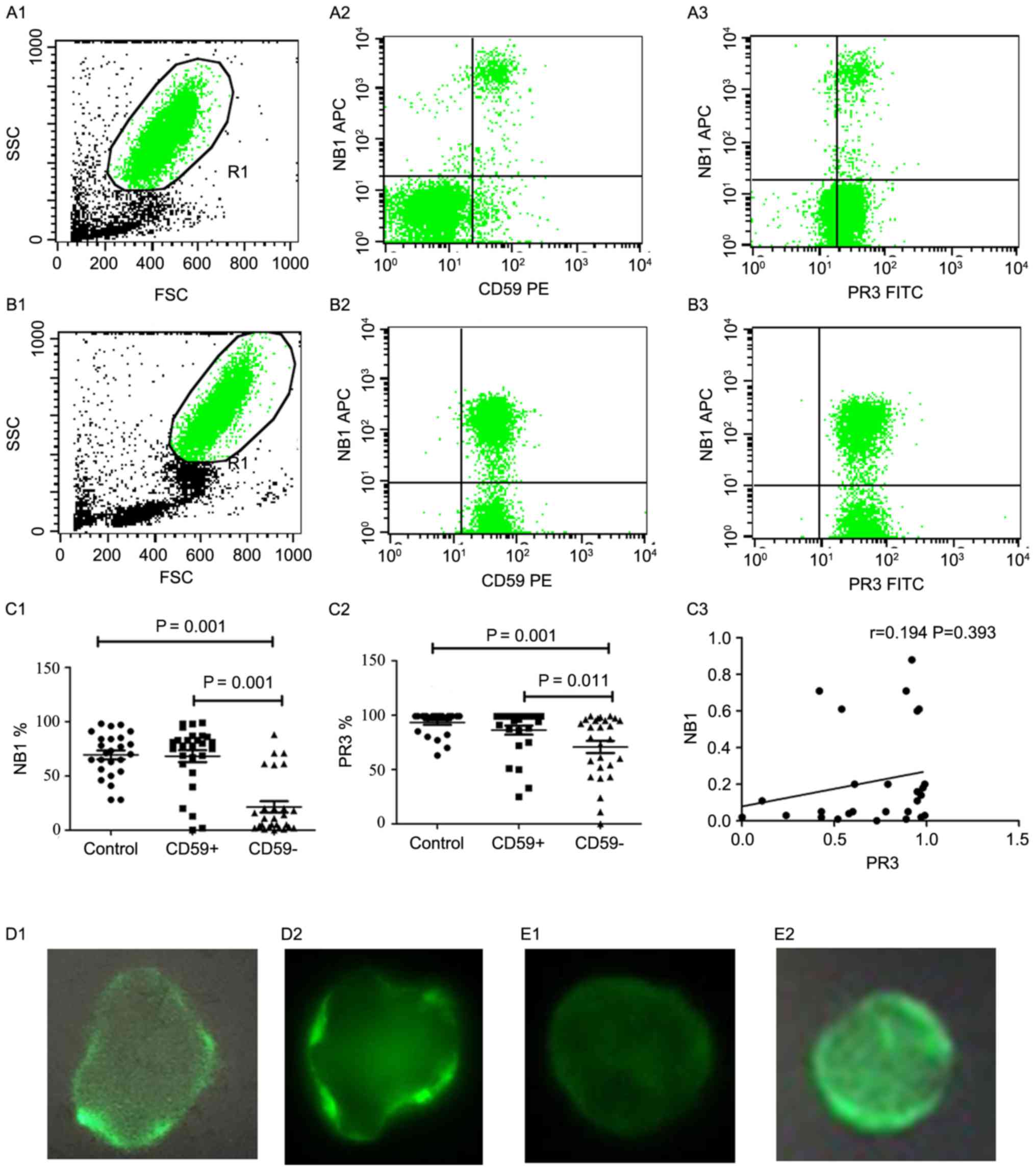
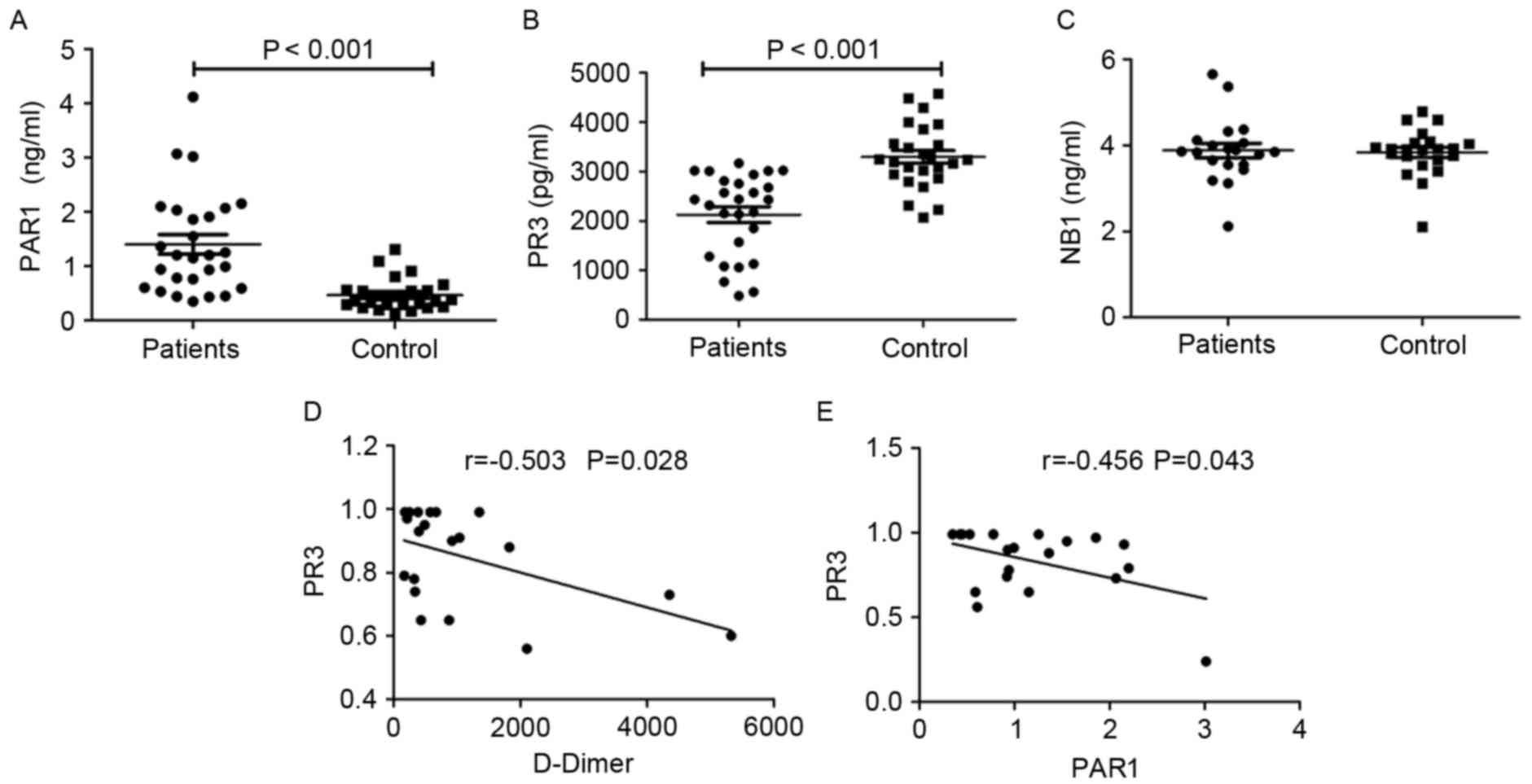
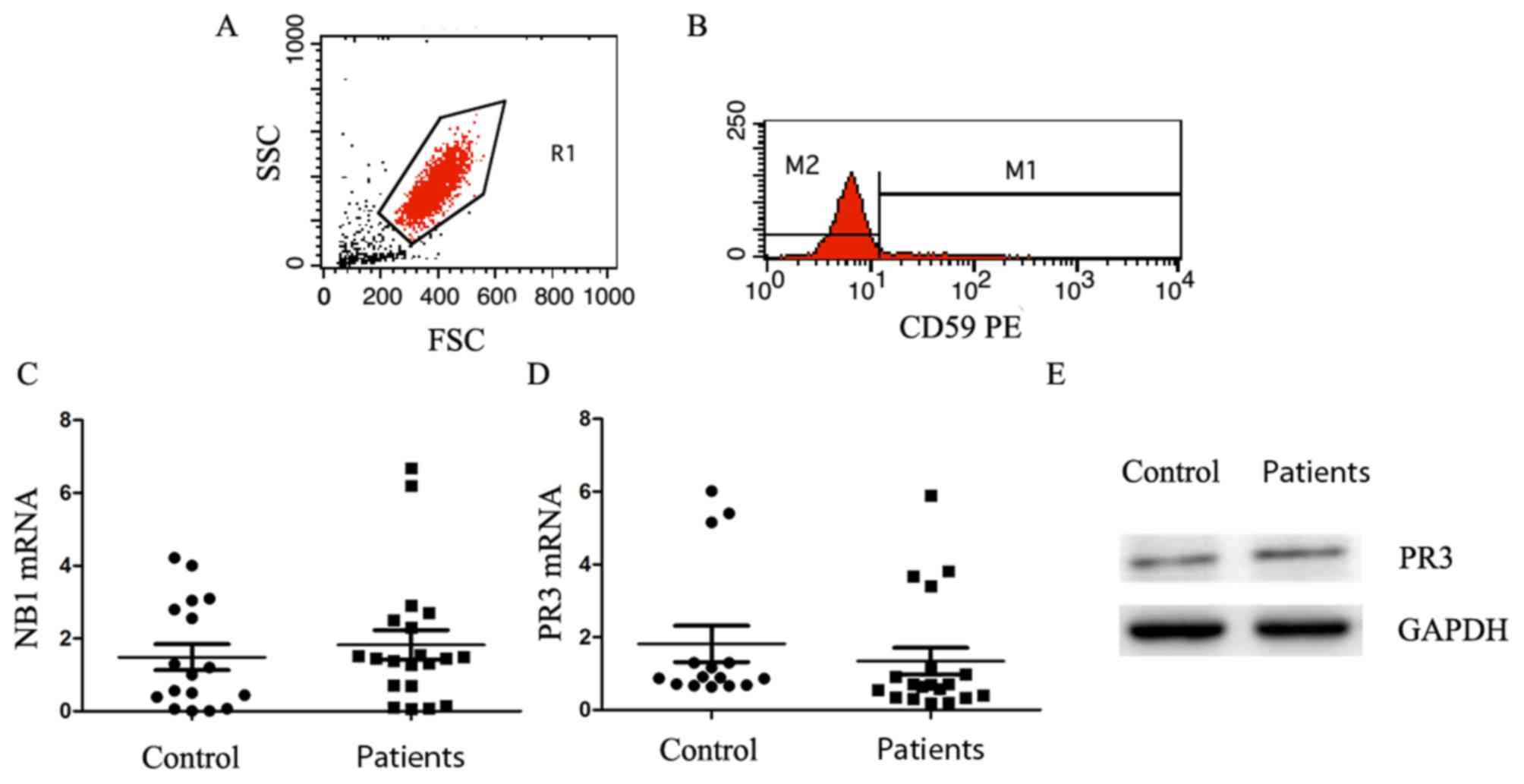
|
1
|
Hillmen P, Lewis SM, Bessler M, Luzzatto L
and Dacie JV: Natural history of paroxysmal nocturnal
hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 333:1253–1258. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Takeda J, Miyata T, Kawagoe K, Iida Y,
Endo Y, Fujita T, Takahashi M, Kitani T and Kinoshita T: Deficiency
of the GPI anchor caused by a somatic mutation of the PIG-A gene in
paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Cell. 73:703–711. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nicholson-Weller A, Spicer DB and Austen
KF: Deficiency of the complement regulatory protein,
‘decay-accelerating factor,’ on membranes of granulocytes,
monocytes, and platelets in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N
Engl J Med. 312:1091–1097. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Diep DB, Nelson KL, Raja SM, Pleshak EN
and Buckley JT: Glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors of membrane
glycoproteins are binding determinants for the channel-forming
toxin aerolysin. J Biol Chem. 273:2355–2360. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brodsky RA, Mukhina GL, Nelson KL,
Lawrence TS, Jones RJ and Buckley JT: Resistance of paroxysmal
nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells to the
glycosylphosphatidylinositol-binding toxin aerolysin. Blood.
93:1749–1756. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Devalet B, Mullier F, Chatelain B, Dogne
JM and Chatelain C: The central role of extracellular vesicles in
the mechanisms of thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal
haemoglobinuria: A review. J Extracell Vesicles. 3:233042014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ziakas PD, Poulou LS and Pomoni A:
Thrombosis in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria at a glance: A
clinical review. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 6:347–353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hill A, Kelly RJ and Hillmen P: Thrombosis
in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 121:4985–4996; quiz
5105. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stroncek DF, Caruccio L and Bettinotti M:
CD177: A member of the LY-6 gene superfamily involved with
neutrophil proliferation and polycythemia vera. J Transl Med.
2:82004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kissel K, Santoso S, Hofmann C, Stroncek D
and Bux J: Molecular basis of the neutrophil glycoprotein NB1
(CD177) involved in the pathogenesis of immune neutropenias and
transfusion reactions. Eur J Immunol. 31:1301–1309. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lalezari P, Murphy GB and Allen FH Jr:
NB1, a new neutrophil-specific antigen involved in the pathogenesis
of neonatal neutropenia. J Clin Invest. 50:1108–1115. 1971.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Toyoda T, Tsukamoto T, Yamamoto M, Ban H,
Saito N, Takasu S, Shi L, Saito A, Ito S, Yamamura Y, et al: Gene
expression analysis of a Helicobacter pylori-infected and high-salt
diet-treated mouse gastric tumor model: Identification of CD177 as
a novel prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer. BMC
Gastroenterol. 13:1222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Teofili L, Martini M, Guidi F, Venditti D,
Leone G and Larocca ML: The PRV-1 gene expression in essential
thrombocythemia. Blood. 104:2995–2996. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Teofili L, Martini M, Luongo M, Di Mario
A, Leone G, De Stefano V and Larocca LM: Overexpression of the
polycythemia rubra vera-1 gene in essential thrombocythemia. J Clin
Oncol. 20:4249–4254. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bux J, Becker F, Seeger W, Kilpatrick D,
Chapman J and Waters A: Transfusion-related acute lung injury due
to HLA-A2-specific antibodies in recipient and NB1-specific
antibodies in donor blood. Br J Haematol. 93:707–713. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
von Vietinghoff S, Tunnemann G, Eulenberg
C, Wellner M, Cristina Cardoso M, Luft FC and Kettritz R: NB1
mediates surface expression of the ANCA antigen proteinase 3 on
human neutrophils. Blood. 109:4487–4493. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Saragih H, Zilian E, Jaimes Y, Paine A,
Figueiredo C, Eiz-Vesper B, Blasczyk R, Larmann J, Theilmeier G,
Burg-Roderfeld M, et al: PECAM-1-dependent heme oxygenase-1
regulation via an Nrf2-mediated pathway in endothelial cells.
Thromb Haemost. 111:1077–1088. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sachs UJ, Andrei-Selmer CL, Maniar A,
Weiss T, Paddock C, Orlova VV, Choi EY, Newman PJ, Preissner KT,
Chavakis T and Santoso S: The neutrophil-specific antigen CD177 is
a counter-receptor for platelet endothelial cell adhesion
molecule-1 (CD31). J Biol Chem. 282:23603–23612. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rao NV, Wehner NG, Marshall BC, Gray WR,
Gray BH and Hoidal JR: Characterization of proteinase-3 (PR-3), a
neutrophil serine proteinase. Structural and functional properties.
J Biol Chem. 266:9540–9548. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Renesto P, Si-Tahar M, Moniatte M, Balloy
V, Van Dorsselaer A, Pidard D and Chignard M: Specific inhibition
of thrombin-induced cell activation by the neutrophil proteinases
elastase, cathepsin G, and proteinase 3: Evidence for distinct
cleavage sites within the aminoterminal domain of the thrombin
receptor. Blood. 89:1944–1953. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mihara K, Ramachandran R, Renaux B,
Saifeddine M and Hollenberg MD: Neutrophil elastase and
proteinase-3 trigger G protein-biased signaling through
proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR1). J Biol Chem.
288:32979–32990. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chinese Society of Hematology, Chinese
Medical Association, . Expert consensus of diagnosis and treatment
of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi.
34:276–279. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qin X, Hu W, Song W, Blair P, Wu G, Hu X,
Song Y, Bauer S, Feelisch M, Leopold JA, et al: Balancing role of
nitric oxide in complement-mediated activation of platelets from
mCd59a and mCd59b double-knockout mice. Am J Hematol. 84:221–227.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pu JJ and Brodsky RA: Paroxysmal nocturnal
hemoglobinuria from bench to bedside. Clin Transl Sci. 4:219–224.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rønne E, Pappot H, Grøndahl-Hansen J,
Høyer-Hansen G, Plesner T, Hansen NE and Danø K: The receptor for
urokinase plasminogen activator is present in plasma from healthy
donors and elevated in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal
haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol. 89:576–581. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ploug M, Plesner T, Rønne E, Ellis V,
Høyer-Hansen G, Hansen NE and Danø K: The receptor for
urokinase-type plasminogen activator is deficient on peripheral
blood leukocytes in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal
hemoglobinuria. Blood. 79:1447–1455. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Engström G, Zöller B, Svensson PJ,
Melander O and Persson M: Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator
receptor and incidence of venous thromboembolism. Thromb Haemost.
115:657–662. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sloand EM, Pfannes L, Scheinberg P, More
K, Wu CO, Horne M and Young NS: Increased soluble urokinase
plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) is associated with
thrombosis and inhibition of plasmin generation in paroxysmal
nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) patients. Exp Hematol. 36:1616–1624.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fu R, Meng Y, Wang Y, Liu H, Liu Y, Li L,
Ding S, Wang G, Song J and Shao Z: The dysfunction of platelets in
paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Thromb Res. 148:50–55. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
von Vietinghoff S, Eulenberg C, Wellner M,
Luft FC and Kettritz R: Neutrophil surface presentation of the
anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-antigen proteinase 3 depends
on N-terminal processing. Clin Exp Immunol. 152:508–516. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bauer S, Abdgawad M, Gunnarsson L,
Segelmark M, Tapper H and Hellmark T: Proteinase 3 and CD177 are
expressed on the plasma membrane of the same subset of neutrophils.
J Leukoc Biol. 81:458–464. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jankowska AM, Szpurka H, Calabro M, Mohan
S, Schade AE, Clemente M, Silverstein RL and Maciejewski JP: Loss
of expression of neutrophil proteinase-3: A factor contributing to
thrombotic risk in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
Haematologica. 96:954–962. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu N, Westra J, Huitema MG, Bijl M,
Brouwer E, Stegeman CA, Heeringa P, Limburg PC and Kallenberg CG:
Coexpression of CD177 and membrane proteinase 3 on neutrophils in
antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated systemic
vasculitis: Anti-proteinase 3-mediated neutrophil activation is
independent of the role of CD177-expressing neutrophils. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:1548–1557. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hu N, Westra J and Kallenberg CG:
Membrane-bound proteinase 3 and its receptors: Relevance for the
pathogenesis of Wegener's Granulomatosis. Autoimmun Rev. 8:510–514.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Han Y, Pasquet JM, Nurden A and Ruan CG:
Mechanism of action of protease-activated receptors 1 and 4 in
platelet activation. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi.
11:495–498. 2003.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kahn ML, Nakanishi-Matsui M, Shapiro MJ,
Ishihara H and Coughlin SR: Protease-activated receptors 1 and 4
mediate activation of human platelets by thrombin. J Clin Invest.
103:879–887. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Peng X, Ramström S, Kurz T, Grenegård M
and Segelmark M: The neutrophil serine protease PR3 induces shape
change of platelets via the Rho/Rho kinase and Ca(2+) signaling
pathways. Thromb Res. 134:418–425. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|