|
1
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis-an inflammatory
disease. N Engl J Med. 340:115–126. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Falk E, Shah PK and Fuster V: Coronary
plaque disruption. Circulation. 92:657–671. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen S, Xiao J, Liu X, Liu MM, Mo ZC, Yin
K, Zhao GJ, Jiang J, Cui LB, Tan CZ, et al: Ibrolipim increases
ABCA1/G1 expression by the LXRα signaling pathway in THP-1
macrophage-derived foam cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 31:1343–1349.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
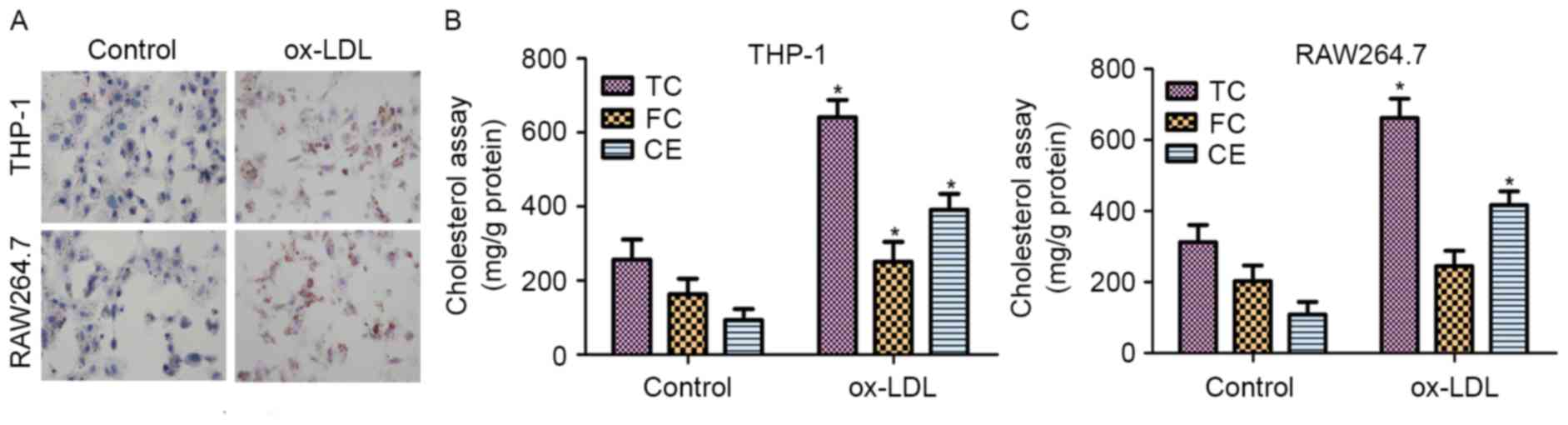
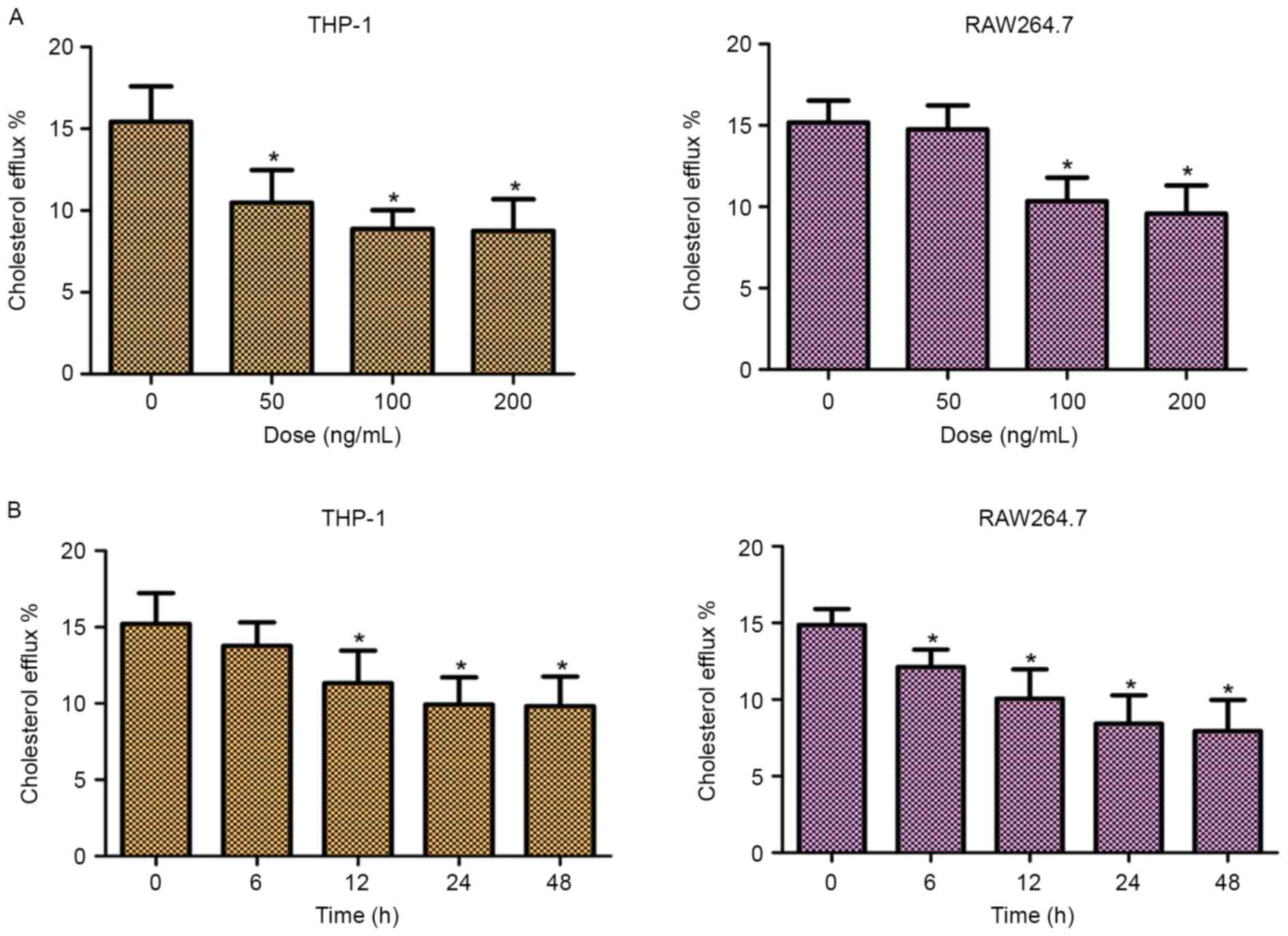
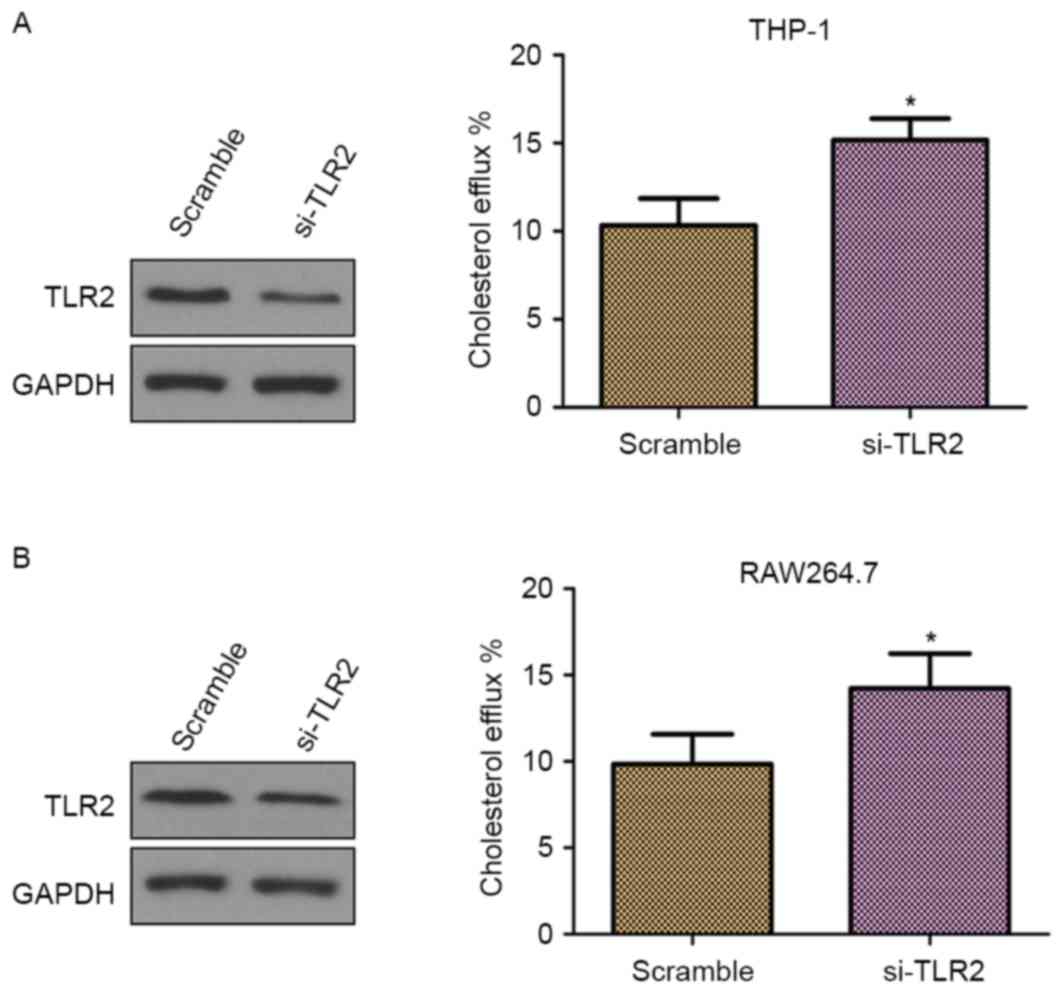
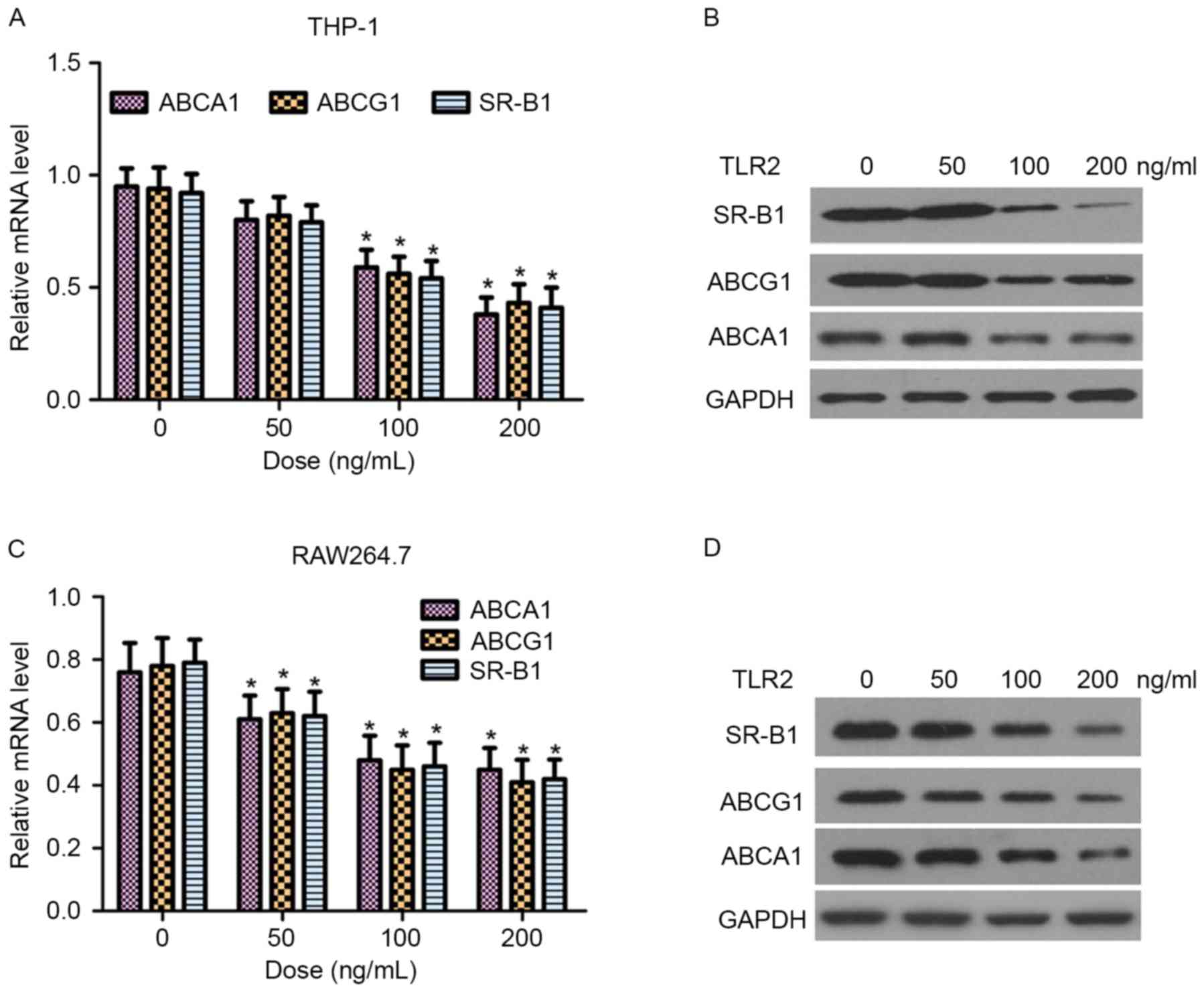
|
|
4
|
Hu C, Dandapat A, Sun L, Chen J, Marwali
MR, Romeo F, Sawamura T and Mehta JL: LOX1 deletion decreases
collagen accumulation in atherosclerotic plaque in low-density
lipoprotein receptor knockout mice fed a high cholesterol diet.
Cardiovasc Res. 79:287–293. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Karunakaran D, Geoffrion M, Wei L, Gan W,
Richards L, Shangari P, DeKemp EM, Beanlands RA, Perisic L,
Maegdefessel L, et al: Targeting macrophage necroptosis for
therapeutic and diagnostic interventions in atherosclerosis. Sci
Adv. 2:e16002242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV and Chistiakov
DA: The complexity of cell composition of the intima of large
arteries: Focus on pericyte-like cells. Cardiovasc Res.
103:438–451. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Randolph GJ: Mechanisms that regulate
macrophage burden in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 114:1757–1771.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Julve J, Llaverias G, Blancovaca F and
Escolàgil JC: Seeking novel targets for improving in vivo
macrophage-specific reverse cholesterol transport: Translating
basic science into new therapies for the prevention and treatment
of atherosclerosis. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 9:220–237. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu YW, Wang Q, Ma X, Li XX, Liu XH, Xiao
J, Liao DF, Xiang J and Tang CK: TGF-beta1 up-regulates expression
of ABCA1, ABCG1 and SR-BI through liver X receptor alpha signaling
pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. J Atheroscler
Thromb. 17:493–502. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gay NJ and Gangloff M: Structure and
function of Toll receptors and their ligands. Annu Rev Biochem.
76:141–165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
De Nardo D: Toll-like receptors:
Activation, signalling and transcriptional modulation. Cytokine.
74:181–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Medzhitov R: Toll-like receptors and
innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 1:135–145. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hantke K and Braun V: Covalent binding of
lipid to protein. Diglyceride and amide-linked fatty acid at the
N-terminal end of the murein-lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli
outer membrane. Eur J Biochem. 34:284–296. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ozinsky A, Smith KD, Hume D and Underhill
DM: Co-operative induction of pro-inflammatory signaling by
Toll-like receptors. J Endotoxin Res. 6:393–396. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mercurio F and Manning AM: NF-kappaB as a
primary regulator of the stress response. Oncogene. 18:6163–6171.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lawrence T: The nuclear factor NF-kappaB
pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0016512009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kobayashi H, Hirata M, Saito T, Itoh S,
Chung U and Kawaguchi H: Transcriptional induction of ADAMTS5
protein by nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) family member RelA/p65 in
chondrocytes during osteoarthritis development. J Biol Chem.
288:28620–28629. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun Z and Andersson R: NF-kappaB
activation and inhibition: A review. Shock. 18:99–106. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vallabhapurapu S and Karin M: Regulation
and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune
system. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:693–733. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu S, Huang Y, Xie Y, Lan T, Le K, Chen J,
Chen S, Gao S, Xu X, Shen X, et al: Evaluation of foam cell
formation in cultured macrophages: An improved method with Oil Red
O staining and DiI-oxLDL uptake. Cytotechnology. 62:473–481. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liang B, Wang X, Yan F, Bian YF, Liu M,
Bai R, Yang HY, Zhang NN, Yang ZM and Xiao CS: Angiotensin-(1–7)
upregulates (ATP-binding cassette transporter A1) ABCA1 expression
through cyclic AMP signaling pathway in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:985–991. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mo ZC, Xiao J, Liu XH, Hu YW, Li XX, Yi
GH, Wang Z, Tang YL, Liao DF and Tang CK: AOPPs inhibits
cholesterol efflux by down-regulating ABCA1 expression in a
JAK/STAT signaling pathway-dependent manner. J Atheroscler Thromb.
18:796–807. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu XY, Lu Q, Ouyang XP, Tang SL, Zhao GJ,
Lv YC, He PP, Kuang HJ, Tang YY, Fu Y, et al: Apelin-13 increases
expression of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 via activating
protein kinase C α signaling in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam
cells. Atherosclerosis. 226:398–407. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao H, Li L, Li L, Gong B, Dong P,
Fordjour PA, Zhu Y and Fan G: Danshensu promotes cholesterol efflux
in RAW264.7 macrophages. Lipids. 51:1083–1092. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ha T, Liu L, Kelley J, Kao R, Williams D
and Li C: Toll-like receptors: New players in myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:1875–1893.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yao S, Zong C, Zhang Y, Sang H, Yang M,
Jiao P, Fang Y, Yang N, Song G and Qin S: Activating transcription
factor 6 mediates oxidized LDL-induced cholesterol accumulation and
apoptosis in macrophages by up-regulating CHOP expression. J
Atheroscler Thromb. 20:94–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pennings M, Meurs I, Ye D, Out R, Hoekstra
M, Van Berkel TJ and Van Eck M: Regulation of cholesterol
homeostasis in macrophages and consequences for atherosclerotic
lesion development. FEBS Lett. 580:5588–5596. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu X, Ukai T, Yurnoto H, Davey M, Goswami
S, Gibson FC III and Genco CA: Toll-like receptor 2 plays a
critical role in the progression of atherosclerosis that is
independent of dietary lipids. Atherosclerosis. 196:146–154. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schoneveld AH, Nijhuis MM Oude, van
Middelaar B, Laman JD, de Kleijn DP and Pasterkamp G: Toll-like
receptor 2 stimulation induces intimal hyperplasia and
atherosclerotic lesion development. Cardiovasc Res. 66:162–169.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mullick AE, Tobias PS and Curtiss LK:
Modulation of atherosclerosis in mice by Toll-like receptor 2. J
Clin Invest. 115:3149–3156. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cao F, Castrillo A, Tontonoz P, Re F and
Byrne GI: Chlamydia pneumoniae-induced macrophage foam cell
formation is mediated by Toll-like receptor 2. Infect Immun.
75:753–759. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao GJ, Mo ZC, Tang SL, Ouyang XP, He PP,
Lv YC, Yao F, Tan YL, Xie W, Shi JF, et al: Chlamydia pneumoniae
negatively regulates ABCA1 expression via TLR2-Nuclear factor-kappa
B and miR-33 pathways in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells.
Atherosclerosis. 235:519–525. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Adorni MP, Zimetti F, Billheimer JT, Wang
N, Rader DJ, Phillips MC and Rothblat GH: The roles of different
pathways in the release of cholesterol from macrophages. J Lipid
Res. 48:2453–2462. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vaughan AM and Oram JF: ABCG1
redistributes cell cholesterol to domains removable by high density
lipoprotein but not by lipid-depleted apolipoproteins. J Biol Chem.
280:30150–30157. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ji A, Meyer JM, Cai L, Akinmusire A, de
Beer MC, Webb NR and van der Westhuyzen DR: Scavenger receptor
SR-BI in macrophage lipid metabolism. Atherosclerosis. 217:106–112.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen S, Sorrentino R, Shimada K, Bulut Y,
Doherty TM, Crother TR and Arditi M: Chlamydia pneumoniae-induced
foam cell formation requires MyD88-dependent and -independent
signaling and is reciprocally modulated by liver X receptor
activation. J Immunol. 181:7186–7193. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brand K, Page S, Rogler G, Bartsch A,
Brandl R, Knuechel R, Page M, Kaltschmidt C, Baeuerle PA and
Neumeier D: Activated transcription factor nuclear factor-kappa B
is present in the atherosclerotic lesion. J Clin Invest.
97:1715–1722. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Janus P, Stokowy T, Jaksik R, Szoltysek K,
Handschuh L, Podkowinski J, Widlak W, Kimmel M and Widlak P: Cross
talk between cytokine and hyperthermia-induced pathways:
Identification of different subsets of NF-κB-dependent genes
regulated by TNFα and heat shock. Mol Genet Genomics.
290:1979–1990. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Edfeldt K, Swedenborg J, Hansson GK and
Yan ZQ: Expression of toll-like receptors in human atherosclerotic
lesions: A possible pathway for plaque activation. Circulation.
105:1158–1161. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He C, Lai P, Weng J, Lin S, Wu K, Du X and
Liu X: Toll-like receptor 2-mediated NF-κB inflammatory responses
in dry eye associated with cGVHD. Mol Vis. 17:2605–2611.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xavier RJ and Podolsky DK: Unravelling the
pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 448:427–434.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|