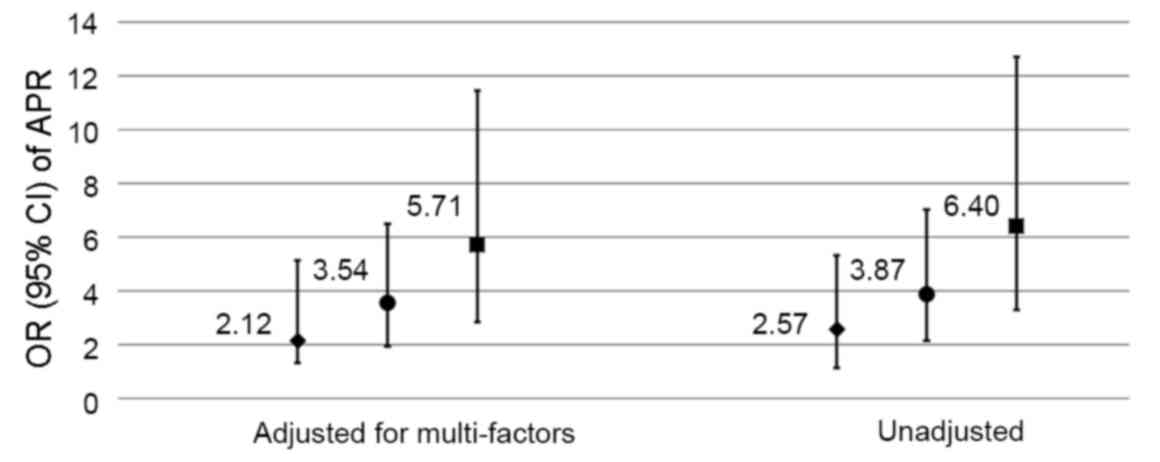
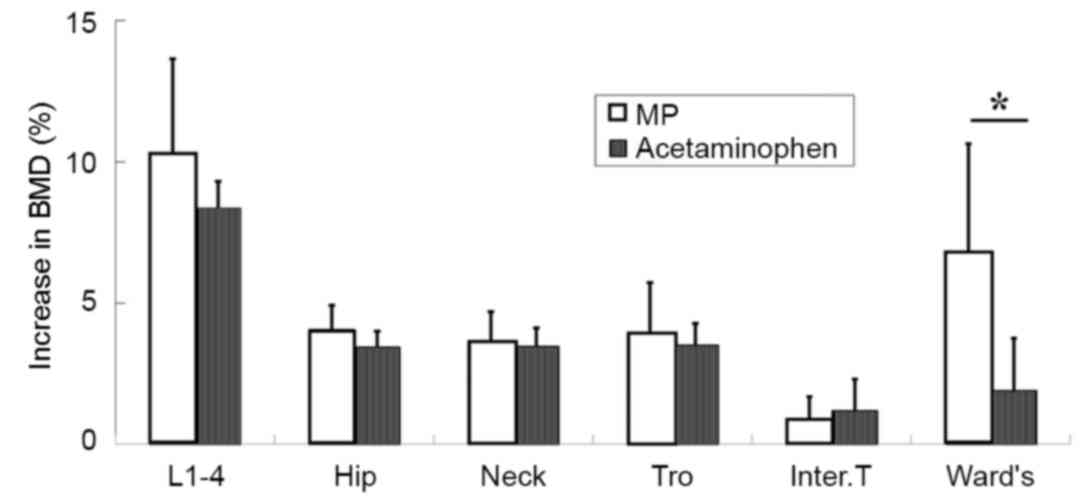
|
1
|
Stafford RS, Drieling RL and Hersh AL:
National trends in osteoporosis visits and osteoporosis treatment,
1988–2003. Arch Intern Med. 164:1525–1530. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nancollas GH, Tang R, Phipps RJ, Henneman
Z, Gulde S, Wu W, Mangood A, Russell RG and Ebetino FH: Novel
insights into actions of bisphosphonates on bone: Differences in
interactions with hydroxyapatite. Bone. 38:617–627. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gasser JA, Ingold P, Venturiere A, Shen V
and Green JR: Long-term protective effects of zoledronic acid on
cancellous and cortical bone in the ovariectomized rat. J Bone
Miner Res. 23:544–551. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Saag K, Lindsay R, Kriegman A, Beamer E
and Zhou W: A single zoledronic acid infusion reduces bone
resorption markers more rapidly than weekly oral alendronate in
postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. Bone.
40:1238–1243. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lyles KW, Colón-Emeric CS, Magaziner JS,
Adachi JD, Pieper CF, Mautalen C, Hyldstrup L, Recknor C,
Nordsletten L, Moore KA, et al: Zoledronic acid and clinical
fractures and mortality after hip fracture. N Engl J Med.
357:1799–1809. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Black DM, Delmas PD, Eastell R, Reid IR,
Boonen S, Cauley JA, Cosman F, Lakatos P, Leung PC, Man Z, et al:
Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatment of postmenopausal
osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 356:1809–1822. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Reid IR, Gamble GD, Mesenbrink P, Lakatos
P and Black DM: Characterization of and risk factors for the
acute-phase response after zoledronic acid. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 95:4380–4387. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wark JD, Bensen W, Recknor C, Ryabitseva
O, Chiodo J III, Mesenbrink P and de Villiers TJ: Treatment with
acetaminophen/paracetamol or ibuprofen alleviates post-dose
symptoms related to intravenous infusion with zoledronic acid 5 mg.
Osteoporos Int. 23:503–512. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schweitzer DH, Oostendorp-van de Ruit M,
van der Pluijm G, Löwik CW and Papapoulos SE: Interleukin-6 and the
acute phase response during treatment of patients with Paget's
disease with the nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate
dimethylaminohydroxypropylidene bisphosphonate. J Bone Miner Res.
10:956–962. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sauty A, Pecherstorfer M, Zimmer-Roth I,
Fioroni P, Juillerat L, Markert M, Ludwig H, Leuenberger P,
Burckhardt P and Thiebaud D: Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis
factor alpha levels after bisphosphonates treatment in vitro and in
patients with malignancy. Bone. 18:133–139. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thiébaud D, Sauty A, Burckhardt P,
Leuenberger P, Sitzler L, Green JR, Kandra A, Zieschang J and de
Palacios P Ibarra: An in vitro and in vivo study of cytokines in
the acute-phase response associated with bisphosphonates. Calcif
Tissue Int. 61:386–392. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dicuonzo G, Vincenzi B, Santini D,
Avvisati G, Rocci L, Battistoni F, Gavasci M, Borzomati D, Coppola
R and Tonini G: Fever after zoledronic acid administration is due
to increase in TNF-alpha and IL-6. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
23:649–654. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thompson K and Rogers MJ: Statins prevent
bisphosphonate-induced gamma, delta-T-cell proliferation and
activation in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 19:278–288. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sato K, Kimura S, Segawa H, Yokota A,
Matsumoto S, Kuroda J, Nogawa M, Yuasa T, Kiyono Y, Wada H and
Maekawa T: Cytotoxic effects of gammadelta T cells expanded ex vivo
by a third generation bisphosphonate for cancer immunotherapy. Int
J Cancer. 116:94–99. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Galluzzo S, Santini D, Vincenzi B, Caccamo
N, Meraviglia F, Salerno A, Dieli F and Tonini G: Immunomodulating
role of bisphosphonates on human gamma delta T cells: An intriguing
and promising aspect of their antitumour activity. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 11:941–954. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rossini M, Adami S, Viapiana O, Ortolani
R, Vella A, Fracassi E and Gatti D: Circulating γδ T cells and the
risk of acute-phase response after zoledronic acid administration.
J Bone Miner Res. 27:227–230. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
NIH Consensus Development Panel on
Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy: Osteoporosis
prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. JAMA. 285:785–795. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Copp DH: Simple and precise micromethod
for EDTA titration of calcium. J Lab Clin Med. 61:1029–1037.
1963.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
2003 Medical dictionary for regulatory
activities (MedDRA). Reston, VA: Northrop Grumman;
|
|
20
|
Holick MF: Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J
Med. 357:266–281. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Modi H, Chung KJ, Yoon HS, Yoo HS and Yoo
JH: Local application of low-dose Depo-Medrol is effective in
reducing immediate postoperative back pain. Int Orthop. 33:737–743.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gabay C and Kushner I: Acute-phase
proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J
Med. 340:448–454. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Desborough JP: The stress response to
trauma and surgery. Br J Anaesth. 85:109–117. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ceciliani F, Giordano A and Spagnolo V:
The systemic reaction during inflammation: The acute-phase
proteins. Protein Pept Lett. 9:211–223. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Penna G, Roncari A, Amuchastegui S, Daniel
KC, Berti E, Colonna M and Adorini L: Expression of the inhibitory
receptor ILT3 on dendritic cells is dispensable for induction of
CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Blood.
106:3490–3497. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen L, Cencioni MT, Angelini DF,
Borsellino G, Battistini L and Brosnan CF: Transcriptional
profiling of gamma delta T cells identifies a role for vitamin D in
the immunoregulation of the V gamma 9V delta 2 response to
phosphate-containing ligands. J Immunol. 174:6144–6152. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bertoldo F, Pancheri S, Zenari S, Boldini
S, Giovanazzi B, Zanatta M, Valenti MT, Carbonare L Dalle and Lo
Cascio V: Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels modulate the acute-phase
response associated with the first nitrogen-containing
bisphosphonate infusion. J Bone Miner Res. 25:447–454. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reid DM, Devogelaer JP, Saag K, Roux C,
Lau CS, Reginster JY, Papanastasiou P, Ferreira A, Hartl F, Fashola
T, et al: Zoledronic acid and risedronate in the prevention and
treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (HORIZON): A
multicentre, double-blind, double-dummy, randomised controlled
trial. Lancet. 373:1253–1263. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Grossman JM, Gordon R, Ranganath VK, Deal
C, Caplan L, Chen W, Curtis JR, Furst DE, McMahon M, Patkar NM, et
al: American College of Rheumatology 2010 recommendations for the
prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.
Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 62:1515–1526. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Siris ES, Harris ST, Rosen CJ, Barr CE,
Arvesen JN, Abbott TA and Silverman S: Adherence to bisphosphonate
therapy and fracture rates in osteoporotic women: Relationship to
vertebral and nonvertebral fractures from 2 US claims databases.
Mayo Clin Proc. 81:pp. 1013–1022. 2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cramer JA, Gold DT, Silverman SL and
Lewiecki EM: A systematic review of persistence and compliance with
bisphosphonates for osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 18:1023–1031.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Briesacher BA, Andrade SE, Yood RA and
Kahler KH: Consequences of poor compliance with bisphosphonates.
Bone. 41:882–887. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Seeman E, Compston J, Adachi J, Brandi ML,
Cooper C, Dawson-Hughes B, Jönsson B, Pols H and Cramer JA:
Non-compliance: The Achilles' heel of anti-fracture efficacy.
Osteoporos Int. 18:711–719. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
McClung M, Recker R, Miller P, Fiske D,
Minkoff J, Kriegman A, Zhou W, Adera M and Davis J: Intravenous
zoledronic acid 5 mg in the treatment of postmenopausal women with
low bone density previously treated with alendronate. Bone.
41:122–128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bhandari M, Bajammal S, Guyatt GH,
Griffith L, Busse JW, Schünemann H and Einhorn TA: Effect of
bisphosphonates on periprosthetic bone mineral density after total
joint arthroplasty. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
87:293–301. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Friedl G, Radl R, Stihsen C, Rehak P,
Aigner R and Windhager R: The effect of a single infusion of
zoledronic acid on early implant migration in total hip
arthroplasty. A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 91:274–281. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eriksen EF, Lyles KW, Colón-Emeric CS,
Pieper CF, Magaziner JS, Adachi JD, Hyldstrup L, Recknor C,
Nordsletten L, Lavecchia C, et al: Antifracture efficacy and
reduction of mortality in relation to timing of the first dose of
zoledronic acid after hip fracture. J Bone Miner Res. 24:1308–1313.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Prieto-Alhambra D, Javaid MK, Judge A,
Murray D, Carr A, Cooper C and Arden NK: Association between
bisphosphonate use and implant survival after primary total
arthroplasty of the knee or hip: Population based retrospective
cohort study. BMJ. 343:d72222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li C, Wang HR, Li XL, Zhou XG and Dong J:
The relation between zoledronic acid infusion and interbody fusion
in patients undergoing transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion
surgery. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 154:731–738. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Park YS, Kim HS, Baek SW, Kong DY and Ryu
JA: The effect of zoledronic acid on the volume of the fusion-mass
in lumbar spinal fusion. Clin Orthop Surg. 5:292–297. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen F, Dai Z, Kang Y, Lv G, Keller ET and
Jiang Y: Effects of zoledronic acid on bone fusion in osteoporotic
patients after lumbar fusion. Osteoporos Int. 27:1469–1476. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li YT, Cai HF and Zhang ZL: Timing of the
initiation of bisphosphonates after surgery for fracture healing: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled
trials. Osteoporos Int. 26:431–441. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xue D, Li F, Chen G, Yan S and Pan Z: Do
bisphosphonates affect bone healing? A meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 9:452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yasen M, Li X, Jiang L, Yuan W, Che W and
Dong J: Effect of zoledronic acid on spinal fusion outcomes in an
ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis. J Orthop Res.
33:1297–1304. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|