|
1
|
Rosado IR, Lavor MS, Alves EG, Fukushima
FB, Oliveira KM, Silva CM, Caldeira FM, Costa PM and Melo EG:
Effects of methylprednisolone, dantrolene, and their combination on
experimental spinal cord injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4617–4626. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Song Q, Xu R, Zhang Q, Ma M and Zhao X:
Therapeutic effect of transplanting bone mesenchymal stem cells on
the hind limbs' motor function of rats with acute spinal cord
injury. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:262–267. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu C, Huang Z, Jiang H and Shi F: The
sirtuin 3 expression profile is associated with pathological and
clinical outcomes in colon cancer patients. Biomed Res Int.
2014:8712632014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo J, Li Y, He Z, Zhang B, Li Y, Hu J,
Han M, Xu Y, Li Y, Gu J, et al: Targeting endothelin receptors A
and B attenuates the inflammatory response and improves locomotor
function following spinal cord injury in mice. Int J Mol Med.
34:74–82. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
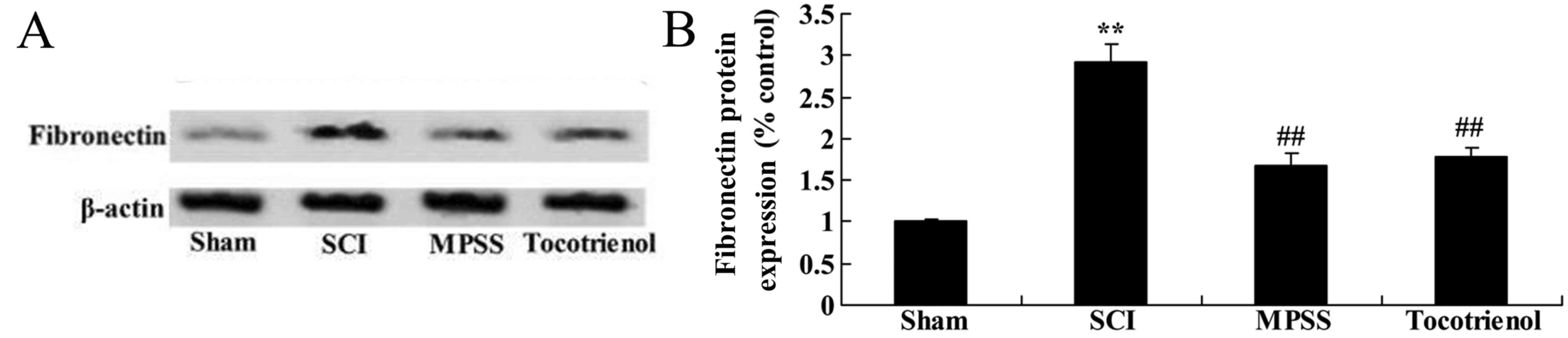
5
|
Grasso G, Meli F, Graziano F, Stagno V,
Imbrucè P, Florena AM, Maugeri R and Iacopino DG: Chronic
inflammation causing spinal cord compression in human
immunodeficiency virus infection. Med Sci Monit. 14:CS134–CS137.
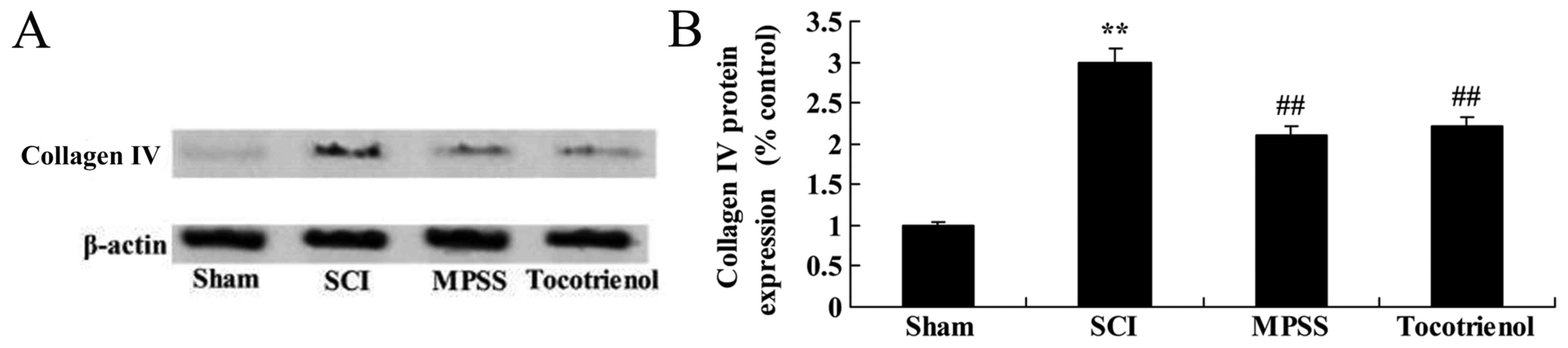
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ji H, Tang H, Lin H, Mao J, Gao L, Liu J
and Wu T: Rho/Rock cross-talks with transforming growth
factor-β/Smad pathway participates in lung fibroblast-myofibroblast
differentiation. Biomed Rep. 2:787–792. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu Z, Yu P, Chen H and Geller HM: Targeted
inhibition of KCa3.1 attenuates TGF-β-induced reactive astrogliosis
through the Smad2/3 signaling pathway. J Neurochem. 130:41–49.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Banh A, Deschamps PA, Gauldie J, Overbeek
PA, Sivak JG and West-Mays JA: Lens-specific expression of TGF-beta
induces anterior subcapsular cataract formation in the absence of
Smad3. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 47:3450–3460. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Loganathan R, Selvaduray KR, Nesaretnam K
and Radhakrishnan AK: Tocotrienols promote apoptosis in human
breast cancer cells by inducing poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
cleavage and inhibiting nuclear factor kappa-B activity. Cell
Prolif. 46:203–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Das S, Mukherjee S, Lekli I, Gurusamy N,
Bardhan J, Raychoudhury U, Chakravarty R, Banerji S, Knowlton AA
and Das DK: Tocotrienols confer resistance to ischemia in
hypercholesterolemic hearts: Insight with genomics. Mol Cell
Biochem. 360:35–45. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zarogoulidis P, Cheva A, Zarampouka K,
Huang H, Li C, Huang Y, Katsikogiannis N and Zarogoulidis K:
Tocopherols and tocotrienols as anticancer treatment for lung
cancer: Future nutrition. J Thorac Dis. 5:349–352. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tanito M, Itoh N, Yoshida Y, Hayakawa M,
Ohira A and Niki E: Distribution of tocopherols and tocotrienols to
rat ocular tissues after topical ophthalmic administration. Lipids.
39:469–474. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sylvester PW, Akl MR, Malaviya A, Parajuli
P, Ananthula S, Tiwari RV and Ayoub NM: Potential role of
tocotrienols in the treatment and prevention of breast cancer.
Biofactors. 40:49–58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang X, Chen C, Ma S, Wang Y, Zhang X and
Su X: Inhibition of monocyte chemoattractant peptide-1 decreases
secondary spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep. 11:4262–4266.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wong WY, Poudyal H, Ward LC and Brown L:
Tocotrienols reverse cardiovascular, metabolic and liver changes in
high carbohydrate, high fat diet-fed rats. Nutrients. 4:1527–1541.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC,
Anderson DK, Faden AI, Gruner JA, Holford TR, Hsu CY, Noble LJ,
Nockels R, et al: MASCIS evaluation of open field locomotor scores:
Effects of experience and teamwork on reliability. Multicenter
Animal Spinal Cord Injury Study. J Neurotrauma. 13:343–359. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Genovese T, Esposito E, Mazzon E, Muià C,
Di Paola R, Meli R, Bramanti P and Cuzzocrea S: Evidence for the
role of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in the
development of spinal cord injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
325:100–114. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Frank J, Chin XW, Schrader C, Eckert GP
and Rimbach G: Do tocotrienols have potential as neuroprotective
dietary factors? Ageing Res Rev. 11:163–180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ahsan H, Ahad A, Iqbal J and Siddiqui WA:
Pharmacological potential of tocotrienols: A review. Nutr Metab
(Lond). 11:522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bao F, Chen Y, Schneider KA and Weaver LC:
An integrin inhibiting molecule decreases oxidative damage and
improves neurological function after spinal cord injury. Exp
Neurol. 214:160–167. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Siddiqui S, Ahsan H, Khan MR and Siddiqui
WA: Protective effects of tocotrienols against lipid-induced
nephropathy in experimental type-2 diabetic rats by modulation in
TGF-β expression. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 273:314–324. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nizar AM, Nazrun AS, Norazlina M, Norliza
M and Ima Nirwana S: Low dose of tocotrienols protects osteoblasts
against oxidative stress. Clin Ter. 162:533–538. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sribnick EA, Wingrave JM, Matzelle DD,
Wilford GG, Ray SK and Banik NL: Estrogen attenuated markers of
inflammation and decreased lesion volume in acute spinal cord
injury in rats. J Neurosci Res. 82:283–293. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tamai H, Sawamura S, Takeda K, Orii R and
Hanaoka K: Anti-allodynic and anti-hyperalgesic effects of
nociceptin receptor antagonist, JTC-801, in rats after spinal nerve
injury and inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. 510:223–228. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
González AM, Garcia T, Samper E, Rickmann
M, Vaquero EC and Molero X: Assessment of the protective effects of
oral tocotrienols in arginine chronic-like pancreatitis. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 301:G846–G855. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yam ML, Hafid SR Abdul, Cheng HM and
Nesaretnam K: Tocotrienols suppress proinflammatory markers and
cyclooxygenase-2 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages. Lipids.
44:787–797. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen G, Zhang Z, Wang S and Lv D: Combined
treatment with FK506 and nerve growth factor for spinal cord injury
in rats. Exp Ther Med. 6:868–872. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu C, Wu W, Zhang B, Xiang J and Zou J:
Temporospatial expression and cellular localization of glutamine
synthetase following traumatic spinal cord injury in adult rats.
Mol Med Rep. 7:1431–1436. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qureshi AA, Reis JC, Papasian CJ, Morrison
DC and Qureshi N: Tocotrienols inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced
pro-inflammatory cytokines in macrophages of female mice. Lipids
Health Dis. 9:1432010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang X, Chen W, Liu W, Wu J, Shao Y and
Zhang X: The role of thrombospondin-1 and transforming growth
factor-beta after spinal cord injury in the rat. J Clin Neurosci.
16:818–821. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park SM, Jung JS, Jang MS, Kang KS and
Kang SK: Transforming growth factor-beta1 regulates the fate of
cultured spinal cord-derived neural progenitor cells. Cell Prolif.
41:248–264. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Andrew JG, Hoyland J, Andrew SM, Freemont
AJ and Marsh D: Demonstration of TGF-beta 1 mRNA by in situ
hybridization in normal human fracture healing. Calcif Tissue Int.
52:74–78. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gensel JC and Zhang B: Macrophage
activation and its role in repair and pathology after spinal cord
injury. Brain Res. 1619:1–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kandasamy M, Lehner B, Kraus S, Sander PR,
Marschallinger J, Rivera FJ, Trümbach D, Ueberham U, Reitsamer HA,
Strauss O, et al: TGF-beta signalling in the adult neurogenic niche
promotes stem cell quiescence as well as generation of new neurons.
J Cell Mol Med. 18:1444–1459. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bachman H, Nicosia J, Dysart M and Barker
TH: Utilizing fibronectin integrin-binding specificity to control
cellular responses. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 4:501–511. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhu Y, Soderblom C, Trojanowsky M, Lee DH
and Lee JK: Fibronectin matrix assembly after spinal cord injury. J
Neurotrauma. 32:1158–1167. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xia M and Zhu Y: Fibronectin enhances
spinal cord astrocyte proliferation by elevating P2Y1 receptor
expression. J Neurosci Res. 92:1078–1090. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
King VR, Hewazy D, Alovskaya A, Phillips
JB, Brown RA and Priestley JV: The neuroprotective effects of
fibronectin mats and fibronectin peptides following spinal cord
injury in the rat. Neuroscience. 168:523–530. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xia M: Fibronectin blocks the recovery of
spinal cord injury by increasing P2Y1 receptor level. Int J Dev
Neurosci. 47:20–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Koopmans G, Hasse B and Sinis N: Chapter
19: The role of collagen in peripheral nerve repair. Int Rev
Neurobiol. 87:363–379. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liesi P and Kauppila T: Induction of type
IV collagen and other basement-membrane-associated proteins after
spinal cord injury of the adult rat may participate in formation of
the glial scar. Exp Neurol. 173:31–45. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|