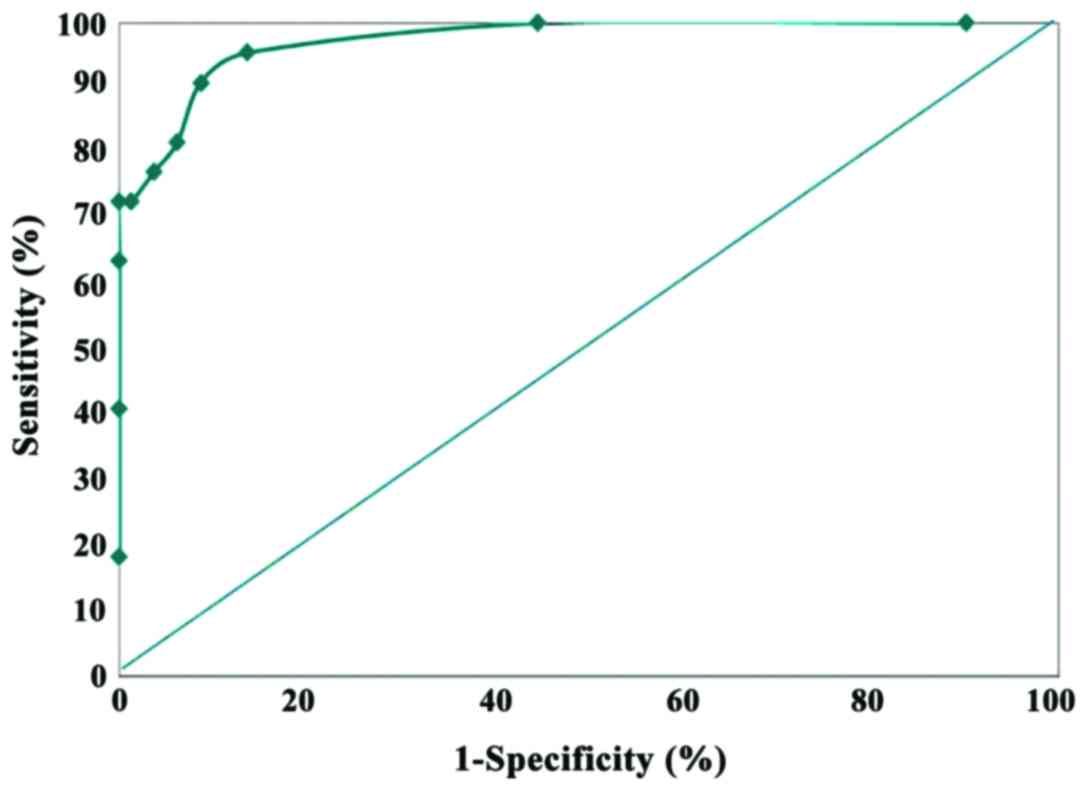
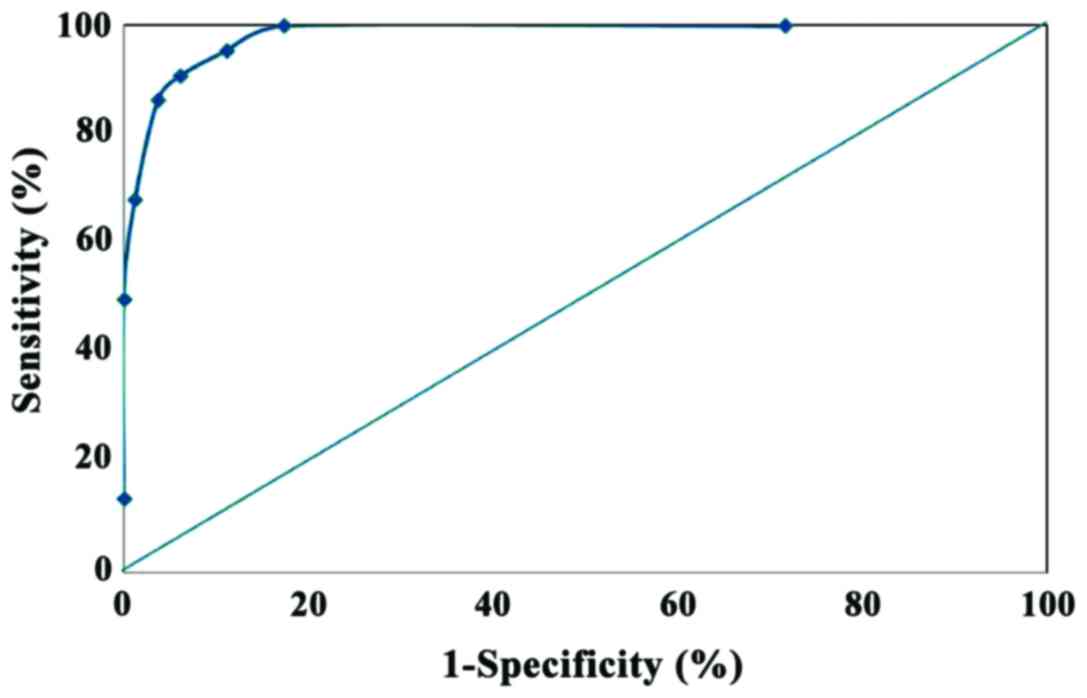
|
1
|
Reddy SL, Grayson AD, Griffiths EM, Pullan
DM and Rashid A: Logistic risk model for prolonged ventilation
after adult cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 84:528–536. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bellomo R, Kellum JA and Ronco C: Defining
acute renal failure: Physiological principles. Intensive Care Med.
30:33–37. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Doddakula K, Al-Sarraf N, Gately K, Hughes
A, Tolan M, Young V and McGovern E: Predictors of acute renal
failure requiring renal replacement therapy post cardiac surgery in
patients with preoperatively normal renal function. Interact
Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 6:314–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Song S, Meyer M, Türk TR, Wilde B,
Feldkamp T, Assert R, Wu K, Kribben A and Witzke O: Serum cystatin
C in mouse models: A reliable and precise marker for renal function
and superior to serum creatinine. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
24:1157–1161. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jin Y, Shao X, Sun B, Miao C, Li Z and Shi
Y: Urinary kidney injury molecule 1 as an early diagnostic
biomarker of obstructive acute kidney injury and development of a
rapid detection method. Mol Med Rep. 15:1229–1235. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Devarajan P: Neutrophil
gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL): A new marker of kidney
disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest (Suppl). 241:89–94. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes
MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, Ruff SM, Zahedi K, Shao M, Bean J, et al:
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker
for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet.
365:1231–1238. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nguyen MT and Devarajan P: Biomarkers for
the early detection of acute kidney injury. Pediatr Nephrol.
23:2151–2157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goldstein SL: Pediatric acute kidney
injury: It's time for real progress. Pediatr Nephrol. 21:891–895.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nunag M, Brogan M and Garrick R:
Mitigating contrast-induced acute kidney injury associated with
cardiac catheterization. Cardiol Rev. 17:263–269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Karkouti K, Wijeysundera DN, Yau TM,
Callum JL, Cheng DC, Crowther M, Dupuis JY, Fremes SE, Kent B,
Laflamme C, et al: Acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: Focus
on modifiable risk factors. Circulation. 119:495–502. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu Y, Wang L, Meng L, Cao GK and Zhang Y:
MIP-1α and NF-κB as indicators of acute kidney injury secondary to
acute lung injury in mechanically ventilated patients. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 20:3830–3834. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nissenson AR: Acute renal failure:
Definition and pathogenesis. Kidney Int (Suppl). 66:S7–S10.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pirgakis KM, Makris K, Dalainas I, Lazaris
AM, Maltezos CK and Liapis CD: Urinary cystatin C as an early
biomarker of acute kidney injury after open and endovascular
abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Ann Vasc Surg. 28:1649–1658.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Parikh CR, Jani A, Melnikov VY, Faubel S
and Edelstein CL: Urinary interleukin-18 is a marker of human acute
tubular necrosis. Am J Kidney Dis. 43:405–414. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Melnikov VY, Faubel S, Siegmund B, Lucia
MS, Ljubanovic D and Edelstein CL: Neutrophil-independent
mechanisms of caspase-1- and IL-18-mediated ischemic acute tubular
necrosis in mice. J Clin Invest. 110:1083–1091. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Parikh CR, Mishra J, Thiessen-Philbrook H,
Dursun B, Ma Q, Kelly C, Dent C, Devarajan P and Edelstein CL:
Urinary IL-18 is an early predictive biomarker of acute kidney
injury after cardiac surgery. Kidney Int. 70:199–203. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Han WK, Wagener G, Zhu Y, Wang S and Lee
HT: Urinary biomarkers in the early detection of acute kidney
injury after cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 4:873–882.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bolignano D, Lacquaniti A, Coppolino G,
Donato V, Campo S, Fazio MR, Nicocia G and Buemi M: Neutrophil
gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and progression of chronic
kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 4:337–344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shemin D and Dworkin LD: Neutrophil
gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for early
acute kidney injury. Crit Care Clin. 27:379–389. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|