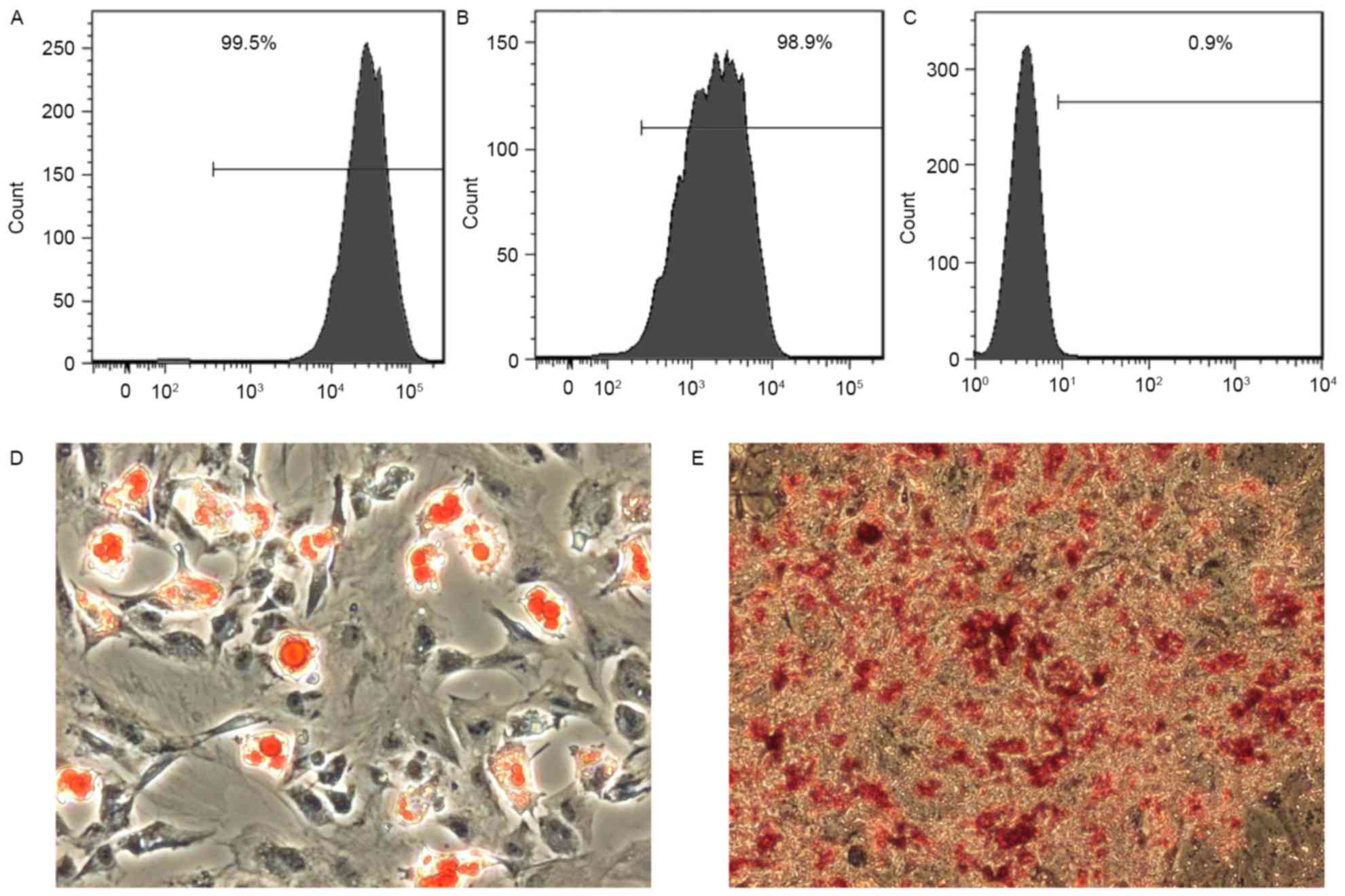
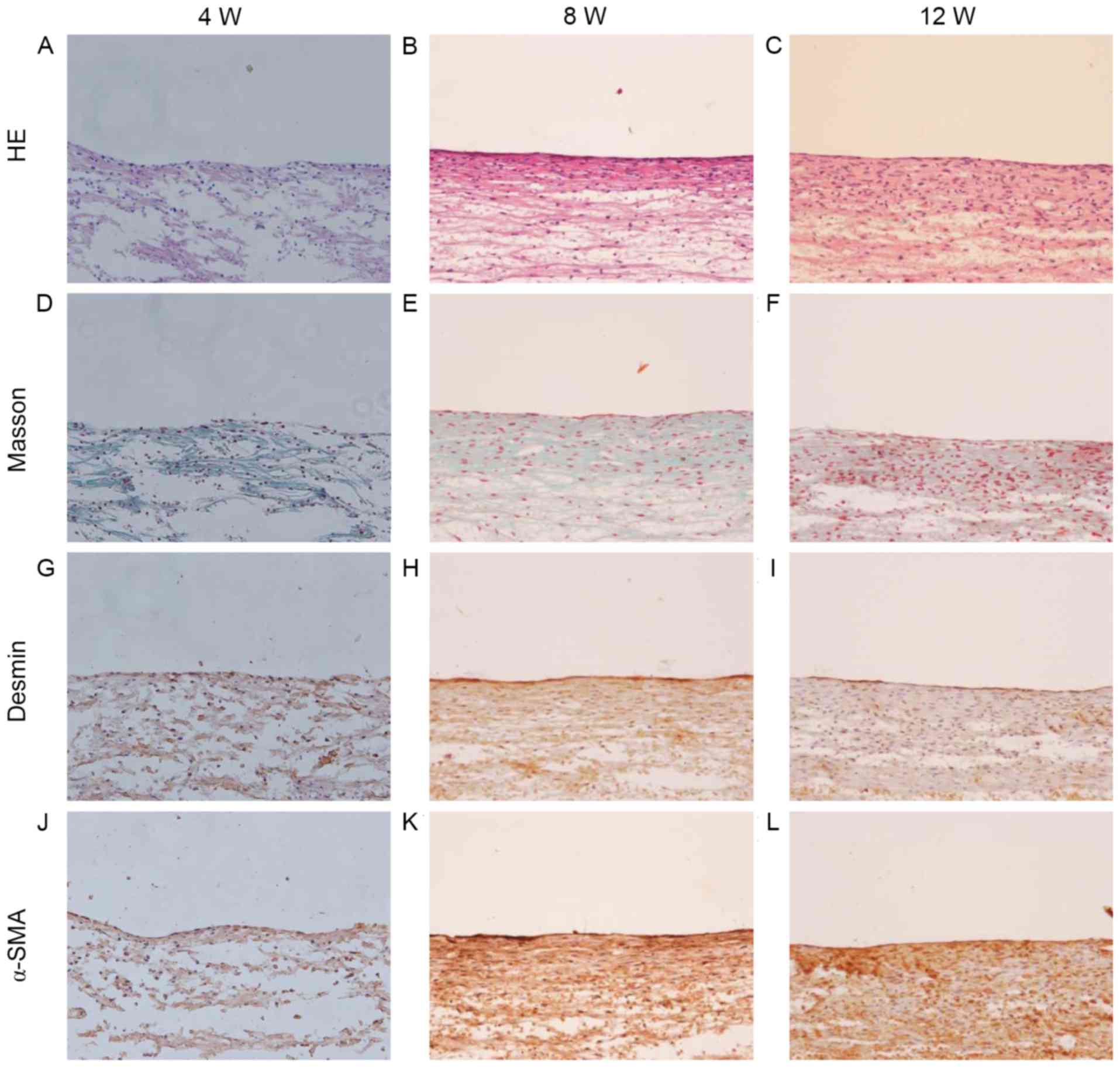
|
1
|
Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D,
Rosier P, Ulmsten U, van Kerrebroeck P, Victor A and Wein A: The
standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function:
Report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International
Continence Society. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 187:116–126. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Klausner AP and Vapnek JM: Urinary
incontinence in the geriatric population. Mt Sinai J Med. 70:54–61.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rutner AB, Levine SR and Schmaelzle JF:
Processed porcine small intestine submucosa as a graft material for
pubovaginal slings: Durability and results. Urology. 62:805–809.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hung MJ, Liu FS, Shen PS, Chen GD, Lin LY
and Ho ES: Analysis of two sling procedures using polypropylene
mesh for treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 84:133–141. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stav K, Dwyer PL, Rosamilia A, Schierlitz
L, Lim YN, Chao F, De Souza A, Thomas E, Murray C, Conway C and Lee
J: Repeat synthetic mid urethral sling procedure for women with
recurrent stress urinary incontinence. J Urol. 183:241–246. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Walter AJ, Morse AN, Leslie KO, Zobitz ME,
Hentz JG and Cornella JL: Changes in tensile strength of cadaveric
human fascia lata after implantation in a rabbit vagina model. J
Urol. 169:1907–1910. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim IG, Piao S, Hong SH, Kim SW, Hwang TK,
Oh SH, Lee JH and Lee JY: The effect of a bioactive
tissue-engineered sling in a rat of stress incontinence model. J
Biomed Mater Res A. 100:286–292. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zou XH, Zhi YL, Chen X, Jin HM, Wang LL,
Jiang YZ, Yin Z and Ouyang HW: Mesenchymal stem cell seeded knitted
silk sling for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence.
Biomaterials. 31:4872–4879. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee JY, Cannon TW, Pruchnic R, Fraser MO,
Huard J and Chancellor MB: The effects of periurethral
muscle-derived stem cell injection on leak point pressure in a rat
model of stress urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor
Dysfunct. 14:31–37. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao W, Zhang C, Jin C, Zhang Z, Kong D,
Xu W and Xiu Y: Periurethral injection of autologous
adipose-derived stem cells with controlled-release nerve growth
factor for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in a rat
model. Eur Urol. 59:155–163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li GY, Zhou F, Gong YQ, Cui WS, Yuan YM,
Song WD, Xin H, Liu T, Li WR, Gao ZZ, et al: Activation of VEGF and
ERK1/2 and improvement of urethral function by adipose-derived stem
cells in a rat stress urinary incontinence model. Urology.
80:953.e1–e8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kim SO, Na HS, Kwon D, Joo SY, Kim HS and
Ahn Y: Bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation
enhances closing pressure and leak point pressure in a female
urinary incontinence rat model. Urol Int. 86:110–116. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mitterberger M, Marksteiner R, Margreiter
E, Pinggera GM, Frauscher F, Ulmer H, Fussenegger M, Bartsch G and
Strasser H: Myoblast and fibroblast therapy for post-prostatectomy
urinary incontinence: 1-year followup of 63 patients. J Urol.
179:226–231. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Niklason LE, Abbott W, Gao J, Klagges B,
Hirschi KK, Ulubayram K, Conroy N, Jones R, Vasanawala A, Sanzgiri
S and Langer R: Morphologic and mechanical characteristics of
engineered bovine arteries. J Vasc Surg. 33:628–638. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, De Ugarte DA,
Huang JI, Mizuno H, Alfonso ZC, Fraser JK, Benhaim P and Hedrick
MH: Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol
Biol Cell. 13:4279–4295. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Arrigoni E, Lopa S, de Girolamo L, Stanco
D and Brini AT: Isolation, characterization and osteogenic
differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells: From small to large
animal models. Cell Tissue Res. 338:401–411. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Zhao L and Hantash BM: Support of
human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell multipotency by a
poloxamer-octapeptide hybrid hydrogel. Biomaterials. 31:5122–5130.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang YH, Ho ML, Chang JK, Chu HC, Lai SC
and Wang GJ: Microporation is a valuable transfection method for
gene expression in human adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Mol
Ther. 17:302–308. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen B, Wang B, Zhang WJ, Zhou G, Cao Y
and Liu W: In vivo tendon engineering with skeletal muscle derived
cells in a mouse model. Biomaterials. 33:6086–6097. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Fu Q, Zhao RY and Deng CL:
Muscular tubes of urethra engineered from adipose-derived stem
cells and polyglycolic acid mesh in a bioreactor. Biotechnol Lett.
36:1909–1916. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shen W, Chen X, Chen J, Yin Z, Heng BC,
Chen W and Ouyang HW: The effect of incorporation of exogenous
stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha within a knitted silk-collagen
sponge scaffold on tendon regeneration. Biomaterials. 31:7239–7249.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu Y, Liu T, Song K, Fan X, Ma X and Cui
Z: Adipose-derived stem cell: A better stem cell than BMSC. Cell
Biochem Funct. 26:664–675. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin G, Wang G, Banie L, Ning H, Shindel
AW, Fandel TM, Lue TF and Lin CS: Treatment of stress urinary
incontinence with adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Cytotherapy.
12:88–95. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu G, Song Y, Zheng X and Jiang Z:
Adipose-derived stromal cell transplantation for treatment of
stress urinary incontinence. Tissue Cell. 43:246–253. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cao D, Liu W, Wei X, Xu F, Cui L and Cao
Y: In vitro tendon engineering with avian tenocytes and
polyglycolic acids: A preliminary report. Tissue Eng. 12:1369–1377.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cao Y, Rodriguez A, Vacanti M, Ibarra C,
Arevalo C and Vacanti CA: Comparative study of the use of poly
(glycolic acid), calcium alginate and pluronics in the engineering
of autologous porcine cartilage. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.
9:475–487. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu ZC, Zhang WJ, Li H, Cui L, Cen L, Zhou
GD, Liu W and Cao Y: Engineering of an elastic large muscular
vessel wall with pulsatile stimulation in bioreactor. Biomaterials.
29:1464–1472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang C, Cen L, Yin S, Liu Q, Liu W, Cao Y
and Cui L: A small diameter elastic blood vessel wall prepared
under pulsatile conditions from polyglycolic acid mesh and smooth
muscle cells differentiated from adipose-derived stem cells.
Biomaterials. 31:621–630. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|