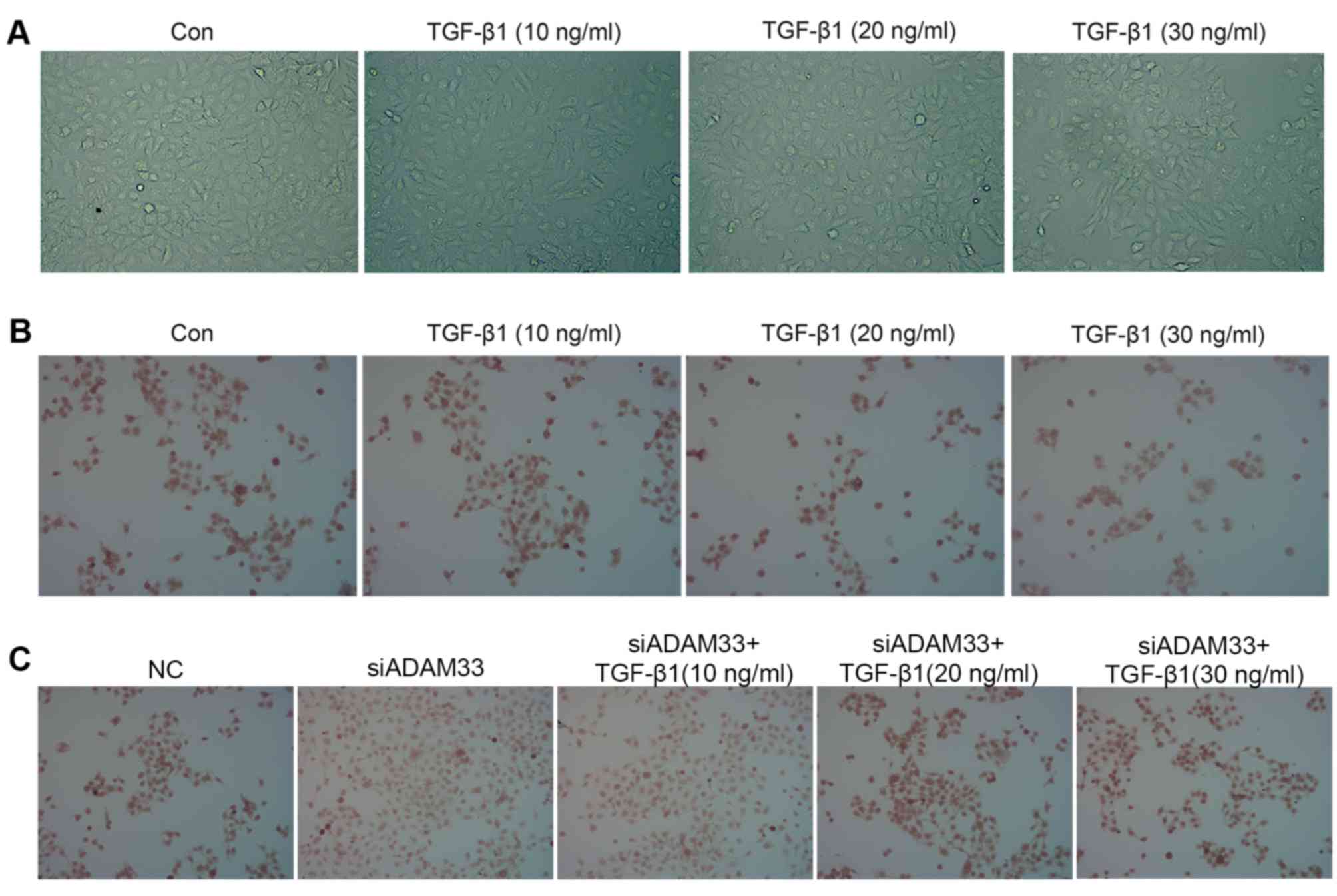
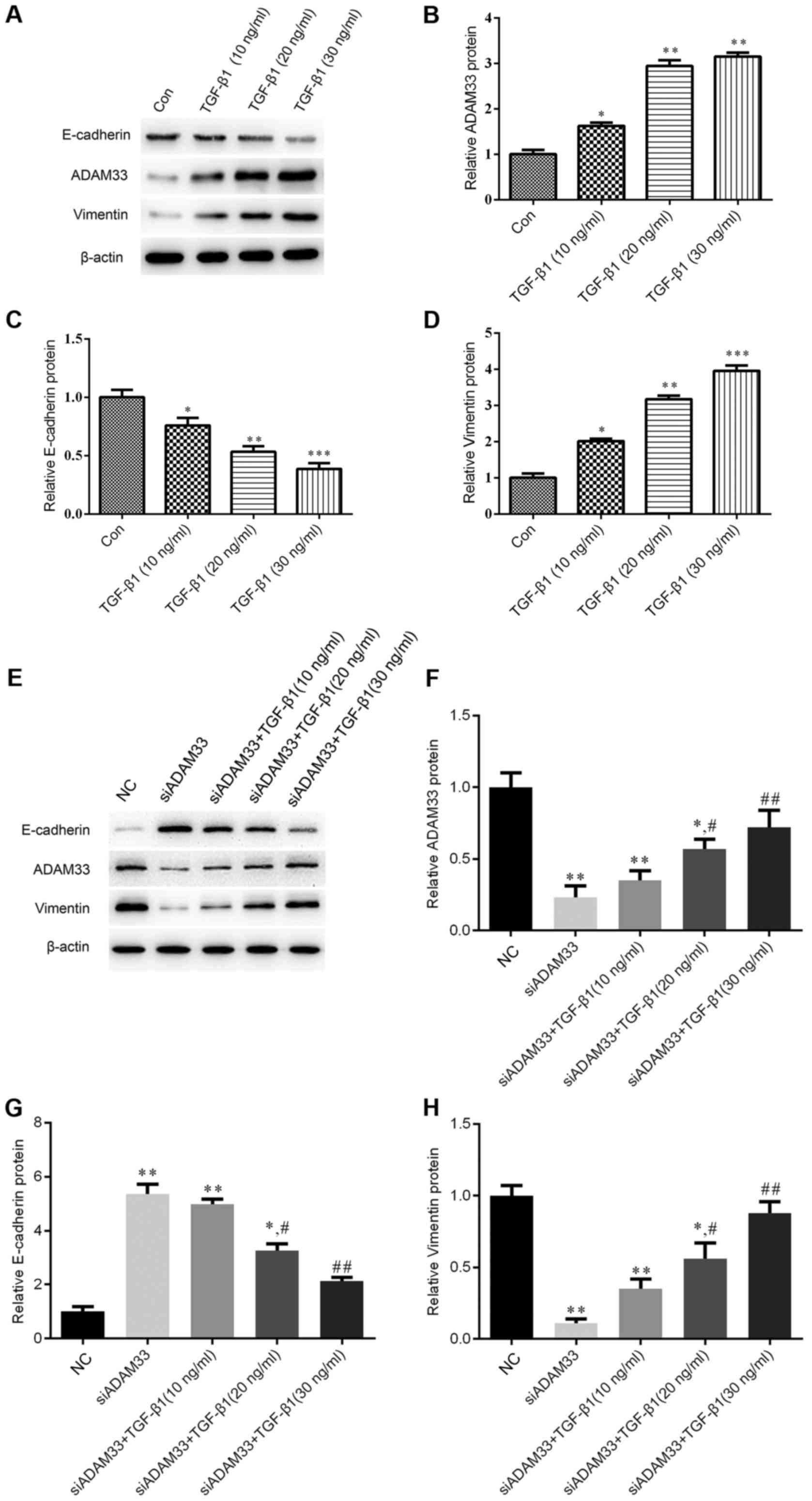
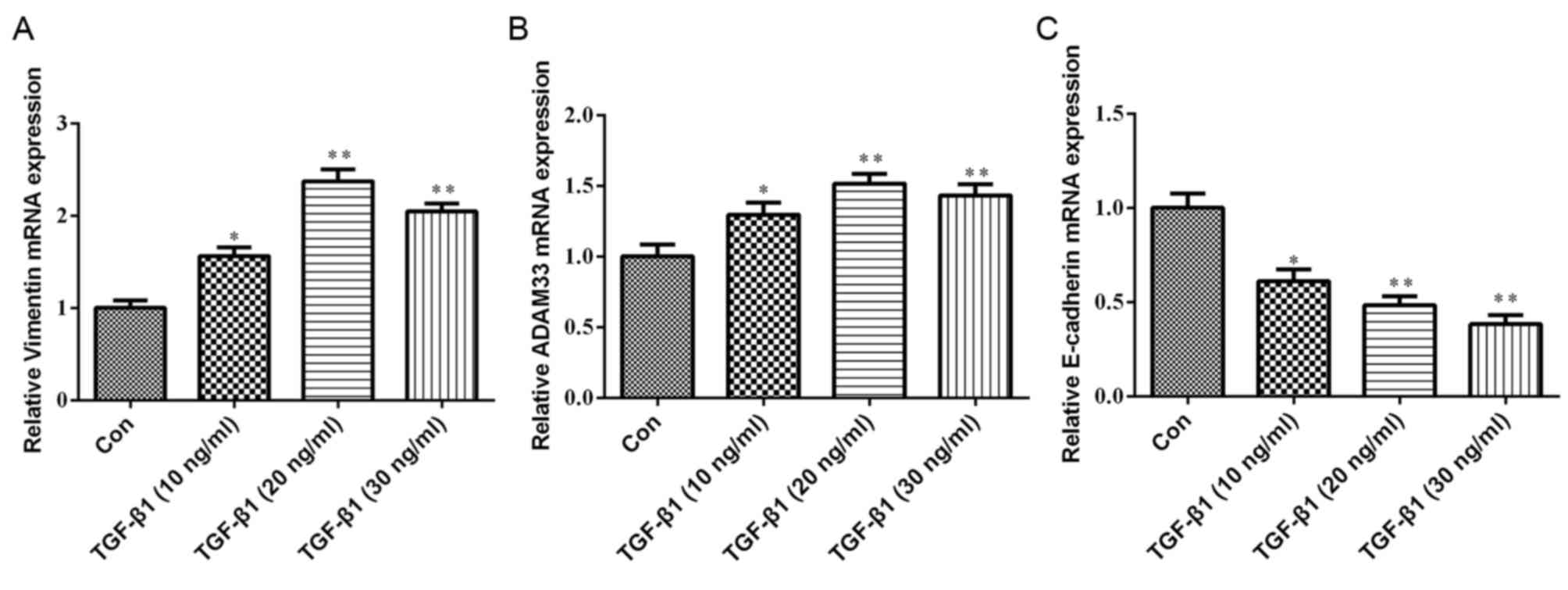
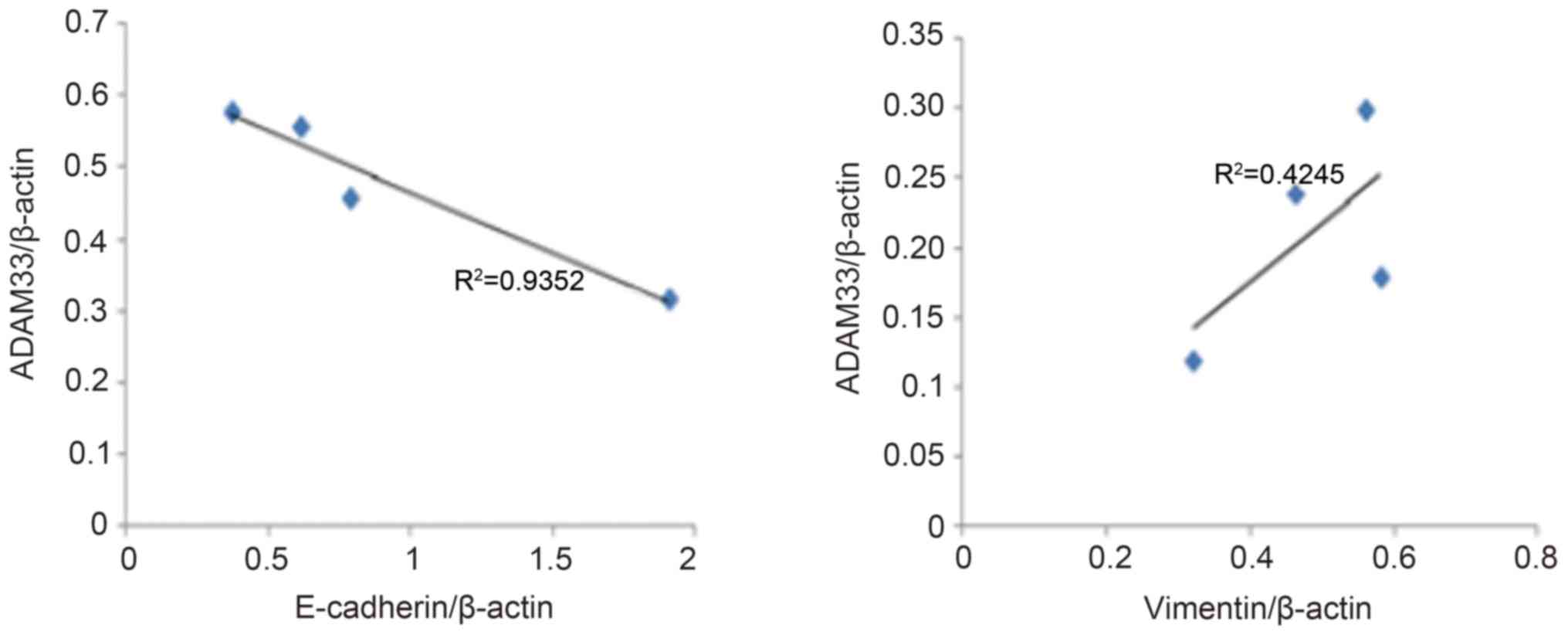
|
1
|
Heijink IH, Postma DS, Noordhoek JA,
Broekema M and Kapus A: House dust mite-promoted
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human bronchial epithelium.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 42:69–79. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hackett TL, Warner SM, Stefanowicz D,
Shaheen F, Pechkovsky DV, Murray LA, Argentieri R, Kicic A, Stick
SM, Bai TR and Knight DA: Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in primary airway epithelial cells from patients with
asthma by transforming growth factor-beta1. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 180:122–133. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hackett TL: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in the pathophysiology of airway remodelling in asthma.
Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 12:53–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Johnson JR, Roos A, Berg T, Nord M and
Fuxe J: Chronic respiratory aeroallergen exposure in mice induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the large airway. PLoS One.
6:e161752011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang JH, Sun LH, Huang SK and Chen AH:
Effect of co-culturing human primary basic fibroblasts with
respiratory syncytial virus-infected 16-HBE cells. Genet Mol Res.
15:150173392016.
|
|
6
|
Ko H, So Y, Jeon H, Jeong MH, Choi HK, Ryu
SH, Lee SW, Yoon HG and Choi KC: TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and acetylation of Smad2 and
Smad3 are negatively regulated by EGCG in human A549 lung cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 335:205–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Van Eerdewegh P, Little RD, Dupuis J, Del
Mastro RG, Falls K, Simon J, Torrey D, Pandit S, McKenny J,
Braunschweiger K, et al: Association of the ADAM33 gene with asthma
and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Nature. 418:426–430. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee JY, Park SW, Chang HK, Kim HY, Rhim T,
Lee JH, Jang AS, Koh ES and Park CS: A disintegrin and
metalloproteinase 33 protein in patients with asthma: Relevance to
airflow limitation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 173:729–735. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Holgate ST: ADAM metallopeptidase domain
33 (ADAM33): Identification and role in airways disease. Drug News
Perspect. 23:381–387. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xiao J, Han J, Wang X, Hua D, Su D, Bao Y
and Lv F: Association of ADAM33 gene with susceptibility to COPD in
Tibetan population of China. Mol Biol Rep. 38:4941–4945. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sunadome H, Matsumoto H, Petrova G,
Kanemitsu Y, Tohda Y, Horiguchi T, Kita H, Kuwabara K, Tomii K,
Otsuka K, et al: IL4Rα and ADAM33 as genetic markers in asthma
exacerbations and type-2 inflammatory endotype. Clin Exp Allergy.
47:998–1006. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ito I, Laporte JD, Fiset PO, Asai K,
Yamauchi Y, Martin JG and Hamid Q: Downregulation of a disintegrin
and metalloproteinase 33 by IFN-gamma in human airway smooth muscle
cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 119:89–97. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jie Z, Jin M, Cai Y, Bai C, Shen Y, Yuan
Z, Hu Y and Holgate S: The effects of Th2 cytokines on the
expression of ADAM33 in allergen-induced chronic airway
inflammation. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 168:289–294. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tripathi P, Awasthi S, Husain N, Prasad R
and Mishra V: Increased expression of ADAM33 protein in asthmatic
patients as compared to non-asthmatic controls. Indian J Med Res.
137:507–514. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Foley SC, Mogas AK, Olivenstein R, Fiset
PO, Chakir J, Bourbeau J, Ernst P, Lemière C, Martin JG and Hamid
Q: Increased expression of ADAM33 and ADAM8 with disease
progression in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 119:863–871. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin F, Song A, Wu J, Jiang X, Long J, Chen
J, Duan Y, Shi Y and Deng L: ADAM33 protein expression and the
mechanics of airway smooth muscle cells and highly correlated in
ovalbumin-sensitized rats. Mol Med Rep. 8:1209–1215. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Haitchi HM, Powell RM, Shaw TJ, Howarth
PH, Wilson SJ, Wilson DI, Holgate ST and Davies DE: ADAM33
expression in asthmatic airways and humanembryonic lungs. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 171:958–965. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang Y, Wicks J, Haitchi HM, Powell RM,
Manuyakorn W, Howarth PH, Holgate ST and Davies DE: Regulation of a
disintegrin and metalloprotease-33 expression by transforming
growth factor-β. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 46:633–640. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang M, Zhang Z, Pan HY, Wang DX, Deng ZT
and Ye XL: TGF-beta1 induces human bronchial epithelial
cell-to-mesenchymal transition in vitro. Lung. 187:187–194. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kamitani S, Yamauchi Y, Kawasaki S, Takami
K, Takizawa H, Nagase T and Kohyama T: Simultaneous stimulation
with TGF-β1 and TNF-α induces epithelial mesenchymal transition in
bronchial epithelial cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 155:119–128.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang ZC, Yi MJ, Ran N, Wang C, Fu P, Feng
XY, Xu L and Qu ZH: Transforming growth factor-β1 induces bronchial
epithelial cells to mesenchymal transition by activating the Snail
pathway and promotes airway remodeling in asthma. Mol Med Rep.
8:1663–1668. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|