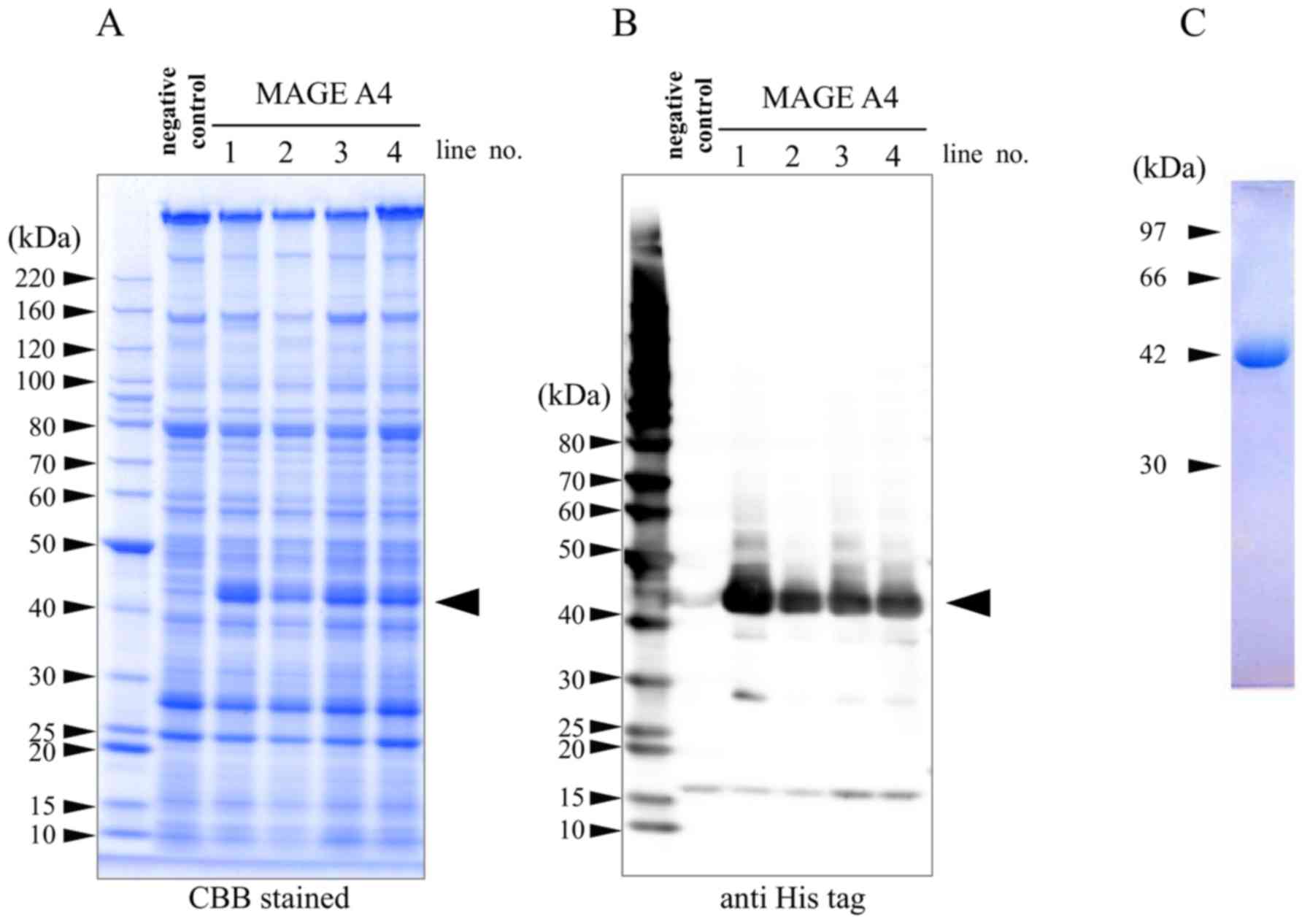
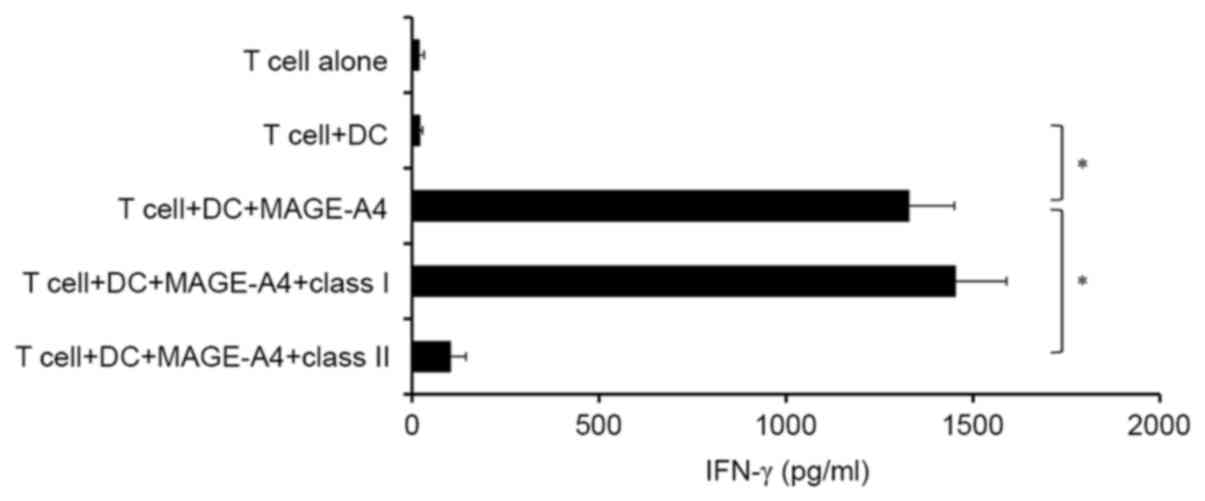
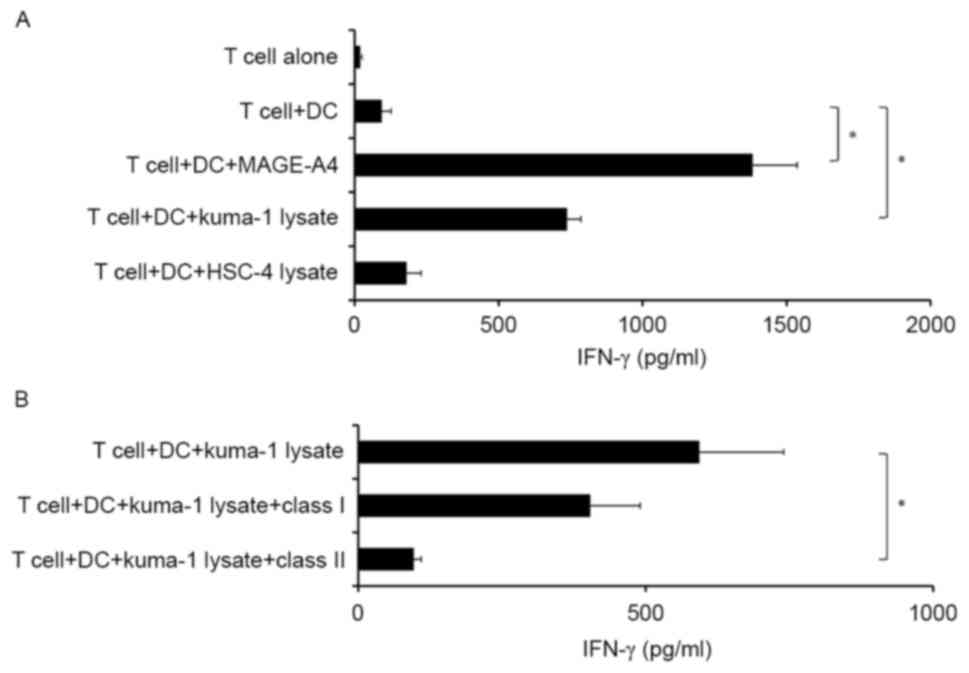
|
1
|
Coulie PG, Van den Eynde BJ, van der
Bruggen P and Boon T: Tumor antigens recognized by T lymphocytes:
At the core of cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:135–146.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hoos A, Parmiani G, Hege K, Sznol M,
Loibner H, Eggermont A, Urba W, Blumenstein B, Sacks N, Keilholz U,
et al: Cancer vaccine clinical trial working group. A clinical
development paradigm for cancer vaccines and related biologics. J
Immunother. 30:1–15. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rosenberg SA, Yang JC and Restifo NP:
Cancer immunotherapy: Moving beyond current vaccines. Nat Med.
10:909–915. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pol J, Bloy N, Buqué A, Eggermont A,
Cremer I, Sautes-Fridman C, Galon J, Tartour E, Zitvogel L, Kroemer
G and Galluzzi L: Trial watch: Peptide-based anticancer vaccines.
Oncoimmunology. 4:e9744112015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Parmiani G, Castelli C, Dalerba P,
Mortarini R, Rivoltini L, Marincola FM and Anichini A: Cancer
immunotherapy with peptide-based vaccines: What have we achieved?
Where are we going? J Natl Cancer Inst. 94:805–818. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tagliamonte M, Petrizzo A, Tornesello ML,
Buonaguro FM and Buonaguro L: Antigen-specific vaccines for cancer
treatment. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 10:3332–3346. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Palomares LA, Estrada-Mondaca S and
Ramírez OT: Production of recombinant proteins: Challenges and
solutions: Methods. Mol Biol. 267:1–52. 2004.
|
|
8
|
Tatematsu K, Kobayashi I, Uchino K,
Sezutsu H, Iizuka T, Yonemura N and Tamura T: Construction of a
binary transgenic gene expression system for recombinant protein
production in the middle silk gland of the silkworm Bombyx mori.
Transgenic Res. 19:473–487. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tateno M, Toyooka M, Shikano Y, Takeda S,
Kuwabara N, Sezutsu H and Tamura T: Production and characterization
of the recombinant human mu-opioid receptor from transgenic
silkworms. J Biochme. 145:37–42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nikaido Y, Kurosawa A, Saikawa H, Kuroiwa
S, Suzuki C, Kuwabara N, Hoshino H, Obata H, Saito S, Saito T, et
al: In vivo and in vitro evaluation of novel μ-opioid receptor
agonist compounds. Eur J Pharmacol. 767:193–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Barrow C, Browning J, MacGregor D, Davis
ID, Sturrock S, Jungbluth AA and Cebon J: Tumor antigen expression
in melanoma varies according to antigen and stage. Clin Cancer Res.
12:764–771. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Montoro JR, Mamede RC, Neder Serafini L,
Saggioro FP, Figueiredo DL, Silva WA Jr, Jungbluth AA, Spagnoli GC
and Zago MA: Expression of cancer-testis antigens MAGE-A4 and
MAGE-C1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 34:1123–1128.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shigematsu Y, Hanagiri T, Shiota H, Kuroda
K, Baba T, Mizukami M, So T, Ichiki Y, Yasuda M, So T, et al:
Clinical significance of cancer/testis antigens expression in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 68:105–110.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takahashi N, Ohkuri T, Homma S, Ohtake J,
Wakita D, Togashi Y, Kitamura H, Todo S and Nishimura T: First
clinical trial of cancer vaccine therapy with artificially
synthesized helper/killer-hybrid epitope long peptide of MAGE-A4
cancer antigen. Cancer Sci. 103:150–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saito T, Wada H, Yamasaki M, Miyata H,
Nishikawa H, Sato E, Kageyama S, Shiku H, Mori M and Doki Y: High
expression of MAGE-A4 and MHC class I antigens in tumor cells and
induction of MAGE-A4 immune responses are prognostic markers of
CHP-MAGE-A4 cancer vaccine. Vaccine. 32:5901–5907. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tada M, Tatematsu K, Ishii-Watabe A,
Harazono A, Takakura D, Hashii N, Sezutsu H and Kawasaki N:
Characterization of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody produced by
transgenic silkworms (Bombyx mori). MAbs. 7:1138–1150. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tamura T, Thibert C, Royer C, Kanda T,
Abraham E, Kamba M, Komoto N, Thomas JL, Mauchamp B, Chavancy G, et
al: Germline transformation of the silkworm Bombyx mori L. Using a
piggyBac transposon derived vector. Nat Biotechnol. 18:81–84. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tatematsu K, Uchino K, Sezutsu H and
Tamura T: Effect of ATG initiation codon context motifs on the
efficiency of translation of mRNA derived from exogenous genes in
the transgenic silkworm, Bombyx mori. SpringerPlus. 3:1362014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eura M, Ogi K, Chikamatsu K, Lee KD,
Nakano K, Masuyama K, Itoh K and Ishikawa T: Expression of the MAGE
gene family in human head-and-neck squamous-cell carcinomas. Int J
Cancer. 64:304–308. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hayashi S, Kumai T, Matsuda Y, Aoki N,
Sato K, Kimura S, Kitada M, Tateno M, Celis E and Kobayashi H:
Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate and enhancer
of zeste homolog 2 as immunotherapeutic targets for lung cancer. J
Transl Med. 9:1912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chikamatsu K, Nakano K, Storkus WJ,
Appella E, Lotze MT, Whiteside TL and DeLeo AB: Generation of
anti-p53 cytotoxic T lymphocytes from human peripheral blood using
autologous dendritic cells. Clin Cancer Res. 5:1281–1288.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang Y: Cancer immunotherapy: Harnessing
the immune system to battle cancer. J Clin Invest. 125:3335–3337.
2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Imamura M, Nakai J, Inoue S, Quan GX,
Kanda T and Tamura T: Targeted gene expression using the GAL4/UAS
system in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Genetics. 165:1329–1340.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ogawa S, Tomita M, Shimizu K and Yoshizato
K: Generation of a transgenic silkworm that secretes recombinant
proteins in the sericin layer of cocoon: Production of recombinant
human serum albumin. J Biotechnol. 128:531–544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Iizuka M, Ogawa S, Takeuchi A, Nakakita S,
Kubo Y, Miyawaki Y, Hirabayashi J and Tomita M: Production of a
recombinant mouse monoclonal antibody in transgenic silkworm
cocoons. FEBS J. 276:5806–5820. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fehres CM, Unger WWJ, Garcia-Vallejo JJ
and van Kooyk Y: Understanding the biology of antigen
cross-presentation for the design of vaccines against cancer. Front
Immunol. 5:1492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gutiérrez-Martínez E, Planès R, Anselmi G,
Reynolds M, Menezes S, Adiko AC, Saveanu L and Guermonprez P:
Cross-presentation of cell-associated antigens by MHC class I in
dendritic cell subsets. Front Immunol. 6:3632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fratta E, Coral S, Covre A, Parisi G,
Colizzi F, Danielli R, Nicolay HJ, Sigalotti L and Maio M: The
biology of cancer testis antigens: Putative function, regulation
and therapeutic potential. Mol Oncol. 5:164–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gjerstorff MF, Andersen MH and Ditzel HJ:
Oncogenic cancer/testis antigens: Prime candidates immunotherapy.
Oncotarget. 6:15772–15787. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cesson V, Rivals JP, Escher A, Piotet E,
Thielemans K, Posevitz V, Dojcinovic D, Monnier P, Speiser D, Bron
L and Romero P: MAGE-A3 and MAGE-A4 specific CD4(+) T cells in head
and neck cancer patients: Detection of naturally acquired responses
and identification of new epitopes. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
60:23–35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cheever MA, Allison JP, Ferris AS, Finn
OJ, Hasting BM, Hecht TT, Mellman I, Prindiville SA, Viner JL,
Weiner LM and Matrisian LM: The prioritization of cancer antigens:
A national cancer institute pilot project for the acceleration of
translational research. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5323–5337. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW,
Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel
JC, et al: Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with
metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 363:711–723. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR,
Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD,
Sosman JA, Atkins MB, et al: Safety, activity, and immune
correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med.
366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|