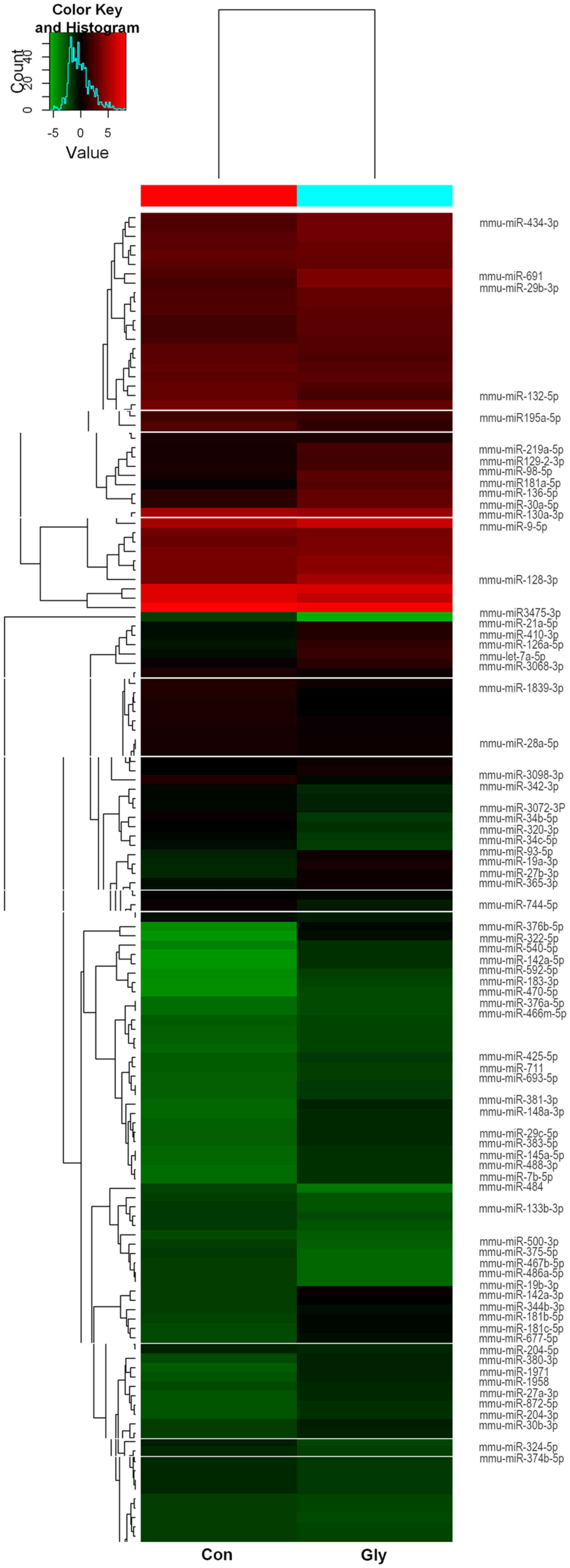
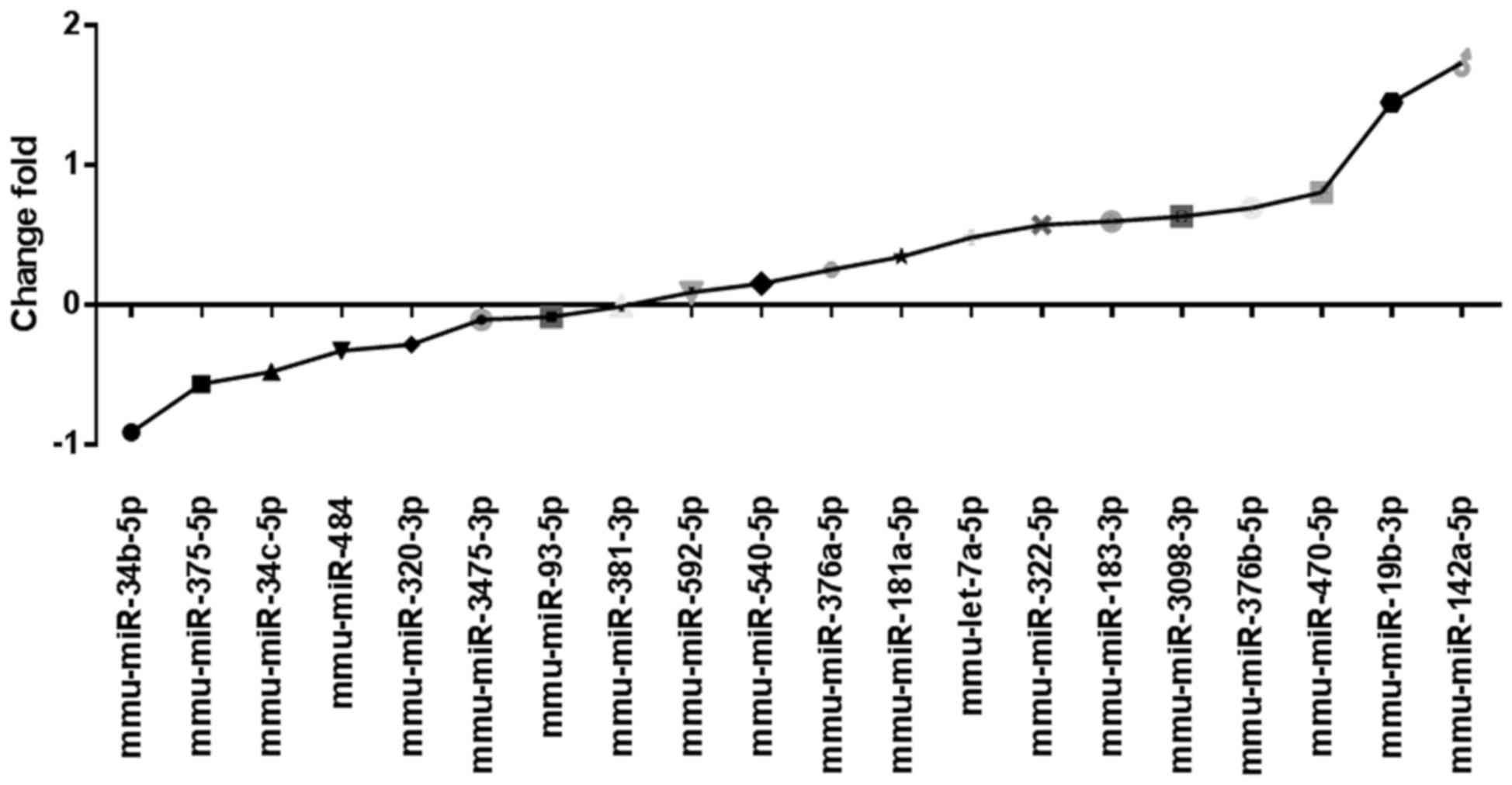
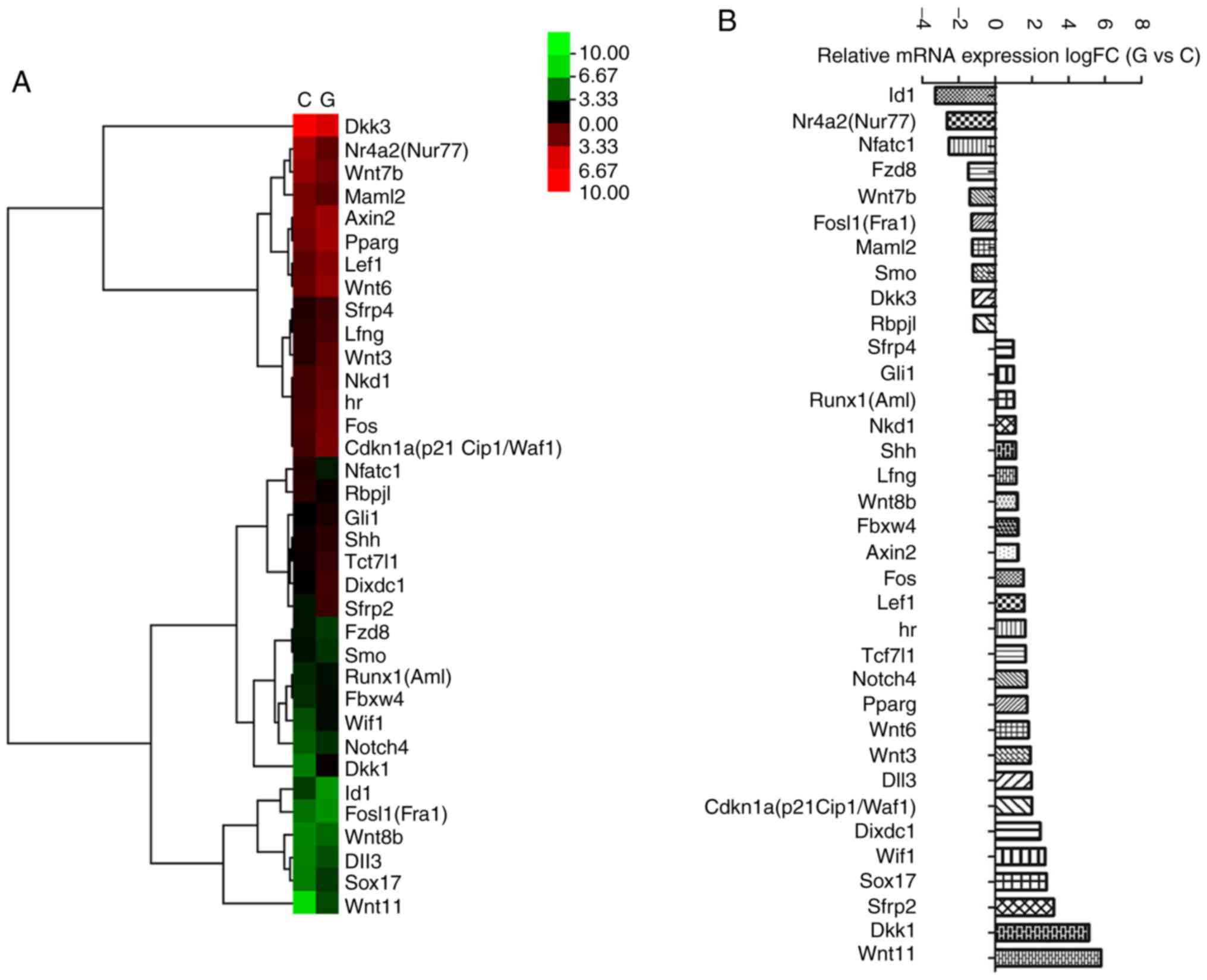
|
1
|
Hernández-Plata I, Giordano M, Díaz-Muñoz
M and Rodriguez VM: The herbicide glyphosate causes behavioral
changes and alterations in dopaminergic markers in male
Sprague-Dawley rat. Neurotoxicology. 46:79–91. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paganelli A, Gnazzo V, Acosta H, Lόpez SL
and Carrasco AE: Glyphosate-based herbicides produce teratogenic
effects on vertebrates by impairing retinoic acid signaling. Chem
Res Toxicol. 23:1586–1595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guyton KZ, Loomis D, Grosse Y, El
Ghissassi F, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Scoccianti C, Mattock H
and Straif K; International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph
Working Group, IARC, Lyon, France, : Carcinogenicity of
tetrachlorvinphos, parathion, malathion, diazinon, and glyphosate.
Lancet Oncol. 16:490–491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Williams GM, Kroes R and Munro IC: Safety
evaluation and risk assessment of the herbicide Roundup and its
active ingredient, glyphosate, for humans. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol.
31:117–165. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gallegos CE, Bartos M, Bras C, Gumilar F,
Antonelli MC and Minetti A: Exposure to a glyphosate-based
herbicide during pregnancy and lactation induces neurobehavioral
alterations in rat offspring. Neurotoxicology. 53:20–28. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sobjak TM, Romão S, do Nascimento CZ, Dos
Santos AFP, Vogel L and Guimarães ATB: Assessment of the oxidative
and neurotoxic effects of glyphosate pesticide on the larvae of
Rhamdia quelen fish. Chemosphere. 182:267–275. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
de Araujo JS, Delgado IF and Paumgartten
FJ: Glyphosate and adverse pregnancy outcomes, a systematic review
of observational studies. BMC Public Health. 16:4722016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Poulsen MS, Rytting E, Mose T and Knudsen
LE: Modeling placental transport: Correlation of in vitro BeWo cell
permeability and ex vivo human placental perfusion. Toxicol In
Vitro. 23:1380–1386. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Coullery RP, Ferrari ME and Rosso SB:
Neuronal development and axon growth are altered by glyphosate
through a WNT non-canonical signaling pathway. Neurotoxicology.
52:150–161. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shelton JF, Geraghty EM, Tancredi DJ,
Delwiche LD, Schmidt RJ, Ritz B, Hansen RL and Hertz-Picciotto I:
Neurodevelopmental disorders and prenatal residential proximity to
agricultural pesticides: The CHARGE study. Environ Health Perspect.
122:1103–1109. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rangasamy S, D'Mello SR and Narayanan V:
Epigenetics, autism spectrum, and neurodevelopmental disorders.
Neurotherapeutics. 10:742–756. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu Y, Chen XT, Luo M, Tang Y, Zhang G, Wu
D, Yang B, Ruan DY and Wang HL: Multiple epigenetic factors predict
the attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder among the Chinese Han
children. J Psychiatr Res. 64:40–50. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Witwer KW, Sisk JM, Gama L and Clements
JE: MicroRNA regulation of IFN-beta protein expression: Rapid and
sensitive modulation of the innate immune response. J Immunol.
184:2369–2376. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu L, Li H, Jia CY, Cheng W, Yu M, Peng M,
Zhu Y, Zhao Q, Dong YW, Shao K, et al: MicroRNA-223 regulates FOXO1
expression and cell proliferation. FEBS Lett. 586:1038–1043. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kandemir H, Erdal ME, Selek S, Ay Öİ,
Karababa IF, Kandemir SB, Ay ME, Yılmaz ŞG, Bayazıt H and Taşdelen
B: Evaluation of several micro RNA (miRNA) levels in children and
adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neurosci
Lett. 580:158–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Casey BJ, Epstein JN, Buhle J, Liston C,
Davidson MC, Tonev ST, Spicer J, Niogi S, Millner AJ, Reiss A, et
al: Frontostriatal connectivity and its role in cognitive control
in parent-child dyads with ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 164:1729–1736.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Somel M, Liu X, Tang L, Yan Z, Hu H, Guo
S, Jiang X, Zhang X, Xu G, Xie G, et al: MicroRNA-driven
developmental remodeling in the brain distinguishes humans from
other primates. PLoS Biol. 9:e10012142011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu LH, Peng M, Yu M, Zhao QL, Li C, Jin
YT, Jiang Y, Chen ZY, Deng NH, Sun H and Wu XZ: Circulating
MicroRNA Let-7d in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
Neuromolecular Med. 17:137–146. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu L, Zhao Q, Zhu X, Peng M, Jia C, Wu W,
Zheng J and Wu XZ: A novel function of microRNA let-7d in
regulation of galectin-3 expression in attention deficit
hyperactivity disorder rat brain. Brain Pathol. 20:1042–1054. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hollins SL, Goldie BJ, Carroll AP, Mason
EA, Walker FR, Eyles DW and Cairns MJ: Ontogeny of small RNA in the
regulation of mammalian brain development. BMC Genomics.
15:7772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shioya M, Obayashi S, Tabunoki H, Arima K,
Saito Y, Ishida T and Satoh J: Aberrant microRNA expression in the
brains of neurodegenerative diseases: miR-29a decreased in
Alzheimer disease brains targets neurone navigator 3. Neuropathol
Appl Neurobiol. 36:320–330. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu JJ, Liu YF, Zhang YP, Zhao CR, Yao WJ,
Li YS, Wang KC, Huang TS, Pang W, Wang XF, et al: VAMP3 and SNAP23
mediate the disturbed flow-induced endothelial microRNA secretion
and smooth muscle hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:pp.
8271–8276. 2017; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alsharafi WA, Xiao B and Li J:
MicroRNA-139-5p negatively regulates NR2A-containing NMDA receptor
in the rat pilocarpine model and patients with temporal lobe
epilepsy. Epilepsia. 57:1931–1940. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Srivastav S, Walitza S and Grünblatt E:
Emerging role of miRNA in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder:
A systematic review. Atten Defic Hyperact Disord. May 10–2017.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luo SX and Huang EJ: Dopaminergic neurons
and brain reward pathways: From neurogenesis to circuit assembly.
Am J Pathol. 186:478–488. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Trujillo-Paredes N, Valencia C,
Guerrero-Flores G, Arzate DM, Baizabal JM, Guerra-Crespo M,
Fuentes-Hernández A, Zea-Armenta I and Covarrubias L: Regulation of
differentiation flux by Notch signalling influences the number of
dopaminergic neurons in the adult brain. Biol Open. 5:336–347.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cattani D, de Liz Oliveira Cavalli VL,
Heinz Rieg CE, Domingues JT, Dal-Cim T, Tasca CI, Mena Barreto
Silva FR and Zamoner A: Mechanisms underlying the neurotoxicity
induced by glyphosate-based herbicide in immature rat hippocampus:
Involvement of glutamate excitotoxicity. Toxicology. 320:34–45.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu CJ, Du JC, Chiou HC, Chung MY, Yang W,
Chen YS, Fuh MR, Chien LC, Hwang B and Chen ML: Increased risk of
attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder associated with exposure
to organophosphate pesticide in Taiwanese children. Andrology.
4:695–705. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Marks AR, Harley K, Bradman A, Kogut K,
Barr DB, Johnson C, Calderon N and Eskenazi B: Organophosphate
pesticide exposure and attention in young Mexican-American
children: The CHAMACOS study. Environ Health Perspect.
118:1768–1774. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Eubig PA, Aguiar A and Schantz SL: Lead
and PCBs as risk factors for attention deficit/hyperactivity
disorder. Environ Health Perspect. 118:1654–1667. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mill J and Petronis A: Pre- and peri-natal
environmental risks for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
(ADHD): The potential role of epigenetic processes in mediating
susceptibility. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 49:1020–1030. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Callaway E: Epigenomics starts to make its
mark. Nature. 508:222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Murgatroyd C, Patchev AV, Wu Y, Micale V,
Bockmühl Y, Fischer D, Holsboer F, Wotjak CT, Almeida OF and
Spengler D: Dynamic DNA methylation programs persistent adverse
effects of early-life stress. Nat Neurosci. 12:1559–1566. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hu Z and Li Z: miRNAs in synapse
development and synaptic plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 45:24–31.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E: Gene
silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression
and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. 12:99–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu L, Liu L, Shi J, Tan M, Xiong J, Li X,
Hu Q, Yi Z and Mao D: MicroRNA-34b mediates hippocampal astrocyte
apoptosis in a rat model of recurrent seizures. BMC Neurosci.
17:562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Luceri C, Bigagli E, Pitozzi V and
Giovannelli L: A nutrigenomics approach for the study of anti-aging
interventions: Olive oil phenols and the modulation of gene and
microRNA expression profiles in mouse brain. Eur J Nutr.
56:865–877. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim NH, Kim HS, Li XY, Lee I, Choi HS,
Kang SE, Cha SY, Ryu JK, Yoon D, Fearon ER, et al: A p53/miRNA-34
axis regulates Snail1-dependent cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. J Cell Biol. 195:417–433. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cha YH, Kim NH, Park C, Lee I, Kim HS and
Yook JI: miRNA-34 intrinsically links p53 tumor suppressor and Wnt
signaling. Cell Cycle. 11:1273–1281. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Isik M, Blackwell TK and Berezikov E:
MicroRNA mir-34 provides robustness to environmental stress
response via the DAF-16 network in C. elegans. Sci Rep.
6:367662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ferretti E, De Smaele E, Miele E, Laneve
P, Po A, Pelloni M, Paganelli A, Di Marcotullio L, Caffarelli E,
Screpanti I, et al: Concerted microRNA control of Hedgehog
signalling in cerebellar neuronal progenitor and tumour cells. EMBO
J. 27:2616–2627. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Stappert L, Borghese L, Roese-Koerner B,
Weinhold S, Koch P, Terstegge S, Uhrberg M, Wernet P and Brüstle O:
MicroRNA-based promotion of human neuronal differentiation and
subtype specification. PloS one. 8:e590112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Andrés-León E, Gómez-López G and Pisano
DG: Prediction of miRNA-mRNA interactions using miRGate. Methods
Mol Biol. 1580:225–237. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Salyakina D, Cukier HN, Lee JM, Sacharow
S, Nations LD, Ma D, Jaworski JM, Konidari I, Whitehead PL, Wright
HH, et al: Copy number variants in extended autism spectrum
disorder families reveal candidates potentially involved in autism
risk. PLoS One. 6:e260492011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pedrosa E, Shah A, Tenore C, Capogna M,
Villa C, Guo X, Zheng D and Lachman HM: β-catenin promoter
ChIP-chip reveals potential schizophrenia and bipolar disorder gene
network. J Neurogenet. 24:182–193. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fimiani C, Goina E, Su Q, Gao G and
Mallamaci A: RNA activation of haploinsufficient Foxg1 gene in
murine neocortex. Sci Rep. 6:393112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ebbing EA, Medema JP, Damhofer H, Meijer
SL, Krishnadath KK, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Bijlsma MF and van
Laarhoven HW: ADAM10-mediated release of heregulin confers
resistance to trastuzumab by activating HER3. Oncotarget.
7:10243–10254. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Saftig P and Lichtenthaler SF: The alpha
secretase ADAM10: A metalloprotease with multiple functions in the
brain. Prog Neurobiol. 135:1–20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nishimura T and Kaibuchi K: Numb controls
integrin endocytosis for directional cell migration with aPKC and
PAR-3. Dev Cell. 13:15–28. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Price DJ, Kennedy H, Dehay C, Zhou L,
Mercier M, Jossin Y, Goffinet AM, Tissir F, Blakey D and Molnár Z:
The development of cortical connections. Eur J Neurosci.
23:910–920. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bonini SA, Ferrari-Toninelli G,
Maccarinelli G, Bettinsoli P, Montinaro M and Memo M: Cytoskeletal
protection: Acting on notch to prevent neuronal dysfunction.
Neurodegener Dis. 13:93–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Goodings L, He J, Wood AJ, Harris WA,
Currie PD and Jusuf PR: In vivo expression of Nurr1/Nr4a2a in
developing retinal amacrine subtypes in zebrafish Tg(nr4a2a:eGFP)
transgenics. J Comp Neurol. 525:1962–1979. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Papachristou P, Dyberg C, Lindqvist M,
Horn Z and Ringstedt T: Transgenic increase of Wnt7b in neural
progenitor cells decreases expression of T-domain transcription
factors and impairs neuronal differentiation. Brain Res.
1576:27–34. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang W, Jossin Y, Chai G, Lien WH, Tissir
F and Goffinet AM: Feedback regulation of apical progenitor fate by
immature neurons through Wnt7-Celsr3-Fzd3 signalling. Nat Commun.
7:109362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dickins EM and Salinas PC: Wnts in action:
From synapse formation to synaptic maintenance. Front Cell
Neurosci. 7:1622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Scott EL and Brann DW: Estrogen regulation
of Dkk1 and Wnt/β-Catenin signaling in neurodegenerative disease.
Brain Res. 1514:63–74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Galli S, Lopes DM, Ammari R, Kopra J,
Millar SE, Gibb A and Salinas PC: Deficient Wnt signalling triggers
striatal synaptic degeneration and impaired motor behaviour in
adult mice. Nat Commun. 5:49922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lu H, Jiang R, Tao X, Duan C, Huang J,
Huan W, He Y, Ge J and Ren J: Expression of Dixdc1 and its role in
astrocyte proliferation after traumatic brain injury. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 37:1131–1139. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kwan V, Meka DP, White SH, Hung CL,
Holzapfel NT, Walker S, Murtaza N, Unda BK, Schwanke B, Yuen RKC,
et al: DIXDC1 Phosphorylation and control of dendritic morphology
are impaired by rare genetic variants. Cell Rep. 17:1892–1904.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Singh KK, Ge X, Mao Y, Drane L, Meletis K,
Samuels BA and Tsai LH: Dixdc1 is a critical regulator of DISC1 and
embryonic cortical development. Neuron. 67:33–48. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang JW and Stifani S: Roles of Runx genes
in nervous system development. Adv Exp Med Biol. 962:103–116. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zagami CJ and Stifani S: Molecular
characterization of the mouse superior lateral parabrachial nucleus
through expression of the transcription factor Runx1. PLoS One.
5:e139442010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Muthu V, Eachus H, Ellis P, Brown S and
Placzek M: Rx3 and Shh direct anisotropic growth and specification
in the zebrafish tuberal/anterior hypothalamus. Development.
143:2651–2663. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Feijόo CG, Oñate MG, Milla LA and Palma
VA: Sonic hedgehog (Shh)-Gli signaling controls neural progenitor
cell division in the developing tectum in zebrafish. Eur J
Neurosci. 33:589–598. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Patel SS, Tomar S, Sharma D, Mahindroo N
and Udayabanu M: Targeting sonic hedgehog signaling in neurological
disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 74:76–97. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang J, Gotz S, Vogt Weisenhorn DM,
Simeone A, Wurst W and Prakash N: A WNT1-regulated developmental
gene cascade prevents dopaminergic neurodegeneration in adult
En1(+/−) mice. Neurobiol Dis. 82:32–45. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Galceran J, Miyashita-Lin EM, Devaney E,
Rubenstein JL and Grosschedl R: Hippocampus development and
generation of dentate gyrus granule cells is regulated by LEF1.
Development. 127:469–482. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ki H, Jung HC, Park JH, Kim JS, Lee KY,
Kim TS and Kim K: Overexpressed LEF-1 proteins display different
nuclear localization patterns of beta-catenin in normal versus
tumor cells. Cell Biol Int. 30:253–261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kuwahara A, Sakai H, Xu Y, Itoh Y,
Hirabayashi Y and Gotoh Y: Tcf3 represses Wnt-β-catenin signaling
and maintains neural stem cell population during neocortical
development. PLoS One. 9:e944082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Mutch CA, Schulte JD, Olson E and Chenn A:
Beta-catenin signaling negatively regulates intermediate progenitor
population numbers in the developing cortex. PLoS One.
5:e123762010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Pérez-Palma E, Andrade V, Caracci MO,
Bustos BI, Villaman C, Medina MA, Ávila ME, Ugarte GD and De
Ferrari GV: Early transcriptional changes induced by Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in hippocampal neurons. Neural Plast. 2016:46728412016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|