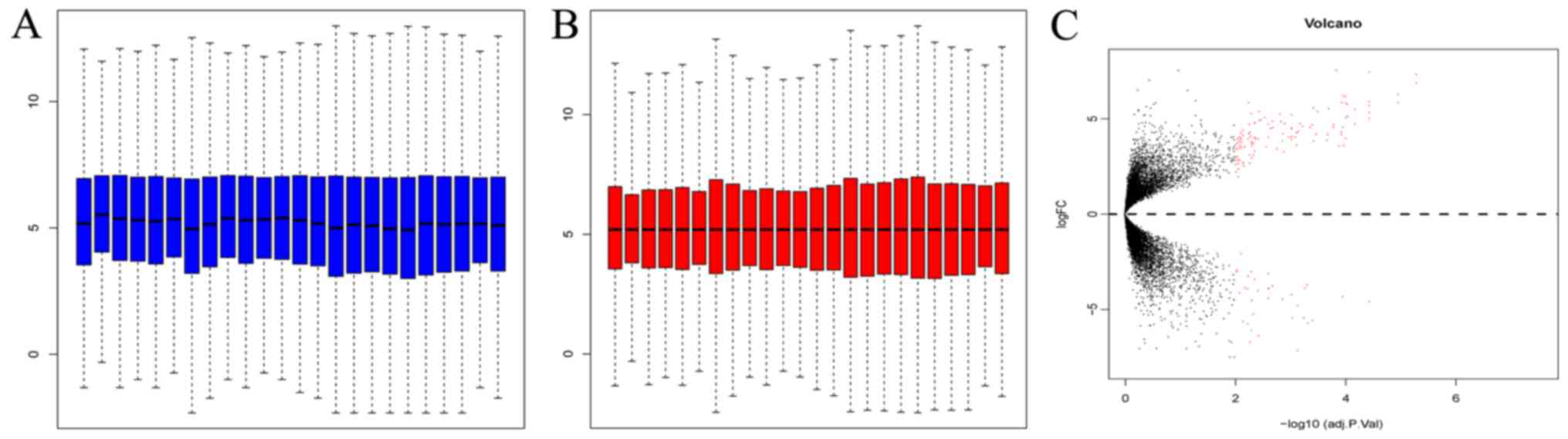
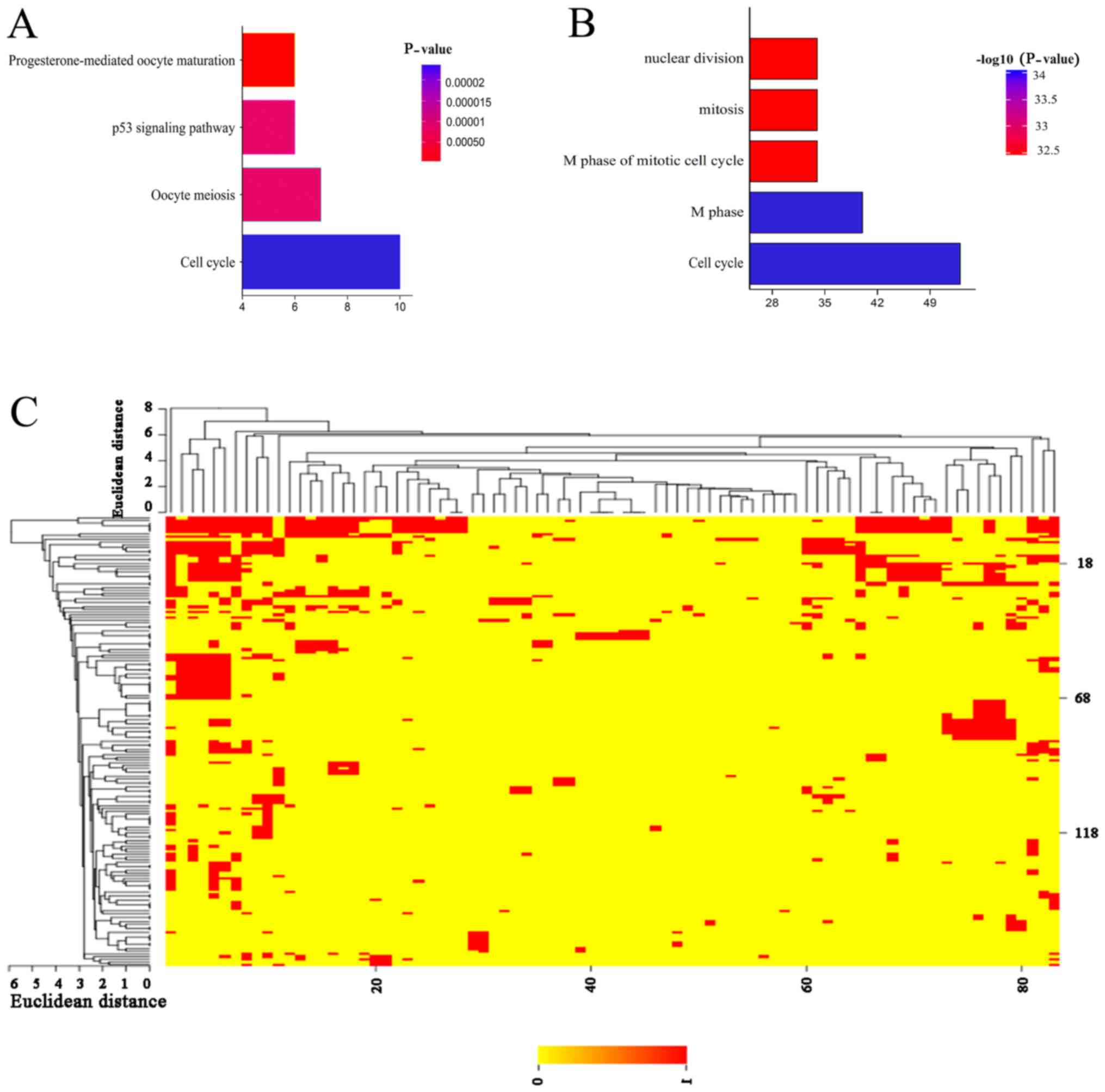
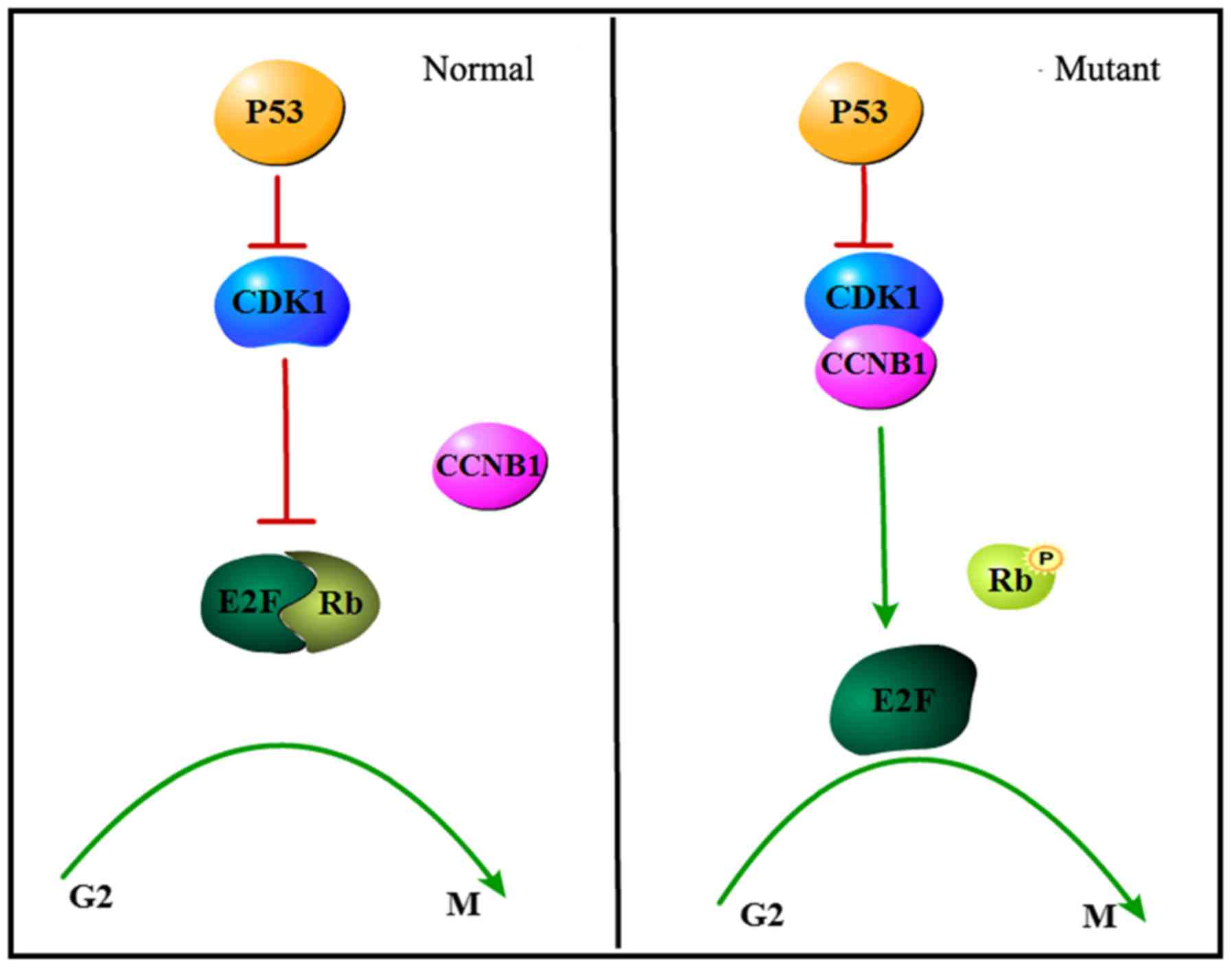
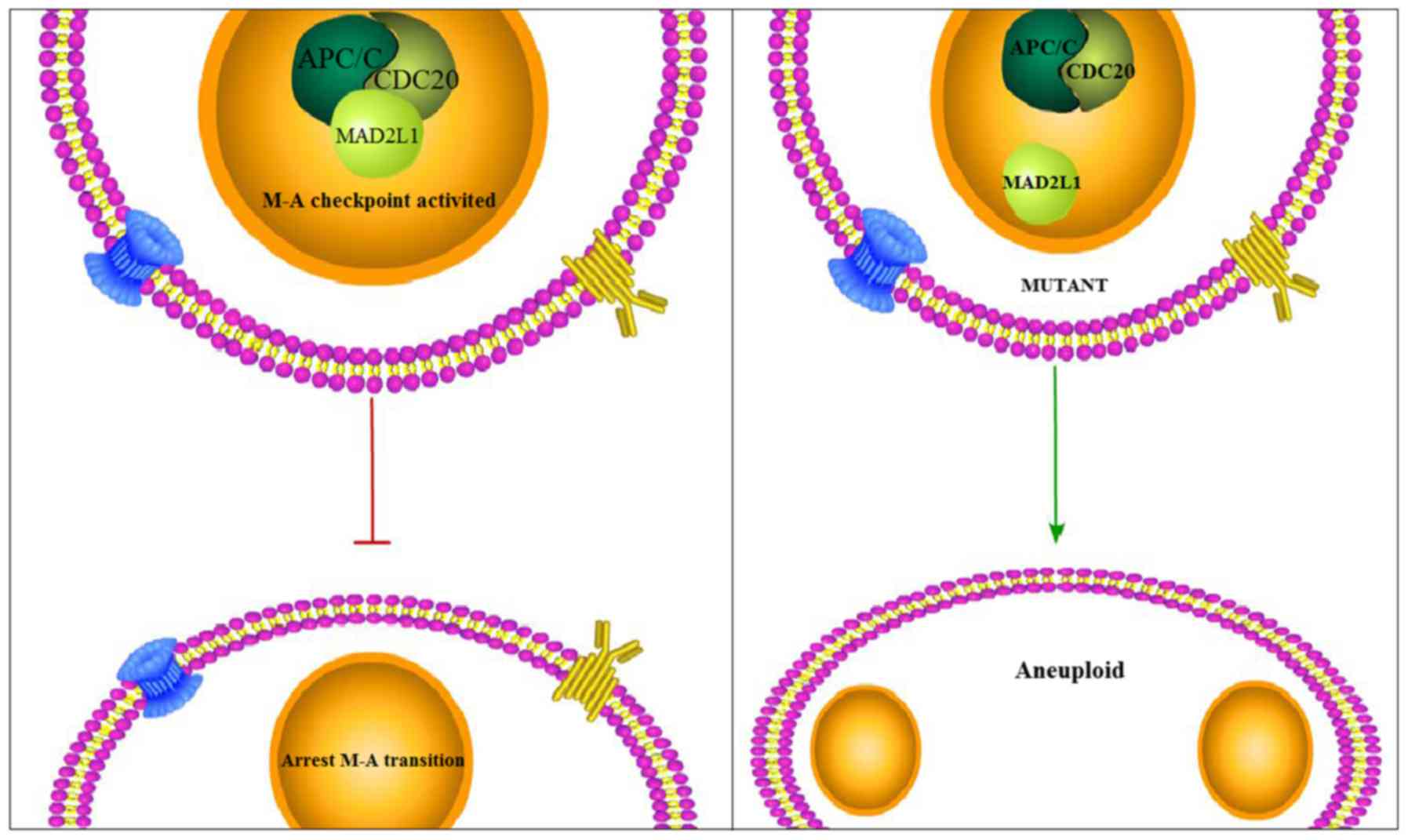
|
1
|
Sutherland KD, Proost N, Brouns I,
Adriaensen D, Song JY and Berns A: Cell of origin of small cell
lung cancer: Inactivation of Trp53 and Rb1 in distinct cell types
of adult mouse lung. Cancer Cell. 19:754–764. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Byers LA and Rudin CM: Small cell lung
cancer: Where do we go from here? Cancer. 121:664–672. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Devesa SS, Bray F, Vizcaino AP and Parkin
DM: International lung cancer trends by histologic type:
Male:female differences diminishing and adenocarcinoma rates
rising. Int J Cancer. 117:294–299. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Herbst RS, Heymach JV and Lippman SM: Lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1367–1380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Arcaro A: Targeted therapies for small
cell lung cancer: Where do we stand? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
95:154–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Simon M, Argiris A and Murren JR: Progress
in the therapy of small cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
49:119–133. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Früh M, De Ruysscher D, Popat S, Crinò L,
Peters S and Felip E; ESMO Guidelines Working Group, : Small-cell
lung cancer (SCLC): ESMO clinical practice guidelines for
diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 24:99–105. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Agra Y, Pelayo M, Sacristan M, Sacristán
A, Serra C and Bonfill X: Chemotherapy versus best supportive care
for extensive small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev:
CD001990. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Argiris A and Murren JR: Staging and
clinical prognostic factors for small-cell lung cancer. Cancer J.
7:437–447. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peifer M, Fernández-Cuesta L, Sos ML,
George J, Seidel D, Kasper LH, Plenker D, Leenders F, Sun R, Zander
T, et al: Integrative genome analyses identify key somatic driver
mutations of small-cell lung cancer. Nat Genet. 44:1104–1110. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gustafsson BI, Kidd M, Chan A,
Malfertheiner MV and Modlin IM: Bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine
tumors. Cancer. 113:5–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lassen U, Osterlind K, Hansen M,
Dombernowsky P, Bergman B and Hansen HH: Long-term survival in
small-cell lung cancer: Posttreatment characteristics in patients
surviving 5 to 18+ years-an analysis of 1,714 consecutive patients.
J Clin Oncol. 13:1215–1220. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rudin CM, Durinck S, Stawiski EW, Poirier
JT, Modrusan Z, Shames DS, Bergbower EA, Guan Y, Shin J, Guillory
J, et al: Comprehensive genomic analysis identifies SOX2 as a
frequently amplified gene in small-cell lung cancer. Nat Genet.
44:1111–1116. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chute JP, Chen T, Feigal E, Simon R and
Johnson BE: Twenty years of phase III trials for patients with
extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: Perceptible progress. J
Clin Oncol. 17:1794–1801. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jahchan NS, Lim JS, Bola B, Morris K,
Seitz G, Tran KQ, Xu L, Trapani F, Morrow CJ, Cristea S, et al:
Identification and targeting of long-term tumor-propagating cells
in small cell lung cancer. Cell Rep. 16:644–656. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Wang H, Wang J, Bao L, Wang L,
Huo J and Wang X: Global analysis of chromosome 1 genes among
patients with lung adenocarcinoma, squamous carcinoma, large-cell
carcinoma, small-cell carcinoma, or non-cancer. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 34:249–264. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR and
Berneman ZN: The cell cycle: A review of regulation, deregulation
and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 36:131–149. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stillman DJ: Dancing the cell cycle
two-step: Regulation of yeast G1-cell-cycle genes by chromatin
structure. Trends Biochem Sci. 38:467–475. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Butz H, Németh K, Czenke D, Likó I,
Czirják S, Zivkovic V, Baghy K, Korbonits M, Kovalszky I, Igaz P,
et al: Systematic investigation of expression of G2/M transition
genes reveals CDC25 alteration in nonfunctioning pituitary
adenomas. Pathol Oncol Res. 23:633–641. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou J, Tian Y, Li J, Lu B, Sun M, Zou Y,
Kong R, Luo Y, Shi Y, Wang K and Ji G: miR-206 is down-regulated in
breast cancer and inhibits cell proliferation through the
up-regulation of cyclinD2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 433:207–212.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li X, Liu F, Lin B, Luo H, Liu M, Wu J, Li
C, Li R, Zhang X, Zhou K and Ren D: miR-150 inhibits proliferation
and tumorigenicity via retarding G1/S phase transition in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 50:1097–1108. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gorlova OY, Demidenko EI, Amos CI and
Gorlov IP: Downstream targets of GWAS-detected genes for breast,
lung and prostate and colon cancer converge to G1/S transition
pathway. Hum Mol Genet. 26:1465–1471. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rao PC, Begum S, Sahai M and Sriram DS:
Coptisine-induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and reactive
oxygen species-dependent mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in
non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells. Tumour Biol. 39:2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lu TP, Tsai MH, Lee JM, Hsu CP, Chen PC,
Lin CW, Shih JY, Yang PC, Hsiao CK, Lai LC and Chuang EY:
Identification of a novel biomarker, SEMA5A, for non-small cell
lung carcinoma in nonsmoking women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 19:2590–2597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Team RRDC: A language and environment for
statistical computing. Computing. 1:12–21. 2013.
|
|
27
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat
Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Altermann E and Klaenhammer TR:
PathwayVoyager: Pathway mapping using the kyoto encyclopedia of
genes and genomes (KEGG) database. BMC Genomics. 6:602005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D,
Bryant D, Guo Y, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki RA:
DAVID bioinformatics resources: Expanded annotation database and
novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists.
Nucleic Acids Res. 35(Web Server issue): W169–W175. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peng WX, Wan YY, Gong AH, Ge L, Jin J, Xu
M and Wu CY: Egr-1 regulates irradiation-induced autophagy through
Atg4B to promote radioresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Oncogenesis. 6:e2922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39(Database Issue): D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hollstein M, Rice K, Greenblatt MS, Soussi
T, Fuchs R, Sørlie T, Hovig E, Smith-Sørensen B, Montesano R and
Harris CC: Database of p53 gene somatic mutations in human tumors
and cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 22:3551–3555. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vaughan C, Pearsall I, Yeudall A, Deb SP
and Deb S: p53: Its mutations and their impact on transcription.
Subcell Biochem. 85:71–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Speidel D: The role of DNA damage
responses in p53 biology. Arch Toxicol. 89:501–517. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Acedo P and Zawacka-Pankau J: p53 family
members-important messengers in cell death signaling in
photodynamic therapy of cancer? Photochem Photobiol Sci.
14:1390–1396. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pflaum J, Schlosser S and Müller M: p53
family and cellular stress responses in cancer. Front Oncol.
4:2852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hussain SP and Harris CC: p53 biological
network: At the crossroads of the cellular-stress response pathway
and molecular carcinogenesis. J Nippon Med Sch. 73:54–64. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Das S, Raj L, Zhao B, Bernstein A,
Aaronson SA and Lee SW: Hzf, a key modulator of p53 mediated
transcription, functions as a critical determinant of cell survival
and death upon genotoxic stress. Cell. 130:624–637. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Han JA, Kim JI, Ongusaha PP, Hwang DH,
Ballou LR, Mahale A, Aaronson SA and Lee SW: p53-mediated induction
of Cox-2 counteracts p53- or genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis.
EMBO J. 21:5635–5644. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Egloff AM, Weissfeld J, Land SR and Finn
OJ: Evaluation of anticyclin B1 serum antibody as a diagnostic and
prognostic biomarker for lung cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1062:29–40.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dutta A, Chandra R, Leiter LM and Lester
S: Cyclins as markers of tumor proliferation: Immunocytochemical
studies in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:pp. 5386–5390.
1995; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kawamoto H, Koizumi H and Uchikoshi T:
Expression of the G2-M checkpoint regulators cyclin B1 and cdc2 in
nonmalignant and malignant human breast lesions: Immunocytochemical
and quantitative image analyses. Am J Pathol. 150:15–23.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Winters ZE, Hunt NC, Bradburn MJ, Royds
JA, Turley H, Harris AL and Norbury CJ: Subcellular localisation of
cyclin B, Cdc2 and p21(WAF1/CIP1) in breast cancer. Association
with prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 37:2405–2412. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Crosby ME: Cell cycle: Principles of
control. Yale J Biol Med. 80:141–143. 2007.
|
|
46
|
Brown NR, Noble ME, Endicott JA and
Johnson LN: The structural basis for specificity of substrate and
recruitment peptides for cyclin-dependent kinases. Nat Cell Biol.
1:438–443. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Müllers E, Silva Cascales H, Burdova K,
Macurek L and Lindqvist A: Residual Cdk1/2 activity after DNA
damage promotes senescence. Aging Cell. 16:575–584. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Singh SK, Banerjee S, Acosta EP, Lillard
JW and Singh R: Resveratrol induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
with docetaxel in prostate cancer cells via a p53/p21WAF1/CIP1 and
p27KIP1 pathway. Oncotarget. 8:17216–17228. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Meraldi P, Lukas J, Fry AM, Bartek J and
Nigg EA: Centrosome duplication in mammalian somatic cells requires
E2F and Cdk2-cyclin A. Nat Cell Biol. 1:88–93. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fang G, Yu H and Kirschner MW: The
checkpoint protein MAD2 and the mitotic regulator CDC20 form a
ternary complex with the anaphase-promoting complex to control
anaphase initiation. Genes Dev. 12:1871–1883. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sudakin V, Chan GKT and Yen TJ: Checkpoint
inhibition of the APC/C in HeLa cells is mediated by a complex of
BUBR1, BUB3, CDC20, and MAD2. J Cell Biol. 154:925–936. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rajagopalan H and Lengauer C: Aneuploidy
and cancer. Nature. 432:338–341. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kim HS, Park KH, Kim SA, Wen J, Park SW,
Park B, Gham CW, Hyung WJ, Noh SH, Kim HK and Song SY: Frequent
mutations of human Mad2, but not Bub1, in gastric cancers cause
defective mitotic spindle checkpoint. Mutat Res. 578:187–201. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yuan B, Xu Y, Woo JH, Wang Y, Bae YK, Yoon
DS, Wersto RP, Tully E, Wilsbach K and Gabrielson E: Increased
expression of mitotic checkpoint genes in breast cancer cells with
chromosomal instability. Clin Cancer Res. 12:405–410. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gao F, Ponte JF, Papageorgis P, Levy M,
Ozturk S, Lambert AW, Pan H, Chinnappan D, Cheng KH, Thiagalingam
A, et al: hBub1 deficiency triggers a novel p53 mediated early
apoptotic checkpoint pathway in mitotic spindle damaged cells.
Cancer Biol Ther. 8:627–635. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nekova TS, Kneitz S, Einsele H, Bargou R
and Stuhler G: Silencing of CDK2, but not CDK1, separates mitogenic
from anti-apoptotic signaling, sensitizing p53 defective cells for
synthetic lethality. Cell Cycle. 15:3203–3209. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tudzarova S, Mulholland P, Dey A, Stoeber
K, Okorokov AL and Williams GH: p53 controls CDC7 levels to
reinforce G1 cell cycle arrest upon genotoxic stress. Cell Cycle.
15:2958–2972. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
May KM, Paldi F and Hardwick KG: Fission
yeast Apc15 Stabilizes MCC-Cdc20-APC/C complexes, ensuring
efficient Cdc20 ubiquitination and checkpoint arrest. Curr Biol.
27:1221–1228. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|