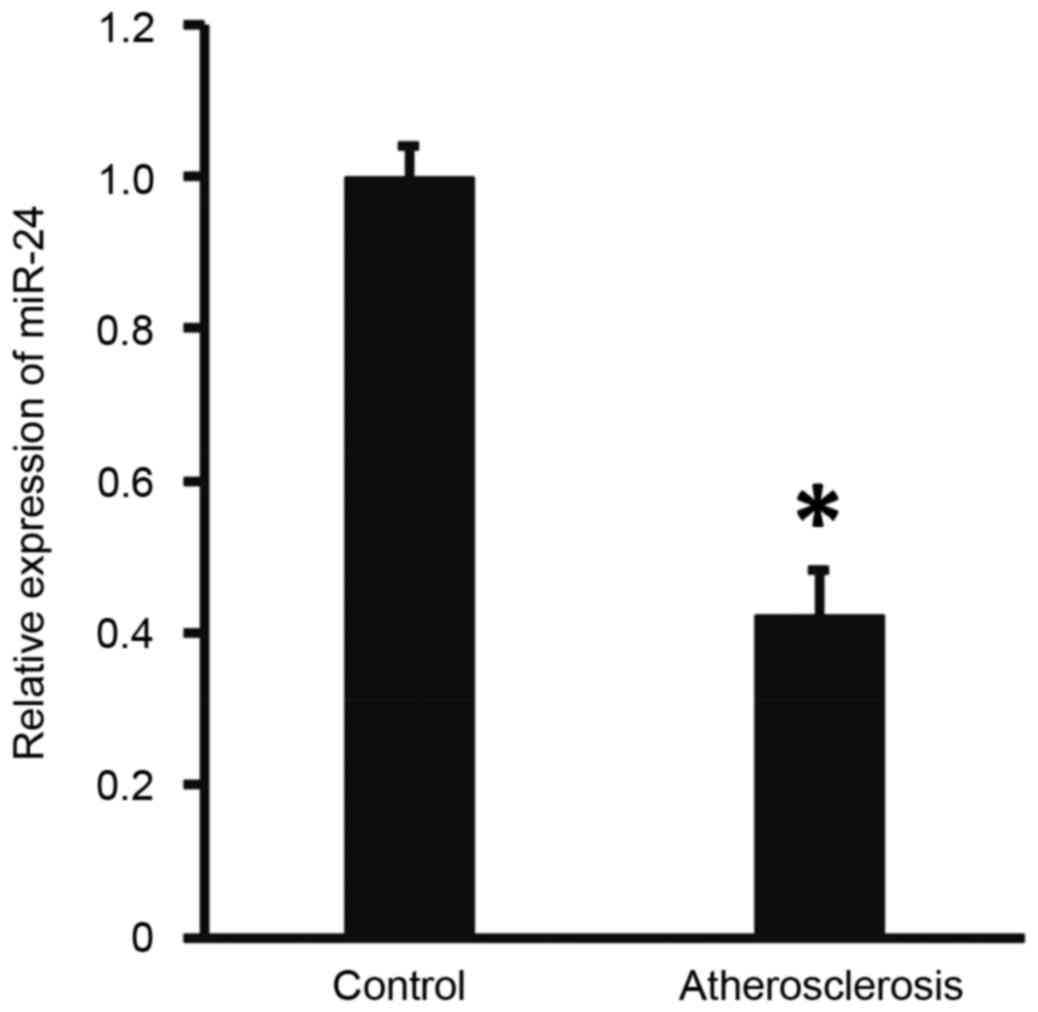
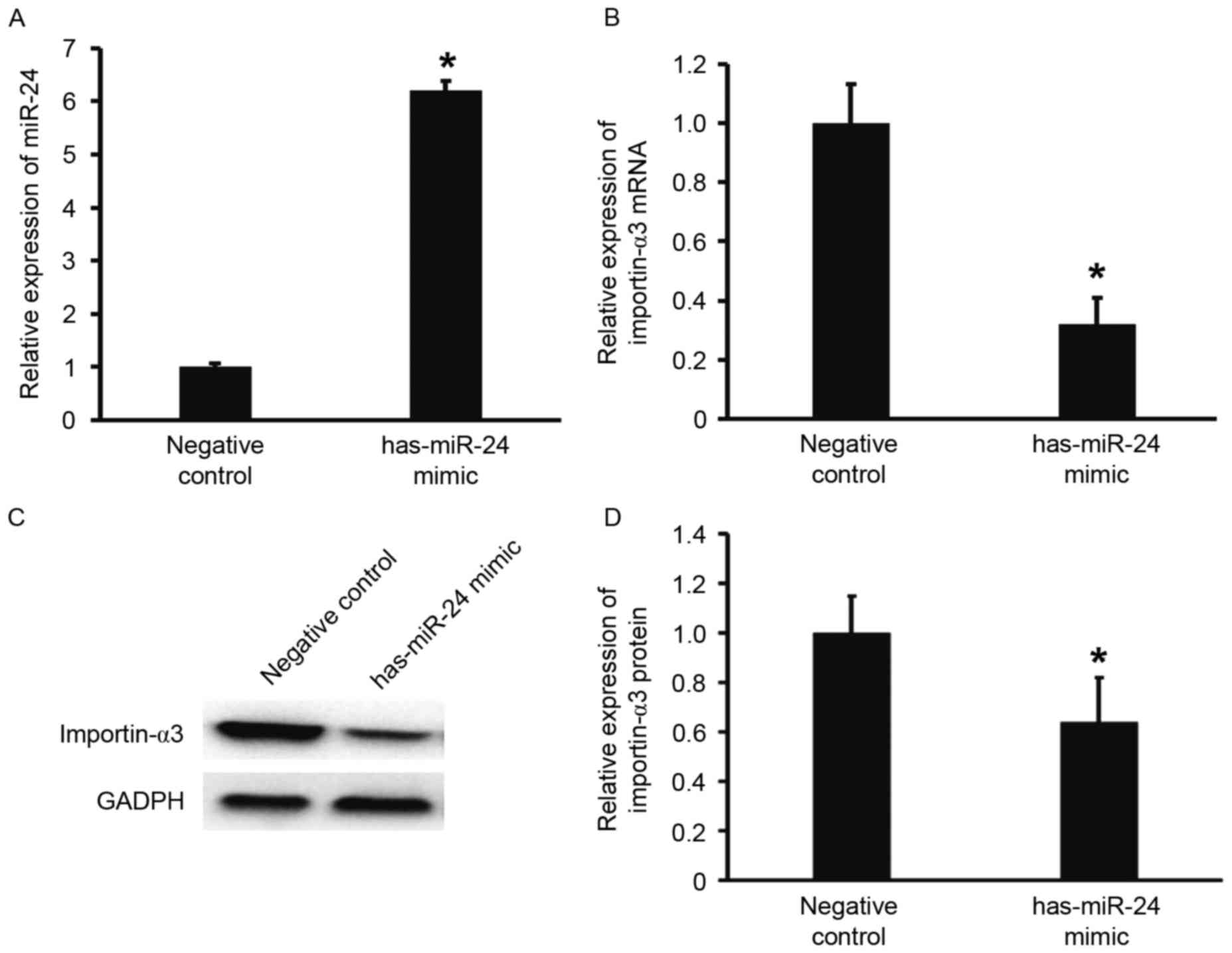
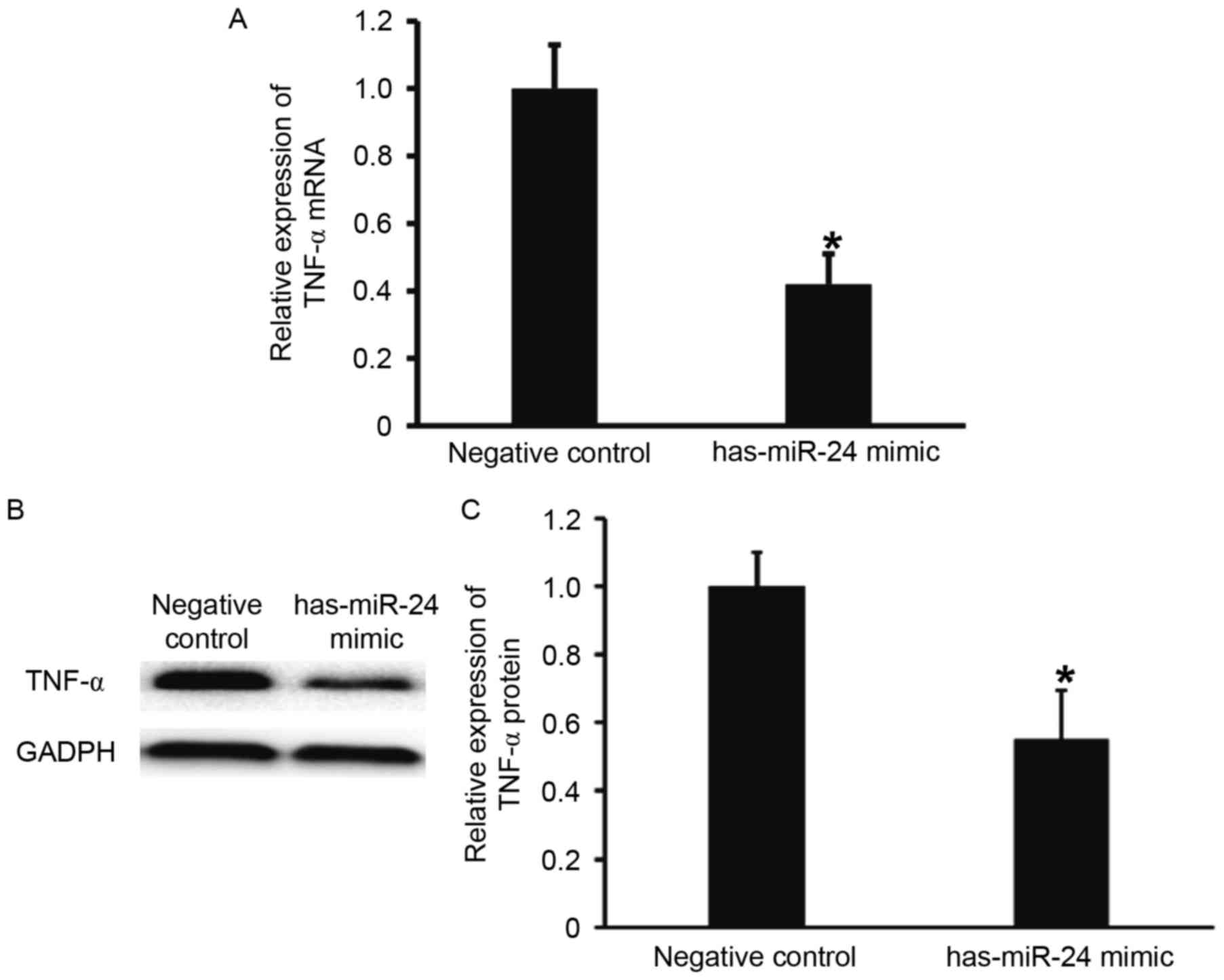
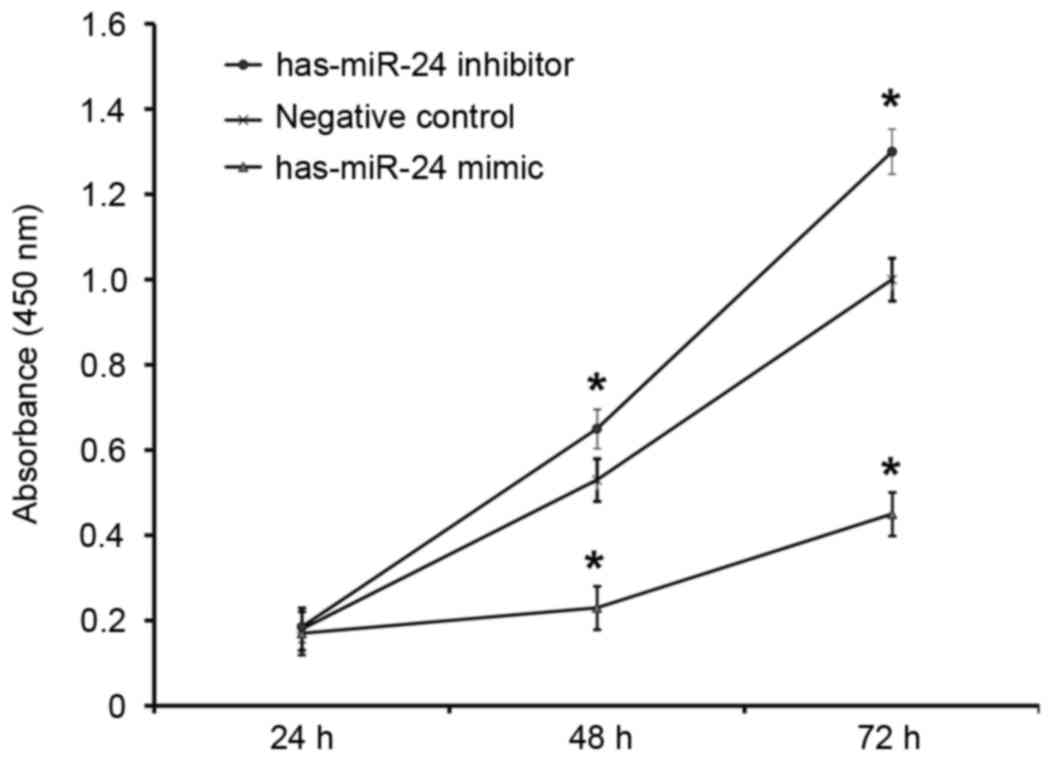
|
1
|
Beckman JA, Creager MA and Libby P:
Diabetes and atherosclerosis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and
management. JAMA. 287:2570–2581. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Malek AM, Alper SL and Izumo S:
Hemodynamic shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis. JAMA.
282:2035–2042. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ross R and Glomset JA: Atherosclerosis and
the arterial smooth muscle cell: Proliferation of smooth muscle is
a key event in the genesis of the lesions of atherosclerosis.
Science. 180:1332–1339. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Katsuda S and Kaji T: Atherosclerosis and
extracellular matrix. J Atheroscler Thromb. 10:267–274. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Morland K, Wing S and Roux A Diez: The
contextual effect of the local food environment on residents'
diets: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Am J Public
Health. 92:1761–1767. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fox CS, Polak JF, Chazaro I, Cupples A,
Wolf PA, D'Agostino RA and O'Donnell CJ: Framingham Heart Study:
Genetic and environmental contributions to atherosclerosis
phenotypes in men and women: Heritability of carotid intima-media
thickness in the Framingham Heart Study. Stroke. 34:397–401. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fenyo IM and Gafencu AV: The involvement
of the monocytes/macrophages in chronic inflammation associated
with atherosclerosis. Immunobiology. 218:1376–1384. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gomez D and Owens GK: Smooth muscle cell
phenotypic switching in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res.
95:156–164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Munro JM and Cotran RS: The pathogenesis
of atherosclerosis: Atherogenesis and inflammation. Lab Invest.
58:249–261. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
de Winther MP, Kanters E, Kraal G and
Hofker MH: Nuclear factor kappaB signaling in atherogenesis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:904–914. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rajendran P, Rengarajan T, Thangavel J,
Nishigaki Y, Sakthisekaran D, Sethi G and Nishigaki I: The vascular
endothelium and human diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 9:1057–1069. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fagerlund R, Kinnunen L, Köhler M,
Julkunen I and Melén K: NF-{kappa}B is transported into the nucleus
by importin {alpha}3 and importin {alpha}4. J Biol Chem.
280:15942–15951. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bouwmeester T, Bauch A, Ruffner H, Angrand
PO, Bergamini G, Croughton K, Cruciat C, Eberhard D, Gagneur J,
Ghidelli S, et al: A physical and functional map of the human
TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. Nat Cell Biol.
6:97–105. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rayner KJ, Fernandez-Hernando C and Moore
KJ: MicroRNAs regulating lipid metabolism in atherogenesis. Thromb
Haemost. 107:642–647. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Koch M, Mollenkopf HJ, Klemm U and Meyer
TF: Induction of microRNA-155 is TLR- and type IV secretion
system-dependent in macrophages and inhibits DNA-damage induced
apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:pp. E1153–E1162. 2012;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nazari-Jahantigh M, Wei Y, Noels H, Akhtar
S, Zhou Z, Koenen RR, Heyll K, Gremse F, Kiessling F, Grommes J, et
al: MicroRNA-155 promotes atherosclerosis by repressing Bcl6 in
macrophages. J Clin Invest. 122:4190–4202. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei Y, Nazari-Jahantigh M, Chan L, Zhu M,
Heyll K, Corbalán-Campos J, Hartmann P, Thiemann A, Weber C and
Schober A: The microRNA-342-5p fosters inflammatory macrophage
activation through an Akt1- and microRNA-155-dependent pathway
during atherosclerosis. Circulation. 127:1609–1619. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ramírez CM, Goedeke L, Rotllan N, Yoon JH,
Cirera-Salinas D, Mattison JA, Suárez Y, de Cabo R, Gorospe M and
Fernández-Hernando C: MicroRNA 33 regulates glucose metabolism. Mol
Cell Biol. 33:2891–2902. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hu J, Xu Y, Hao J, Wang S, Li C and Meng
S: MiR-122 in hepatic function and liver diseases. Protein Cell.
3:364–371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shirasaki T, Honda M, Shimakami T, Horii
R, Yamashita T, Sakai Y, Sakai A, Okada H, Watanabe R, Murakami S,
et al: MicroRNA-27a regulates lipid metabolism and inhibits
hepatitis C virus replication in human hepatoma cells. J Virol.
87:5270–5286. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie Y, Tobin LA, Camps J, Wangsa D, Yang
J, Rao M, Witasp E, Awad KS, Yoo N, Ried T and Kwong KF:
MicroRNA-24 regulates XIAP to reduce the apoptosis threshold in
cancer cells. Oncogene. 32:2442–2451. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Meloni M, Marchetti M, Garner K,
Littlejohns B, Sala-Newby G, Xenophontos N, Floris I, Suleiman MS,
Madeddu P, Caporali A and Emanueli C: Local inhibition of
microRNA-24 improves reparative angiogenesis and left ventricle
remodeling and function in mice with myocardial infarction. Mol
Ther. 21:1390–1402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maegdefessel L, Spin JM, Raaz U, Eken SM,
Toh R, Azuma J, Adam M, Nakagami F, Heymann HM, Chernogubova E, et
al: miR-24 limits aortic vascular inflammation and murine abdominal
aneurysm development. Nat Commun. 5:52142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Murata K, Furu M, Yoshitomi H, Ishikawa M,
Shibuya H, Hashimoto M, Imura Y, Fujii T, Ito H, Mimori T and
Matsuda S: Comprehensive microRNA analysis identifies miR-24 and
miR-125a-5p as plasma biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS
One. 8:e691182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hansson GK: Inflammation, atherosclerosis,
and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 352:1685–1695. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Hansson GK: Leducq
Transatlantic Network on Atherothrombosis: Inflammation in
atherosclerosis: From pathophysiology to practice. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 54:2129–2138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Packard RR and Libby P: Inflammation in
atherosclerosis: From vascular biology to biomarker discovery and
risk prediction. Clin Chem. 54:24–38. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chachaj A, Drozdz K and Szuba A: Reverse
cholesterol transport processes and their role in artherosclerosis
regression. Postepy Biochem. 54:301–307. 2008.(In Polish).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hansson GK and Hermansson A: The immune
system in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol. 12:204–212. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Di Gregoli K, Jenkins N, Salter R, White
S, Newby AC and Johnson JL: MicroRNA-24 regulates macrophage
behavior and retards atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 34:1990–2000. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kelley JB, Talley AM, Spencer A, Gioeli D
and Paschal BM: Karyopherin alpha7 (KPNA7), a divergent member of
the importin alpha family of nuclear import receptors. BMC Cell
Biol. 11:632010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Naqvi AR, Fordham JB, Ganesh B and Nares
S: miR-24, miR-30b and miR-142-3p interfere with antigen processing
and presentation by primary macrophages and dendritic cells. Sci
Rep. 6:329252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xiang Y, Cheng J, Wang D, Hu X, Xie Y,
Stitham J, Atteya G, Du J, Tang WH, Lee SH, et al: Hyperglycemia
repression of miR-24 coordinately upregulates endothelial cell
expression and secretion of von Willebrand factor. Blood.
125:3377–3387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu XD, Wu X, Yin YL, Liu YQ, Geng MM,
Yang HS, Blachier F and Wu GY: Effects of dietary L-arginine or
N-carbamylglutamate supplementation during late gestation of sows
on the miR-15b/16, miR-221/222, VEGFA and eNOS expression in
umbilical vein. Amino Acids. 42:2111–2119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rippe C, Blimline M, Magerko KA, Lawson
BR, LaRocca TJ, Donato AJ and Seals DR: MicroRNA changes in human
arterial endothelial cells with senescence: Relation to apoptosis,
eNOS and inflammation. Exp Gerontol. 47:45–51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Boon RA, Seeger T, Heydt S, Fischer A,
Hergenreider E, Horrevoets AJ, Vinciguerra M, Rosenthal N, Sciacca
S, Pilato M, et al: MicroRNA-29 in aortic dilation: Implications
for aneurysm formation. Circ Res. 109:1115–1119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lal A, Navarro F, Maher CA, Maliszewski
LE, Yan N, O'Day E, Chowdhury D, Dykxhoorn DM, Tsai P, Hofmann O,
et al: miR-24 Inhibits cell proliferation by targeting E2F2, MYC,
and other cell-cycle genes via binding to ‘seedless’ 3′UTR microRNA
recognition elements. Mol Cell. 35:610–625. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Amelio I, Lena AM, Viticchiè G,
Shalom-Feuerstein R, Terrinoni A, Dinsdale D, Russo G, Fortunato C,
Bonanno E, Spagnoli LG, et al: miR-24 triggers epidermal
differentiation by controlling actin adhesion and cell migration. J
Cell Biol. 199:347–363. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|