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rojas-Corrales MO, Berrocoso E,
Gibert-Rahola J and Micó JA: Antidepressant-like effects of
tramadol and other central analgesics with activity on monoamines
reuptake, in helpless rats. Life Sci. 72:143–152. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang N, Shi M, Wang JY and Luo F:
Brain-network mechanisms underlying the divergent effects of
depression on spontaneous versus evoked pain in rats: A multiple
single-unit study. Exp Neurol. 250:165–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Taguchi T, Katanosaka K, Yasui M, Hayashi
K, Yamashita M, Wakatsuki K, Kiyama H, Yamanaka A and Mizumura K:
Peripheral and spinal mechanisms of nociception in a rat
reserpine-induced pain model. Pain. 156:415–427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stevenson GW, Mercer H, Cormier J, Dunbar
C, Benoit L, Adams C, Jezierski J, Luginbuhl A and Bilsky EJ:
Monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis produces
pain-depressed wheel running in rats: Implications for preclinical
behavioral assessment of chronic pain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav.
98:35–42. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stein C, Millan MJ and Herz A: Unilateral
inflammation of the hindpaw in rats as a model of prolonged noxious
stimulation: Alterations in behavior and nociceptive thresholds.
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 31:445–451. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Arora V, Kuhad A, Tiwari V and Chopra K:
Curcumin ameliorates reserpine-induced pain-depression dyad:
Behavioural, biochemical, neurochemical and molecular evidences.
Psychoneuroendocrinology. 36:1570–1581. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chang CY, Guo HR, Tsai WC, Yang KL, Lin
LC, Cheng TJ and Chuu JJ: Subchronic arsenic exposure induces
anxiety-like behaviors in normal mice and enhances depression-like
behaviors in the chemically induced mouse model of depression.
Biomed Res Int. 2015:1590152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ibironke GF and Rasal KS: Forced swimming
stress-related hypoalgesia: Nondependence on the histaminergic
mechanisms. Neurophysiology. 45:340–343. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Łapo IB, Konarzewski M and Sadowski B:
Analgesia induced by swim stress: Interaction between analgesic and
thermoregulatory mechanisms. Pflugers Arch. 446:463–469. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
McDevitta RA and Neumaier JF: Regulation
of dorsal raphe nucleus function by serotonin autoreceptors: A
behavioral perspective. J Chem Neuroanat. 41:234–246. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Han JS: 5-hydroxytryptamineNeuroscience.
Han ZG and Liu Y: 1. 3rd. Peking University Medical Press; Beijing:
pp. 382–351. 2009, (In Chinese).
|
|
43
|
Hale MW, Dady KF, Evans AK and Lowry CA:
Evidence for in vivo thermosensitivity of serotonergic neurons in
the rat dorsal raphe nucleus and raphe pallidus nucleus implicated
in thermoregulatory cooling. Exp Neurol. 227:264–278. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nagakura Y, Oe T, Aoki T and Matsuoka N:
Biogenic amine depletion causes chronic muscular pain and tactile
allodynia accompanied by depression: A putative animal model of
fibromyalgia. Pain. 146:26–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sniezek DP and Siddiqui IJ: Acupuncture
for treating anxiety and depression in women: A clinical systematic
review. Med Acupunct. 25:164–172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Park H, Yoo D, Kwon S, Yoo TW, Park HJ,
Hahm DH, Lee H and Kim ST: Acupuncture stimulation at HT7
alleviates depression-induced behavioral changes via regulation of
the serotonin system in the prefrontal cortex of
maternally-separated rat pups. J Physiol Sci. 62:351–357. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ogata A, Sugenoya J, Nishimura N and
Matsumoto T: Low and high frequency acupuncture stimulation
inhibits mental stress-induced sweating in humans via different
mechanisms. Auton Neurosci. 118:93–101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fung SJ and Chan SH: Primary afferent
depolarization evoked by electroacupuncture in the lumbar cord of
the cat. Exp Neurol. 52:168–176. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Du J, Sun ZL, Jia J, Wang X and Wang XM:
High-frequency electro-acupuncture stimulation modulates
intracerebral γ-aminobutyric acid content in rat model of
Parkinson's disease. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 63:305–310. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rui G, Guangjian Z, Yong W, Jie F, Yanchao
C, Xi J and Fen L: High frequency electro-acupuncture enhances
striatum DAT and D1 receptor expression, but decreases D2 receptor
level in 6-OHDA lesioned rats. Behav Brain Res. 237:263–269. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|