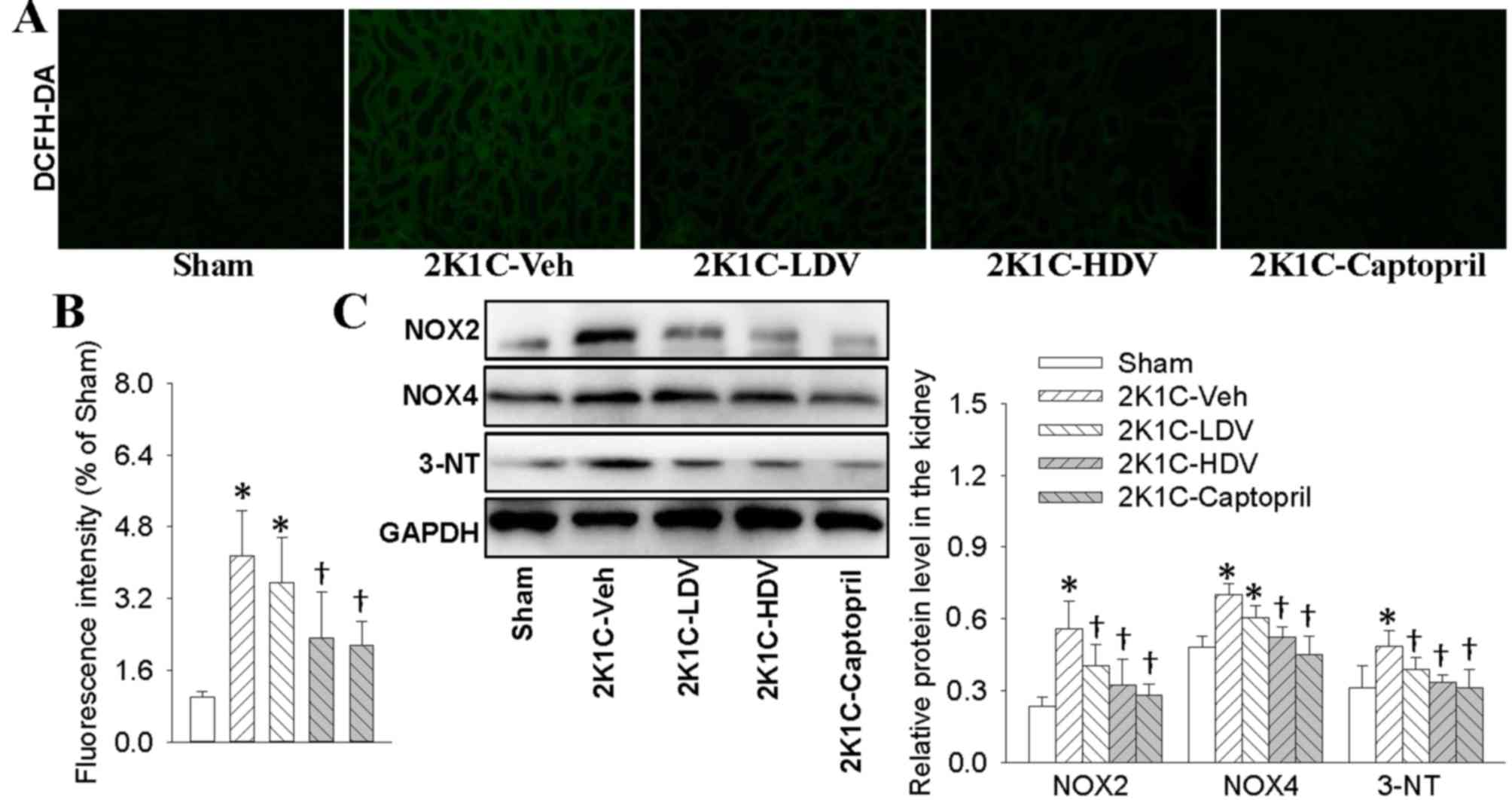
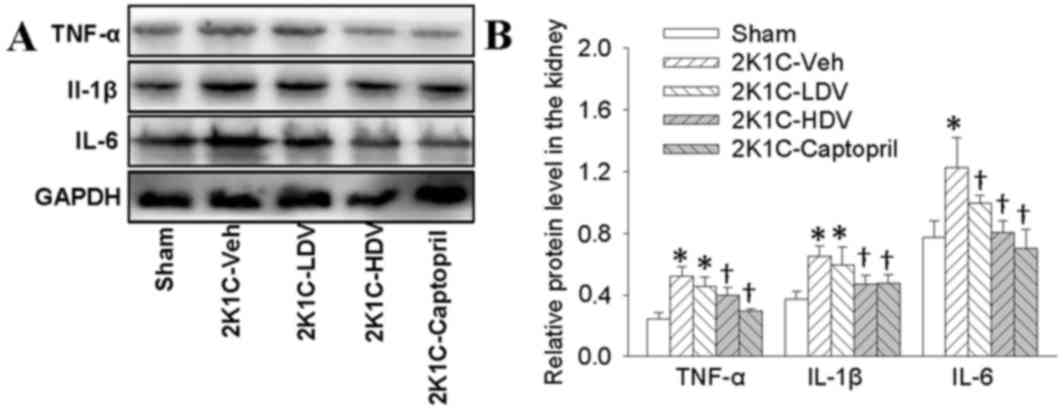
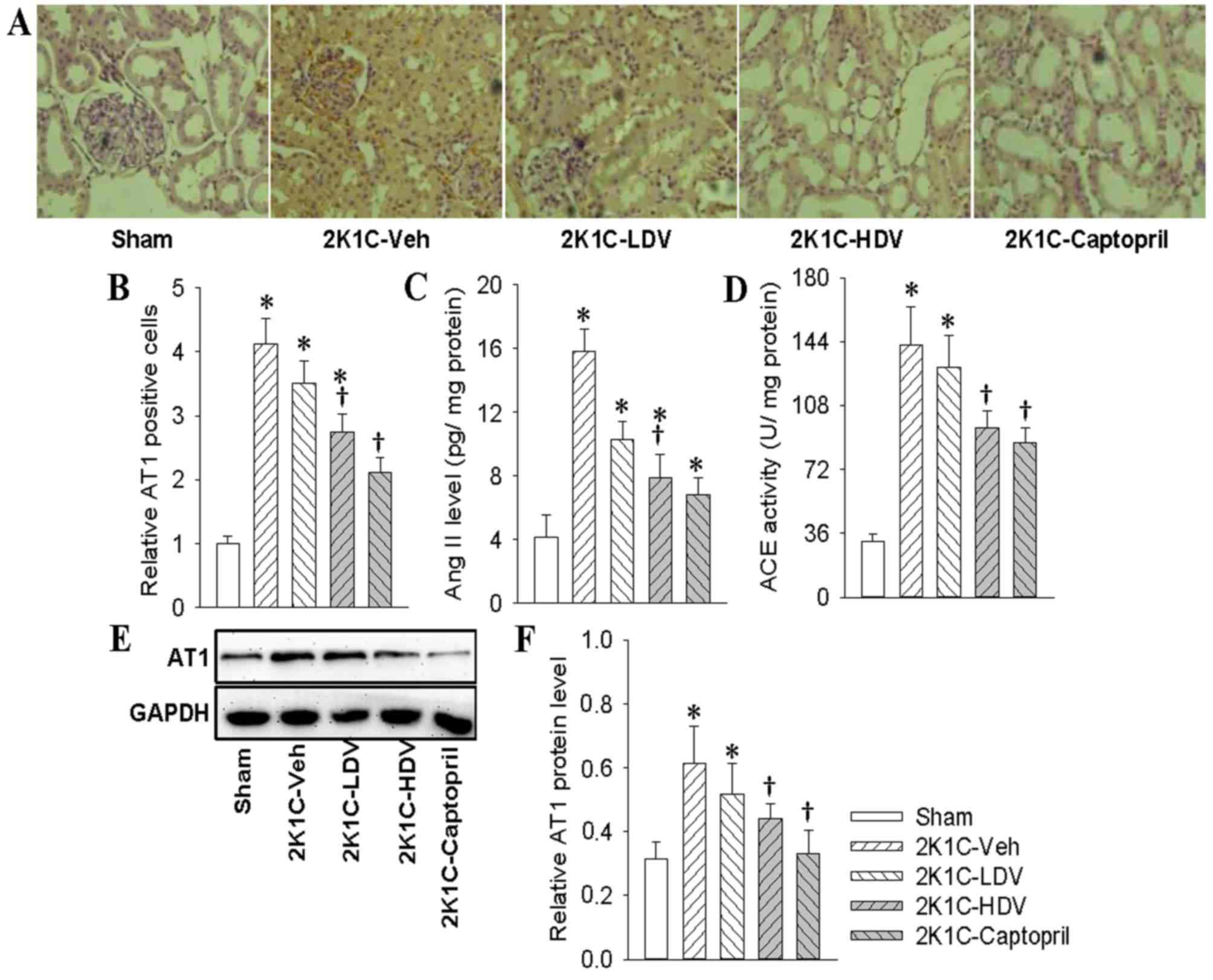
|
1
|
Wang Z, do Carmo JM, Aberdein N, Zhou X,
Williams JM, da Silva AA and Hall JE: Synergistic interaction of
hypertension and diabetes in promoting kidney injury and the role
of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Hypertension. 69:879–891. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Retnakaran R, Cull CA, Thorne KI, Adler AI
and Holman RR; UKPDS Study Group, : Risk factors for renal
dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: U.K. Diabetes. 55:1832–1839. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Janssen U, Riley SG, Vassiliadou A, Floege
J and Phillips AO: Hypertension superimposed on type II diabetes in
Goto Kakizaki rats induces progressive nephropathy. Kidney Int.
63:2162–2170. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Frenay AR, Yu L, van der Velde AR,
Vreeswijk-Baudoin I, López-Andrés N, van Goor H, Silljé HH, Ruifrok
WP and de Boer RA: Pharmacological inhibition of galectin-3
protects against hypertensive nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 308:F500–F509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Becker GJ and Hewitson TD: The role of
tubulointerstitial injury in chronic renal failure. Curr Opin
Nephrol Hypertens. 9:133–138. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Padda RS, Shi Y, Lo CS, Zhang SL and Chan
JS: Angiotensin-(1–7): A novel peptide to treat hypertension and
nephropathy in diabetes? J Diabetes Metab. 6:2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miloradović Z, Ivanov M, Jovović D,
Karanović D, Vajić UJ, Marković-Lipkovski J, Mihailović-Stanojević
N and Milanović JG: Angiotensin 2 type 1 receptor blockade
different affects postishemic kidney injury in normotensive and
hypertensive rats. J Physiol Biochem. 72:813–820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gai Z, Gui T, Hiller C and Kullak-Ublick
GA: Farnesoid X receptor protects against kidney injury in
uninephrectomized obese mice. J Biol Chem. 291:2397–2411. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Linkermann A, Chen G, Dong G, Kunzendorf
U, Krautwald S and Dong Z: Regulated cell death in AKI. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 25:2689–2701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Granger JP: An emerging role for
inflammatory cytokines in hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 290:H923–H924. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brouwers FP, de Boer RA, van der Harst P,
Struck J, de Jong PE, de Zeeuw D, Gans RO, Gansevoort RT, Hillege
HL, van Gilst WH and Bakker SJ: Influence of age on the prognostic
value of mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin in the general population.
Heart. 98:1348–1353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peterson JC, Adler S, Burkart JM, Greene
T, Hebert LA, Hunsicker LG, King AJ, Klahr S, Massry SG and Seifter
JL: Blood pressure control, proteinuria, and the progression of
renal disease. The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study. Ann
Intern Med. 123:754–762. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Crews DC, Plantinga LC, Miller ER III,
Saran R, Hedgeman E, Saydah SH, Williams DE and Powe NR; Centers
for Disease Control and Prevention Chronic Kidney Disease
Surveillance Team, : Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in
persons with undiagnosed or prehypertension in the United States.
Hypertension. 55:1102–1109. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Veeramani C, Al-Numair KS, Chandramohan G,
Alsaif MA and Pugalendi KV: Antihyperlipidemic effect of Melothria
maderaspatana leaf extracts on DOCA-salt induced hypertensive rats.
Asian Pac J Trop Med. 5:434–439. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu D, Shi M, Bao J, Yu X, Li Y and Liu W:
Genipin ameliorates hypertension-induced renal damage via the
angiotensin II-TLR/MyD88/MAPK pathway. Fitoterapia. 112:244–253.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu XP, Pang YJ, Zhu WW, Zhao TT, Zheng M,
Wang YB, Sun ZJ and Sun SJ: Benazepril, an angiotensin-converting
enzyme inhibitor, alleviates renal injury in spontaneously
hypertensive rats by inhibiting advanced glycation
end-product-mediated pathways. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
36:287–296. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Balsevich JJ, Ramirez-Erosa I, Hickie RA,
Dunlop DM, Bishop GG and Deibert LK: Antiproliferative activity of
Saponaria vaccaria constituents and related compounds. Fitoterapia.
83:170–181. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xie F, Cai W, Liu Y, Li Y, Du B, Feng L
and Qiu L: Vaccarin attenuates the human EA.hy926 endothelial cell
oxidative stress injury through inhibition of Notch signaling. Int
J Mol Med. 35:135–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qiu Y, Qiu L, Cui J and Wei Q: Bacterial
cellulose and bacterial cellulose-vaccarin membranes for wound
healing. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 59:303–309. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu X, Zhou Z, Zhang Q, Cai W, Zhou Y, Sun
H and Qiu L: Vaccarin administration ameliorates hypertension and
cardiovascular remodeling in renovascular hypertensive rats. J Cell
Biochem. Jul 6–2017.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
21
|
Zhang LL, Ding L, Zhang F, Gao R, Chen Q,
Li YH, Kang YM and Zhu GQ: Salusin-β in rostral ventrolateral
medulla increases sympathetic outflow and blood pressure via
superoxide anions in hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 32:1059–1067.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou YB, Sun HJ, Chen D, Liu TY, Han Y,
Wang JJ, Tang CS, Kang YM and Zhu GQ: Intermedin in paraventricular
nucleus attenuates sympathetic activity and blood pressure via
nitric oxide in hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 63:330–337. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang NB, Huang ZG, Cui WD and Ding BP:
Effects of puerarin on expression of cardiac Smad3 and Smad7 mRNA
in spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Ethnopharmacol. 138:737–740.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ghazi-Khansari M, Mohammadi-Karakani A,
Sotoudeh M, Mokhtary P, Pour-Esmaeil E and Maghsoud S: Antifibrotic
effect of captopril and enalapril on paraquat-induced lung fibrosis
in rats. J Appl Toxicol. 27:342–349. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu JB, Zhou Y, Liang CL, Zhang XJ, Lai JM,
Ye SF, Ouyang H, Lin J and Zhou JY: Cyclovirobuxinum D alleviates
cardiac hypertrophy in hyperthyroid rats by preventing apoptosis of
cardiac cells and inhibiting the p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase signaling pathway. Chin J Integr Med. Mar 17–2016.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
26
|
Chen WW, Sun HJ, Zhang F, Zhou YB, Xiong
XQ, Wang JJ and Zhu GQ: Salusin-β in paraventricular nucleus
increases blood pressure and sympathetic outflow via vasopressin in
hypertensive rats. Cardiovasc Res. 98:344–351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang C, Liu X, Tang Y, Peng H, Ye Z, Zhang
J, Tang H and Lou T: Medium from mesangial cells incubated with
aggregated IgA1 from IgA nephropathy patients reduces podocyte
adhesion through activation of the renin angiotensin system. Swiss
Med Wkly. 141:w133042011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takai S, Jin D, Chen H, Li W, Yamamoto H,
Yamanishi K, Miyazaki M, Higashino H, Yamanishi H and Okamura H:
Chymase inhibition improves vascular dysfunction and survival in
stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens.
32:1637–1649. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun HJ, Liu TY, Zhang F, Xiong XQ, Wang
JJ, Chen Q, Li YH, Kang YM, Zhou YB, Han Y, et al: Salusin-β
contributes to vascular remodeling associated with hypertension via
promoting vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and vascular
fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1709–1718. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun HJ, Zhao MX, Ren XS, Liu TY, Chen Q,
Li YH, Kang YM, Wang JJ and Zhu GQ: Salusin-β promotes vascular
smooth muscle cell migration and intimal hyperplasia after vascular
injury via ROS/NFκB/MMP-9 pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal.
24:1045–1057. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim MJ, Ryu JC, Kwon Y, Lee S, Bae YS,
Yoon JH and Ryu JH: Dual oxidase 2 in lung epithelia is essential
for hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury in mice. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 21:1803–1818. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sun HJ, Chen D, Han Y, Zhou YB, Wang JJ,
Chen Q, Li YH, Gao XY, Kang YM and Zhu GQ: Relaxin in
paraventricular nucleus contributes to sympathetic overdrive and
hypertension via PI3K-Akt pathway. Neuropharmacology. 103:247–256.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cuevas CA, Tapia-Rojas C, Cespedes C,
Inestrosa NC and Vio CP: β-Catenin-dependent signaling pathway
contributes to renal fibrosis in hypertensive rats. Biomed Res Int.
2015:7260122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Z, Zhu Q, Li PL, Dhaduk R, Zhang F,
Gehr TW and Li N: Silencing of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α gene
attenuates chronic ischemic renal injury in two-kidney, one-clip
rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 306:F1236–F1242. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cavallari LH, Fashingbauer LA, Camp JR,
King ST and Geenen DL: Hypertension-induced renal fibrosis and
spironolactone response vary by rat strain and mineralocorticoid
receptor gene expression. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst.
9:146–153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE and
Hsu CY: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death,
cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med.
351:1296–1305. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Whitman IR, Feldman HI and Deo R: CKD and
sudden cardiac death: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and therapeutic
approaches. J Am Soc Nephrol. 23:1929–1939. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Muntner P, Anderson A, Charleston J, Chen
Z, Ford V, Makos G, O'Connor A, Perumal K, Rahman M, Steigerwalt S,
et al: Hypertension awareness, treatment, and control in adults
with CKD: Results from the chronic renal insufficiency cohort
(CRIC) Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 55:441–451. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Piret SE, Olinger E, Reed AA, Nesbit MA,
Hough TA, Bentley L, Devuyst O, Cox RD and Thakker RV: Mouse model
for inherited renal fibrosis associated with endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Dis Model Mech. 10:773–786. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Park JK, Theuer S, Kirsch T, Lindschau C,
Klinge U, Heuser A, Plehm R, Todiras M, Carmeliet P, Haller H, et
al: Growth arrest specific protein 6 participates in DOCA-induced
target-organ damage. Hypertension. 54:359–364. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Campagnaro BP, Tonini CL, Doche LM,
Nogueira BV, Vasquez EC and Meyrelles SS: Renovascular hypertension
leads to DNA damage and apoptosis in bone marrow cells. DNA Cell
Biol. 32:458–466. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li P, Huang PP, Yang Y, Liu C, Lu Y, Wang
F, Sun W and Kong XQ: Renal sympathetic denervation attenuates
hypertension and vascular remodeling in renovascular hypertensive
rats. J Appl Physiol (1985). 122:121–129. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shi Y, Lo CS, Padda R, Abdo S, Chenier I,
Filep JG, Ingelfinger JR, Zhang SL and Chan JS: Angiotensin-(1–7)
prevents systemic hypertension, attenuates oxidative stress and
tubulointerstitial fibrosis, and normalizes renal
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and Mas receptor expression in
diabetic mice. Clin Sci (Lond). 128:649–663. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cowley AW Jr: Renal medullary oxidative
stress, pressure-natriuresis, and hypertension. Hypertension.
52:777–786. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Araujo M and Wilcox CS: Oxidative stress
in hypertension: Role of the kidney. Antioxid Redox Signal.
20:74–101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Manning RD Jr, Tian N and Meng S:
Oxidative stress and antioxidant treatment in hypertension and the
associated renal damage. Am J Nephrol. 25:311–317. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Daehn I, Casalena G, Zhang T, Shi S,
Fenninger F, Barasch N, Yu L, D'Agati V, Schlondorff D, Kriz W, et
al: Endothelial mitochondrial oxidative stress determines podocyte
depletion in segmental glomerulosclerosis. J Clin Invest.
124:1608–1621. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Eddy AA: Molecular basis of renal
fibrosis. Pediatr Nephrol. 15:290–301. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lassegue B, San Martin A and Griendling
KK: Biochemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology of NADPH oxidases
in the cardiovascular system. Circ Res. 110:1364–1390. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Taylor NE, Glocka P, Liang M and Cowley AW
Jr: NADPH oxidase in the renal medulla causes oxidative stress and
contributes to salt-sensitive hypertension in Dahl S rats.
Hypertension. 47:692–698. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cowley AW Jr, Yang C, Zheleznova NN,
Staruschenko A, Kurth T, Rein L, Kumar V, Sadovnikov K, Dayton A,
Hoffman M, et al: Evidence of the importance of Nox4 in production
of hypertension in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertension.
67:440–450. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu N, Shen H, Liu H, Wang Y, Bai Y and Han
P: Acute blood glucose fluctuation enhances rat aorta endothelial
cell apoptosis, oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine
expression in vivo. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 15:1092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ruiz S, Pergola PE, Zager RA and Vaziri
ND: Targeting the transcription factor Nrf2 to ameliorate oxidative
stress and inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int.
83:1029–1041. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Meguid El Nahas A and Bello AK: Chronic
kidney disease: The global challenge. Lancet. 365:331–340. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hartner A, Klanke B, Cordasic N, Amann K,
Schmieder RE, Veelken R and Hilgers KF: Statin treatment reduces
glomerular inflammation and podocyte damage in rat
deoxycorticosterone-acetate-salt hypertension. J Hypertens.
27:376–385. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang J, Patel MB, Griffiths R, Mao A,
Song YS, Karlovich NS, Sparks MA, Jin H, Wu M, Lin EE and Crowley
SD: Tumor necrosis factor-α produced in the kidney contributes to
angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. Hypertension. 64:1275–1281.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Rincón J, Correia D, Arcaya JL, Finol E,
Fernández A, Pérez M, Yaguas K, Talavera E, Chávez M, Summer R and
Romero F: Role of Angiotensin II type 1 receptor on renal NAD(P)H
oxidase, oxidative stress and inflammation in nitric oxide
inhibition induced-hypertension. Life Sci. 124:81–90. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhou L, Mo H, Miao J, Zhou D, Tan RJ, Hou
FF and Liu Y: Klotho ameliorates kidney injury and fibrosis and
normalizes blood pressure by targeting the renin-angiotensin
system. Am J Pathol. 185:3211–3223. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Crowley SD, Gurley SB, Herrera MJ, Ruiz P,
Griffiths R, Kumar AP, Kim HS, Smithies O, Le TH and Coffman TM:
Angiotensin II causes hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy through
its receptors in the kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:pp.
17985–17990. 2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ruggenenti P, Cravedi P and Remuzzi G:
Mechanisms and treatment of CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 23:1917–1928.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhang JS, Zhang YL, Wang HX, Xia YL, Wang
L, Jiang YN, Li HH and Liu Y: Identification of genes related to
the early stage of Angiotensin II-induced acute renal injury by
microarray and integrated gene network analysis. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 34:1137–1151. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kuriyama S: The relation between green tea
consumption and cardiovascular disease as evidenced by
epidemiological studies. J Nutr. 138:1548S–1553S. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Israili ZH and Hall WD: Cough and
angioneurotic edema associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme
inhibitor therapy. A review of the literature and pathophysiology.
Ann Intern Med. 117:234–242. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|