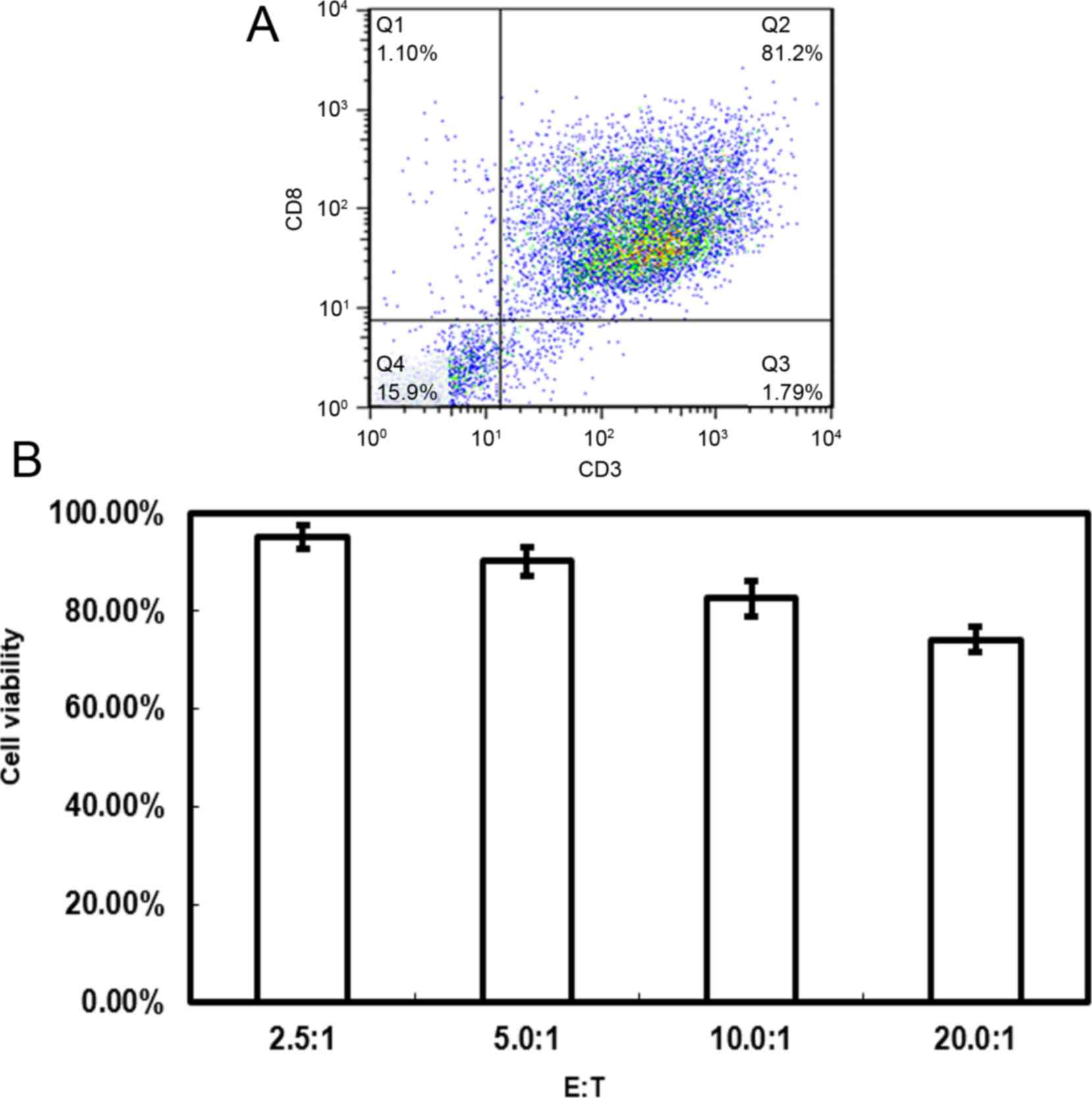
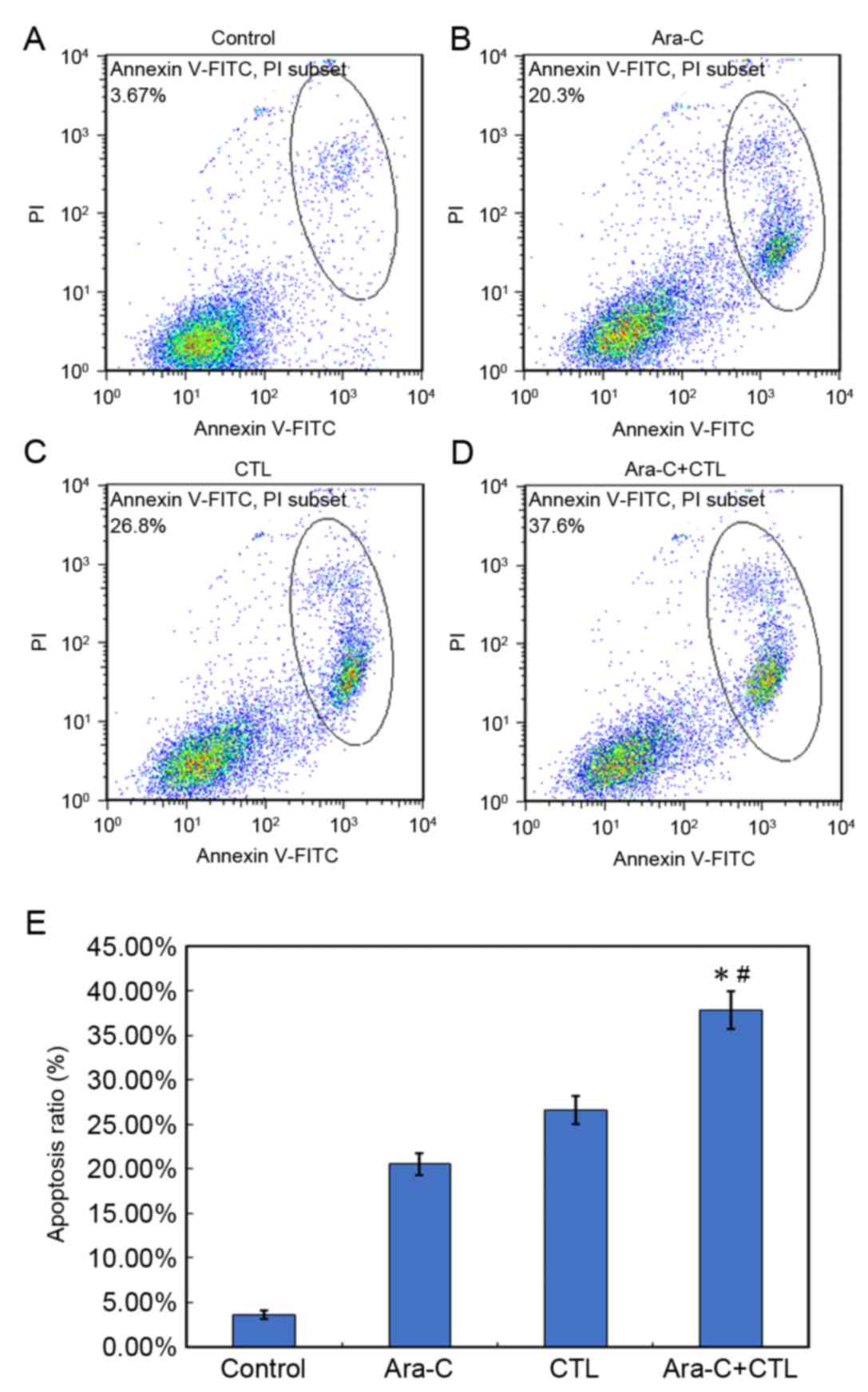
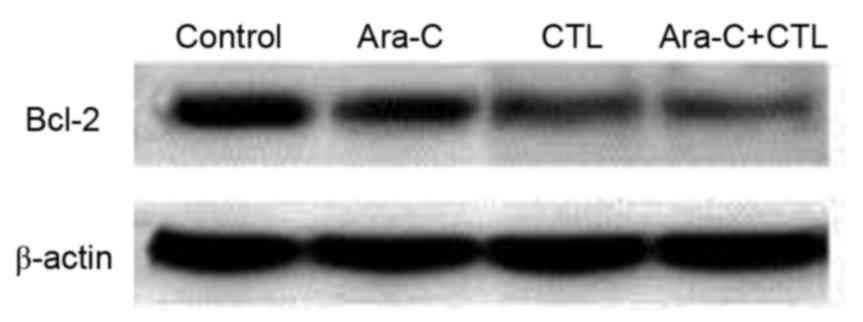
|
1
|
Rubnitz JE, Inaba H, Dahl G, Ribeiro RC,
Bowman WP, Taub J, Pounds S, Razzouk BI, Lacayo NJ, Cao X, et al:
Minimal residual disease-directed therapy for childhood acute
myeloid leukaemia: Results of the AML02 multicentre trial. Lancet
Oncol. 11:543–552. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Niewerth D, Creutzig U, Bierings MB and
Kaspers GJ: A review on allogeneic stem cell transplantation for
newly diagnosed pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
116:2205–2214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Couzin-Frankel J: Breakthrough of the year
2013. Cancer immunotherapy. Science. 342:1432–1433. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Greiner J, Schmitt M, Li L, Giannopoulos
K, Bosch K, Schmitt A, Dohner K, Schlenk RF, Pollack JR, Dohner H
and Bullinger L: Expression of tumor-associated antigens in acute
myeloid leukemia: Implications for specific immunotherapeutic
approaches. Blood. 108:4109–4117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Castella B, Vitale C, Coscia M and Massaia
M: Vγ9Vδ2 T cell-based immunotherapy in hematological malignancies:
From bench to bedside. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:2419–2432. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Van Driessche A, Berneman ZN and Van
Tendeloo VF: Active specific immunotherapy targeting the wilms'
tumor protein 1 (WT1) for patients with hematological malignancies
and solid tumors: Lessons from early clinical trials. Oncologist.
17:250–259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brossart P, Schneider A, Dill P, Schammann
T, Grünebach F, Wirths S, Kanz L, Bühring HJ and Brugger W: The
epithelial tumor antigen MUC1 is expressed in hematological
malignancies and is recognized by MUC1-specific cytotoxic
T-lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 61:6846–6850. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Theobald M, Biggs J, Hernández J,
Lustgarten J, Labadie C and Sherman LA: Tolerance to p53 by A2.
1-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 185:833–841. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Burstein HJ and Schwartz RS: Molecular
origins of cancer. N Engl J Med. 358:5272008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Berger C, Turtle CJ, Jensen MC and Riddell
SR: Adoptive transfer of virus-specific and tumor-specific T cell
immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 21:224–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brimnes MK, Gang AO, Donia M, Straten P
Thor, Svane IM and Hadrup SR: Generation of autologous
tumor-specific T cells for adoptive transfer based on vaccination,
in vitro restimulation and CD3/CD28 dynabead-induced T cell
expansion. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 61:1221–1231. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hirohashi Y, Torigoe T, Inoda S, Morita R,
Kochin V and Sato N: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes: Sniping cancer stem
cells. Oncoimmunology. 1:123–125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Falkenburg JF, Wafelman AR, Joosten P,
Smit WM, van Bergen CA, Bongaerts R, Lurvink E, van der Hoorn M,
Kluck P, Landegent JE, et al: Complete remission of accelerated
phase chronic myeloid leukemia by treatment with leukemia-reactive
cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Blood. 94:1201–1208. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yee C, Thompson J, Byrd D, Riddell SR,
Roche P, Celis E and Greenberg PD: Adoptive T cell therapy using
antigen-specific CD8+ T cell clones for the treatment of patients
with metastatic melanoma: In vivo persistence, migration, and
antitumor effect of transferred T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:pp. 16168–16173. 2002; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bracci L, Schiavoni G, Sistigu A and
Belardelli F: Immune-based mechanisms of cytotoxic chemotherapy:
Implications for the design of novel and rationale-based combined
treatments against cancer. Cell Death Differ. 21:15–25. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ramakrishnan R, Huang C, Cho HI, Lloyd M,
Johnson J, Ren X, Altiok S, Sullivan D, Weber J, Celis E and
Gabrilovich DI: Autophagy induced by conventional chemotherapy
mediates tumor cell sensitivity to immunotherapy. Cancer Res.
72:5483–5493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ramakrishnan R, Assudani D, Nagaraj S,
Hunter T, Cho HI, Antonia S, Altiok S, Celis E and Gabrilovich DI:
Chemotherapy enhances tumor cell susceptibility to CTL-mediated
killing during cancer immunotherapy in mice. J Clin Invest.
120:1111–1124. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shurin GV, Tourkova IL, Kaneno R and
Shurin MR: Chemotherapeutic agents in noncytotoxic concentrations
increase antigen presentation by dendritic cells via an
IL-12-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 183:137–144. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
English D and Andersen BR: Single-step
separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear
leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J
Immunol Methods. 5:249–252. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Deng R, Wang SM, Yin T, Ye TH, Shen GB, Li
L, Zhao JY, Sang YX, Duan XG and Wei YQ: Inhibition of tumor growth
and alteration of associated macrophage cell type by an HO-1
inhibitor in breast carcinoma-bearing mice. Oncol Res. 20:473–482.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kruger NJ: The Bradford Method for Protein
Quantitation. Methods Mol Biol. 32:9–15. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garnett CT, Schlom J and Hodge JW:
Combination of docetaxel and recombinant vaccine enhances T-cell
responses and antitumor activity: Effects of docetaxel on immune
enhancement. Clin Cancer Res. 14:3536–3544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gelbard A, Garnett CT, Abrams SI, Patel V,
Gutkind JS, Palena C, Tsang KY, Schlom J and Hodge JW: Combination
chemotherapy and radiation of human squamous cell carcinoma of the
head and neck augments CTL-mediated lysis. Clin Cancer Res.
12:1897–1905. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gameiro SR, Caballero JA, Higgins JP,
Apelian D and Hodge JW: Exploitation of differential homeostatic
proliferation of T-cell subsets following chemotherapy to enhance
the efficacy of vaccine-mediated antitumor responses. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 60:1227–1242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nowak AK, Robinson BW and Lake RA: Synergy
between chemotherapy and immunotherapy in the treatment of
established murine solid tumors. Cancer Res. 63:4490–4496.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hill SC, Youde SJ, Man S, Teale GR,
Baxendale AJ, Hislop A, Davies CC, Luesley DM, Blom AM, Rickinson
AB, et al: Activation of CD40 in cervical carcinoma cells
facilitates CTL responses and augments chemotherapy-induced
apoptosis. J Immunol. 174:41–50. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vanneman M and Dranoff G: Combining
immunotherapy and targeted therapies in cancer treatment. Nat Rev
Cancer. 12:237–251. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang T and Herlyn D: Combination of
active specific immunotherapy or adoptive antibody or lymphocyte
immunotherapy with chemotherapy in the treatment of cancer. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 58:475–492. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mardiros A, Dos Santos C, McDonald T,
Brown CE, Wang X, Budde LE, Hoffman L, Aguilar B, Chang WC,
Bretzlaff W, et al: T cells expressing CD123-specific chimeric
antigen receptors exhibit specific cytolytic effector functions and
antitumor effects against human acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
122:3138–3148. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang QS, Wang Y, Lv HY, Han QW, Fan H, Guo
B, Wang LL and Han WD: Treatment of CD33-directed chimeric antigen
receptor-modified T cells in one patient with relapsed and
refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Ther. 23:184–191. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|