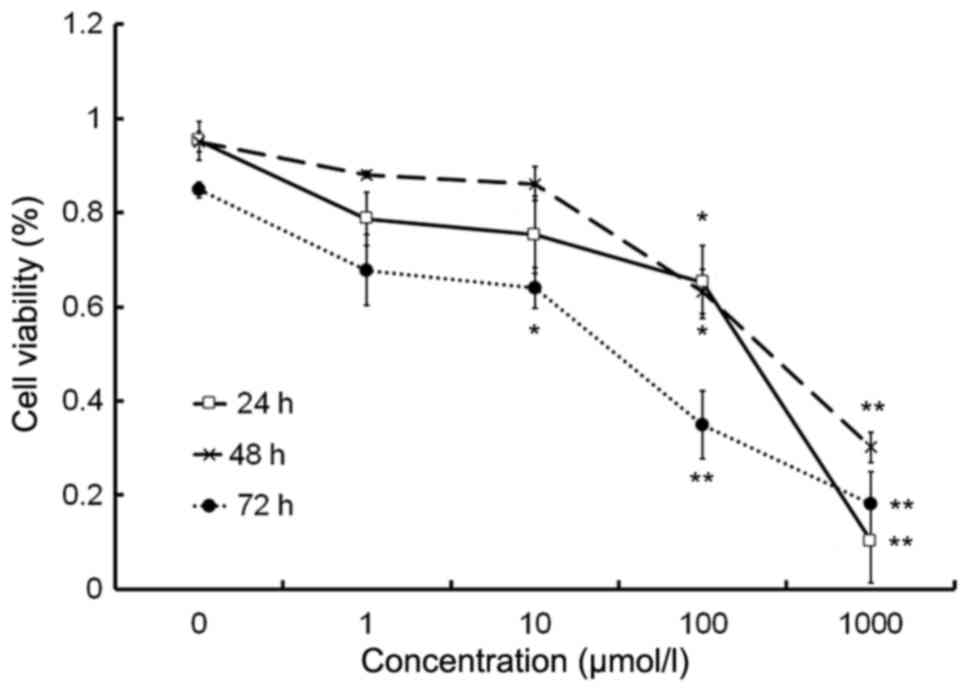
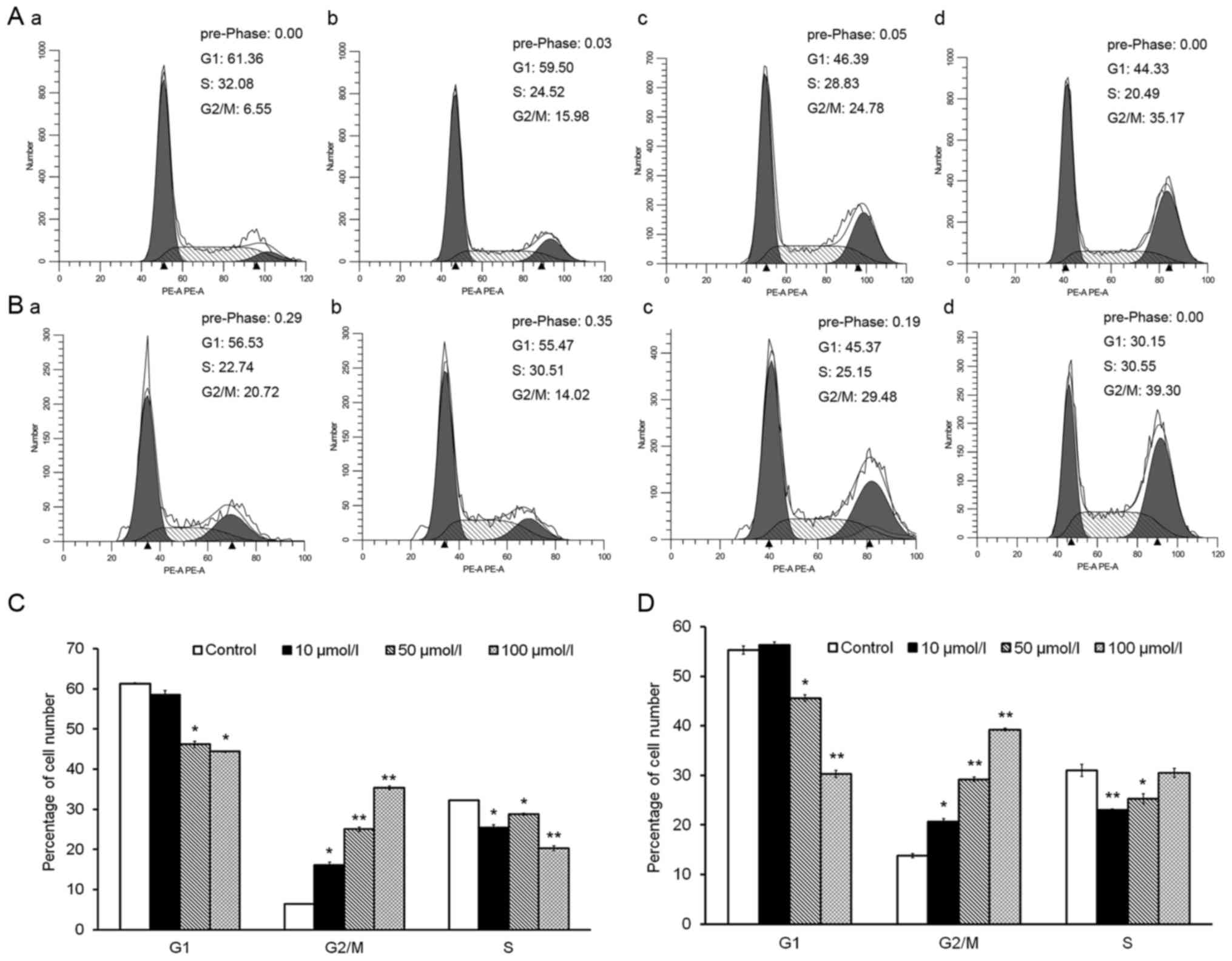
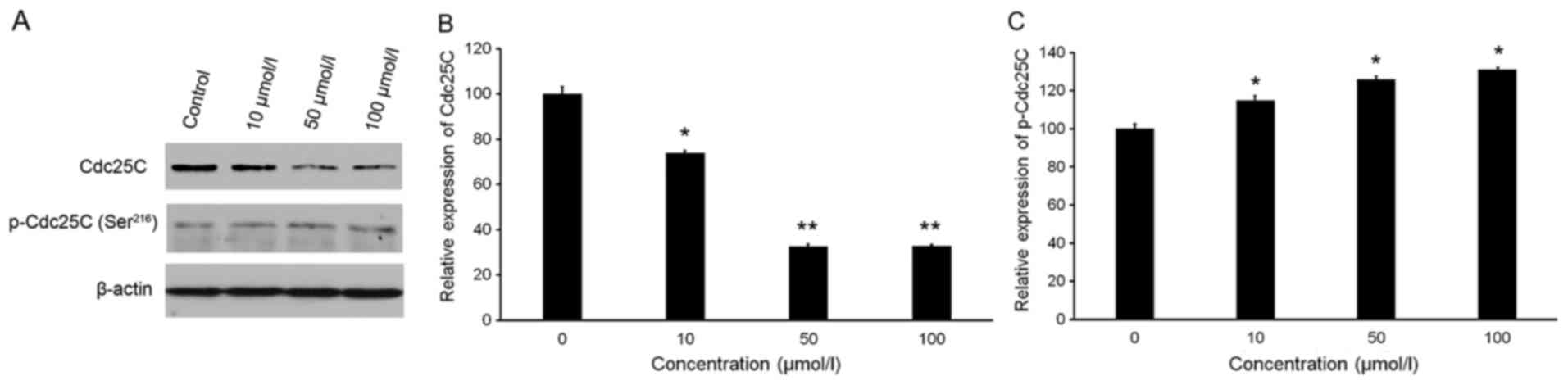
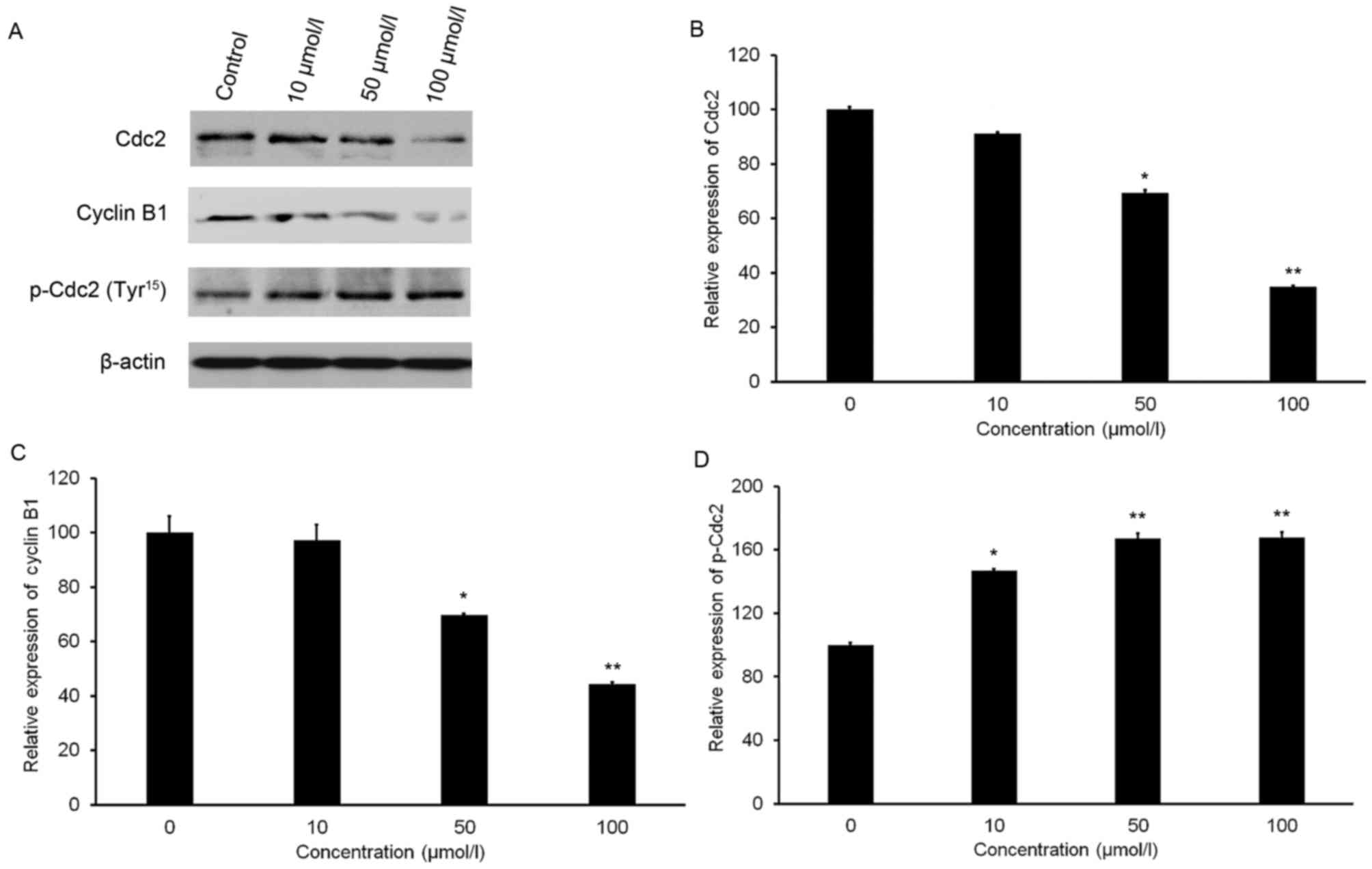
|
1
|
Arbyn M, Castellsagué X, de Sanjosé S,
Bruni L, Saraiya M and Bray F: Worldwide burden of cervical cancer
in 2008. Ann Oncol. 22:2675–2686. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Farrand L, Oh SW, Song YS and Tsang BK:
Phytochemicals: A multitargeted approach to gynecologic cancer
therapy. Biomed Res Int. 2014:8901412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kumar D, Basu S, Parija L, Rout D, Manna
S, Dandapat J and Debata PR: Curcumin and ellagic acid
synergistically induce ROS generation, DNA damage, p53 accumulation
and apoptosis in HeLa cervical carcinoma cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 81:31–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Debata PR, Castellanos MR, Fata JE,
Baggett S, Rajupet S, Szerszen A, Begum S, Mata A, Murty VV, Opitz
LM and Banerjee P: A novel curcumin-based vaginal cream Vacurin
selectively eliminates apposed human cervical cancer cells. Gynecol
Oncol. 129:145–153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thacker PC and Karunagaran D: Curcumin and
emodin down-regulate TGF-β signaling pathway in human cervical
cancer cells. PLoS One. 10:e01200452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maher DM, Bell MC, O'Donnell EA, Gupta BK,
Jaggi M and Chauhan SC: Curcumin suppresses human papillomavirus
oncoproteins, restores p53, Rb, and PTPN13 proteins and inhibits
benzo[a]pyrene-induced upregulation of HPV E7. Mol Carcinog.
50:47–57. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Narayanan BA, Geoffroy O, Willingham MC,
Re GG and Nixon DW: p53/p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression and its possible
role in G1 arrest and apoptosis in ellagic acid treated cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 136:215–221. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Chi G, Shen B, Tian Y and Feng H:
Isorhamnetin ameliorates LPS-induced inflammatory response through
downregulation of NF-κB signaling. Inflammation. 39:1291–1301.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang JS, Shih CM, Wang SH, Chen TT, Lin
CN and Ko WC: Mechanisms of suppression of nitric oxide production
by 3-O-methylquercetin in RAW 264.7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol.
103:281–287. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang JH, Kim SC, Shin BY, Jin SH, Jo MJ,
Jegal KH, Kim YW, Lee JR, Ku SK, Cho IJ and Ki SH: O-Methylated
flavonol isorhamnetin prevents acute inflammation through blocking
of NF-κB activation. Food Chem Toxicol. 59:362–372. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Saud SM, Young MR, Jones-Hall YL, Ileva L,
Evbuomwan MO, Wise J, Colburn NH, Kim YS and Bobe G:
Chemopreventive activity of plant flavonoid isorhamnetin in
colorectal cancer is mediated by oncogenic Src and β-catenin.
Cancer Res. 73:5473–5484. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang JH, Shin BY, Han JY, Kim MG, Wi JE,
Kim YW, Cho IJ, Kim SC, Shin SM and Ki SH: Isorhamnetin protects
against oxidative stress by activating Nrf2 and inducing the
expression of its target genes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
274:293–301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Q, Ren FQ, Yang CL, Zhou LM, Liu YY,
Xiao J, Zhu L and Wang ZG: Anti-proliferation effects of
isorhamnetin on lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 16:3035–3042. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sobral F, Calhelha RC, Barros L, Dueñas M,
Tomás A, Santos-Buelga C, Vilas-Boas M and Ferreira IC: Flavonoid
composition and antitumor activity of bee bread collected in
northeast Portugal. Molecules. 22(pii): E2482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi X, Liu D, Zhang J, Hu P, Shen W, Fan
B, Ma Q and Wang X: Extraction and purification of total flavonoids
from pine needles of Cedrus deodara contribute to anti-tumor in
vitro. BMC Complement Altern Med. 16:2452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Strober W: Trypan blue exclusion test of
cell viability. Curr Protoc Immunol. 111:A3.B.1–3. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lv TZ and Wang GS: Antiproliferation
potential of withaferin A on human osteosarcoma cells via the
inhibition of G2/M checkpoint proteins. Exp Ther Med. 10:323–329.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Burd EM: Human papillomavirus and cervical
cancer. Clin Microbiol Rev. 16:1–17. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miao R, Wei J, Lv M, Cai Y, Du Y, Hui X
and Wang Q: Conjugation of substituted ferrocenyl to thiadiazine as
apoptosis-inducing agents targeting the Bax/Bcl-2 pathway. Eur J
Med Chem. 46:5000–5009. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu Y, Ching YP, Zhou Y, Chiu JF, Chen F
and He QY: Multiple pathways were involved in tubeimoside-1-induced
cytotoxicity of HeLa cells. J Proteomics. 75:491–501. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Meyn MS: Ataxia-telangiectasia and
cellular responses to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 55:5991–6001.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shiloh Y: Ataxia-telangiectasia: Closer to
unraveling the mystery. Eur J Hum Genet. 3:116–138. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Khanna KK and Jackson SP: DNA
double-strand breaks: Signaling, repair and the cancer connection.
Nat Genet. 27:247–254. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
O'Neill T, Giarratani L, Chen P, Iyer L,
Lee CH, Bobiak M, Kanai F, Zhou BB, Chung JH and Rathbun GA:
Determination of substrate motifs for human Chk1 and hCds1/Chk2 by
the oriented peptide library approach. J Biol Chem.
277:16102–16115. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao H and Piwnica-Worms H: ATR-mediated
checkpoint pathways regulate phosphorylation and activation of
human Chk1. Mol Cell Biol. 21:4129–4139. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ahn JY, Schwarz JK, Piwnica-Worms H and
Canman CE: Threonine 68 phosphorylation by ataxia telangiectasia
mutated is required for efficient activation of Chk2 in response to
ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 60:5934–5936. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hirao A, Cheung A, Duncan G, Girard PM,
Elia AJ, Wakeham A, Okada H, Sarkissian T, Wong JA, Sakai T, et al:
Chk2 is a tumor suppressor that regulates apoptosis in both an
ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM)-dependent and an
ATM-independent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 22:6521–6532. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Agarwal C, Tyagi A and Agarwal R: Gallic
acid causes inactivating phosphorylation of cdc25A/cdc25C-cdc2 via
ATM-Chk2 activation, leading to cell cycle arrest, and induces
apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma DU145 cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
5:3294–3302. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pines J and Hunter T: Human cyclin A is
adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from
cyclin B. Nature. 346:760–763. 1990. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Russell P and Nurse P: The mitotic inducer
nim1+ functions in a regulatory network of protein
kinase homologs controlling the initiation of mitosis. Cell.
49:569–576. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kumagai A and Dunphy WG: The cdc25 protein
controls tyrosine dephosphorylation of the cdc2 protein in a
cell-free system. Cell. 64:903–914. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jordan MA: Mechanism of action of
antitumor drugs that interact with microtubules and tubulin. Curr
Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2:1–17. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|