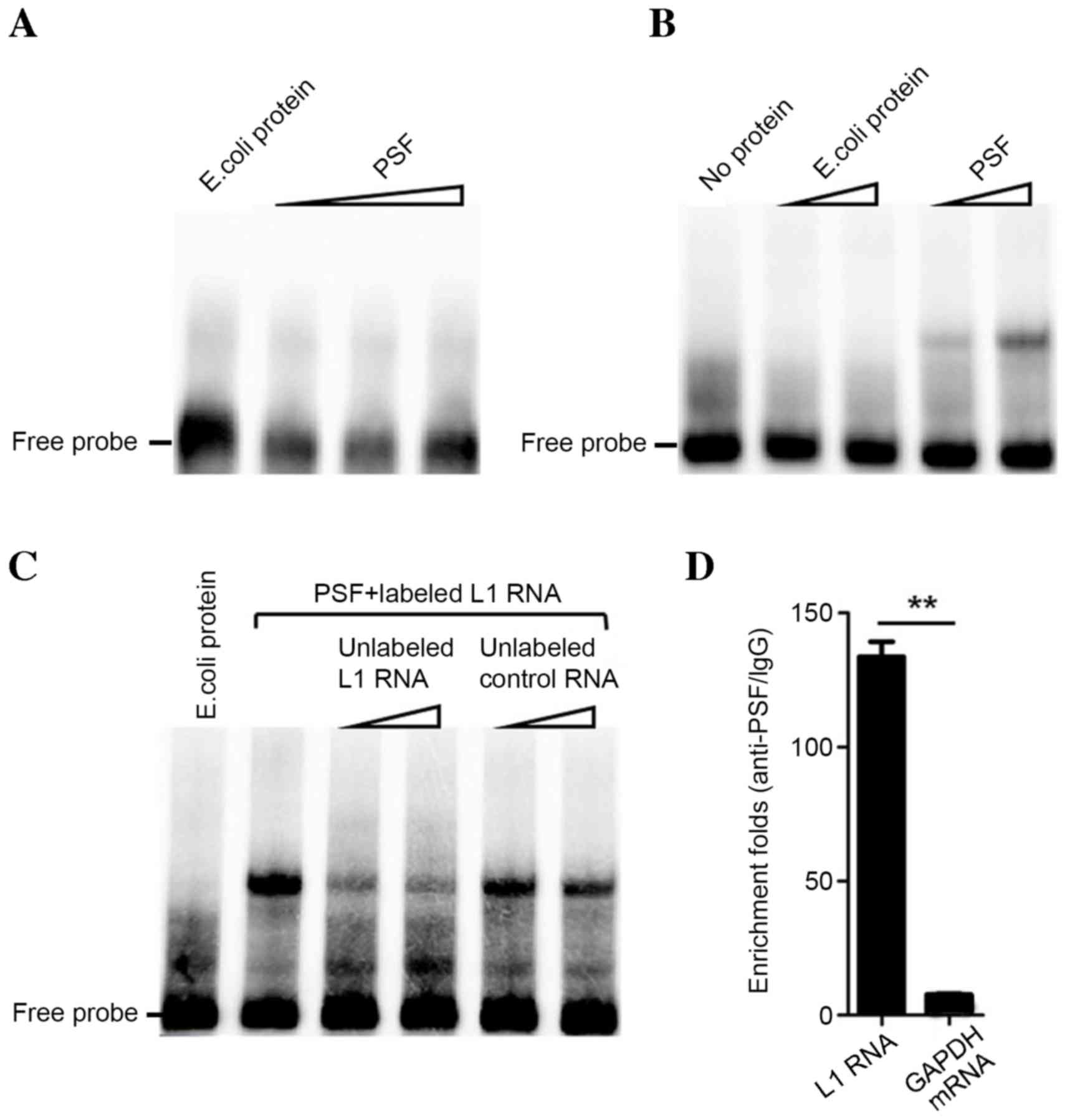
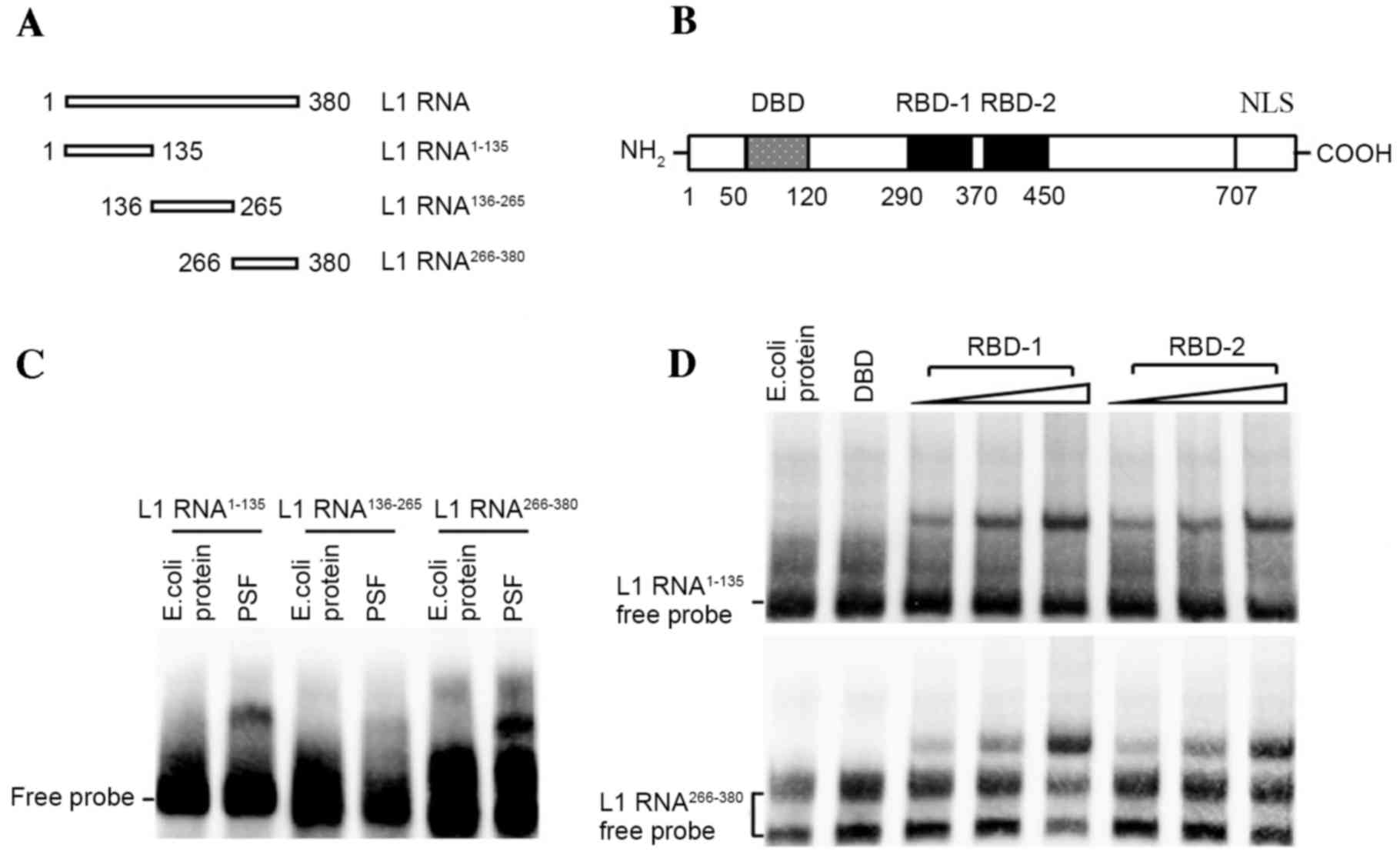
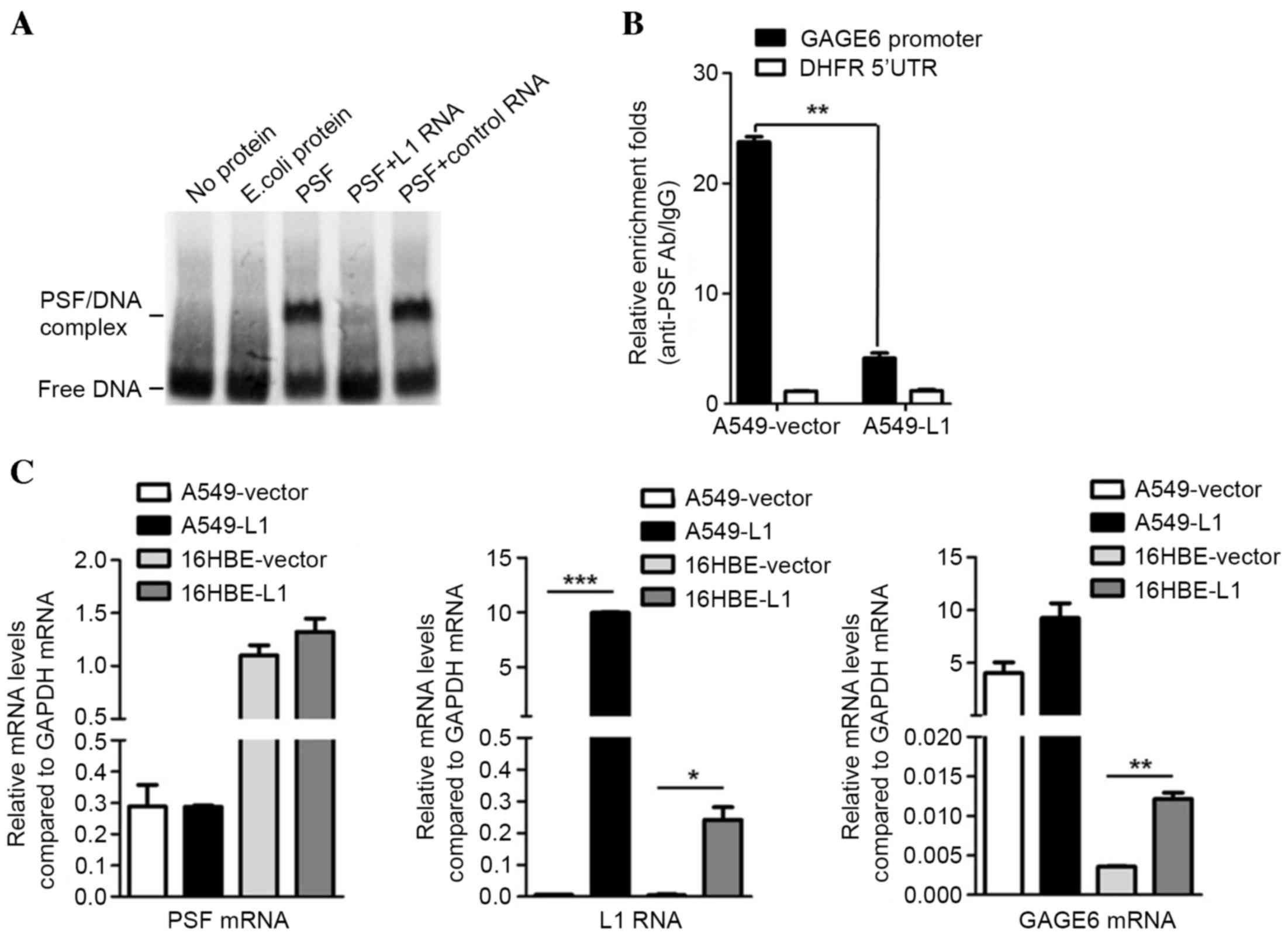
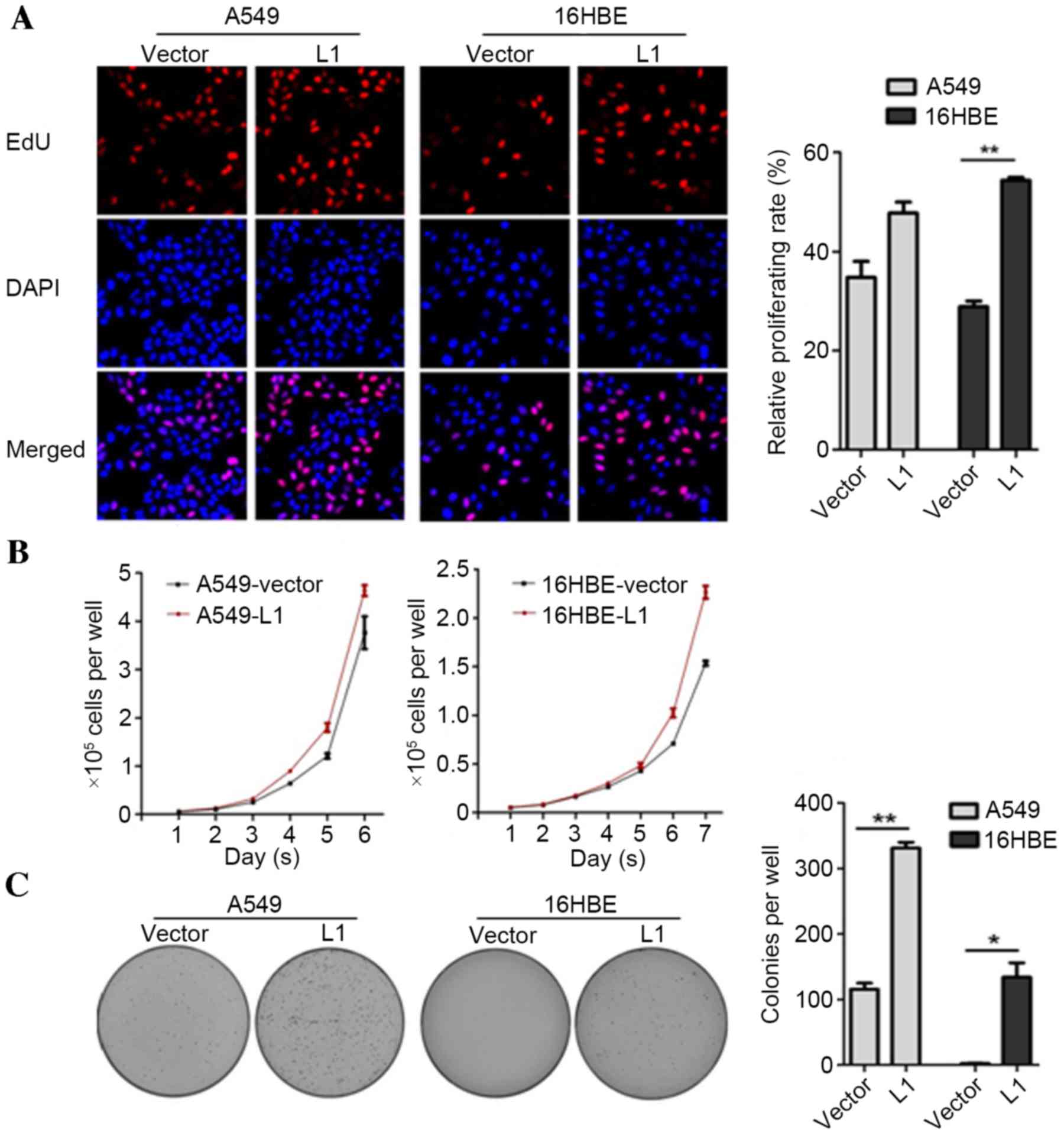
|
1
|
Guo XL, Li D, Hu F, Song JR, Zhang SS,
Deng WJ, Sun K, Zhao QD, Xie XQ, Song YJ, et al: Targeting
autophagy potentiates chemotherapy-induced apoptosis and
proliferation inhibition in hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
320:171–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ng J and Wu J: Hepatitis B- and hepatitis
C-related hepatocellular carcinomas in the United States:
similarities and differences. Hepat Mon. 12:e76352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McGivern DR and Lemon SM: Virus-specific
mechanisms of carcinogenesis in hepatitis C virus associated liver
cancer. Oncogene. 30:1969–1983. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tsai WL and Chung RT: Viral
hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene. 29:2309–2324. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kowalska E, Ripperger JA, Muheim C, Maier
B, Kurihara Y, Fox AH, Kramer A and Brown SA: Distinct roles of
DBHS family members in the circadian transcriptional feedback loop.
Mol Cell Biol. 32:4585–4594. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lowery LA, Rubin J and Sive H:
Whitesnake/sfpq is required for cell survival and neuronal
development in the zebrafish. Dev Dyn. 236:1347–1357. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Patton JG, Porro EB, Galceran J, Tempst P
and Nadal-Ginard B: Cloning and characterization of PSF, a novel
pre-mRNA splicing factor. Genes Dev. 7:393–406. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Urban RJ, Bodenburg Y, Kurosky A, Wood TG
and Gasic S: Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein-associated
splicing factor is a negative regulator of transcriptional activity
of the porcine P450scc insulin-like growth factor response element.
Mol Endocrinol. 14:774–782. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Urban RJ, Bodenburg YH and Wood TG: NH2
terminus of PTB-associated splicing factor binds to the porcine
P450scc IGF-I response element. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
283:E423–E427. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li L, Feng TT, Lian Y, Zhang G, Garen A
and Song X: Role of human noncoding RNAs in the control of
tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:pp. 12956–12961. 2009;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kazazian HH Jr: Mobile elements: Drivers
of genome evolution. Science. 303:1626–1632. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aporntewan C, Phokaew C, Piriyapongsa J,
Ngamphiw C, Ittiwut C, Tongsima S and Mutirangura A:
Hypomethylation of intragenic LINE-1 represses transcription in
cancer cells through AGO2. PLoS One. 6:e179342011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chowdhury S, Cleves MA, MacLeod SL, James
SJ, Zhao W and Hobbs CA: Maternal DNA hypomethylation and
congenital heart defects. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol.
91:69–76. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tangkijvanich P, Hourpai N, Rattanatanyong
P, Wisedopas N, Mahachai V and Mutirangura A: Serum LINE-1
hypomethylation as a potential prognostic marker for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta. 379:127–133. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu HC, Wang Q, Yang HI, Tsai WY, Chen CJ
and Santella RM: Global DNA methylation levels in white blood cells
as a biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma risk: A nested
case-control study. Carcinogenesis. 33:1340–1345. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lau CC, Sun T, Ching AK, He M, Li JW, Wong
AM, Co NN, Chan AW, Li PS, Lung RW, et al: Viral-human chimeric
transcript predisposes risk to liver cancer development and
progression. Cancer Cell. 25:335–349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Song X, Sun Y and Garen A: Roles of PSF
protein and VL30 RNA in reversible gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 102:pp. 12189–12193. 2005; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang G, Cui Y, Zhang GF, Garen A and Song
X: Regulation of proto-oncogene transcription, cell proliferation,
and tumorigenesis in mice by PSF protein and a VL30 noncoding RNA.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:pp. 16794–16798. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang YJ, Wu HC, Yazici H, Yu MW, Lee PH
and Santella RM: Global hypomethylation in hepatocellular carcinoma
and its relationship to aflatoxin B(1) exposure. World J Hepatol.
4:169–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ogino S, Kawasaki T, Nosho K, Ohnishi M,
Suemoto Y, Kirkner GJ and Fuchs CS: LINE-1 hypomethylation is
inversely associated with microsatellite instability and CpG island
methylator phenotype in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer.
122:2767–2773. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Goel A, Xicola RM, Nguyen TP, Doyle BJ,
Sohn VR, Bandipalliam P, Reyes J, Cordero C, Balaguer F, Castells
A, et al: Aberrant DNA methylation in hereditary nonpolyposis
colorectal cancer without mismatch repair deficiency.
Gastroenterology. 138:1854–1862. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sunami E, De Maat M, Vu A, Turner RR and
Hoon DS: LINE-1 hypomethylation during primary colon cancer
progression. PLoS One. 6:e188842011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Eynde B, Peeters O, De Backer O, Gaugler
B, Lucas S and Boon T: A new family of genes coding for an antigen
recognized by autologous cytolytic T lymphocytes on a human
melanoma. J Exp Med. 182:689–698. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Trivedi M, Shah J, Hodgson N, Byun HM and
Deth R: Morphine induces redox-based changes in global DNA
methylation and retrotransposon transcription by inhibition of
excitatory amino acid transporter type 3-mediated cysteine uptake.
Mol Pharmacol. 85:747–757. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Burns KH and Boeke JD: Human transposon
tectonics. Cell. 149:740–752. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|