|
1
|
Ni DF: Olfactory disorders and olfactory
function test. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 17:571–575.
2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
2
|
Stenner M, Vent J, Huttenbrink KB, Hummel
T and Damm M: Topical therapy in anosmia: Relevance of
steroid-responsiveness. Laryngoscope. 18:1681–1686. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg
J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, Zuberbier T, Baena-Cagnani CE, Canonica
GW, van Weel C, et al: Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma
(ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the world health
organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 86 Suppl 63:86–160.
2008.
|
|
4
|
Guilemany JM, García-Piñero A, Alobid I,
Cardelús S, Centellas S, Bartra J, Valero A, Picado C and Mullol J:
Persistent allergic rhinitis has a moderate impact on the sense of
smell, depending on both nasal congestion and inflammation.
Laryngoscope. 119:233–238. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gu ZY: Respiratory tract inflammation.
Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 36:397–399. 2001.(In
Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Amit A, Saxena VS, Pratibha N, D'Souza P,
Bagchi M, Bagchi D and Stohs SJ: Mast cell stabilization,
lipoxygenase inhibition, hyaluronidase inhibition, antihistaminic
and antispasmodic activities of Aller-7, a novel botanical
formulation for allergic rhinitis. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 29:107–115.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mott AE, Cain WS, Lafreniere D, Leonard G,
Gent JF and Frank ME: Topical corticosteroid treatment of anosmia
associated with nasal and sinus disease. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 123:367–372. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Simola M and Malmberg H: Sense of smell in
allergic and nonallergic rhinitis. Allergy. 53:190–194. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kirtsreesakul V and Naclerio RM: Role of
allergy in rhinosinusitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 4:17–23.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moll B, Klimek L, Eggers G and Mann W:
Comparison of olfactory function in patients with seasonal and
perennial allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 53:297–301. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cowart BJ, Flynn-Rodden K, McGeady SJ and
Lowry LD: Hyposmia in allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
91:747–751. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rombaux P, Collet S, Eloy P, Ledeghen S
and Bertrand B: Smell disorders in ENT clinic. B-ENT. 1 Suppl
1:97–109. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Doty RL and Mishra A: Olfactory and its
alteration by nasal obstruction, rhinitis, and rhinosinusitis.
Laryngoscope. 111:409–423. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guss J, Doghramji L, Reger C and Chiu AG:
Olfactory dysfunction in allergic rhinitis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol
Relat Spec. 71:268–272. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van Beek TA and Montoro P: Chemical
analysis and quality control of Ginkgo biloba leaves,
extracts, and phytopharmaceuticals. J Chromatogr A. 1216:2002–2032.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Berghard A, Buck LB and Liman ER: Evidence
for distinct signaling mechanisms in two mammalian olfactory sense
organ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:2365–2369. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Buck LB: The molecular architecture of
odor and pheromone sensing in mammals. Cell. 100:611–618. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kass MD, Moberly AH, Rosenthal MC, Guang
SA and McGann JP: Odor-specific, olfactory marker protein-mediated
sparsening of primary olfactory input to the brain after odor
exposure. J Neurosci. 33:6594–6602. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee AC, He J and Ma M: Olfactory marker
protein is critical for functional maturation of olfactory sensory
neurons and development of mother preference. J Neurosci.
31:2974–2982. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Faulcon P, Biacabe B and Bonfils P:
Contribution of corticosteroid treatment in neurosensorial
anosomia: A series of 62 patients. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac.
117:374–377. 2000.(In French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Heilmann S, Huettenbrink KB and Hummel T:
Local and systemic administration of corticosteroid in the
treatment of olfactory loss. Am J Rhinol. 18:29–33. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stevens MH: Steroid-dependent anosmia.
Laryngoscope. 111:200–203. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hilberg O: Effect of terfenadine and
budesonide on nasal symptoms, olfaction, and nasal airway patency
following allergen challenge. Allergy. 50:683–688. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guan J, Ni DF, Wang J, Zhu Y, Xu C, Chen X
and Liu J: Therapy for olfactory disorder associated with URTI
along with nasal and accessory nasal diseases. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan
Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 24:484–488. 2010.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miescher SM and Vogel M: Molecular aspects
of allergy. Mol Aspects Med. 23:413–462. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takahashi N, Aramaki Y and Tsuchiy S:
Allergic rhinitis model with Brown Norway rat and evaluation of
antiallergic drugs. J Pharmacobiodyn. 13:414–420. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakaya M, Dohi M, Okunishi K, Nakagome K,
Tanaka R, Imamura M, Baba S, Takeuchi N, Yamamoto K and Kaga K:
Noninvasive system for evaluating allergen-induced nasal
hypersensitivity in murine allergic rhinitis. Lab Invest.
86:917–926. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tanaka K, Okamoto Y, Nagaya Y, Nishimura
F, Takeoka A, Hanada S, Kohno S and Kawai M: A nasal allergy model
developed in the guinea pig by application of 2,4-toluene
diisocyanate. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 85:392–397. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sehmi R, Wood LJ, Watson R, Foley R, Hamid
Q, O'Byrne PM and Denburg JA: Allergen-induced increases in IL-5
receptor alpha-subunit expression on bone marrow-derived CD34+
cells from asthmatic subjects. A novel marker of progenitor cell
commitment towards eosinophilic differentiation. J Clin Invest.
100:2466–2475. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
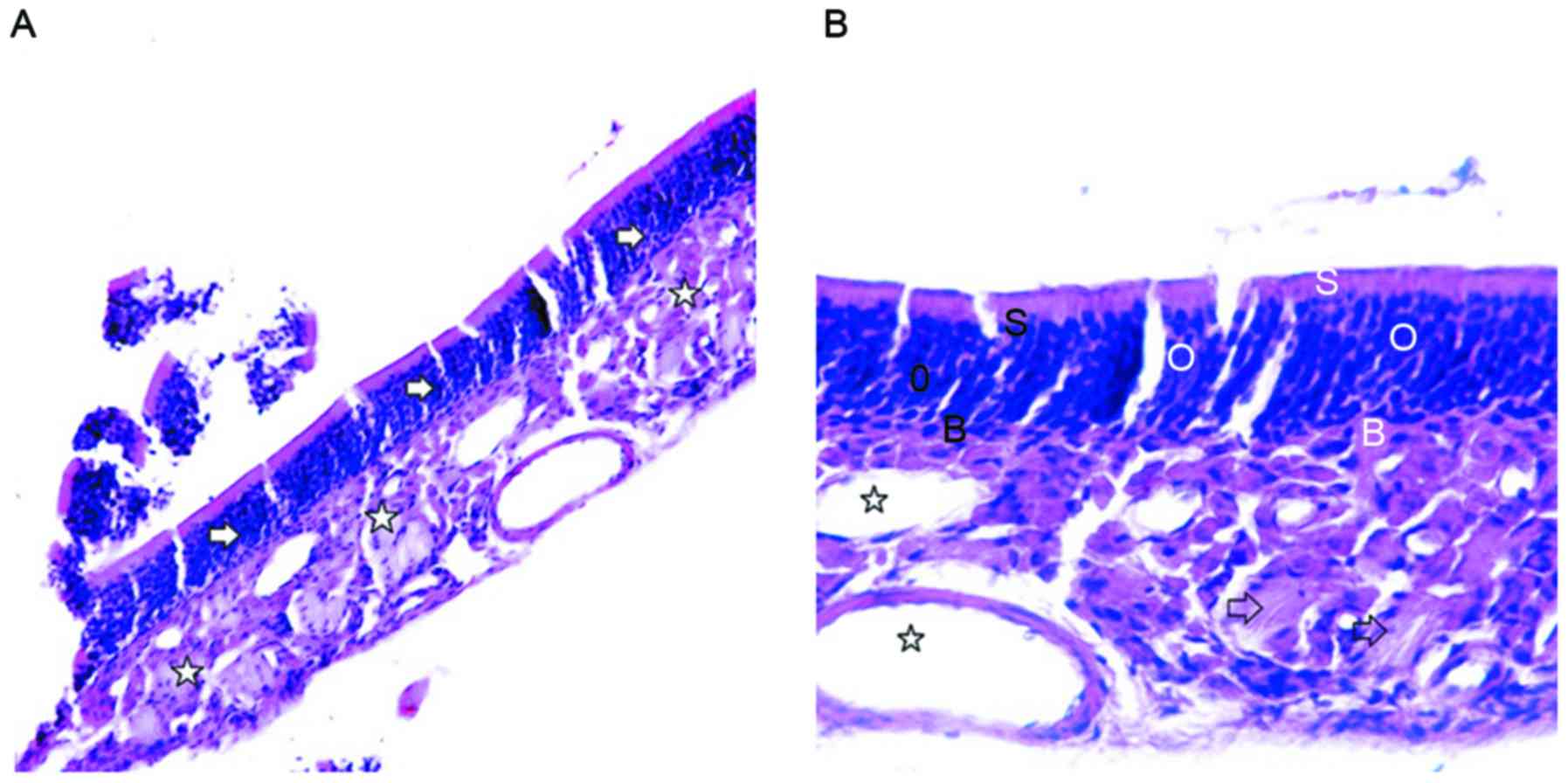
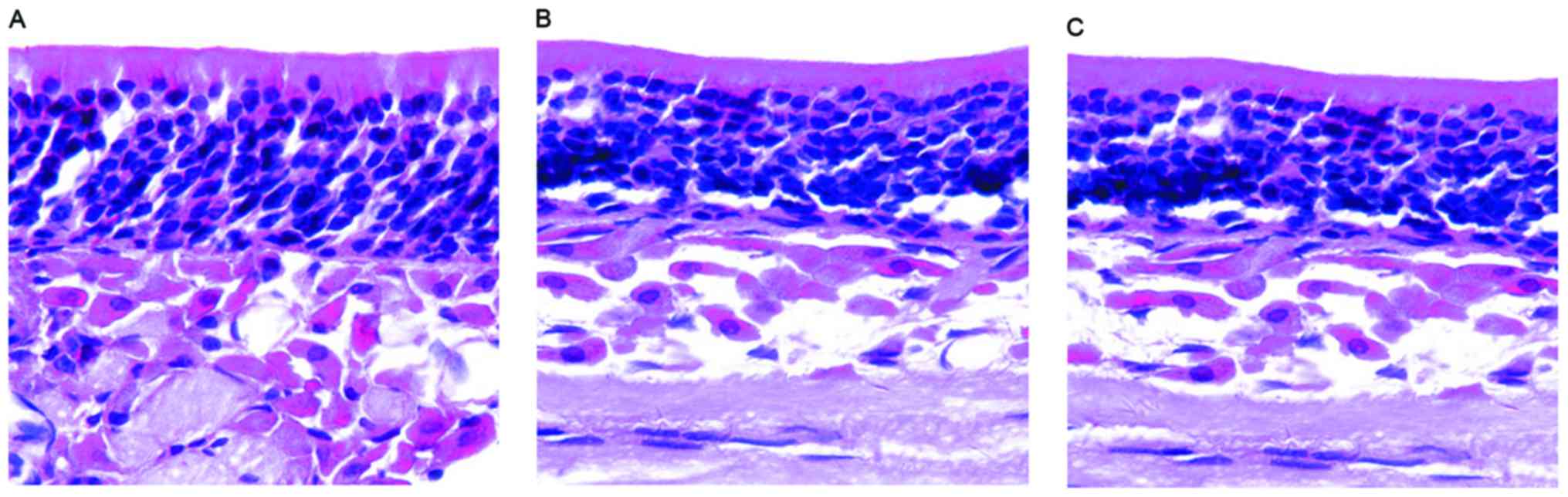
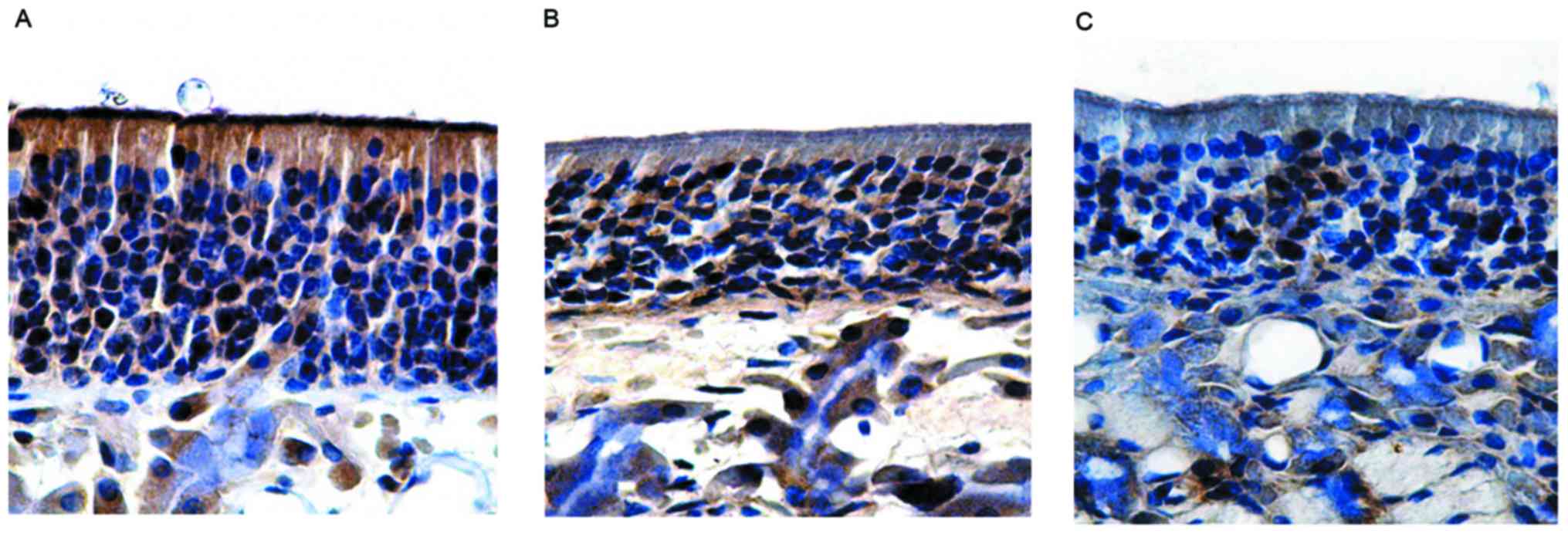
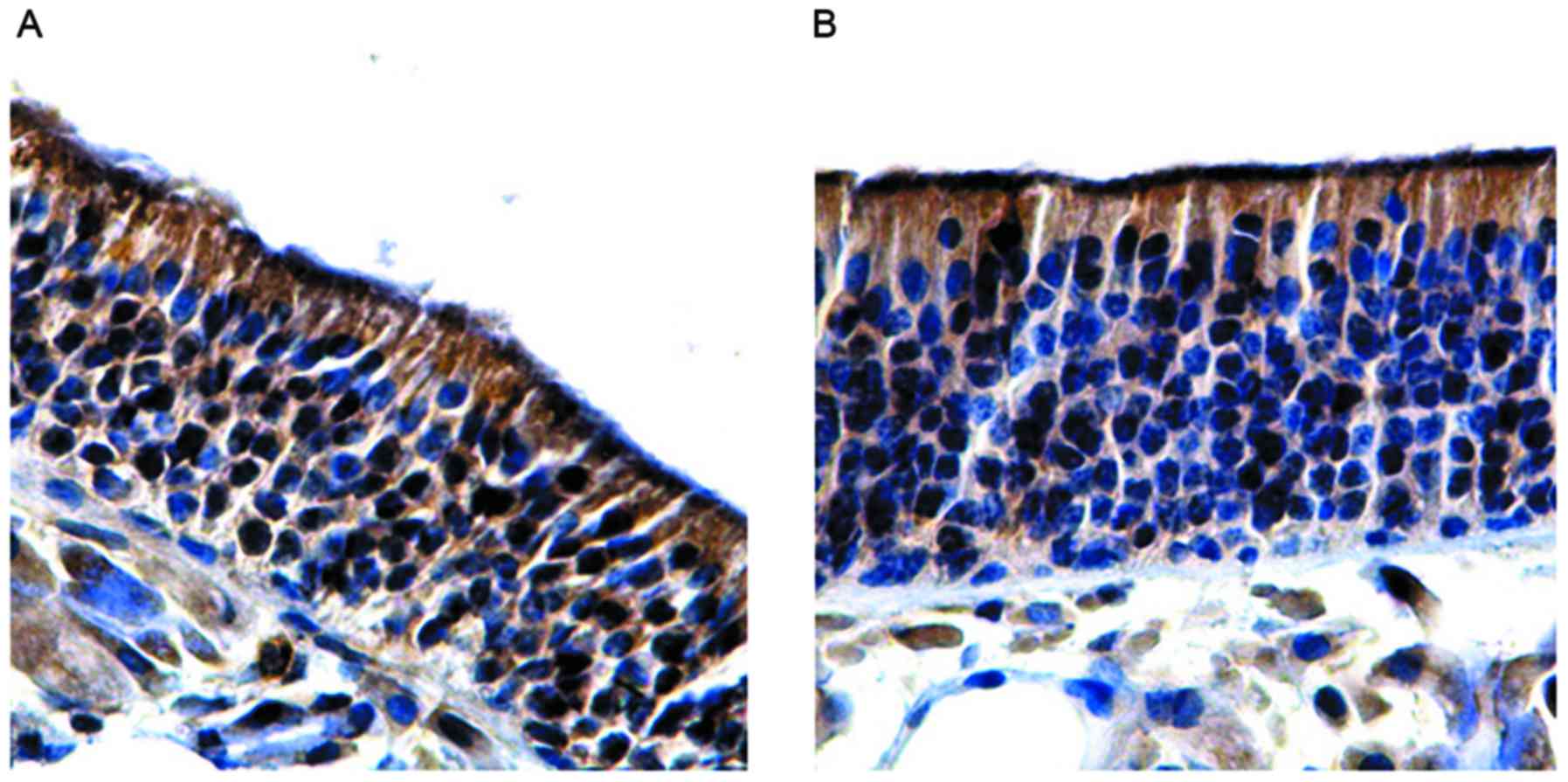
Lin J, Wei YX, Wang XD and Yang L:
Observation of the olfactory mucosa in mice with allergic rhinitis
olfactory dysfunction. Zhongguo Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke.
15:465–468. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Carr VM, Robinson AM and Kern RC:
Tissue-specific effects of allergic rhinitis in mouse nasal
epithelia. Chem Senses. 37:655–668. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wirth S, Stemmelin J, Will B, Christen
YVES and Di Scala G: Facilitative effects of EGb 761 on olfactory
recognition in young and aged rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav.
65:321–326. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nathan BP, Yost J, Litherland MT, Struble
RG and Switzer PV: Olfactory function in apoE knockout mice. Behav
Brain Res. 150:1–7. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liebenauer LL and Slotnick BM: Social
organization and aggression in a group of olfactory bulbectomized
male mice. Physiol Behav. 60:403–409. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Seiden AM and Duncan HJ: The diagnosis of
a conductive olfactory loss. Laryngoscope. 111:9–14. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Klimek L and Eggers G: Olfactory
dysfunction in allergic rhinitis is related to nasal eosinophilic
inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 100:158–164. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Doty RL and Mishra A: Olfaction and its
alternation by nasal obstruction, rhinitis, and rhinosinusitis.
Laryngoscope. 111:409–423. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen ZH and Ni DF: Research progress of
odorant receptor. Guo Ji Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi.
15:465–468. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
39
|
Hummel T, Rissom K, Reden J, Hähner A,
Weidenbecher M and Hüttenbrink KB: Effects of olfactory training in
patients with olfactory loss. Laryngoscope. 119:496–499. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Henkin RI, Potolicchio SJ Jr and Levy LM:
Improvement in smell and taste dysfunction after repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation. Am J Otolarnygol. 32:38–46.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hotchkiss WT: Influence of prednisone on
nasal polyposis with anosmia; preliminary report. AMA Arch
Otolaryngol. 64:478–479. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fukazawa K, Fujii M, Tomofuji S, Ogasawara
H, Seo W and Sakagami M: Local injection of dexamethasone acetate
suspension into the nasal mucosa in cases of olfactory disturbance.
Nippon Jibinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 102:1175–1183. 1999.(In Japanese).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Seo BS, Lee HJ, Mo JH, Lee CH, Rhee CS and
Kim JW: Treatment of postviral olfactory loss with glucocorticoids,
Ginkgo biloba, and mometasone nasal spray. Arch Otolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 135:1000–1004. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee GS, Cho JH, Park CS, Jung SH, Lee DH,
Jun BC, Song CE and Cho KJ: The effect of Ginkgo biloba on
the expression of intermediate-early antigen (c-fos) in the
experimentally induced anosmic mouse. Auris Nasus Larynx.
36:287–291. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Robinson AM, Kern RC, Foster JD, Fong KJ
and Pitovski DZ: Expression of glucocorticoid receptor mRNA and
protein in the olfactory mucosa: Physiologic and pathophysiologic
implications. Laryngoscope. 108:1238–1242. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Takanosawa M, Nishino H, Ohta Y and
Ichimura K: Glucocorticoids enhance regeneration of murine
olfactory epithelium. Acta Otolaryngol. 129:1002–1009. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wei Y, Zhang C, Miao X, Xing F, Liu X,
Zhao H, Zhan X and Han D: Effects of glucocorticoid on cyclic
nucleotide-gated channels of olfactory receptor neurons. J
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 38:90–95. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|