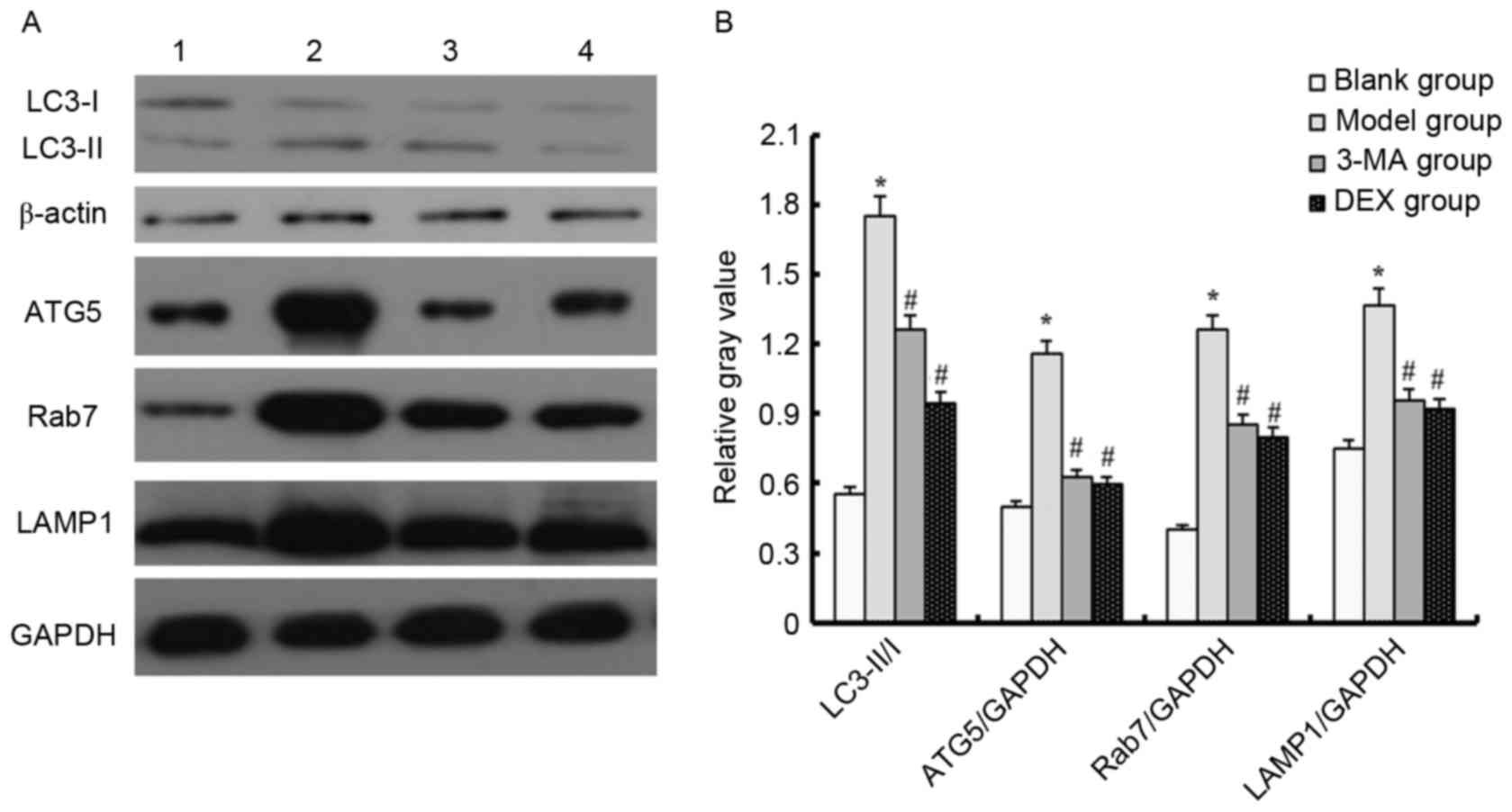
|
1
|
Wang L, Chen JM, Wang B, Wu DQ, Li H, Lu
H, Wu H and Chai Y: Protective effect of quercetin on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting
inflammatory cell influx. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 239:1653–1662.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Herold S, Gabrielli NM and Vadász I: Novel
concepts of acute lung injury and alveolar-capillary barrier
dysfunction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 305:L665–L681.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matthay MA and Howard JP: Progress in
modelling acute lung injury in a pre-clinical mouse model. Eur
Respir J. 39:1062–1063. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
de Haro C, Martin-Loeches I, Torrents E
and Artigas A: Acute respiratory distress syndrome: Prevention and
early recognition. Ann Intensive Care. 3:112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Griet M, Zelaya H, Mateos MV, Salva S,
Juarez GE, de Valdez GF, Villena J, Salvador GA and Rodriguez AV:
Soluble factors from Lactobacillus reuteri CRL1098 have
anti-Inflammatory effects in acute lung injury induced by
lipopolysaccharide in mice. PLoS One. 9:e1100272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao LL, Hu GC, Zhu SS, Li JF and Liu GJ:
Propofol pretreatment attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
lung injury in rats by activating the phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt
pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res. 47:1062–1067. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ryter SW, Nakahira K, Haspel JA and Choi
AM: Autophagy in pulmonary diseases. Annu Rev Physiol. 74:377–401.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu QP, Zhou DX, Lin P, Gao XL, Pan L and
Jin FG: Participation of autophagy in acute lung injury induced by
seawater. Exp Lung Res. 39:441–452. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sen V, Güzel A, Şen HS, Ece A, Uluca U,
Söker S, Doğan E, Kaplan İ and Deveci E: Preventive effects of
dexmedetomidine on the liver in a rat model of acid-induced acute
lung injury. Biomed Res Int. 2014:6218272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu Q, Li R, Soromou L, Chen N, Yuan X, Sun
G, Li B and Feng H: p-Synephrine suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibition of the
NF-kB signaling pathway. Inflamm Res. 63:429–439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Karim M, Kanazawa T, Daigaku Y, Fujimura
S, Miotto G and Kadowaki M: Cytosolic LC3 ratio as a sensitive
index of macroautophagy in isolated rat hepatocytes and H4-II-E
cells. Autophagy. 3:553–560. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang KY, Arcaroli JJ and Abraham E: Early
alterations in neutrophil activation are associated with outcome in
acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 167:1567–1574. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Minhajuddin M, Fazal F, Bijli KM, Amin MR
and Rahman A: Inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin
potentiates thrombin-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1
expression by accelerating and stabilizing NF-kappa B activation in
endothelial cells. J Immunol. 174:5823–5829. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang S, Li Y, Fan J, Wang Z, Zeng X, Sun
Y, Song P and Ju D: The role of autophagy in the neurotoxicity of
cationic PAMAM dendrimers. Biomaterials. 35:7588–7597. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu Y, Liu J, Wu YF, Lou J, Mao YY, Shen HH
and Chen ZH: mTOR and autophagy in regulation of acute lung injury:
A review and perspective. Microbes Infect. 16:727–734. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiao H, Heering P, Hu P, Liu Z, Zhao M,
Aratani Y, Maeda N, Falk RJ and Jennette JC: Antineutrophil
cytoplasmic autoantibodies specific for myeloperoxidase cause
glomerulonephritis and vasculitis in mice. J Clin Invest.
110:955–963. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang CL, Tsai PS and Huang CJ: Effects of
dexmedetomidine on regulating pulmonary inflammation in a rat model
of ventilator-induced lung injury. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan.
46:151–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Can M, Gul S, Bektas S, Hanci V and
Acikgoz S: Effects of dexmedetomidine or methylprednisolone on
inflammatory responses in spinal cord injury. Acta Anaesthesiol
Scand. 53:1068–1072. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gertler R, Brown C, Mitchell DH and
Silvius EN: Dexmedetomidine: A novel sedative-analgesic agent. Proc
(Bayl Univ Med Cent). 14:pp. 13–21. 2001; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xie C, Li Y, Liang J, Xiao J, Zhao Z and
Li T: The effect of dexmedetomidine on autophagy and apoptosis in
intestinal ischemia reperfusion-induced lung injury. Zhonghua Jie
He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 38:761–764. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang MH, Zhou XM, Gao JL, Wang KJ and Cui
JZ: PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway participates in neuroprotection by
dexmedetomidine inhibits neuronic autophagy following traumatic
brain injury in rats. Int J Res Med Sci. 2:1569–1575. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yang HZ, Wang JP, Mi S, Liu HZ, Cui B, Yan
HM, Yan J, Li Z, Liu H, Hua F, et al: TLR4 activity is required in
the resolution of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis after acute
and chronic lung injury. Am J Pathol. 180:275–292. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao H, Leu SW, Shi L, Dedaj R, Zhao G,
Garg HG, Shen L, Lien E, Fitzgerald KA, Shiedlin A, et al: TLR4 is
a negative regulator in noninfectious lung inflammation. J Immunol.
184:5308–5314. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Doi K, Ishizu T, Tsukamoto-Sumida M,
Hiruma T, Yamashita T, Ogasawara E, Hamasaki Y, Yahagi N, Nangaku M
and Noiri E: The high-mobility group protein B1-Toll-like receptor
4 pathway contributes to the acute lung injury induced by bilateral
nephrectomy. Kidney Int. 86:316–326. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yen YT, Yang HR, Lo HC, Hsieh YC, Tsai SC,
Hong CW and Hsieh CH: Enhancing autophagy with activated protein C
and rapamycin protects against sepsis-induced acute lung injury.
Surgery. 153:689–698. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|