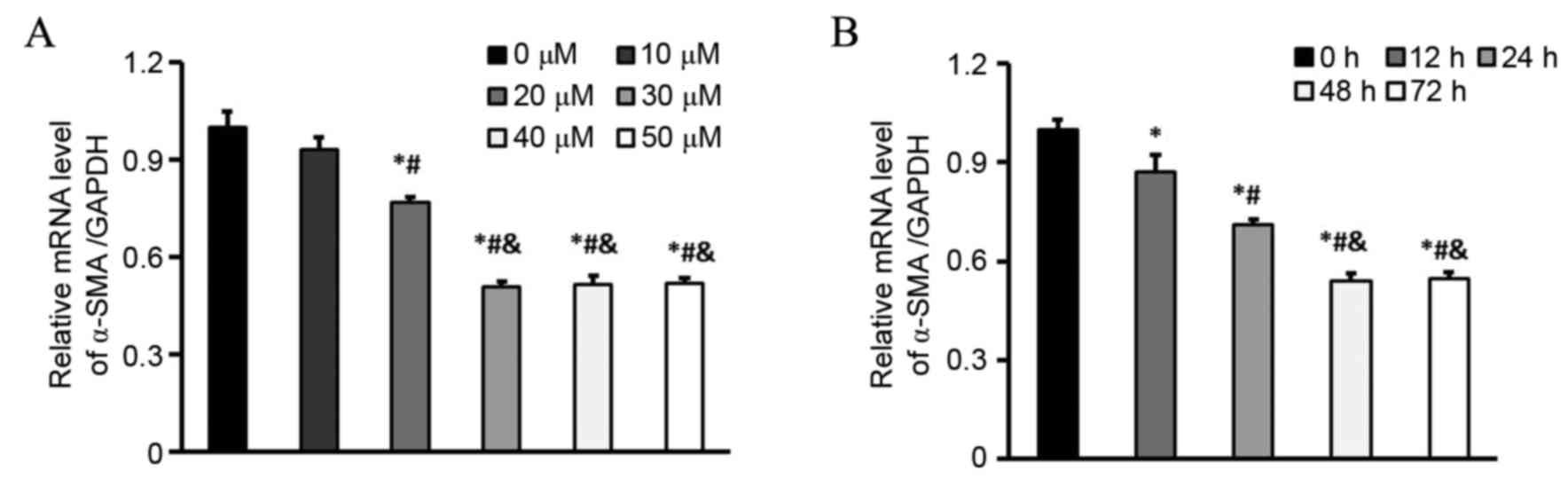
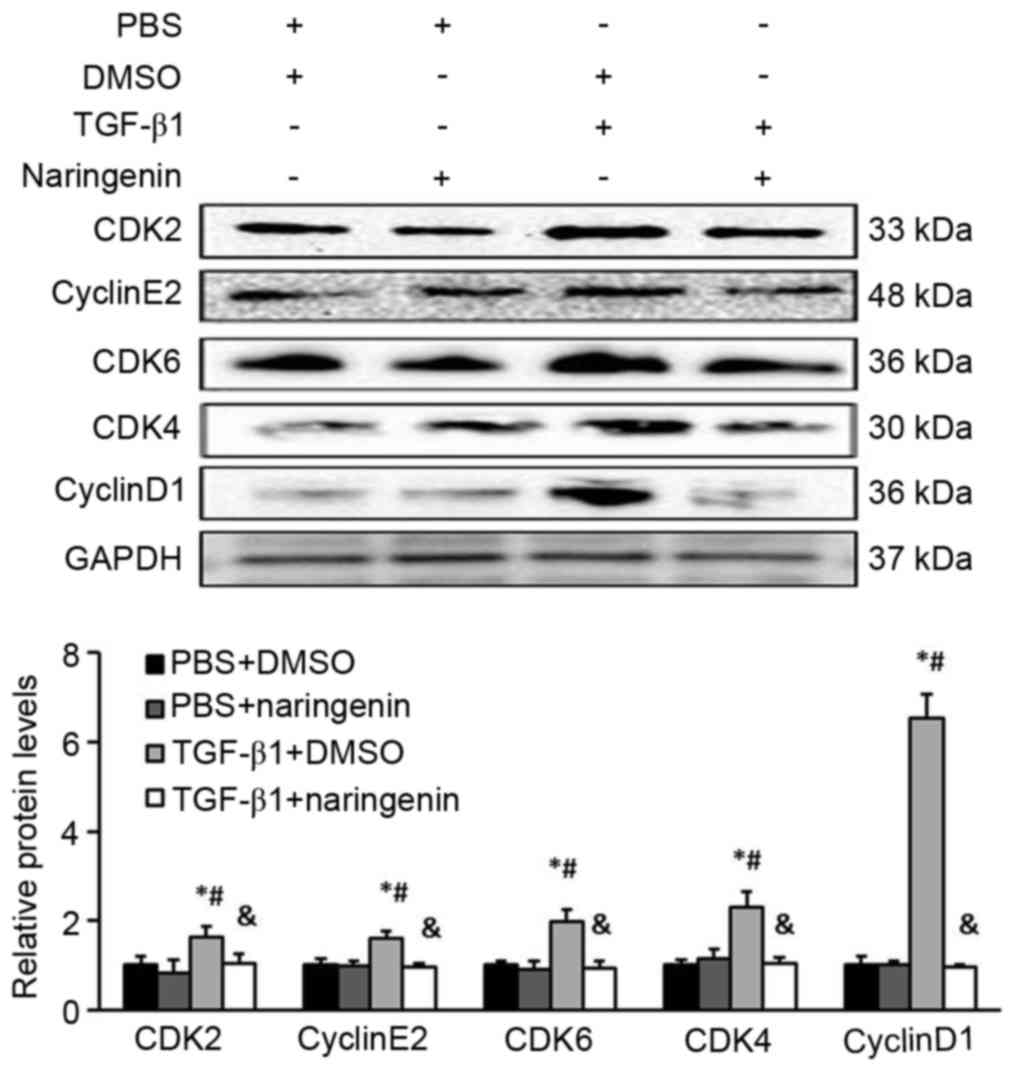
|
1
|
Yi X, Li X, Zhou Y, Ren S, Wan W, Feng G
and Jiang X: Hepatocyte growth factor regulates the TGF-β1-induced
proliferation, differentiation and secretory function of cardiac
fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med. 34:381–390. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou Y, Yi X, Wang T and Li M: Effects of
angiotensin II on transient receptor potential melastatin 7 channel
function in cardiac fibroblasts. Exp Ther Med. 9:2008–2012. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li M, Yi X, Ma L and Zhou Y: Hepatocyte
growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor regulate atrial
fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and rheumatic heart
disease via the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.
Exp Ther Med. 6:1121–1126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou YM, Li MJ, Zhou YL, Ma LL and Yi X:
Growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15), novel biomarker for
assessing atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and
rheumatic heart disease. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:21201–21207.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stempien-Otero A, Kim DH and Davis J:
Molecular networks underlying myofibroblast fate and fibrosis. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 97:153–161. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Travers JG, Kamal FA, Robbins J, Yutzey KE
and Blaxall BC: Cardiac fibrosis: The fibroblast awakens. Circ Res.
118:1021–1040. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moore-Morris T, Cattaneo P, Puceat M and
Evans SM: Origins of cardiac fibroblasts. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
91:1–5. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
van Putten S, Shafieyan Y and Hinz B:
Mechanical control of cardiac myofibroblasts. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
93:133–142. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Zarpelon AC, Mizokami
SS, Borghi SM, Bordignon J, Silva RL, Cunha TM, Alves-Filho JC,
Cunha FQ, Casagrande R and Verri WA Jr: The citrus flavonone
naringenin reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory pain and
leukocyte recruitment by inhibiting NF-κB activation. J Nutr
Biochem. 33:8–14. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xing BH, Yang FZ and Wu XH: Naringenin
enhances the efficacy of human embryonic stem cell-derived
pancreatic endoderm in treating gestational diabetes mellitus mice.
J Pharmacol Sci. 131:93–100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang F, Dong W, Zeng W, Zhang L, Zhang C,
Qiu Y, Wang L, Yin X, Zhang C and Liang W: Naringenin prevents
TGF-β1 secretion from breast cancer and suppresses pulmonary
metastasis by inhibiting PKC activation. Breast Cancer Res.
18:382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang N, Yang Z, Yuan Y, Li F, Liu Y, Ma
Z, Liao H, Bian Z, Zhang Y, Zhou H, et al: Naringenin attenuates
pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Exp Ther Med.
10:2206–2212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chtourou Y, Slima AB, Makni M, Gdoura R
and Fetoui H: Naringenin protects cardiac
hypercholesterolemia-induced oxidative stress and subsequent
necroptosis in rats. Pharmacol Rep. 67:1090–1097. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roche P and Czubryt MP: Transcriptional
control of collagen I gene expression. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord
Drug Targets. 14:107–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li AH, Liu PP, Villarreal FJ and Garcia
RA: Dynamic changes in myocardial matrix and relevance to disease:
Translational perspectives. Circ Res. 114:916–927. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Langan TJ and Chou RC: Synchronization of
mammalian cell cultures by serum deprivation. Methods Mol Biol.
761:75–83. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin X, Yang X, Li Q, Ma Y, Cui S, He D,
Lin X, Schwartz RJ and Chang J: Protein tyrosine phosphatase-like A
regulates myoblast proliferation and differentiation through MyoG
and the cell cycling signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 32:297–308.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lundberg AS and Weinberg RA: Functional
inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein requires sequential
modification by at least two distinct cyclin-cdk complexes. Mol
Cell Biol. 18:753–761. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lauper N, Beck AR, Cariou S, Richman L,
Hofmann K, Reith W, Slingerland JM and Amati B: Cyclin E2: A novel
CDK2 partner in the late G1 and S phases of the mammalian cell
cycle. Oncogene. 17:2637–2643. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee JJ, Yi H, Kim IS, Nhiem NX, Kim YH and
Myung CS: (2S)-naringenin from Typha angustata inhibits vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation via a G0/G1 arrest. J
Ethnopharmacol. 139:873–878. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bendris N, Lemmers B and Blanchard JM:
Cell cycle, cytoskeleton dynamics and beyond: The many functions of
cyclins and CDK inhibitors. Cell Cycle. 14:1786–1798. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|