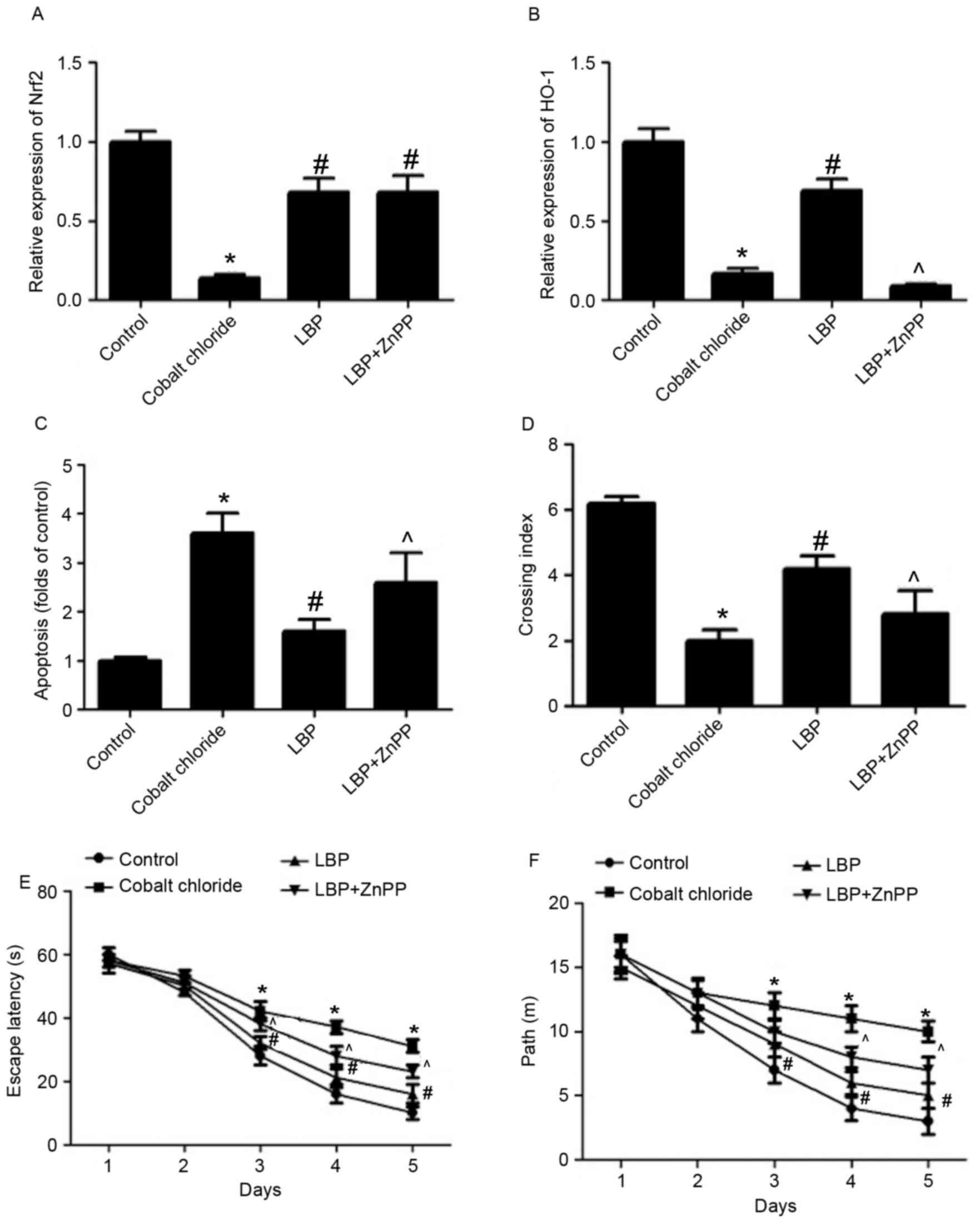
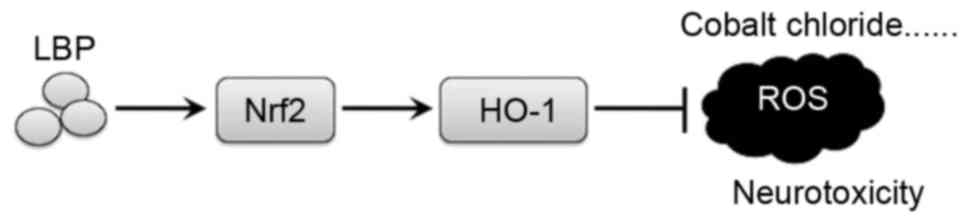
|
1
|
Paulsen JS, Nance M, Kim JI, Carlozzi NE,
Panegyres PK, Erwin C, Goh A, McCusker E and Williams JK: A review
of quality of life after predictive testing for and earlier
identification of neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Neurobiol.
110:2–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gratwicke J, Jahanshahi M and Foltynie T:
Parkinson's disease dementia: A neural networks perspective. Brain.
138:1454–1476. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bhat AH, Dar KB, Anees S, Zargar MA,
Masood A, Sofi MA and Ganie SA: Oxidative stress, mitochondrial
dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases; A mechanistic insight.
Biomed Pharmacother. 74:101–110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao Y and Zhao B: Oxidative stress and
the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2013:3165232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang X and Hai C: Redox modulation of
adipocyte differentiation: Hypothesis of ‘Redox Chain’ and novel
insights into intervention of adipogenesis and obesity. Free
Radical Bio Med. 89:99–125. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Greilberger J, Koidl C, Greilberger M,
Lamprecht M, Schroecksnadel K, Leblhuber F, Fuchs D and Oettl K:
Malondialdehyde, carbonyl proteins and albumin-disulphide as useful
oxidative markers in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's
disease. Free Radic Res. 42:633–638. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sultana R, Perluigi M and Butterfield
Allan D: Lipid peroxidation triggers neurodegeneration: A redox
proteomics view into the Alzheimer disease brain. Free Radic Biol
Med. 62:157–169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Blesa J, Trigo-Damas I, Quiroga-Varela A
and Jackson-Lewis VR: Oxidative stress and Parkinson's disease.
Front Neuroanat. 9:912015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wong ES, Tan JM, Wang C, Zhang Z, Tay SP,
Zaiden N, Ko HS, Dawson VL, Dawson TM and Lim KL: Relative
sensitivity of parkin and other cysteine-containing enzymes to
stress-induced solubility alterations. J Biol Chem.
282:12310–12318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang HX and Ng TB: Natural products with
hypoglycemic, hypotensive, hypocholesterolemic, antiatherosclerotic
and antithrombotic activities. Life Sci. 65:2663–2677. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen S, Liang L, Wang Y, Diao J, Zhao C,
Chen G, He Y, Luo C, Wu X and Zhang Y: Synergistic
immunotherapeutic effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide and
interferon-α2b on the murine Renca renal cell carcinoma cell line
in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med Rep. 12:6727–6737. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao R, Cai Y, Shao X and Ma B: Improving
the activity of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on sub-health mice.
Food Funct. 6:2033–2040. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Lv J, Yang B, Liu F, Tian Z, Cai Y,
Yang D, Ouyang J, Sun F, Shi Y and Xia P: Lycium barbarum
polysaccharide attenuates type II collagen-induced arthritis in
mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 78:318–323. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiao J, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Tipoe GL, Xing F and
So KF: Lycium barbarum polysaccharide attenuates alcoholic cellular
injury through TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Int J Biol
Macromol. 69:73–78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao Q, Dong B, Chen J, Zhao B, Wang X,
Wang L, Zha S and Wang Y, Zhang J and Wang Y: Effect of drying
methods on physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of
wolfberry (Lycium barbarum) polysaccharide. Carbohydr Polym.
127:176–181. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bie M, Lv Y, Ren C, Xing F, Cui Q, Xiao J
and So KF: Lycium barbarum polysaccharide improves bipolar pulse
current-induced microglia cell injury through modulating autophagy.
Cell Transplant. 24:419–428. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao J, Chen C, Liu Y, Li Y, Long Z, Wang
H, Zhang Y, Sui J, Wu Y, Liu L and Yang C: Lycium barbarum
polysaccharide improves traumatic cognition via reversing imbalance
of apoptosis/regeneration in hippocampal neurons after stress. Life
Sci. 121:124–134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang T, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhou R, Ma L, Hao Y,
Jin S, Du J, Zhao C, Sun T and Yu J: Lycium barbarum polysaccharide
prevents focal cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting neuronal
apoptosis in mice. PLoS One. 9:e907802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Caltana L, Merelli A, Lazarowski A and
Brusco A: Neuronal and glial alterations due to focal cortical
hypoxia induced by direct cobalt chloride (CoCl2) brain injection.
Neurotox Res. 15:348–358. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Caltana L, Rutolo D, Nieto ML and Brusco
A: Further evidence for the neuroprotective role of oleanolic acid
in a model of focal brain hypoxia in rats. Neurochem Int. 79:79–87.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guan D, Su Y, Li Y, Wu C, Meng Y, Peng X
and Cui Y: Tetramethylpyrazine inhibits CoCl2 -induced
neurotoxicity through enhancement of Nrf2/GCLc/GSH and suppression
of HIF1α/NOX2/ROS pathways. J Neurochem. 134:551–565. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dai Y, Li W, Zhong M, Chen J, Liu Y, Cheng
Q and Li T: Preconditioning and post-treatment with cobalt chloride
in rat model of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Brain
Dev. 36:228–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pearson JN and Patel M: The role of
oxidative stress in organophosphate and nerve agent toxicity. Ann N
Y Acad Sci. 1378:17–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lan AP, Chen J, Chai ZF and Hu Y: The
neurotoxicity of iron, copper and cobalt in Parkinson's disease
through ROS-mediated mechanisms. Biometals. 29:665–678. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Venkatesan R, Subedi L, Yeo EJ and Kim SY:
Lactucopicrin ameliorates oxidative stress mediated by
scopolamine-induced neurotoxicity through activation of the NRF2
pathway. Neurochem Int. 99:133–146. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gao K, Liu M, Cao J, Yao M, Lu Y, Li J,
Zhu X, Yang Z and Wen A: Protective effects of Lycium barbarum
polysaccharide on 6-OHDA-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells through
the ROS-NO pathway. Molecules. 20:293–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu X, Hu S, Zhu L, Ding J, Zhou Y and Li
G: Effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on oxidative stress
in hyperlipidemic mice following chronic composite psychological
stress intervention. Mol Med Rep. 11:3445–3450. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qi B, Ji Q, Wen Y, Liu L, Guo X, Hou G,
Wang G and Zhong J: Lycium barbarum polysaccharides protect human
lens epithelial cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis
and senescence. PLoS One. 9:e1102752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rui C, Yuxiang L, Yinju H, Qingluan Z,
Yang W, Qipeng Z, Hao W, Lin M, Juan L, Chengjun Z, et al:
Protective effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on neonatal
rat primary cultured hippocampal neurons injured by oxygen-glucose
deprivation and reperfusion. J Mol Histol. 43:535–542. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li SY, Yang D, Yeung CM, Yu WY, Chang RC,
So KF, Wong D and Lo AC: Lycium barbarum polysaccharides reduce
neuronal damage, blood-retinal barrier disruption and oxidative
stress in retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One.
6:e163802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vriend J and Reiter RJ: The
Keap1-Nrf2-antioxidant response element pathway: A review of its
regulation by melatonin and the proteasome. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
401:213–220. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Na HK and Surh YJ: Oncogenic potential of
Nrf2 and its principal target protein heme oxygenase-1. Free Radic
Biol Med. 67:353–365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ollinger R, Yamashita K, Bilban M, Erat A,
Kogler P, Thomas M, Csizmadia E, Usheva A, Margreiter R and Bach
FH: Bilirubin and biliverdin treatment of atherosclerotic diseases.
Cell Cycle. 6:39–43. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gan L and Johnson JA: Oxidative damage and
the Nrf2-ARE pathway in neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1842:1208–1218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Narasimhan M, Riar AK, Rathinam ML,
Vedpathak D, Henderson G and Mahimainathan L: Hydrogen peroxide
responsive miR153 targets Nrf2/ARE cytoprotection in paraquat
induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity. Toxicol Lett. 228:179–191.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Park SY, Kim DY, Kang JK, Park G and Choi
YW: Involvement of activation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway in protection
against 6-OHDA-induced SH-SY5Y cell death by α-iso-cubebenol.
Neurotoxicology. 44:160–168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ye F, Li X, Li L, Yuan J and Chen J: t-BHQ
provides protection against lead neurotoxicity via Nrf2/HO-1
pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:20759152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dwivedi S, Rajasekar N, Hanif K, Nath C
and Shukla R: Sulforaphane ameliorates okadaic Acid-Induced memory
impairment in rats by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway.
Mol Neurobiol. 53:5310–5323. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kwon SH, Ma SX, Hwang JY, Lee SY and Jang
CG: Involvement of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in
sulfuretin-induced protection against amyloid beta25-35
neurotoxicity. Neuroscience. 304:14–28. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang Y, Li W, Li Y, Wang Q, Gao L and Zhao
J: Dietary Lycium barbarum polysaccharide induces Nrf2/ARE pathway
and ameliorates insulin resistance induced by high-fat via
activation of PI3K/AKT signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2014:1456412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
He M, Pan H, Chang RC, So KF, Brecha NC
and Pu M: Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway
contributes to the protective effects of Lycium barbarum
polysaccharides in the rodent retina after
ischemia-reperfusion-induced damage. Plos One. 9:e848002014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|