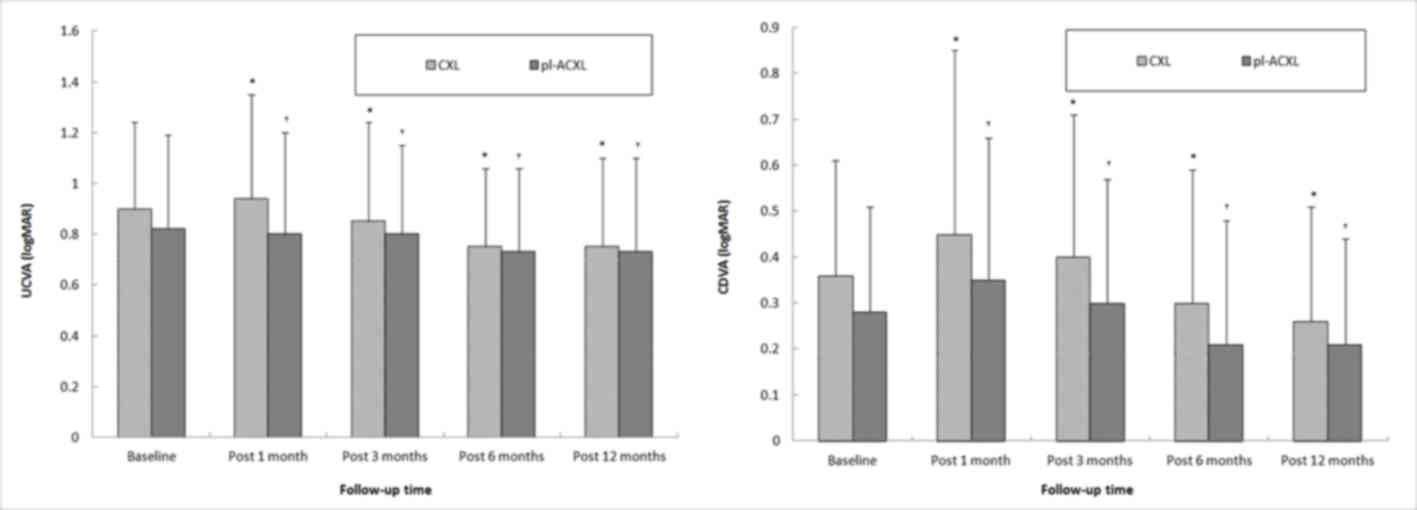
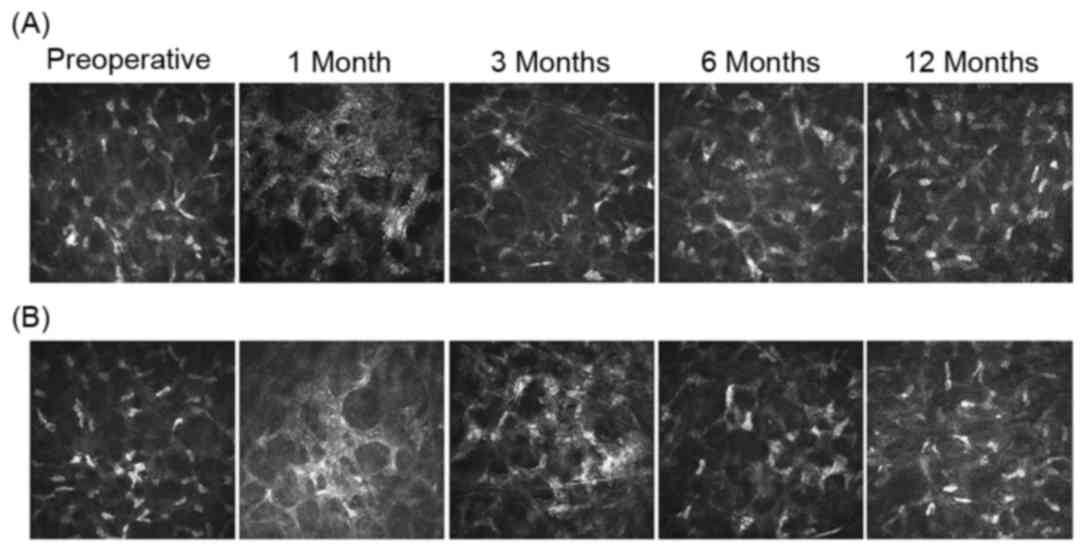
|
1
|
Edrington TB, Zadnik K and Barr JT:
Keratoconus. Optom Clin. 4:65–73. 2004.
|
|
2
|
Leccisotti A, Aslanides IM, Moore JE and
Shah S: Keratoconus and Keratoectasia: Advancements in diagnosis
and treatment. J Ophthalmol. 2012:5260582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Georgiou T, Funnell CL, Cassels-Brown A
and O'Conor R: Influence of ethnic origin on the incidence of
keratoconus and associated atopic disease in Asians and white
patients. Eye. 18:379–383. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Meek KM, Tuft SJ, Huang Y, Gill PS, Hayes
S, Newton RH and Bron AJ: Changes in collagen orientation and
distribution in keratoconus corneas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
46:1948–1956. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roberts CJ and Dupps WJ Jr: Biomechanics
of corneal ectasia and biomechanical treatments. J Cataract Refract
Surg. 40:991–998. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wittig-Silva C, Chan E, Islam FM, Wu T,
Whiting M and Snibson GR: A randomized, controlled trial of corneal
collagen cross-linking in progressive keratoconus: Three-year
results. Ophthalmology. 121:812–821. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meiri Z, Keren S, Rosenblatt A, Sarig T,
Shenhav L and Varssano D: Efficacy of corneal collagen
cross-linking for the treatment of keratoconus: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Cornea. 35:2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kling S, Remon L, Pérez-Escudero A,
Merayo-Lloves J and Marcos S: Corneal biomechanical changes after
collagen cross-linking from porcine eye inflation experiments.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:3961–3968. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wollensak G, Spoerl E and Seiler T:
Stress-strain measurements of human and porcine corneas after
riboflavin-ultraviolet-A-induced cross-linking. J Cataract Refract
Surg. 29:1780–1785. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Spoerl E, Wollensak G and Seiler T:
Increased resistance of crosslinked cornea against enzymatic
digestion. Curr Eye Res. 29:35–40. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Raiskup-Wolf F, Hoyer A, Spoerl E and
Pillunat LE: Collagen crosslinking with riboflavin and
ultraviolet-A light in keratoconus: Long-term results. J Cataract
Refract Surg. 34:796–801. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hersh PS, Greenstein SA and Fry KL:
Corneal collagen crosslinking for keratoconus and corneal ectasia:
One-year results. J Cataract Refract Surg. 37:149–160. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hashemi H, Seyedian MA, Miraftab M,
Fotouhi A and Asgari S: Corneal collagen cross-linking with
riboflavin and ultraviolet a irradiation for keratoconus: Long-term
results. Ophthalmology. 120:1515–1520. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Spoerl E, Mrochen M, Sliney D, Trokel S
and Seiler T: Safety of UVA-riboflavin cross-linking of the cornea.
Cornea. 26:385–389. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wernli J, Schumacher S, Spoerl E and
Mrochen M: The efficacy of corneal cross-linking shows a sudden
decrease with very high intensity UV light and short treatment
time. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:1176–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mrochen M: Current status of accelerated
corneal cross-linking. Indian J Ophthalmol. 61:428–429. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kurt T, Ozgurhan EB, Yildirim Y, Akcay BI,
Cosar MG, Bozkurt E and Taskapili M: Accelerated (18 mW/cm(2))
corneal cross-linking for progressive keratoconus: 18-Month
results. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 32:186–191. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Richoz O, Hammer A, Tabibian D, Gatzioufas
Z and Hafezi F: The Biomechanical effect of corneal collagen
cross-linking (CXL) with riboflavin and UV-A is oxygen dependent.
Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2:62013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hammer A, Richoz O, Mosquera Arba S,
Tabibian D, Hoogewoud F and Hafezi F: Corneal biomechanical
properties at different corneal cross-linking (CXL) irradiances.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 55:2881–2884. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peyman A, Nouralishahi A, Hafezi F, Kling
S and Peyman M: Stromal demarcation line in pulsed versus
continuous light accelerated corneal cross-linking for keratoconus.
J Refract Surg. 32:206–208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kamiya K, Ishii R, Shimizu K and Igarashi
A: Evaluation of corneal elevation, pachymetry and keratometry in
keratoconic eyes with respect to the stage of Amsler-Krumeich
classification. Br J Ophthalmol. 98:459–463. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Krumeich JH and Kezirian GM: Circular
keratotomy to reduce astigmatism and improve vision in stage I and
II keratoconus. J Refract Surg. 25:357–365. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
O'Brart DP, Chan E, Samaras K, Patel P and
Shah SP: A randomised, prospective study to investigate the
efficacy of riboflavin/ultraviolet A (370 nm) corneal collagen
cross-linkage to halt the progression of keratoconus. Br J
Ophthalmol. 95:1519–1524. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Konstantopoulos A and Mehta JS:
Conventional versus accelerated collagen cross-linking for
keratoconus. Eye Contact Lens. 41:65–71. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Razmjoo H, Rahimi B, Kharraji M, Koosha N
and Peyman A: Corneal haze and visual outcome after collagen
crosslinking for keratoconus: A comparison between total epithelium
off and partial epithelial removal methods. Adv Biomed Res.
3:2212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Salomão MQ, Chaurasia SS, Sinha-Roy A,
Ambrósio R Jr, Esposito A, Sepulveda R, Agrawal V and Wilson SE:
Corneal wound healing after ultraviolet-A/riboflavin collagen
cross-linking: a rabbit study. J Refract Surg. 27:401–407. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kymionis GD, Portaliou DM, Diakonis VF,
Kontadakis GA, Krasia MS, Papadiamantis AG, Coskunseven E and
Pallikaris AI: Posterior linear stromal haze formation after
simultaneous photorefractive keratectomy followed by corneal
collagen cross-linking. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:5030–5033.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Waszczykowska A and Jurowski P: Two-year
accelerated corneal cross-linking outcome in patients with
progressive keratoconus. Biomed Res Int. 2015:3251572015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Caporossi A, Mazzotta C, Baiocchi S and
Caporossi T: Long-term results of riboflavin ultraviolet a corneal
collagen cross-linking for keratoconus in Italy: The Siena eye
cross study. Am J Ophthalmol. 149:585–593. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mazzotta C, Traversi C, Paradiso AL,
Latronico ME and Rechichi M: Pulsed light accelerated crosslinking
versus continuous light accelerated crosslinking: One-year results.
J Ophthalmol. 2014:6047312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Beshtawi IM, Akhtar R, Hillarby MC,
O'Donnell C, Zhao X, Brahma A, Carley F, Derby B and Radhakrishnan
H: Biomechanical properties of human corneas following low- and
high-intensity collagen cross-linking determined with scanning
acoustic microscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:5273–5280. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Seiler T and Hafezi F: Corneal
cross-linking-induced stromal demarcation line. Cornea.
25:1057–1059. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kohlhaas M, Spoerl E, Schilde T, Unger G,
Wittig C and Pillunat LE: Biomechanical evidence of the
distribution of cross-links in corneas treated with riboflavin and
ultraviolet A light. J Cataract Refract Surg. 32:279–283. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vinciguerra P, Camesasca FI, Albè E and
Trazza S: Corneal collagen cross-linking for ectasia after excimer
laser refractive surgery: 1-year results. J Refract Surg.
26:486–497. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mazzotta C, Balestrazzi A, Traversi C,
Baiocchi S, Caporossi T, Tommasi C and Caporossi A: Treatment of
progressive keratoconus by riboflavin-UVA-induced cross-linking of
corneal collagen: Ultrastructural analysis by Heidelberg Retinal
Tomograph II in vivo confocal microscopy in humans. Cornea.
26:390–397. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jordan C, Patel DV, Abeysekera N and
Mcghee CN: In vivo confocal microscopy analyses of corneal
microstructural changes in a prospective study of collagen
cross-linking in keratoconus. Ophthalmology. 121:469–474. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ku JY, Niederer RL, Patel DV, Sherwin T
and Mcghee CN: Laser scanning in vivo confocal analysis of
keratocyte density in keratoconus. Ophthalmology. 115:845–850.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Messmer EM, Meyer P, Herwig MC, Loeffler
KU, Schirra F, Seitz B, Thiel M, Reinhard T, Kampik A and
Auw-Haedrich C: Morphological and immunohistochemical changes after
corneal cross-linking. Cornea. 32:111–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|