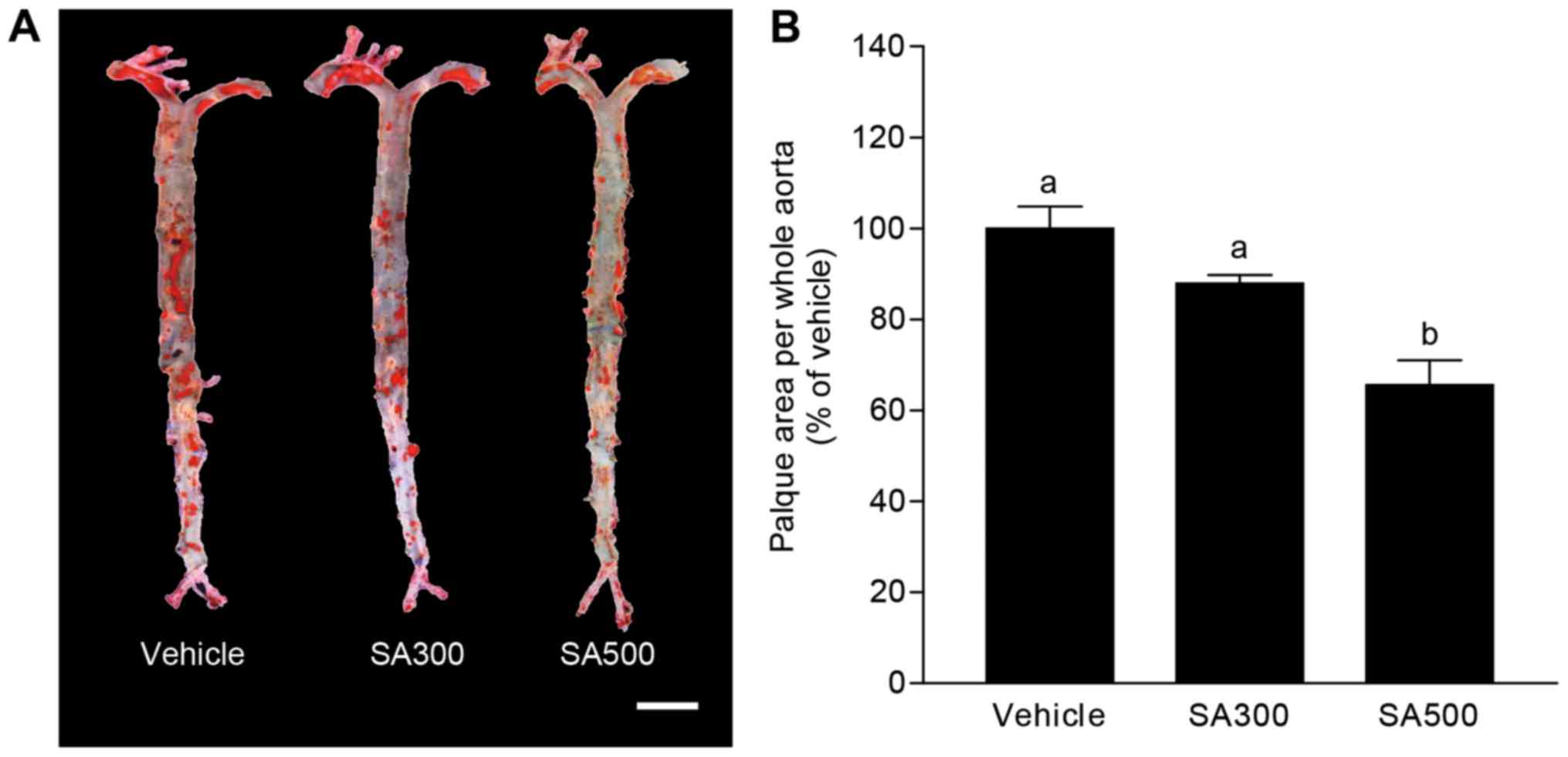
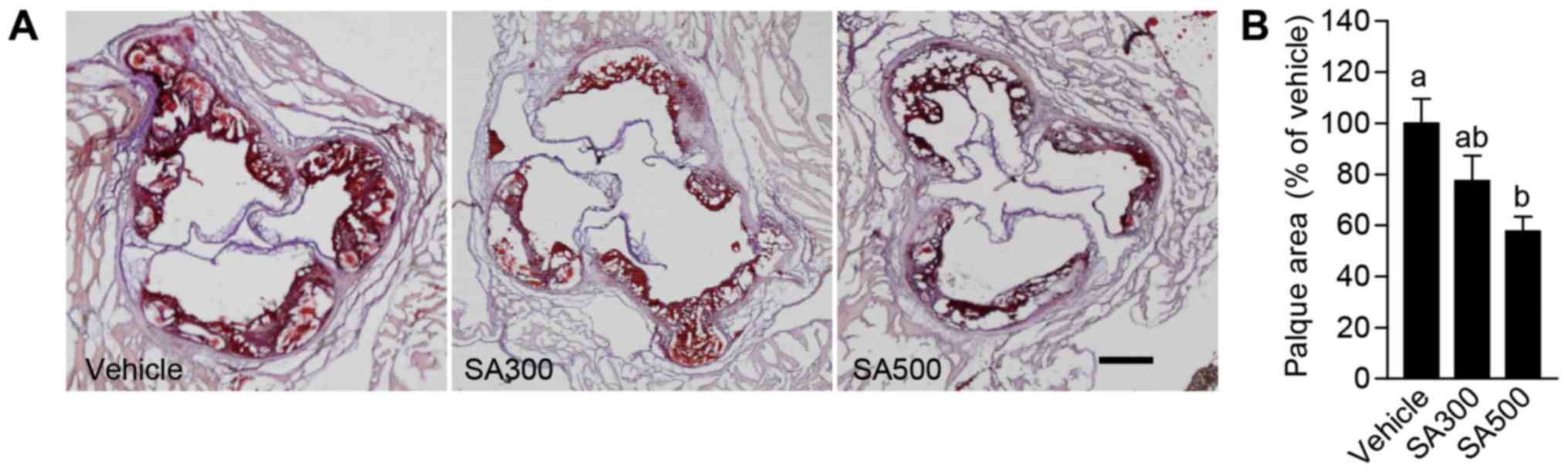
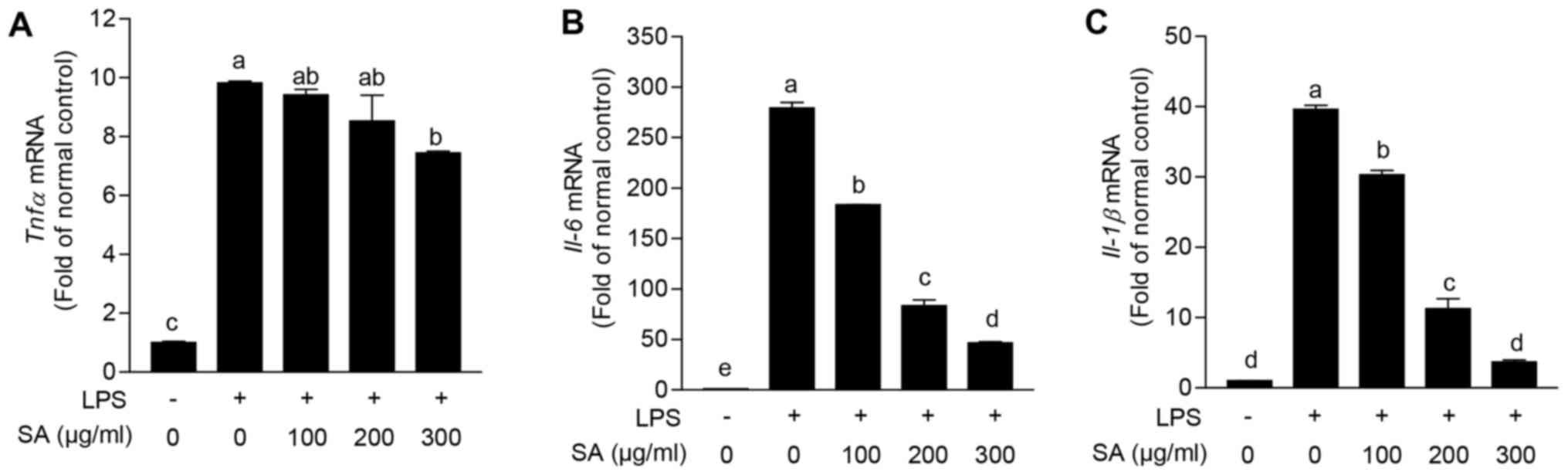
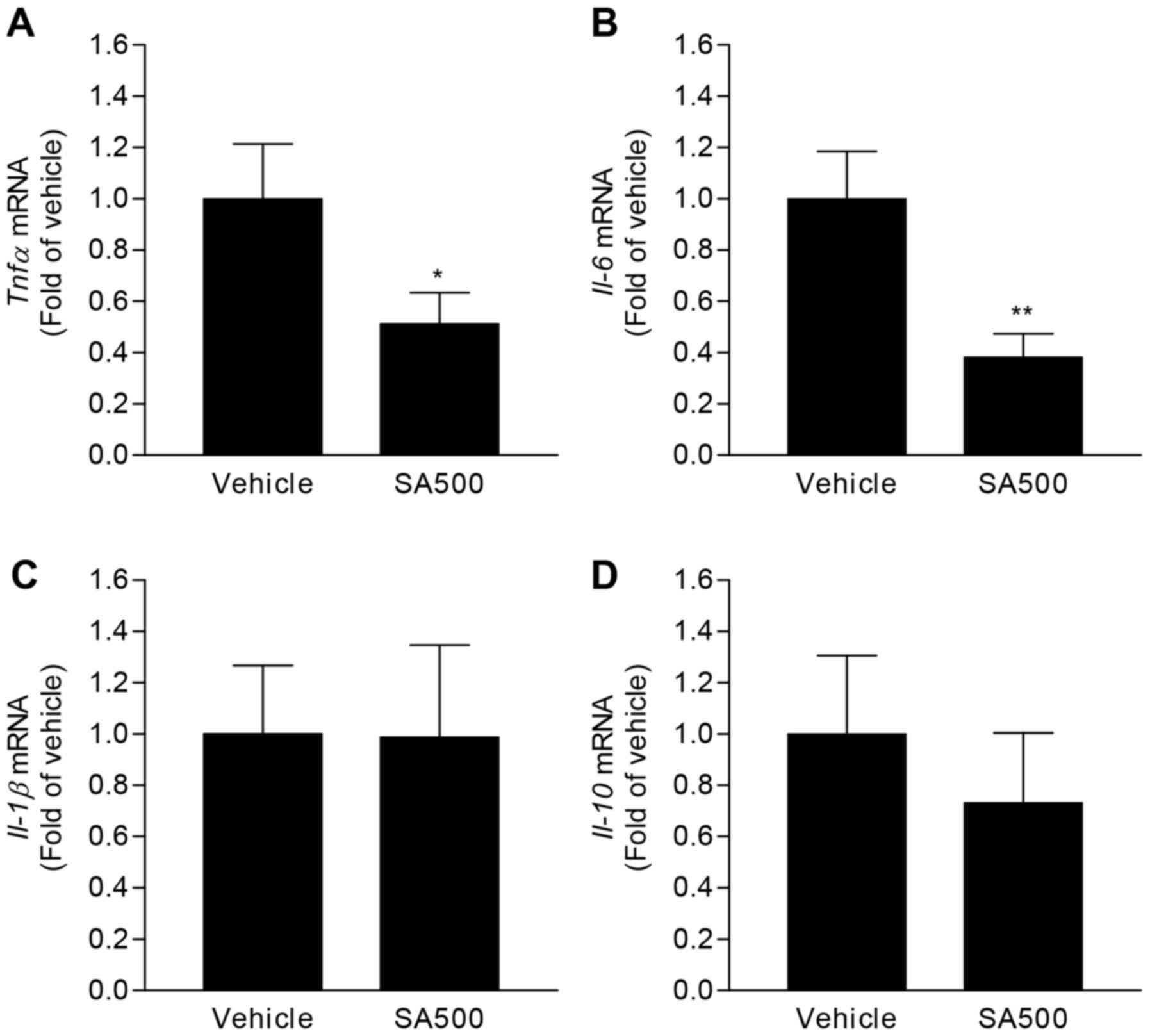
|
1
|
Lusis AJ: Atherosclerosis. Nature.
407:233–241. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman
M, Das SR, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Floyd J, Fornage M, Gillespie C,
et al: Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report
From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 135:e146–e603.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vargas JD, Manichaikul A, Wang XQ, Rich
SS, Rotter JI, Post WS, Polak JF, Budoff MJ and Bluemke DA: Common
genetic variants and subclinical atherosclerosis: The Multi-Ethnic
Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Atherosclerosis. 245:230–236.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hicken MT, Adar SD, Hajat A, Kershaw KN,
Do DP, Barr RG, Kaufman JD and Diez Roux AV: Air pollution,
cardiovascular outcomes and social disadvantage: The Multi-ethnic
Study of Atherosclerosis. Epidemiology. 27:42–50. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Spring B, Moller AC, Colangelo LA,
Siddique J, Roehrig M, Daviglus ML, Polak JF, Reis JP, Sidney S and
Liu K: Healthy lifestyle change and subclinical atherosclerosis in
young adults: Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults
(CARDIA) study. Circulation. 130:10–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tian J, Gu X, Sun Y, Ban X, Xiao Y, Hu S
and Yu B: Effect of statin therapy on the progression of coronary
atherosclerosis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 12:702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hoffmann H, Frieler K, Schlattmann P, Hamm
B and Dewey M: Influence of statin treatment on coronary
atherosclerosis visualised using multidetector computed tomography.
Eur Radiol. 20:2824–2833. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tabas I, García-Cardeña G and Owens GK:
Recent insights into the cellular biology of atherosclerosis. J
Cell Biol. 209:13–22. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Witztum JL and Steinberg D: Role of
oxidized low density lipoprotein in atherogenesis. J Clin Invest.
88:1785–1792. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Libby P: Inflammation in atherosclerosis.
Nature. 420:868–874. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rocha VZ and Libby P: Obesity,
inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 6:399–409.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hansson GK and Libby P: The immune
response in atherosclerosis: A double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol.
6:508–519. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kobayashi H, Kurokawa S and Ikeda K:
Dairyland populations of bur cucumber (Sicyos angulatus) as
a possible seed source for riverbank populations along the Abukuma
River, Japan. Weed Biol Manag. 12:147–155. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lee SM, Radhakrishnan R, Kang SM, Kim JH,
Lee IY, Moon BK, Yoon BW and Lee IJ: Phytotoxic mechanisms of bur
cucumber seed extracts on lettuce with special reference to
analysis of chloroplast proteins, phytohormones and nutritional
elements. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 122:230–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hulina N: New dangerous weed in Croatia:
Sicyos angulatus L. (Cucurbitaceae). Poljopr Znan Smotra.
61:259–264. 1996.
|
|
16
|
Watanabe O, Kurokawa S, Sasaki H, Nishida
T, Onoue T and Yoshimura Y: Geographic scale distribution and
occurrence pattern of invasive weeds. Grassl Sci. 48:440–450.
2002.
|
|
17
|
Badimon L and Vilahur G: LDL-cholesterol
versus HDL-cholesterol in the atherosclerotic plaque: Inflammatory
resolution versus thrombotic chaos. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1254:18–32.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ait-Oufella H, Taleb S, Mallat Z and
Tedgui A: Recent advances on the role of cytokines in
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:969–979. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ramji DP and Davies TS: Cytokines in
atherosclerosis: Key players in all stages of disease and promising
therapeutic targets. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 26:673–685. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Blankenberg S, Barbaux S and Tiret L:
Adhesion molecules and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis.
170:191–203. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Merritt WT: Nitric oxide: An important
bioregulator. Transplant Proc. 25:2014–2016. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gimbrone MA Jr and García-Cardeña G:
Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 118:620–636. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vidal F, Colomé C, Martínez-González J and
Badimon L: Atherogenic concentrations of native low-density
lipoproteins down-regulate nitric-oxide-synthase mRNA and protein
levels in endothelial cells. Eur J Biochem. 252:378–384. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Law MR, Wald NJ and Rudnicka AR:
Quantifying effect of statins on low density lipoprotein
cholesterol, ischaemic heart disease, and stroke: Systematic review
and meta-analysis. BMJ. 326:14232003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Trigatti BL, Krieger M and Rigotti A:
Influence of the HDL receptor SR-BI on lipoprotein metabolism and
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:1732–1738. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McLaren JE, Michael DR, Ashlin TG and
Ramji DP: Cytokines, macrophage lipid metabolism and foam cells:
Implications for cardiovascular disease therapy. Prog Lipid Res.
50:331–347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McKellar GE, McCarey DW, Sattar N and
McInnes IB: Role for TNF in atherosclerosis? Lessons from
autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 6:410–417. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pober JS and Sessa WC: Evolving functions
of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:803–815.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ohta H, Wada H, Niwa T, Kirii H, Iwamoto
N, Fujii H, Saito K, Sekikawa K and Seishima M: Disruption of tumor
necrosis factor-alpha gene diminishes the development of
atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis. 180:11–17.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huber SA, Sakkinen P, Conze D, Hardin N
and Tracy R: Interleukin-6 exacerbates early atherosclerosis in
mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 19:2364–2367. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang K, Huang XZ, Li XN, Feng M, Li L,
Cai XJ, Zhang C, Liu XL, Zhang MX, Zhang Y, et al: Interleukin 6
destabilizes atherosclerotic plaques by downregulating
prolyl-4-hydroxylase alpha1 via a mitogen-activated protein kinase
and c-Jun pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 528:127–133. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schuett H, Oestreich R, Waetzig GH, Annema
W, Luchtefeld M, Hillmer A, Bavendiek U, von Felden J, Divchev D,
Kempf T, et al: Transsignaling of interleukin-6 crucially
contributes to atherosclerosis in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 32:281–290. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schieffer B, Selle T, Hilfiker A,
Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Grote K, Tietge UJ, Trautwein C, Luchtefeld M,
Schmittkamp C, Heeneman S, et al: Impact of interleukin-6 on plaque
development and morphology in experimental atherosclerosis.
Circulation. 110:3493–3500. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Song L and Schindler C: IL-6 and the acute
phase response in murine atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis.
177:43–51. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kirii H, Niwa T, Yamada Y, Wada H, Saito
K, Iwakura Y, Asano M, Moriwaki H and Seishima M: Lack of
interleukin-1beta decreases the severity of atherosclerosis in
ApoE-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:656–660.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Clarke MC, Talib S, Figg NL and Bennett
MR: Vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis induces
interleukin-1-directed inflammation: Effects of
hyperlipidemia-mediated inhibition of phagocytosis. Circ Res.
106:363–372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shemesh S, Kamari Y, Shaish A, Olteanu S,
Kandel-Kfir M, Almog T, Grosskopf I, Apte RN and Harats D:
Interleukin-1 receptor type-1 in non-hematopoietic cells is the
target for the pro-atherogenic effects of interleukin-1 in
apoE-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis. 222:329–336. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Weber C, Zernecke A and Libby P: The
multifaceted contributions of leukocyte subsets to atherosclerosis:
Lessons from mouse models. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:802–815. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Moore KJ, Sheedy FJ and Fisher EA:
Macrophages in atherosclerosis: A dynamic balance. Nat Rev Immunol.
13:709–721. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Akihisa T, Tamura T and Matsumoto T:
24-Methylene-25-methyllathosterol: A sterol from Sicyos
angulatus. Phytochemistry. 26:575–577. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Na CS, Lee YH, Murai Y, Iwashina T, Kim TW
and Hong SH: Flavonol 3,7-diglycosides from the aerial parts of
Sicyos angulatus (Cucurbitaceae) in Korea and Japan. Biochem
Syst Ecol. 48:235–237. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|