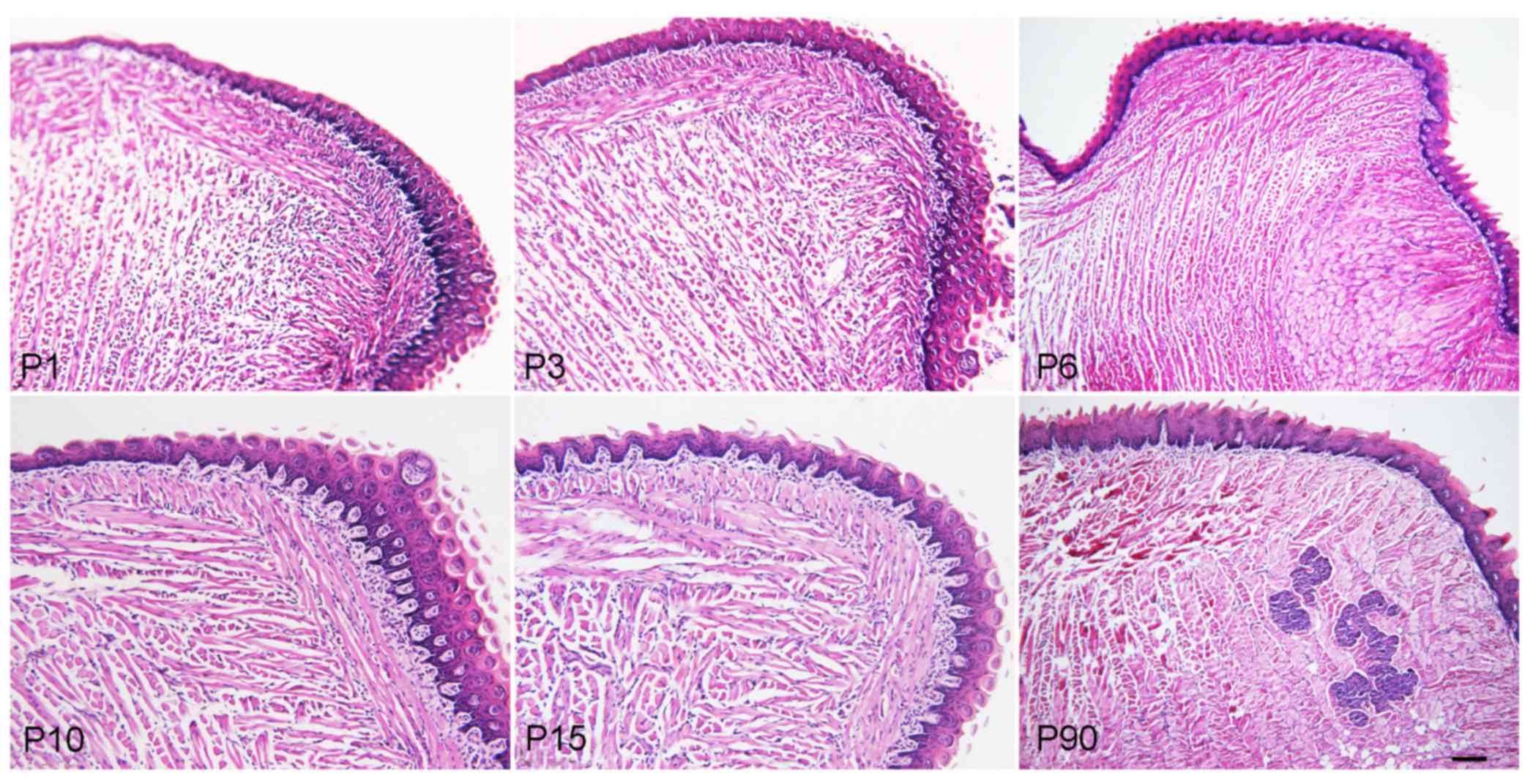
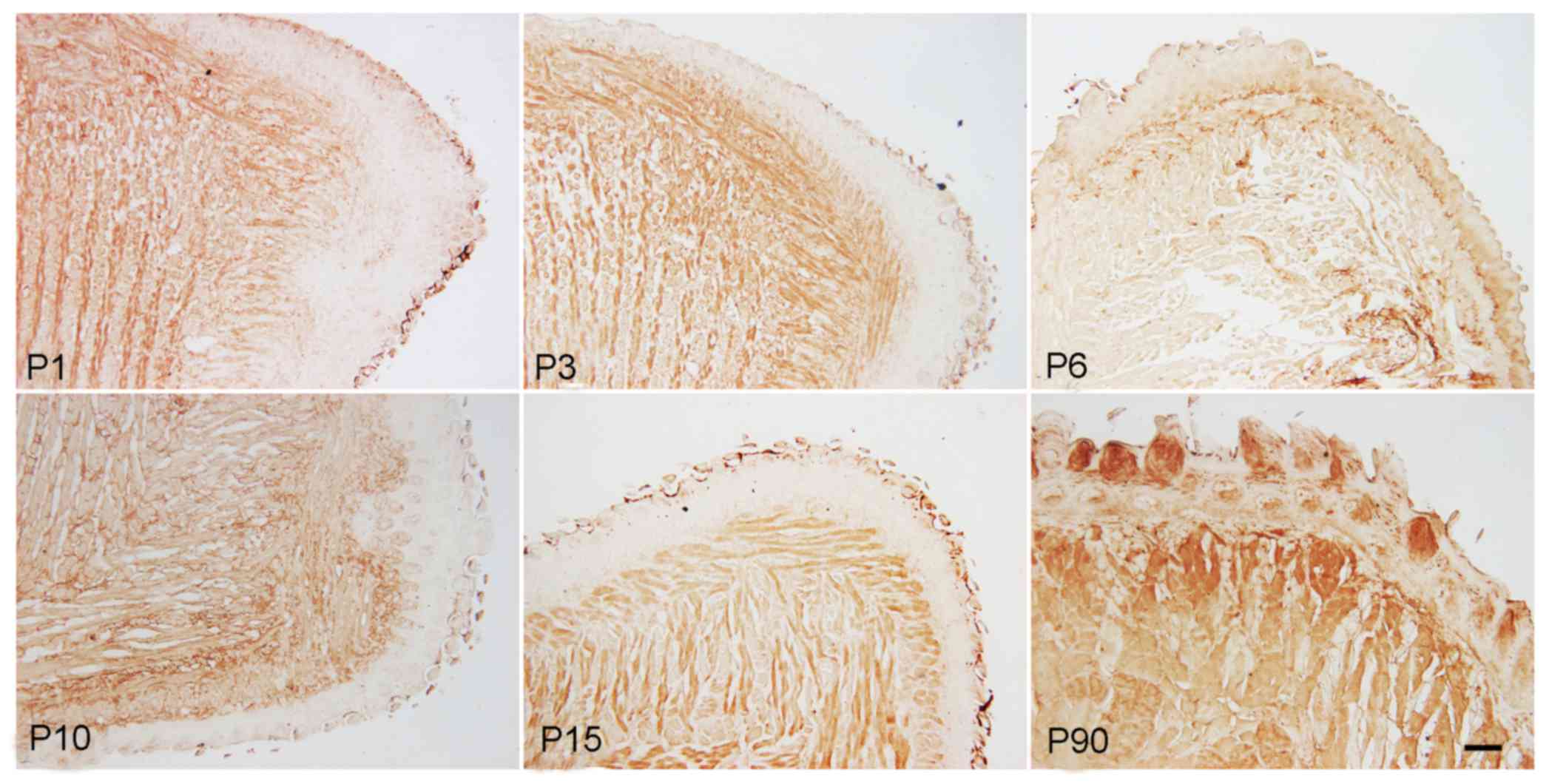
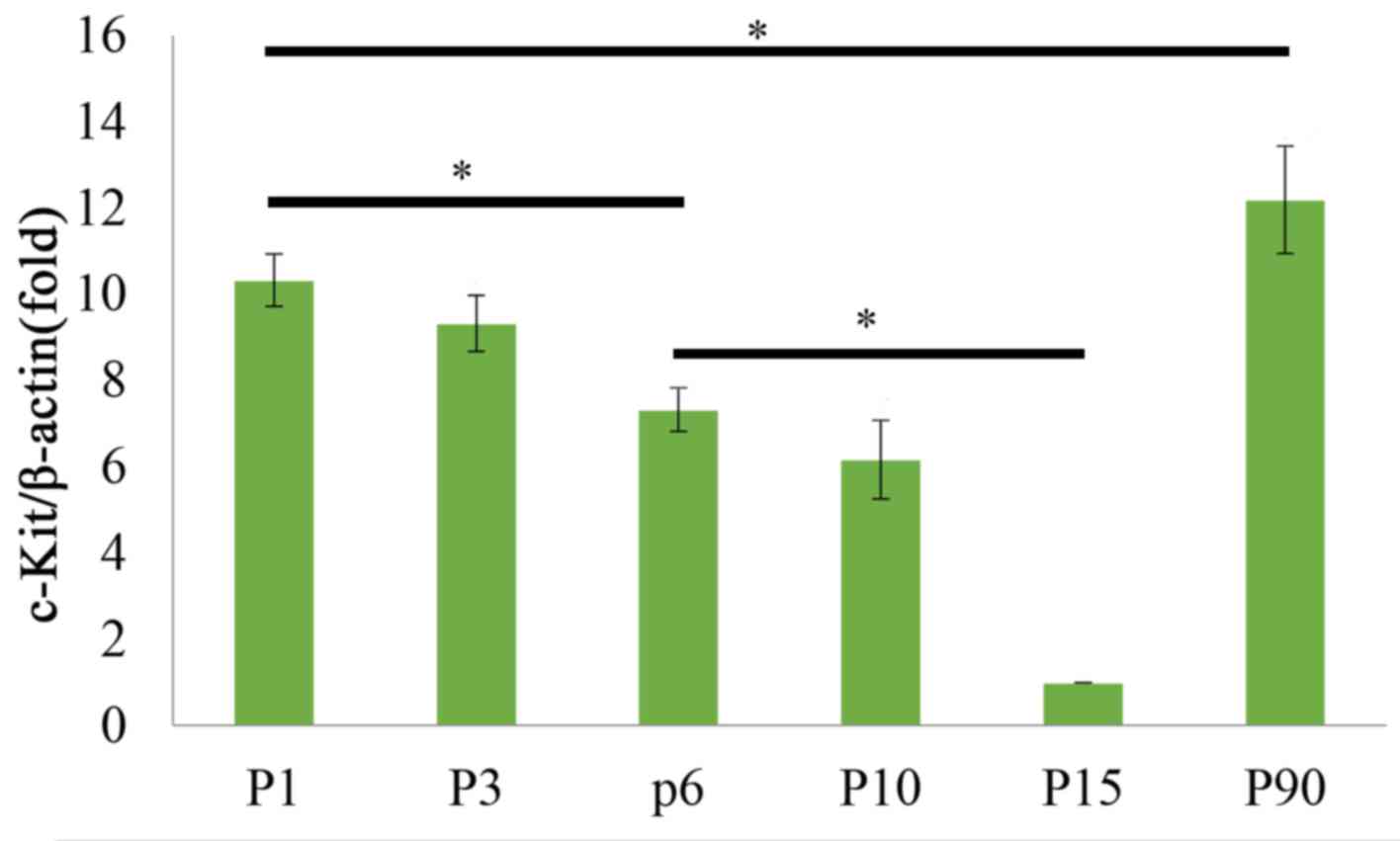
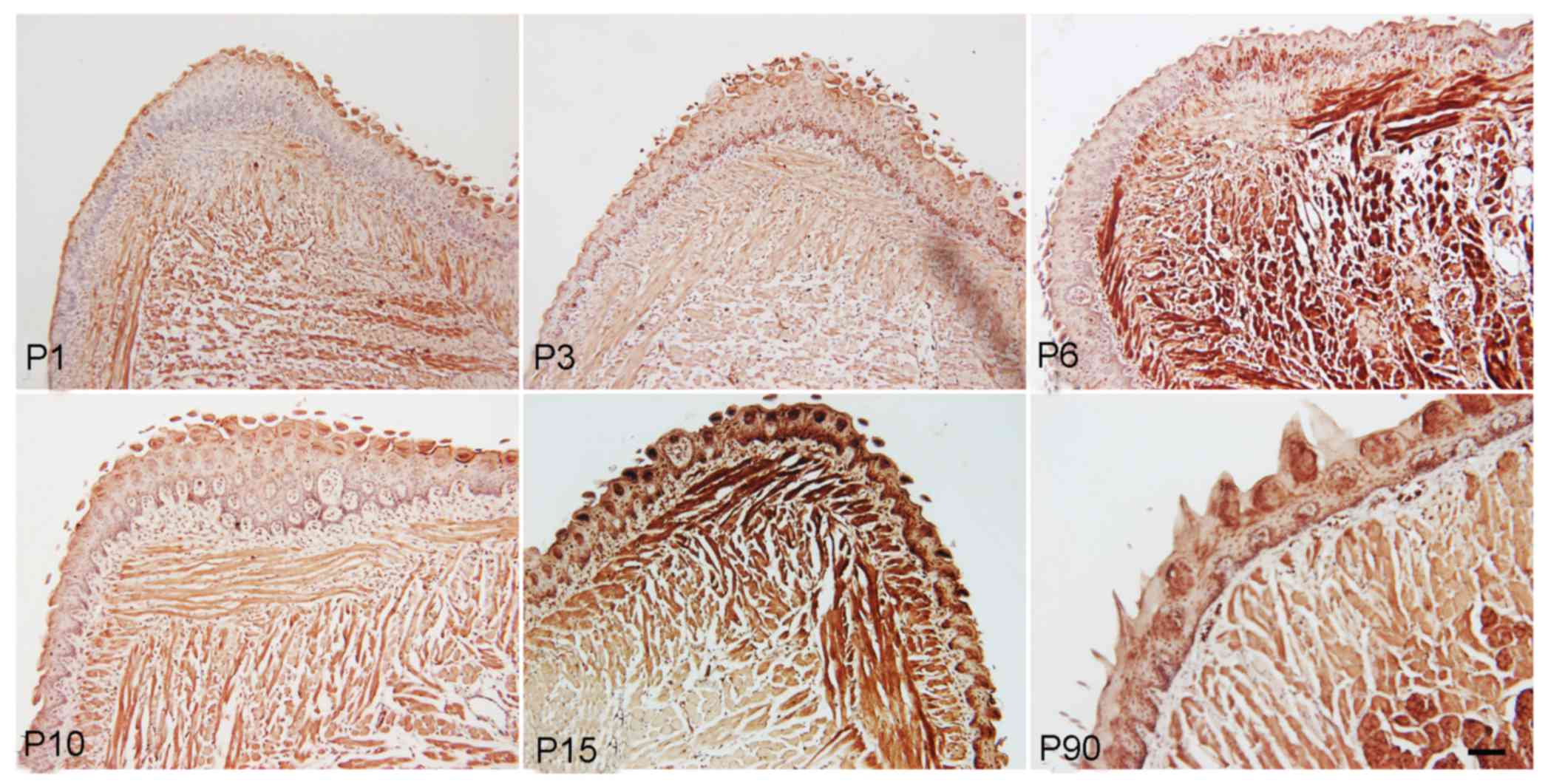
|
1
|
Cong W, Liu B, Liu S, Sun M, Liu H, Yang
Y, Wang R and Xiao J: Implications of the Wnt5a/CaMKII pathway in
retinoic acid-induced myogenic tongue abnormalities of developing
mice. Sci Rep. 4:60822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Iwata J, Suzuki A, Pelikan RC, Ho TV and
Chai Y: Noncanonical transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) signaling
in cranial neural crest cells causes tongue muscle developmental
defects. J Biol Chem. 288:29760–29770. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shuler CF and Dalrymple KR: Molecular
regulation of tongue and craniofacial muscle differentiation. Crit
Rev Oral Biol Med. 12:3–17. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maciejewski A, Szymczyk C and Wierzgoń J:
Triple skin island fibula free flap: A good choice for combined
mandible and tongue defect reconstruction. J Reconstr Microsurg.
24:461–468. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2 (-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang X, Qi S, Wang J, Xia D, Qin L, Zheng
Z, Wang L, Zhang C, Jin L, Ding G, et al: Spatial and temporal
expression of c-Kit in the development of the murine submandibular
gland. J Mol Histol. 45:381–389. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miller IJ Jr and Smith DV: Proliferation
of taste buds in the foliate and vallate papillae of postnatal
hamsters. Growth Dev Aging. 52:123–131. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu HX, Ermilov A, Grachtchouk M, Li L,
Gumucio DL, Dlugosz AA and Mistretta CM: Multiple shh signaling
centers participate in fungiform papilla and taste bud formation
and maintenance. Dev Biol. 382:82–97. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Song XM, Ye JH, Yuan Y, Zhang SY, Jiang HB
and Wu YN: Radial forearm free flap for reconstruction of a large
defect after radical ablation of carcinoma of the tongue and floor
of the mouth: Some new modifications. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat
Spec. 72:106–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hindi SM and Kumar A: TRAF6 regulates
satellite stem cell self-renewal and function during regenerative
myogenesis. J Clin Invest. 126:151–168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Collins CA, Olsen I, Zammit PS, Heslop L,
Petrie A, Partridge TA and Morgan JE: Stem cell function,
self-renewal, and behavioral heterogeneity of cells from the adult
muscle satellite cell niche. Cell. 122:289–301. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wagers AJ and Conboy IM: Cellular and
molecular signatures of muscle regeneration: Current concepts and
controversies in adult myogenesis. Cell. 122:659–667. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Noda S, Horiguchi K, Ichikawa H and
Miyoshi H: Repopulating activity of ex vivo-expanded murine
hematopoietic stem cells resides in the CD48-c-Kit+Sca-1+lineage
marker- cell population. Stem Cells. 26:646–655. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sandstedt J, Jonsson M, Dellgren G,
Lindahl A, Jeppsson A and Asp J: Human C-kit+CD45- cardiac stem
cells are heterogeneous and display both cardiac and endothelial
commitment by single-cell qPCR analysis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 443:234–238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang YK, Han XY and Che ZY: Effects of
buyang huanwu tang combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell
transplantation on the expression of VEGF and Ki-67 in the brain
tissue of the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model rat. J Tradit
Chin Med. 30:278–282. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yamane A, Mayo M, Shuler C, Crowe D,
Ohnuki Y, Dalrymple K and Saeki Y: Expression of myogenic
regulatory factors during the development of mouse tongue striated
muscle. Arch Oral Biol. 45:71–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kawabe Y, Wang YX, McKinnell IW, Bedford
MT and Rudnicki MA: Carm1 regulates Pax7 transcriptional activity
through MLL1/2 recruitment during asymmetric satellite stem cell
divisions. Cell Stem Cell. 11:333–345. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kirkpatrick LJ, Allouh MZ, Nightingale CN,
Devon HG, Yablonka-Reuveni Z and Rosser BW: Pax7 shows higher
satellite cell frequencies and concentrations within intrafusal
fibers of muscle spindles. J Histochem Cytochem. 56:831–840. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee H, Habas R and Abate-Shen C: MSX1
cooperates with histone H1b for inhibition of transcription and
myogenesis. Science. 304:1675–1678. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kodaka Y, Tanaka K, Kitajima K,
Tanegashima K, Matsuda R and Hara T: LIM homeobox transcription
factor Lhx2 inhibits skeletal muscle differentiation in part via
transcriptional activation of Msx1 and Msx2. Exp Cell Res.
331:309–319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|