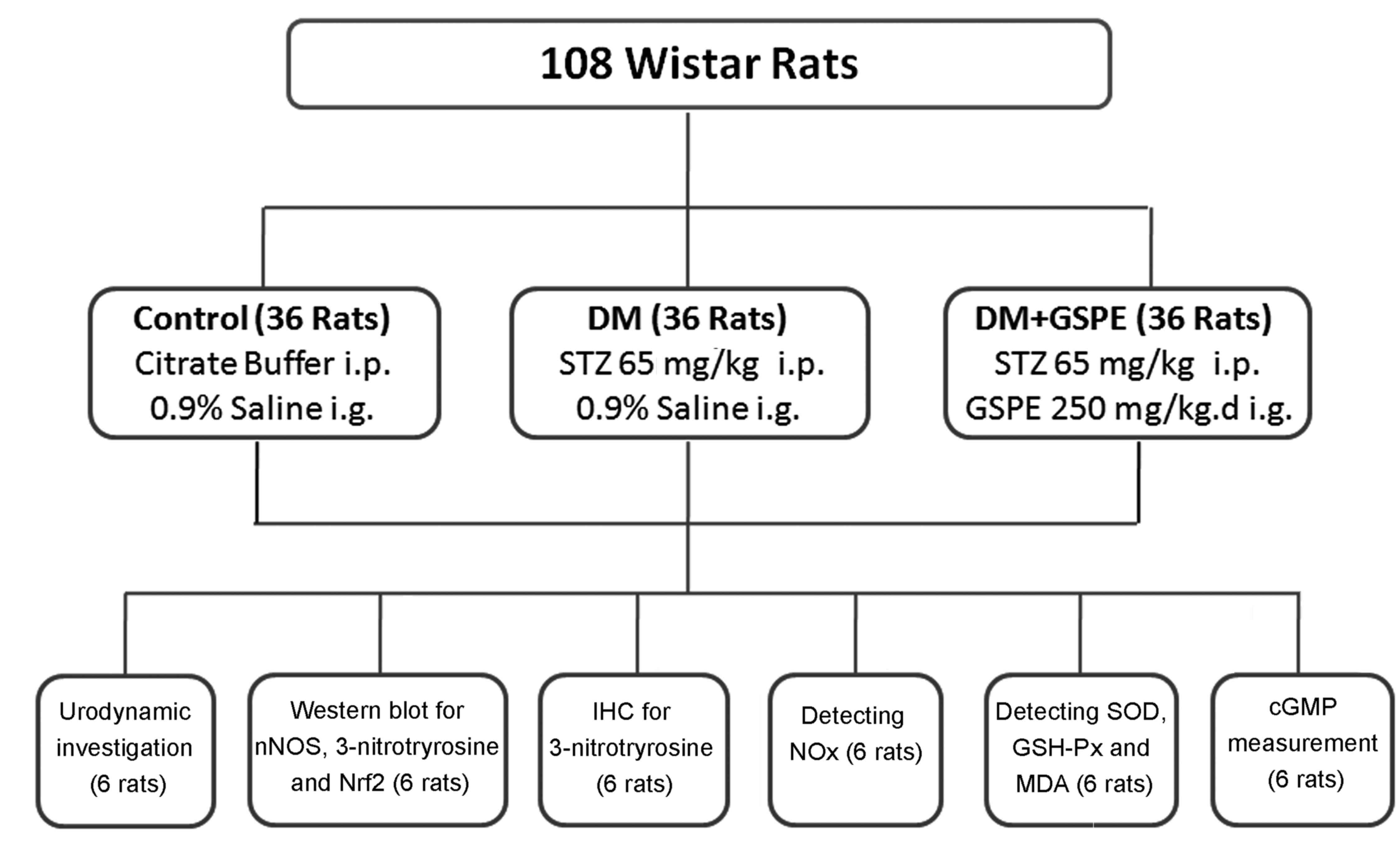
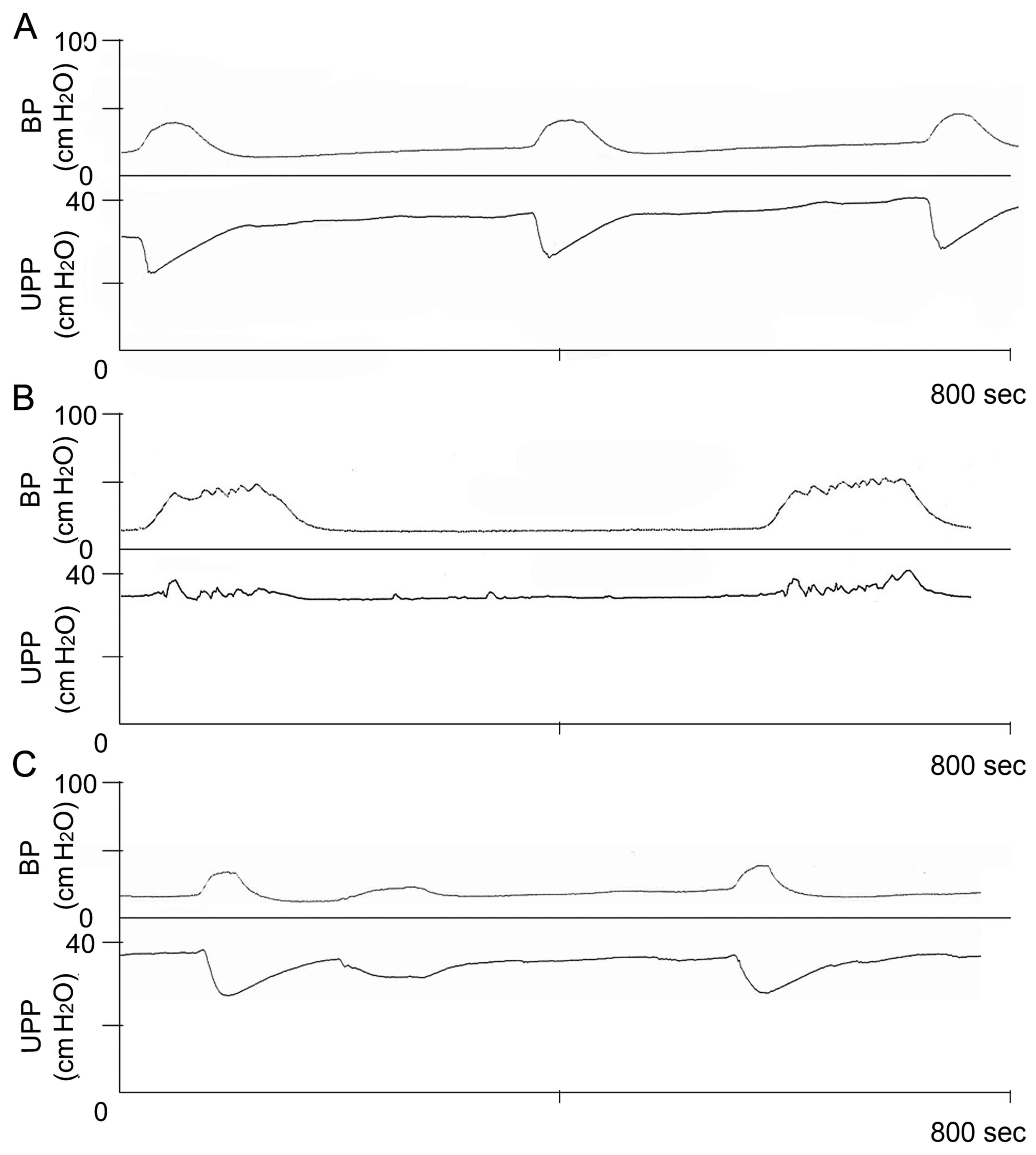
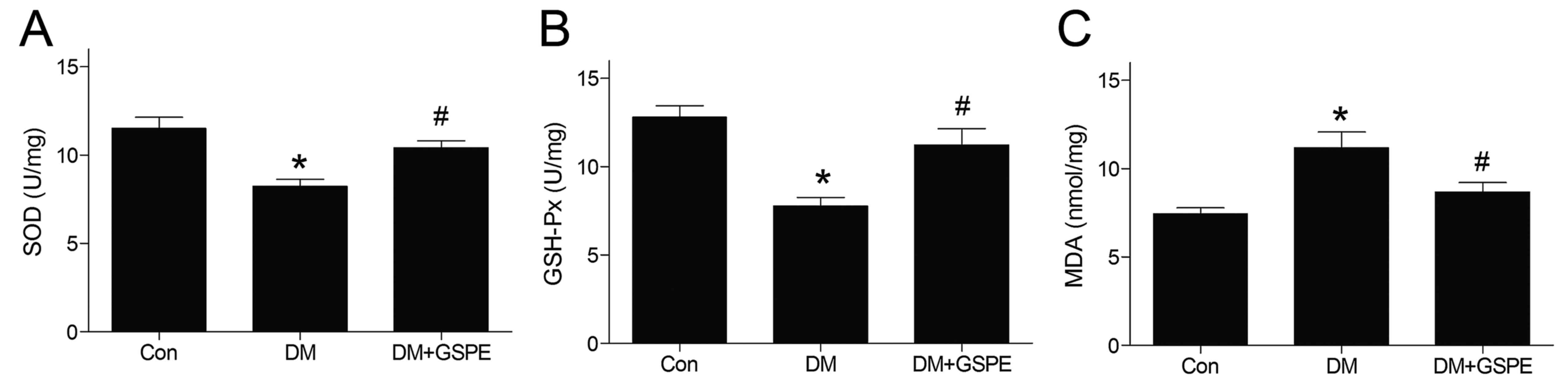
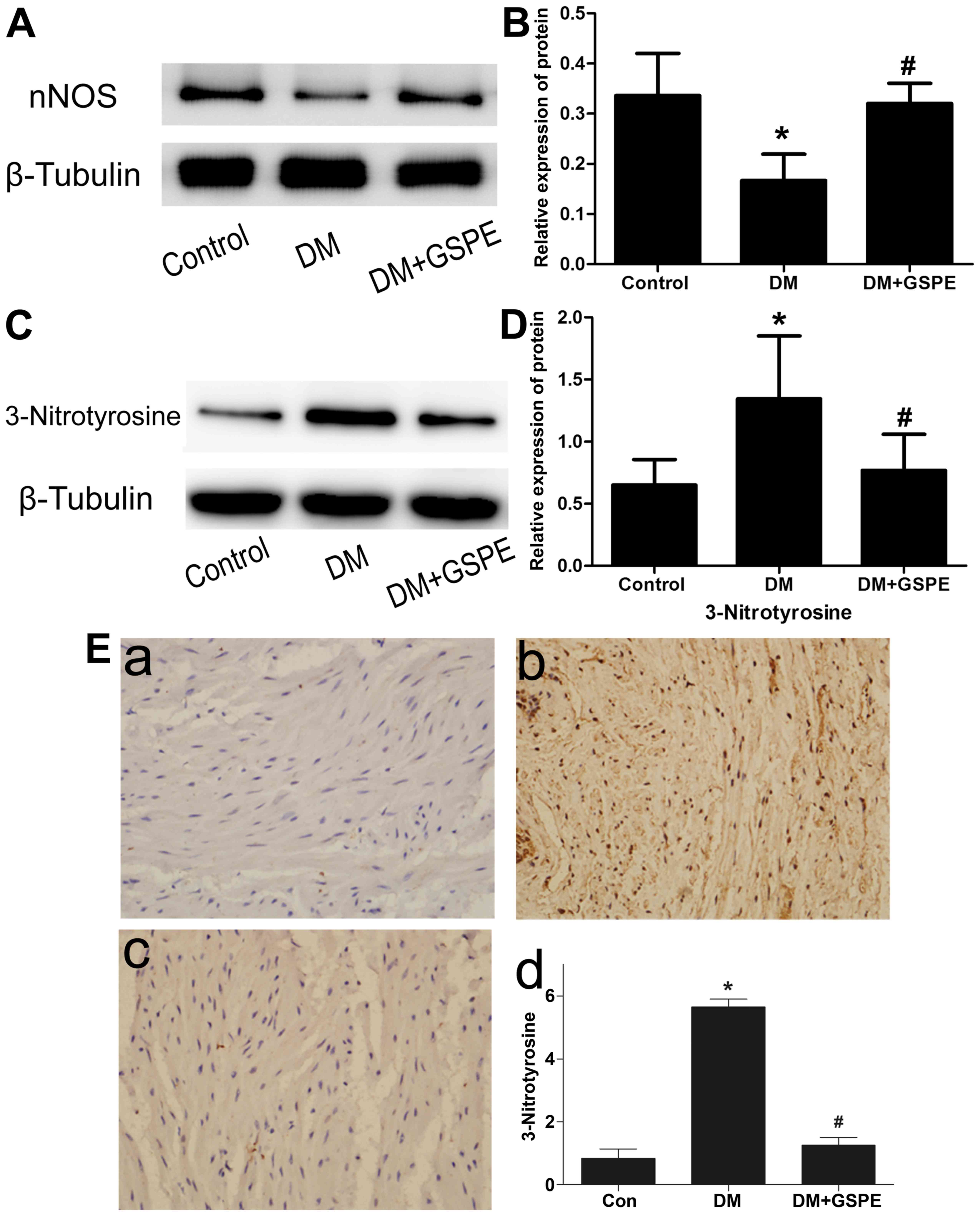
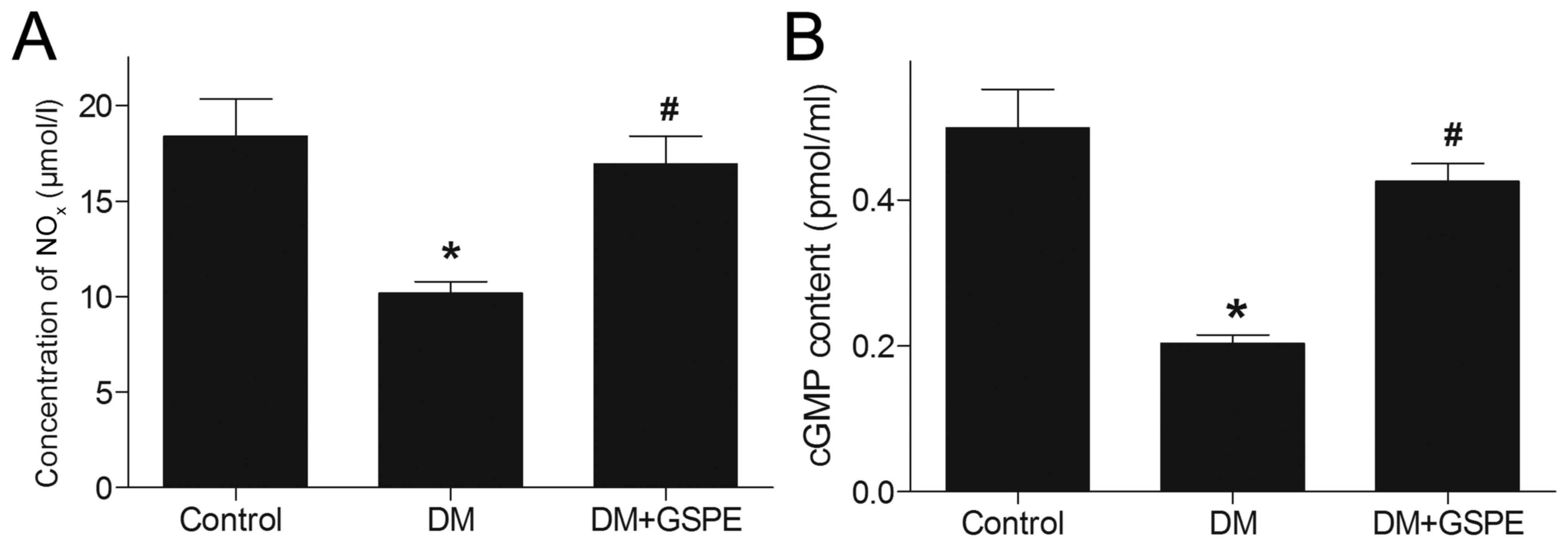
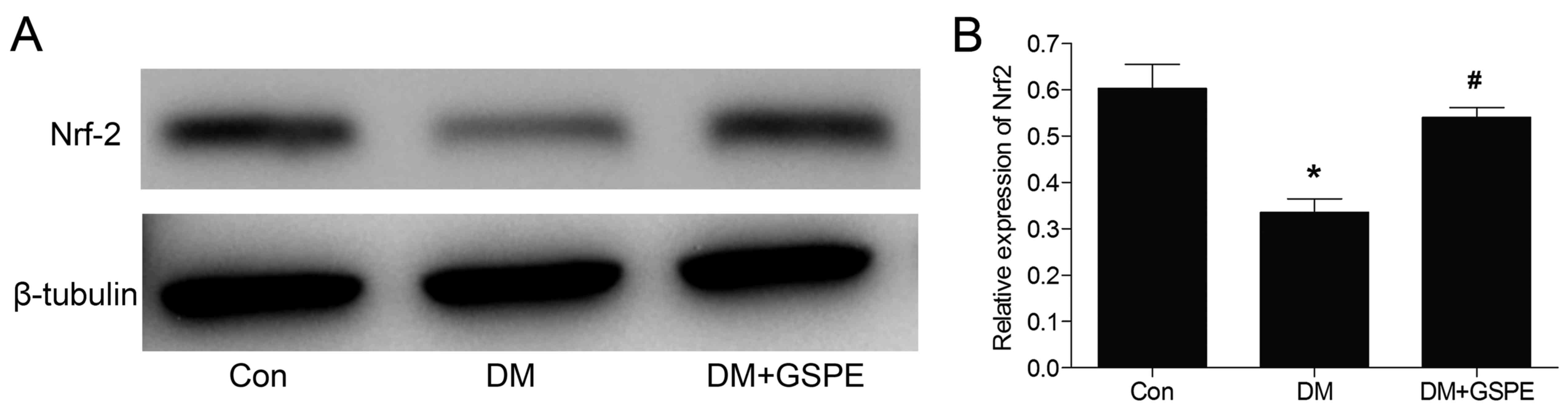
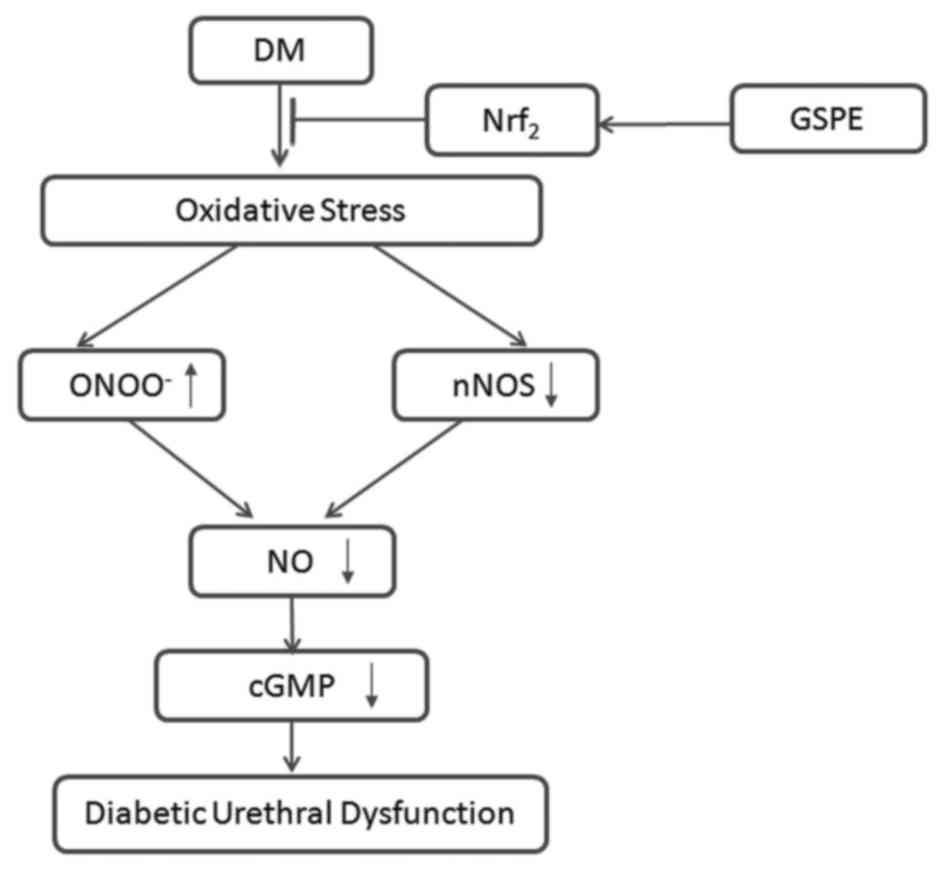
|
1
|
Yonekubo S, Tatemichi S, Maruyama K and
Kobayashi M: Alpha1A-adrenoceptor antagonist improves underactive
bladder associated with diabetic cystopathy via bladder blood flow
in rats. BMC Urol. 17:642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dong X, Song Q, Zhu J, Zhao J, Liu Q,
Zhang T, Long Z, Li J, Wu C, Wang Q, et al: Interaction of
Caveolin-3 and HCN is involved in the pathogenesis of diabetic
cystopathy. Sci Rep. 6:248442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sasaki K, Chanceller MB, Phelan MW,
Yokoyama T, Fraser MO, Seki S, Kubo K, Kumon H, Groat WC and
Yoshimura N: Diabetic cystopathy correlates with a long-term
decrease in nerve growth factor levels in the bladder and
lumbosacral dorsal root Ganglia. J Urol. 168:1259–1264. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang Z, Dolber PC and Fraser MO: Diabetic
urethropathy compounds the effects of diabetic cystopathy. J Uorl.
178:2213–2219. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bennett BC, Kruse MN, Roppolo JR, Flood
HD, Fraser M and de Groat WC: Neural control of urethral outlet
activity in vivo: Role of nitric oxide. J Urol. 153:2004–2009.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Persson K, Alm P, Uvelius B and Andersson
KE: Nitrergic and cholinergic innervation of the rat lower urinary
tract after pelvic ganglionectomy. Am J Physiol. 274:R389–R397.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Warner TD, Mitchell JA, Sheng H and Murad
F: Effects of cyclic GMP on smooth muscle relaxation. Adv
Pharmacol. 26:171–194. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Beshay E and Carrier S: Oxidative stress
plays a role in diabetes-induced bladder dysfunction in a rat
model. Urology. 64:1062–1067. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Szaleczky E, Prechl J, Feher J and Somogyi
A: Alternation in enzymatic antioxidant defence in diabetes
mellitus-a rational approach. Postgrad Med J. 75:8791999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Förstermann U and Sessa WC: Nitric oxide
synthases: Regulation and function. Eur Heart J. 33:829–837,
837a-837d. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ding Y, Dai X, Jiang Y, Zhang Z, Bao L, Li
Y, Zhang F, Ma X, Cai X, Jing L, et al: Grape seed proanthocyanidin
extracts alleviate oxidative stress and ER stress in skeletal
muscle of low-dose streptozotocin- and high-carbohydrate/high-fat
diet-induced diabetic rats. Mol Nutri Food Res. 57:365–369. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mansouri E, Panahi M, Ghaffari MA and
Ghorbani A: Effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on
oxidative stress induced by diabetes in rat kidney. Iran Biomed J.
15:100–106. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Casanova E, Baselga-Escudero L,
Ribas-Latre A, Cedó L, Arola-Arnal A, Pinent M, Bladé C, Arola L
and Salvadó MJ: Chronic intake of proanthocyanidins and
docosahexaenoic acid improves skeletal muscle oxidative capacity in
diet-obese rats. J Nutri Biochem. 25:1003–1010. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Peng N, Clark JT, Prasain J, Kim H, White
CR and Wyss JM: Antihypertensive and cognitive effects of grape
polyphenols in estrogen-depleted, female, spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
289:R771–R775. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Whitman SA, Long M, Wondrak GT, Zheng H
and Zhang DD: Nrf2 modulates contractile and metabolic properties
of skeletal muscle in streptozotocin-induced diabetic atrophy. Exp
Cell Res. 319:2673–2683. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang W, Zhu YH, Zhou D, Wu Q, Song D,
Dicksved J and Wang JF: Oral administration of a select mixture of
bacillus probiotics affects the gut Microbiota and goblet cell
function following Escherichia coli challenge in newly weaned pigs
of genotype muc4 that are supposed To Be Enterotoxigenic E. coli
F4ab/ac receptor negative. Appl Environ Microbiol.
83:pii:e02747–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jung SY, Fraser MO, Ozawa H, Yokoyama O,
Yoshiyama M, De Groat WC and Chancellor MB: Urethral afferent nerve
activity affects the micturition reflex; implication for the
relationship between stress incontinence and detrusor instability.
J Urol. 162:204–212. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zik B, Altunbas K, Tutuncu S, Ozden O,
Ozquden Akkoc CG, Peker S and Sevimli A: Effects of capsaicin on
nitric oxide synthase isoforms in prepubertal rat ovary. Biotech
Histochem. 87:218–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang D, Li Y, Hou G, Wang P, Zhang J,
Laudon V and Shi B: Pygeum africanum: Effect on oxidative stress in
early diabetes-induced bladder. Int Urol Nephrol. 42:401–408. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang M, An C, Gao Y, Leak RK, Chen J and
Zhang F: Emerging roles of Nrf2 and phase II antioxidant enzymes in
neuroprotection. Proq Neurobiol. 100:30–47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Torimoto K, Hirao Y, Matsuyoshi H, De
Groat WC, Chancellor MB and Yoshimura N: Alpha1-adrenergic
mechanism in diabetic urethral dysfunction in rats. J Urol.
173:1027–1032. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Masuda H, Tsujii T, Okuno T, Kihara K,
Goto M and Azuma H: Localization and role of nitric oxide synthase
and endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitors in the rabbit lower
urinary tract. J Urol. 167:2235–2240. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li H, Jamal J, Plaza C, Pineda SH, Chreifi
G, Jing Q, Cinelli MA, Silverman RB and Poulos TL: Structures of
human constitutive nitric oxide synthases. Acta Crystallogr D Biol
Crystallogr. 70:2667–2674. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mumtaz FH, Sullivan ME, Thompson CS,
Dashwood MR, Naseem KM, Bruckdorfer KR, Mikhailidis DP and Morgan
RJ: Alterations in the nitric oxide synthase binding sites and
non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic mediated smooth muscle relaxation
in the diabetic rabbit bladder outlet: Possible relevance to the
pathogenesis of diabetic cystopathy. J Urol. 162:558–566. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Warner T, Mitchell JA, Sheng H and Murad
F: Effects of cyclic GMP on smooth muscle relaxation. Adv
Pharmacol. 26:171–194. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feng Z, Wei RB, Hong Q, Cui SY and Chen
XM: Grape seed extract enhances eNOS expression and NO production
through regulating calcium-mediated AKT phosphorylation in
H2O2-treated endothelium. Cell Biol Int. 34:1055–1061. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Caremel R, Oger-Roussel S, Behr-Roussel D,
Grise P and Giuliano FA: Nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine
monophosphate signalling mediates an inhibitory action on sensory
pathways of the micturition reflex in the rat. Eur Urol.
58:616–625. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Marla SS, Lee J and Groves JT:
Peroxynitrite rapidly permeates phospholipid membranes. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 94:pp. 14243–14248. 1997; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Szabó C: The pathophysiological role of
peroxynitrite in shock, inflammation, and ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Shock. 6:79–88. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kobayashi M and Yamamoto M: Molecular
mechanisms activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway of antioxidant gene
regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 7:385–394. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Niture SK, Khatri R and Jaiswal AK:
Regulation of Nrf2-an update. Free Radic Biol Med. 66:36–44. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|