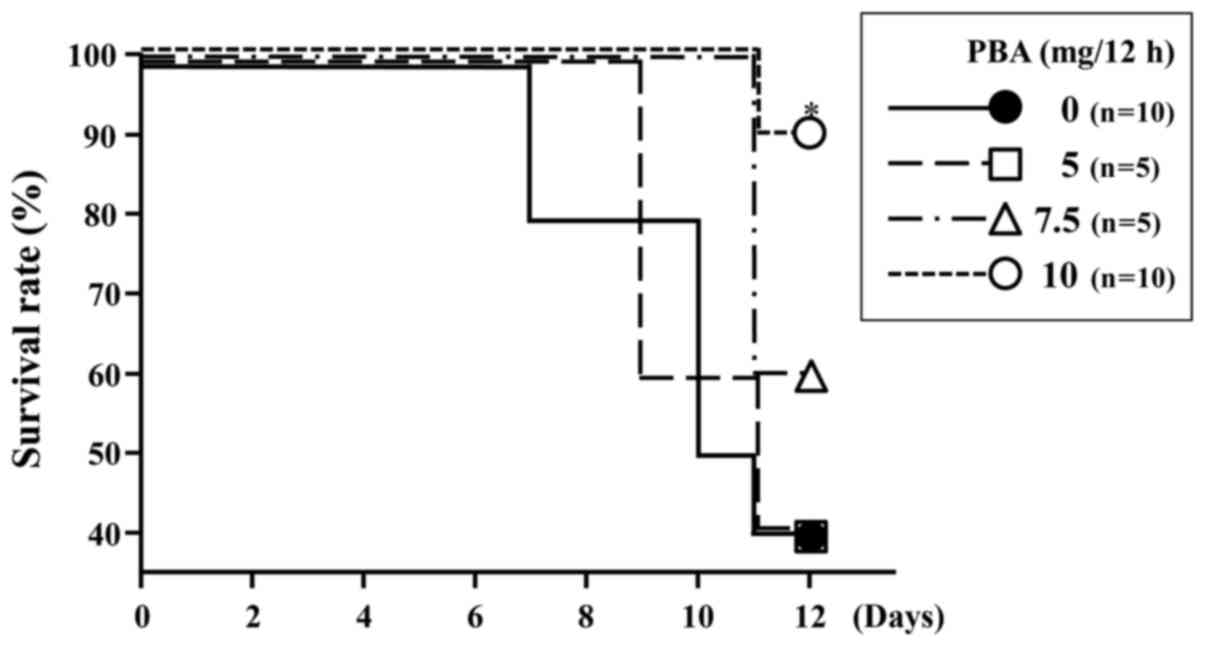
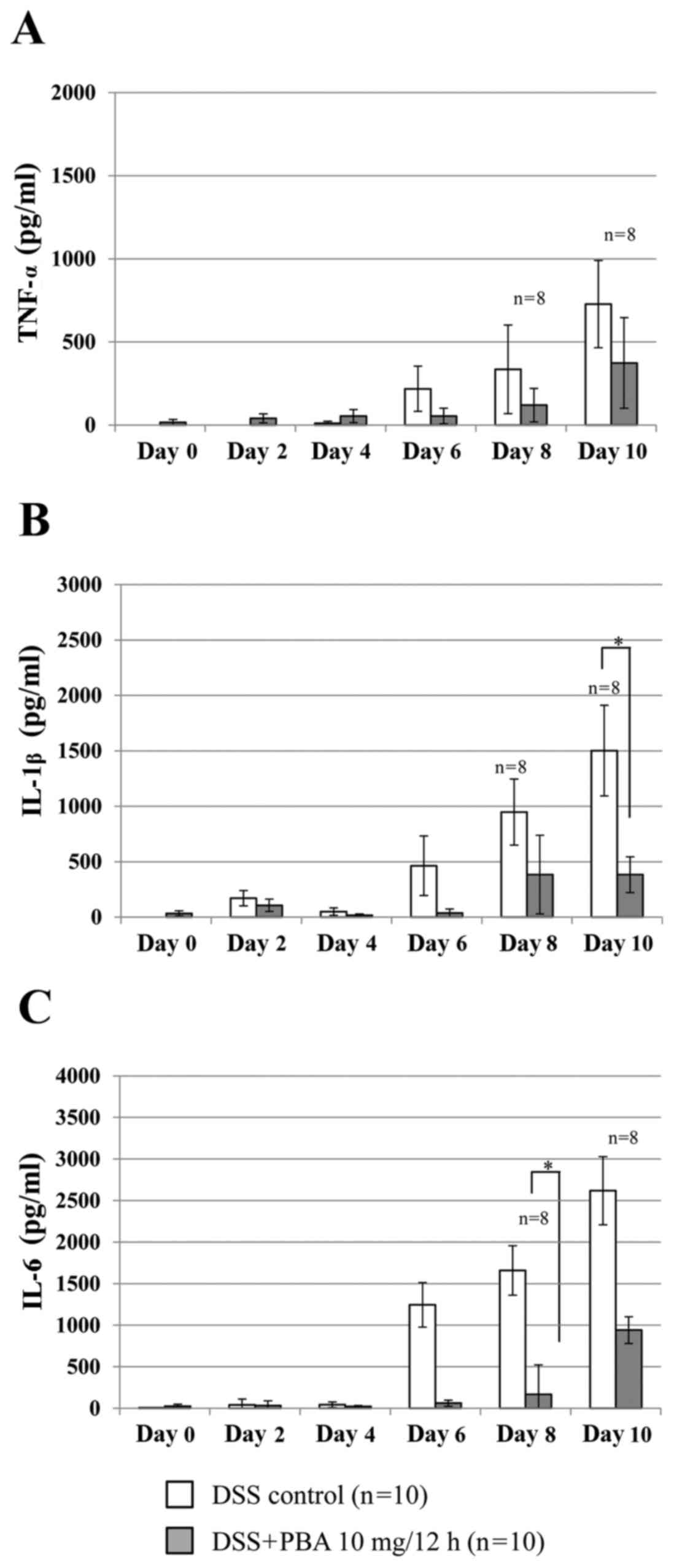
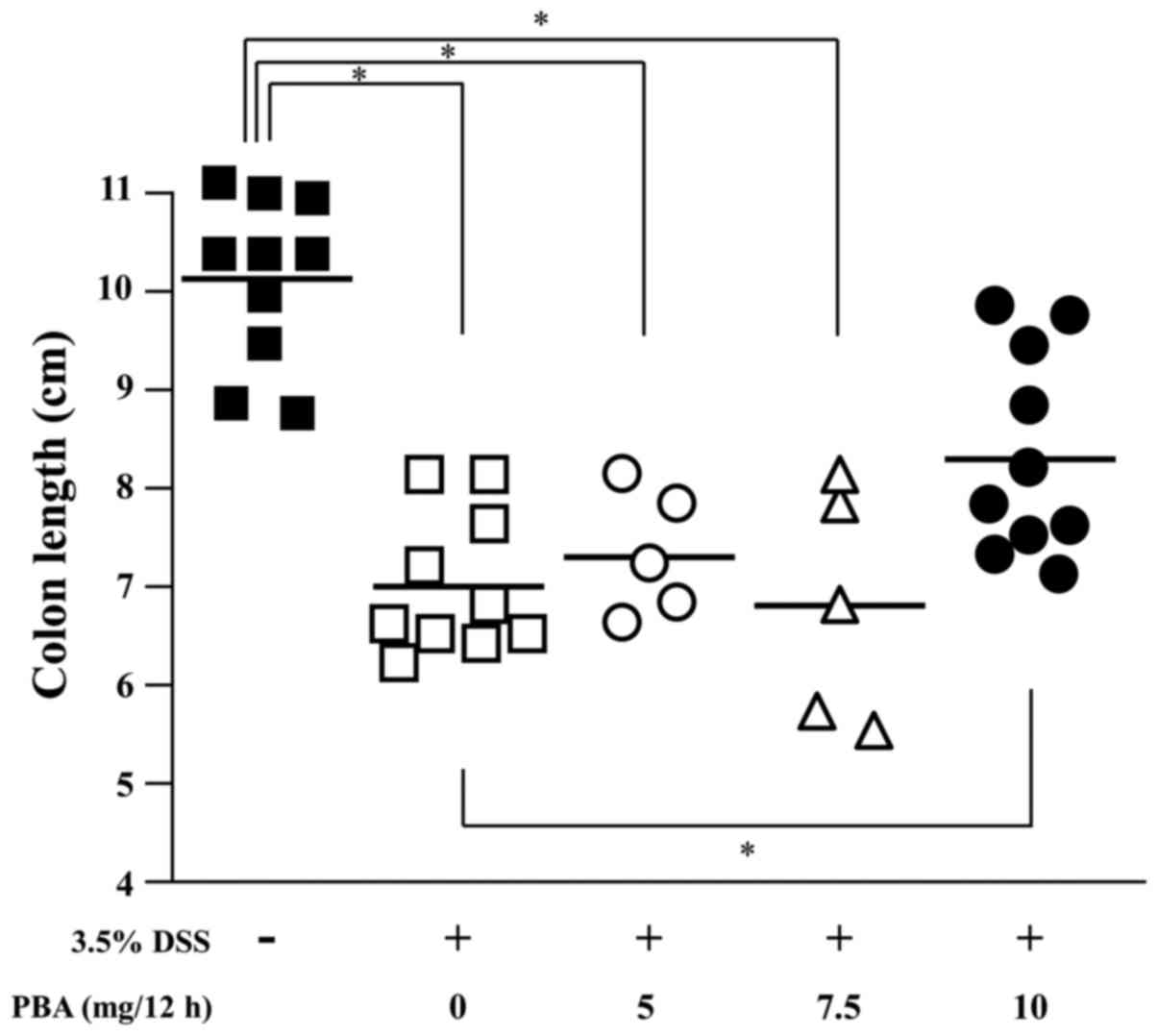
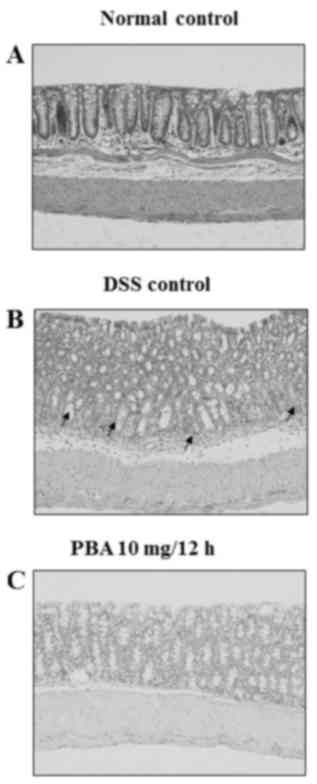
|
1
|
de Souza HS and Fiocchi C:
Immunopathogenesis of IBD: Current state of the art. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:13–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Podolsky DK: Inflammatory bowel disease. N
Engl J Med. 347:417–429. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang YZ and Li YY: Inflammatory bowel
disease: Pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 20:91–99. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leitner GC and Vogelsang H:
Pharmacological- and non-pharmacological therapeutic approaches in
inflammatory bowel disease in adults. World J Gastrointest
Pharmacol Ther. 7:5–20. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coelho T, Andreoletti G, Ashton JJ,
Pengelly RJ, Gao Y, RamaKrishnan A, Batra A, Beattie RM, Williams
AP and Ennis S: Immuno-genomic profiling of patients with
inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review of genetic and
functional in vivo studies of implicated genes. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
20:1813–1819. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dupaul-Chicoine J, Dagenais M and Saleh M:
Crosstalk between the intestinal microbiota and the innate immune
system in intestinal homeostasis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 19:2227–2237. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ananthakrishnan AN: Environmental risk
factors for inflammatory bowel diseases: A review. Dig Dis Sci.
60:290–298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Maloy KJ and Powrie F: Intestinal
homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease.
Nature. 474:298–306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Scharl M and Rogler G: Inflammatory bowel
disease pathogenesis: What is new? Curr Opin Gastroenterol.
28:301–309. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sands BE: Therapy of inflammatory bowel
disease. Gastroenterology. 118 2 Suppl 1:S68–S82. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ko JK and Auyeung KK: Inflammatory bowel
disease: Etiology, pathogenesis and current therapy. Curr Pharm
Des. 20:1082–1096. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pedersen J, Coskun M, Soendergaard C,
Salem M and Nielsen OH: Inflammatory pathways of importance for
management of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol.
20:64–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Katz JA: Management of inflammatory bowel
disease in adults. J Dig Dis. 8:65–71. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamamoto T, Umegae S and Matsumoto K:
Mucosal healing in patients with ulcerative colitis during a course
of selective leukocytapheresis therapy: A prospective cohort study.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 16:1905–1911. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Diaz GA, Krivitzky LS, Mokhtarani M, Rhead
W, Bartley J, Feigenbaum A, Longo N, Berquist W, Berry SA,
Gallagher R, et al: Ammonia control and neurocognitive outcome
among urea cycle disorder patients treated with glycerol
phenylbutyrate. Hepatology. 57:2171–2179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iannitti T and Palmieri B: Clinical and
experimental applications of sodium phenylbutyrate. Drugs R D.
11:227–249. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kusaczuk M, Bartoszewicz M and
Cechowska-Pasko M: Phenylbutyric Acid: Simple structure-multiple
effects. Curr Pharm Des. 21:2147–2166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Roy A, Ghosh A, Jana A, Liu X, Brahmachari
S, Gendelman HE and Pahan K: Sodium phenylbutyrate controls
neuroinflammatory and antioxidant activities and protects
dopaminergic neurons in mouse models of Parkinson's disease. PLoS
One. 7:e381132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo ZF, Feng B, Mu J, Qi W, Zeng W, Guo
YH, Pang Q, Ye ZL, Liu L and Yuan FH: Effects of 4-phenylbutyric
acid on the process and development of diabetic nephropathy induced
in rats by streptozotocin: Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-oxidative activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 246:49–57.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park JS, Lee EJ, Lee JC, Kim WK and Kim
HS: Anti-inflammatory effects of short chain fatty acids in
IFN-gamma-stimulated RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells: involvement
of NF-kappaB and ERK signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol.
7:70–77. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morinaga M, Kon K, Saito H, Arai K, Kusama
H, Uchiyama A, Yamashina S, Ikejima K and Watanabe S: Sodium
4-phenylbutyrate prevents murine dietary steatohepatitis caused by
trans-fatty acid plus fructose. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 57:183–191.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ono K, Ikemoto M, Kawarabayashi T, Ikeda
M, Nishinakagawa T, Hosokawa M, Shoji M, Takahashi M and Nakashima
M: A chemical chaperone, sodium 4-phenylbutyric acid, attenuates
the pathogenic potency in human alpha-synuclein A30P + A53T
transgenic mice. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 15:649–654. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ono K, Nimura S, Nishinakagawa T,
Hideshima Y, Enjyoji M, Nabeshima K and Nakashima M: Sodium
4-phenylbutyrate suppresses the development of dextran sulfate
sodium-induced colitis in mice. Exp Ther Med. 7:573–578. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wirtz S, Neufert C, Weigmann B and Neurath
MF: Chemically induced mouse models of intestinal inflammation. Nat
Protoc. 2:541–546. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS and
Sedergran DJ: Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium
experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest. 69:238–249.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dionne S, D'Agata ID, Hiscott J, Vanounou
T and Seidman EG: Colonic explant production of IL-1and its
receptor antagonist is imbalanced in inflammatory bowel disease
(IBD). Clin Exp Immunol. 112:435–442. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tountas NA, Casini-Raggi V, Yang H, Di
Giovine FS, Vecchi M, Kam L, Melani L, Pizarro TT, Rotter JI and
Cominelli F: Functional and ethnic association of allele 2 of the
interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene in ulcerative colitis.
Gastroenterology. 117:806–813. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kwon KH, Murakami A, Hayashi R and
Ohigashi H: Interleukin-1beta targets interleukin-6 in progressing
dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 337:647–654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rutgeerts P, Van Assche G and Vermeire S:
Optimizing anti-TNF treatment in inflammatory bowel disease.
Gastroenterology. 126:1593–1610. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yun L and Hanauer S: Selecting appropriate
anti-TNF agents in inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:235–248. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bosani M, Ardizzone S and Porro GB:
Biologic targeting in the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases.
Biologics. 3:77–97. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Baert F, Noman M, Vermeire S, Van Assche
G, D'Haens G, Carbonez A and Rutgeerts P: Influence of
immunogenicity on the long-term efficacy of infliximab in Crohn's
disease. N Engl J Med. 348:601–608. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Farrell RJ, Alsahli M, Jeen YT, Falchuk
KR, Peppercorn MA and Michetti P: Intravenous hydrocortisone
premedication reduces antibodies to infliximab in Crohn's disease:
A randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 124:917–924. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|